C++-二叉搜索树的查找&插入&删除-二叉搜索树代码实现-二叉搜索树性能分析及解决方案
Posted 天津 唐秙
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了C++-二叉搜索树的查找&插入&删除-二叉搜索树代码实现-二叉搜索树性能分析及解决方案相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. 二叉搜索树
1.1 概念
二叉搜索树又叫做二叉排序树或者是一棵空树,具有以下性质:
-
若它的左子树不为空,则左子树上所有节点的值都小于根节点的值
-
若它的右子树不为空,则右子树上所有节点的值都大于根节点的值
-
它的左右子树也是二叉搜索树
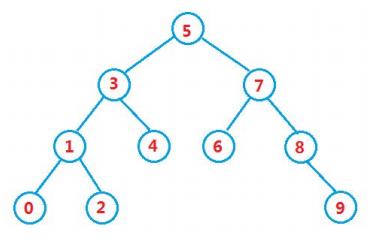
int a[] = {5,3,4,1,7,8,2,6,0,9}
1.2 二叉搜索树操作
1.2.1 二叉搜索树的查找
思路:
- 在根不为空的前提下:
- 如果根节点key == target,返回true
- 如果根节点key > target,在key的左子树查找
- 如果根节点key < target,在key的右子树查找
- 根为空,返回false
实现:
BSTNode<T>* Search(BSTNode<T> *t, const T &key)const
{
if (t == nullptr || t->data == key)
return t;
if (key < t->data)
return Search(t->left, key);
else
return Search(t->right, key);
}
1.2.2 二叉搜索树的插入
思路:
- 如果树为空,直接将插入的数据为root节点
- 如果树不为空,将插入数据和根节点进行比较
- 数据大于根节点的值,往树的右边走
- 数据小于根节点的值,往树的左边走
- 数据等于根节点的值,返回,插入失败,因为已经存在该数据
实现:
bool Insert(BSTNode<T> *&t, const T &x)
{
if (t == nullptr)
{
t = new BSTNode<T>(x);
return true;
}
if (x < t->data)
return Insert(t->left, x);
else if (x > t->data)
return Insert(t->right, x);
return false;
}
1.2.3 二叉搜索树的删除
思路:
- 首先查找元素是否存在于二叉搜索树中,如果不存在,则返回
- 删除的节点存在
- (1)要删除的节点无孩子节点
- (2)要删除的节点只有左孩子
- (3)要删除的节点只有右孩子
- (4)要删除的节点既有左孩子也有右孩子
实现:
bool Remove(BSTNode<T> *&t, const T &x)
{
if (t == nullptr)
return false;
if (x < t->data)
Remove(t->left, x);
else if (x > t->data)
Remove(t->right, x);
else
{
BSTNode<T> *q;
if (t->left == nullptr && t->right == nullptr)
{
delete t;
t = nullptr;
}
else if (t->left != nullptr && t->right == nullptr)
{
q = t;
t = t->left;
delete q;
}
else if (t->right != nullptr && t->left == nullptr)
{
q = t;
t = t->right;
delete q;
}
else
{
q = t->left;
while (q->right != nullptr)
q = q->right;
t->data = q->data;
Remove(t->left, q->data);
}
return true;
}
}
1.3 二叉搜索树的实现
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <assert.h>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
class BSTree;
template<class T>
class BSTNode
{
friend class BSTree<T>;
public:
BSTNode() :data(T()), left(nullptr), right(nullptr)
{}
BSTNode(T d, BSTNode<T> *left = nullptr, BSTNode<T> *right = nullptr)
:data(d), left(left), right(right)
{}
~BSTNode()
{}
private:
T data;
BSTNode<T>* left;
BSTNode<T>* right;
};
template<class T>
class BSTree
{
public:
BSTree() : root(nullptr)
{}
BSTree(vector<T> &v) : root(nullptr)
{
for (const auto &e : v)
Insert(e);
}
public:
T& Min()const
{
return Min(root);
}
T& Max()const
{
return Max(root);
}
BSTNode<T>* Search(const T &key)const
{
return Search(root, key);
}
bool Insert(const T &x)
{
return Insert(root, x);
}
bool Remove(const T &x)
{
return Remove(root, x);
}
void Sort()const
{
Sort(root);
}
protected:
T& Max(BSTNode<T> *t)const
{
assert(t != nullptr);
while (t->right != nullptr)
t = t->right;
return t->data;
}
T& Min(BSTNode<T> *t)const
{
assert(t != nullptr);
while (t->left != nullptr)
t = t->left;
return t->data;
}
BSTNode<T>* Search(BSTNode<T> *t, const T &key)const
{
if (t == nullptr || t->data == key)
return t;
if (key < t->data)
return Search(t->left, key);
else
return Search(t->right, key);
}
bool Insert(BSTNode<T> *&t, const T &x)
{
if (t == nullptr)
{
t = new BSTNode<T>(x);
return true;
}
if (x < t->data)
return Insert(t->left, x);
else if (x > t->data)
return Insert(t->right, x);
return false;
}
bool Remove(BSTNode<T> *&t, const T &x)
{
if (t == nullptr)
return false;
if (x < t->data)
Remove(t->left, x);
else if (x > t->data)
Remove(t->right, x);
else
{
BSTNode<T> *q;
if (t->left == nullptr && t->right == nullptr)
{
delete t;
t = nullptr;
}
else if (t->left != nullptr && t->right == nullptr)
{
q = t;
t = t->left;
delete q;
}
else if (t->right != nullptr && t->left == nullptr)
{
q = t;
t = t->right;
delete q;
}
else
{
q = t->left;
while (q->right != nullptr)
q = q->right;
t->data = q->data;
Remove(t->left, q->data);
}
return true;
}
}
void Sort(BSTNode<T> *t)const
{
if (t != nullptr)
{
Sort(t->left);
cout << t->data << ' ';
Sort(t->right);
}
}
private:
BSTNode<T> *root;
};
int main()
{
vector<int> iv{ 10, 15, 18, 12, 20, 5, 9, 7, 3 };
BSTree<int> bst(iv);
bst.Sort();
bst.Insert(13);
bst.Remove(18);
cout << endl;
bst.Sort();
cout << endl;
cout << bst.Max() << endl;
cout << bst.Min() << endl;
cout << bst.Search(20) << endl;
return 0;
}
1.4 二叉搜索树的性能分析
二叉搜索树的插入和删除都必须优先进行查找,因此查找效率代表了二叉搜索树的各操作的主要性能。我们假设某个元素的查找概率相等,如果二叉搜索树的高度越低,平均的比较次数就越少,但是由于树的插入顺序不一样,最后得到的二叉搜索树的结构也可能不一样,比如:再最优的情况下,二叉搜索树为完全二叉树,其平均比较次数为log2^N,最差情况下,二叉搜索树为单支树,这和顺序查找是一样的,其平均比较次数为N/2,那么,当二叉搜索树变成了单支树,就会失去二叉搜索树的性能,因此提出了平衡二叉搜索树。
以上是关于C++-二叉搜索树的查找&插入&删除-二叉搜索树代码实现-二叉搜索树性能分析及解决方案的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章