不讲武德(手动狗头):面试官上来就甩给我几道多线程代码题叫我手撕,我心里拔凉拔凉的~~~
Posted CRUD速写大师
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了不讲武德(手动狗头):面试官上来就甩给我几道多线程代码题叫我手撕,我心里拔凉拔凉的~~~相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前言
栗花落香奈乎
女主真好看

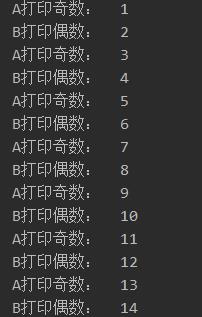
两个线程,一个线程打印奇数,一个线程打印偶数
ReentrantLock + Condition 来实现
public class Main {
private static Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
static Condition c1 = lock.newCondition();
static Condition c2 = lock.newCondition();
//数字
static volatile int num = 1;
public static void main(String[] args) {
//线程A
new Thread(() -> {
lock.lock();
try{
while (true) {
//如果是奇数
if (num % 2 == 1) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "打印奇数:\\t" + num);
num++;
c2.signal();
c1.await();
}
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
lock.unlock();
}
},"A").start();
//线程B
new Thread(() -> {
lock.lock();
try{
while (true) {
//如果是偶数
if (num % 2 == 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "打印偶数:\\t" + num);
num++;
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
c1.signal();
c2.await();
}
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
lock.unlock();
}
},"B").start();
}
}
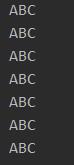
三个线程打印ABC
public class Main {
private static int state = 0;
private static final Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public static void main(String[] args) {
//打印A
Thread a = new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
lock.lock();
try{
if (state % 3 == 0) {
System.out.print("A");
state++;
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
lock.unlock();
}
}
});
//打印B
Thread b = new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
lock.lock();
try{
if (state % 3 == 1) {
System.out.print("B");
state++;
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
lock.unlock();
}
}
});
//打印C
Thread c = new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
lock.lock();
try{
if (state % 3 == 2) {
System.out.println("C");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
state++;
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
lock.unlock();
}
}
});
a.start();
b.start();
c.start();
}
}
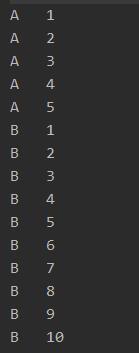
线程打印A5次,B10次,C15次
public class Test01 {
private int number = 1;
private static Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
static Condition c1 = lock.newCondition();
static Condition c2 = lock.newCondition();
static Condition c3 = lock.newCondition();
public void printNum(int num,Condition st,Condition start,int currentNum,int futureNum) {
lock.lock();
try{
while (number != currentNum) {
st.await();
}
for (int i = 1; i <= num; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\\t" + i);
}
number = futureNum;
start.signal();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
lock.unlock();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test01 test01 = new Test01();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
test01.printNum(5,c1,c2,1,2);
}
},"AAA").start();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
test01.printNum(10,c2,c3,2,3);
}
},"BBB").start();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
test01.printNum(15,c3,c1,3,1);
}
},"CCC").start();
}
}
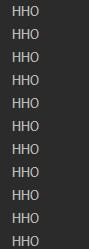
图没截完
创建水分子
实现两个方法生成一个水分子H2O,一个方法输出一个O,另一个方法输出一个H,水分子需要由2个H和一个O构成,
public class Main {
private static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private static Condition c1 = lock.newCondition();
private static Condition c2 = lock.newCondition();
private static AtomicInteger num = new AtomicInteger(1);
public static void printH2() {
lock.lock();
try{
System.out.print("H");
if (num.intValue() % 2 == 0) {
c2.signal();
c1.await();
}else {
num.incrementAndGet();
printH2();
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
lock.unlock();
}
}
public static void printO() {
lock.lock();
try{
System.out.println("O");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
num.incrementAndGet();
c1.signal();
c2.await();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
lock.unlock();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
printH2();
}
},"1").start();
new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
printO();
}
},"2").start();
}
}
生产者、消费者阻塞普通版
public class Test01 {
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private Condition condition = lock.newCondition();
private volatile int num = 0;
//生产者
public void produce() {
lock.lock();
try{
//如果不等于0,那么就不去生产
while (num != 0) {
condition.await();
}
//生产
num++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\\t生产:" + num);
//唤醒
condition.signal();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
lock.unlock();
}
}
//消费者
public void consumer() {
lock.lock();
try{
//如果恒等于0,那么就不能去消费
while (num == 0) {
condition.await();
}
//消费
num--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\\t消费:" + num);
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
//唤醒
condition.signal();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
lock.unlock();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test01 test = new Test01();
new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
test.produce();
}
},"A").start();
new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
test.consumer();
}
},"B").start();
}
}
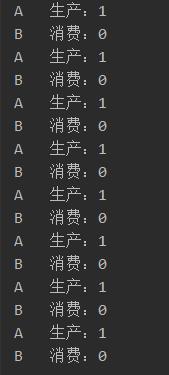
生产者、消费者阻塞队列版
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//将阻塞队列容量初始化为5
MySource source = new MySource(new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(5));
new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\\t 生产线程启动");
try {
source.myProduct();
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"Product").start();
new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\\t 消费线程启动");
System.out.println();
try {
source.myConsumer();
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},<以上是关于不讲武德(手动狗头):面试官上来就甩给我几道多线程代码题叫我手撕,我心里拔凉拔凉的~~~的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章