LeetCode第127题—单词接龙—Python实现
Posted StriveZs
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了LeetCode第127题—单词接龙—Python实现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
title: LeetCode No.127
categories:
- OJ
- LeetCode
tags:
- Programing
- LeetCode
- OJ
LeetCode第127题—单词接龙
自己代码的开源仓库:click here 欢迎Star和Fork 😃
题目描述
字典 wordList 中从单词 beginWord 和 endWord 的 转换序列 是一个按下述规格形成的序列:
序列中第一个单词是 beginWord 。
序列中最后一个单词是 endWord 。
每次转换只能改变一个字母。
转换过程中的中间单词必须是字典 wordList 中的单词。
给你两个单词 beginWord 和 endWord 和一个字典 wordList ,找到从 beginWord 到 endWord 的 最短转换序列 中的 单词数目 。如果不存在这样的转换序列,返回 0。
示例 1:
输入:beginWord = "hit", endWord = "cog", wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log","cog"]
输出:5
解释:一个最短转换序列是 "hit" -> "hot" -> "dot" -> "dog" -> "cog", 返回它的长度 5。
示例 2:
输入:beginWord = "hit", endWord = "cog", wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log"]
输出:0
解释:endWord "cog" 不在字典中,所以无法进行转换。
提示:
1 <= beginWord.length <= 10
endWord.length == beginWord.length
1 <= wordList.length <= 5000
wordList[i].length == beginWord.length
beginWord、endWord 和 wordList[i] 由小写英文字母组成
beginWord != endWord
wordList 中的所有字符串 互不相同
解题思路
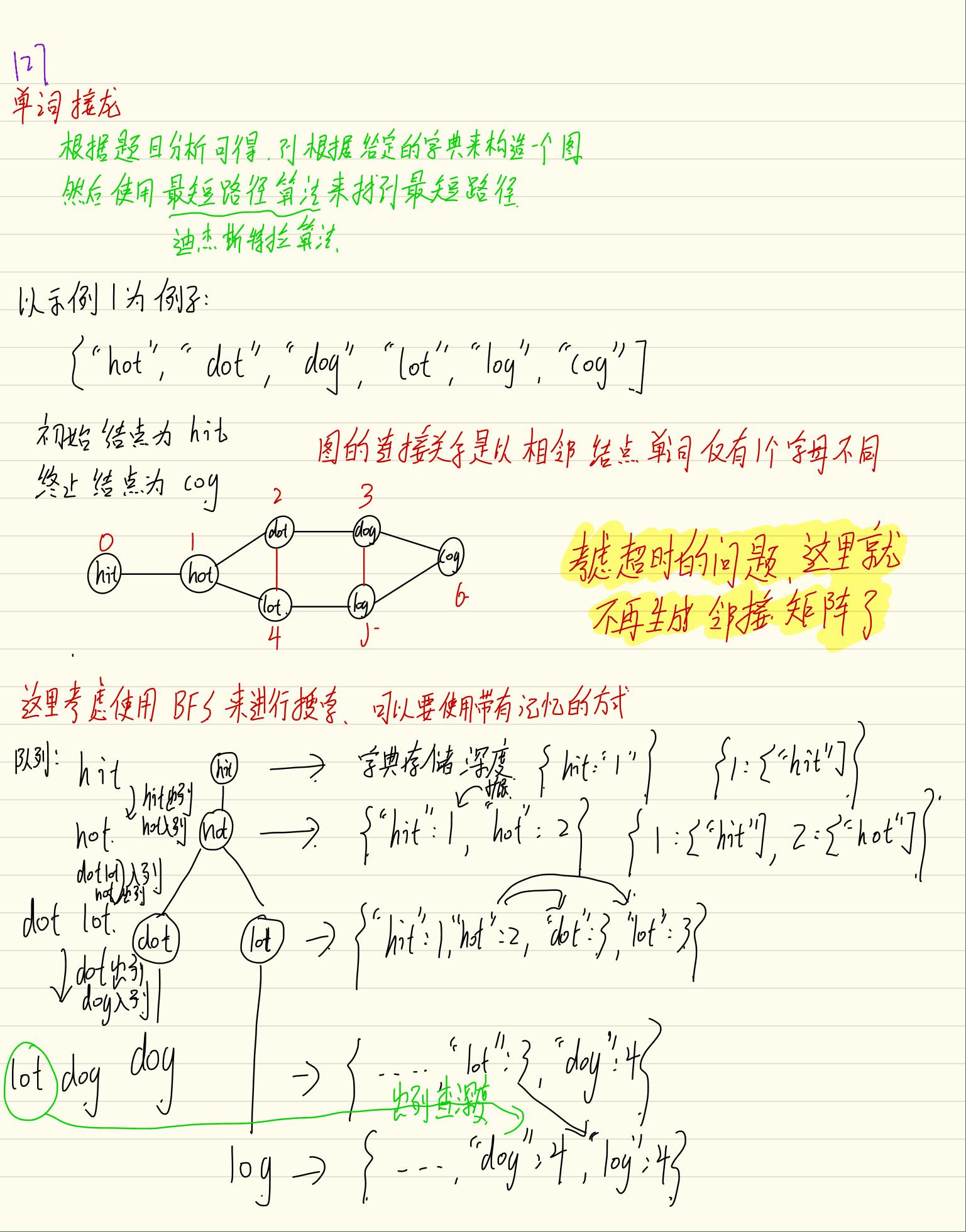
Python使用BFS的话,还是会超时,最长的那个过不去,这里就参考大佬的方法。
反正都是小写字母,每次只变动一位,干脆拿到一个节点时生成所有可能的下一个节点,新生成的节点只要再列表中就参与计算。
代码
使用了邻接矩阵的超时版本
class Solution(object):
def one_chart_different(self, str1, str2):
"""
判断输入的两个字符串是不是只有一个不一样, 默认输入的两个字符串长度相同
:param str1: String
:param str2: String
:return: Boolean True/False
"""
num = 0
for i in range(len(str1)):
if str1[i] != str2[i]:
num += 1
if num > 1:
return False
if num == 0:
return False
return True
# fixme: 使用BFS进行广度优先搜索
def BFS_memory_search(self, start, end_num, adjacent_matrix):
"""
使用带有记忆的BFS来进行搜索,层数逐渐增加就可以了,直到最先扩展到最终节点就结束
有点类似树扩展的方法,用字典来记录深度
:param start: Int 给点初始节点在邻接矩阵中的下标
:param end_num: 终止节点
:param adjacent_matrix: 邻接矩阵
:return: distance, path 返回距离和路径
"""
inf = float('inf')
# 初始化操作
depth_dict = {} # 记忆深度词典
depth_dict[start] = 1 # 初始化
quene = [] # 队列
quene.append(start)
n = len(adjacent_matrix) # 节点个数
step = None
for i in range(1,n):
if len(quene) == 0:
return step
node = quene.pop(0) # 队首出列
for j in range(n):
if adjacent_matrix[node][j] != inf and j not in depth_dict.keys(): # 证明可以扩展
quene.append(j) # 入队
depth_dict[j] = depth_dict[node] + 1 # 深度记录
if j == end_num and end_num in depth_dict.keys():
step = depth_dict[j]
return step
return step
def ladderLength(self, beginWord, endWord, wordList):
"""
:type beginWord: str
:type endWord: str
:type wordList: List[str]
:rtype: List[List[str]]
根据给定的字典list构造一个图,考虑使用邻接矩阵构建一个图
"""
inf = float('inf')
if endWord not in wordList:
return 0
if beginWord not in wordList:
nodeList = [beginWord] + wordList # 构造所有节点列表
else:
nodeList = wordList
nodeList.remove(nodeList[nodeList.index(beginWord)])
nodeList = [beginWord] + wordList # 将初始节点至为第一个
numList = [i for i in range(len(nodeList))] # 构造每个节点对应的数字状态
node_num_dict = dict(zip(nodeList,numList)) # 构建对应关系的字典
num_node_dict = dict(zip(numList,nodeList)) # 构造反向对应关系
adjacent_matrix = [[inf for _ in range(len(nodeList))] for _ in range(len(nodeList))] # 邻接矩阵
# 构建邻接矩阵
for i in nodeList:
for j in nodeList:
if i != j:
if len(i) == len(j):
if self.one_chart_different(i,j):
adjacent_matrix[node_num_dict[i]][node_num_dict[j]] = 1
adjacent_matrix[node_num_dict[j]][node_num_dict[i]] = 1
step = self.BFS_memory_search(0,nodeList.index(endWord),adjacent_matrix)
if step == None:
return 0
return step
if __name__ == '__main__':
s = Solution()
print(s.ladderLength(beginWord = "talk", endWord = "tail", wordList = ["talk","tons","fall","tail","gale","hall","negs"]))
去掉邻接矩阵直接判断的版本
别人没超时,我用Python又又超时了,我爆哭.
class Solution(object):
def one_chart_different(self, str1, str2):
"""
判断输入的两个字符串是不是只有一个不一样, 默认输入的两个字符串长度相同
:param str1: String
:param str2: String
:return: Boolean True/False
"""
num = 0
for i in range(len(str1)):
if str1[i] != str2[i]:
num += 1
if num > 1:
return False
if num == 0:
return False
return True
def new_version(self, beginWord, endWord, wordList):
quene = []
quene.append(beginWord)
step = 0
while len(quene) != 0:
step += 1
sz = len(quene)
while sz > 0:
hope = quene.pop(0)
if hope == endWord:
return step
# 对每个word进行判断
for i in range(len(wordList)):
if len(wordList[i]) == 0 or len(wordList[i]) != len(beginWord):
continue
# 判断差异性
if self.one_chart_different(hope,wordList[i]):
quene.append(wordList[i])
wordList[i] = ""
sz -= 1
return 0
if __name__ == '__main__':
s = Solution()
print(s.new_version(beginWord = "hit", endWord = "cog", wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log"]))
参考大佬的版本
反正都是小写字母,每次只变动一位,干脆拿到一个节点时生成所有可能的下一个节点,新生成的节点只要再列表中就参与计算。
这次终于通过了,不过耗时几百毫秒。
def ladderLength(self, beginWord: str, endWord: str, wordList: List[str]) -> int:
if endWord not in wordList:
return 0
l = len(endWord)
ws = set(wordList)
head = {beginWord}
tail = {endWord}
tmp = list('abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz')
res = 1
while head:
if len(head) > len(tail):
head, tail = tail, head
q = set()
for cur in head:
for i in range(l):
for j in tmp:
word = cur[:i] + j + cur[i+1:]
if word in tail:
return res + 1
if word in ws:
q.add(word)
ws.remove(word)
head = q
res += 1
return 0
以上是关于LeetCode第127题—单词接龙—Python实现的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章