节点大小可变的环形队列实现
Posted rtoax
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了节点大小可变的环形队列实现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
在文章《Linux C语言在用户态实现一个低时延通知(eventfd)+轮询(无锁队列ring)机制的消息队列》中介绍了用户态低时延消息队列的实现,下面我们简单介绍优化步骤。同时在《对POSIX和SystemV消息队列优化:用户态消息队列》对消息队列接口进行了优化,里面使用的环形队列的节点大小是固定的,如何实现不固定节点大小的环形队列呢?直接上代码:
源码链接:https://github.com/Rtoax/test/tree/master/ipc/ring/variable-node-size
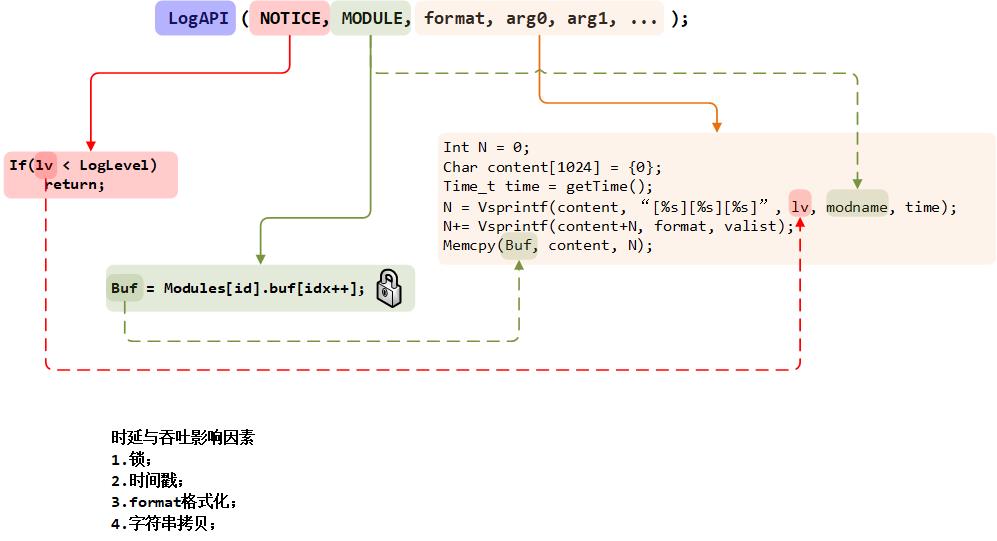
本文意在解决日志管理系统的时延和吞吐瓶颈问题:
ring.h
/**
* 可变节点大小的队列
*
* 作者:荣涛
* 日期:
* 2021年6月1日 创建 并完成初始版本
*
*/
#ifndef ____RING_H
#define ____RING_H 1
#include <assert.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#ifndef likely
#define likely(x) __builtin_expect(!!(x), 1)
#endif
#ifndef unlikely
#define unlikely(x) __builtin_expect(!!(x), 0)
#endif
#ifndef __cachelinealigned
#define __cachelinealigned __attribute__((aligned(64)))
#endif
#ifndef _unused
#define _unused __attribute__((unused))
#endif
static void inline _unused mbarrier() { asm volatile("": : :"memory"); }
static void inline _unused mrwbarrier() { asm volatile("mfence":::"memory"); }
static void inline _unused mrbarrier() { asm volatile("lfence":::"memory"); }
static void inline _unused mwbarrier() { asm volatile("sfence":::"memory"); }
static void inline _unused __relax() { asm volatile ("pause":::"memory"); }
struct __ring_node {
unsigned int _valide:1;
unsigned int _reserve:7;
unsigned int _data_size:8; //最大数据大小 256
char _data[];
}__attribute__((packed));
struct __ring {
size_t _nodes_size; //总大小
volatile size_t _head;
volatile size_t _tail;
char _nodes[];
} __cachelinealigned;
static size_t _unused __power_of_2(unsigned int size)
{
unsigned int i;
for (i=0; (1U << i) < size; i++);
return 1U << i;
}
static struct __ring* _unused __ring_create(size_t size)
{
size_t nodes_size = __power_of_2(size);
size_t total_size = nodes_size + sizeof(struct __ring);
printf("nodes_size = %d, total_size = %d\\n", nodes_size, total_size);
struct __ring *new_ring = (struct __ring *)malloc(total_size);
assert(new_ring && "OOM error");
memset(new_ring, 0x00, total_size);
new_ring->_nodes_size = nodes_size;
new_ring->_head = size/2;
new_ring->_tail = size/2;
return new_ring;
}
/*
----- 空闲
##### 已使用
***** 即将填充
%%%%% 空闲但不使用
*/
static inline bool _unused __ring_enqueue(struct __ring *ring, const void *msg, const size_t size)
{
assert(ring);
assert(msg);
assert(size < ring->_nodes_size);
const size_t node_size = size + sizeof(struct __ring_node);
size_t head = ring->_head;
size_t tail = ring->_tail;
size_t next_tail = (tail + node_size) & (ring->_nodes_size-1);
/* tail指针将翻转
next_tail head tail
**-------##########%%%%%%%%%%%
*/
bool beyond = (next_tail < tail);
if(unlikely(beyond)) {
// printf("beyond.\\n");
struct __ring_node *tmp = (struct __ring_node *)&ring->_nodes[tail];
tmp->_data_size = ring->_nodes_size - tail;
tmp->_valide = 0;
tail = 0;
next_tail = node_size;
if(next_tail >= head) {
// printf("full1. (%d,%d)\\n", ring->_head, ring->_tail);
return false;
}
} else {
/*
head tail next_tail
---------##########*****------
*/
if(ring->_nodes_size - tail < node_size) {
// printf("full3. (%d,%d)\\n", ring->_head, ring->_tail);
return false;
}
/*
tail head
###***---#################%%%%
next_tail
*/
if(tail < head && next_tail > head) {
// printf("full4. (%d,%d)\\n", ring->_head, ring->_tail);
return false;
}
}
struct __ring_node *node = (struct __ring_node *)&ring->_nodes[tail];
node->_data_size = size;
node->_valide = 1;
memcpy(node->_data, msg, size);
mwbarrier();
// printf("insert: head = %d, tail = %d, size = %ld, node = %p\\n", ring->_head, tail, node->_data_size, node);
ring->_tail = tail + node_size;
return true;
}
static bool inline _unused __ring_dequeue( struct __ring *const ring, void *msg, size_t *size)
{
assert(ring);
assert(msg);
assert(size);
size_t tail = ring->_tail;
size_t head = ring->_head;
try_again:
if (head == tail) {
// printf("empty.\\n");
return false;
}
struct __ring_node *node = (struct __ring_node *)&ring->_nodes[head];
/* 结尾的 不可用包 %%%
next_tail head tail
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx%%%
*/
if(!node->_valide) {
// printf("invalide node.\\n");
mbarrier();
ring->_head = 0;
head = 0;
goto try_again;
}
*size = node->_data_size;
const size_t node_size = (*size) + sizeof(struct __ring_node);
memcpy(msg, node->_data, *size);
mbarrier();
bool beyond = !!((head + node_size) > ring->_nodes_size);
ring->_head = beyond?0:(head + node_size) & (ring->_nodes_size-1);
// printf("delete: head = %d, tail = %d, size = %ld, node = %p\\n", ring->_head, tail, node->_data_size, node);
return true;
}
#endif /*<____RING_H>*/
test.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include "ring.h"
struct msg {
#define MSG_MAGIC 0x1234abcd
int magic;
int magic2;
int magic3;
int magic4;
int magic5;
char pad[];
};
struct __ring* ring = NULL;
void *enqueue(void*arg)
{
int i = 0;
while(1) {
i ++;
size_t size = sizeof(struct msg) + i%100;
struct msg *m = (struct msg *)malloc(size);
m->magic = MSG_MAGIC;
while(!__ring_enqueue(ring, m, size)) {
__relax();
}
// printf("enqueue: msg.magic = 0x%x, size = %ld\\n", m->magic, size);
free(m);
}
}
void *dequeue(void*arg)
{
char buffer[1024];
size_t size;
while(1) {
while(__ring_dequeue(ring, buffer, &size)) {
struct msg *m = (struct msg *)buffer;
// printf("dequeue: msg.magic = 0x%x, size = %ld\\n", m->magic, size);
}
__relax();
}
}
int main()
{
unsigned int ring_size = getpagesize()*100;
// unsigned int ring_size = 128;
ring = __ring_create(ring_size);
pthread_t tasks[4];
pthread_create(&tasks[0], NULL, dequeue, NULL);
pthread_create(&tasks[1], NULL, enqueue, NULL);
pthread_join(tasks[0], NULL);
pthread_join(tasks[1], NULL);
return 0;
}
以上是关于节点大小可变的环形队列实现的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章