NC52275 图的遍历
Posted 吃花椒的妙酱
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了NC52275 图的遍历相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
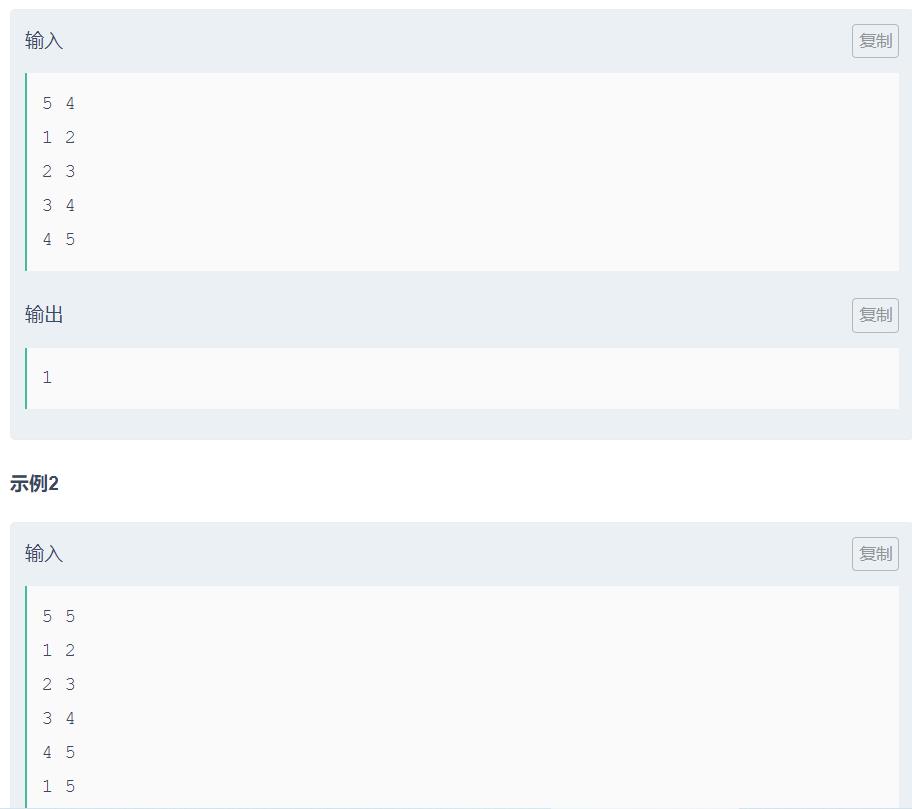
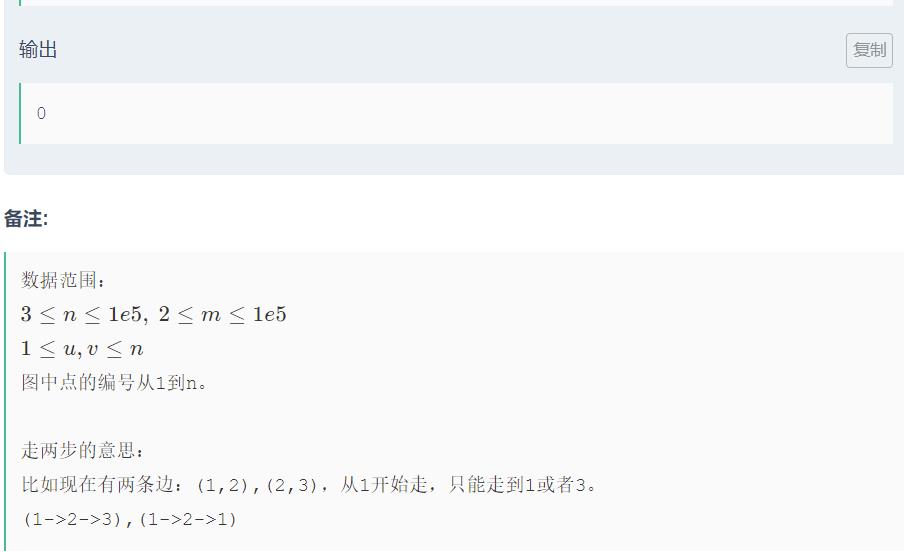
可以发现当,当出现奇环并且整张图联通时,可以跳两格遍历所有的点。
问题转换为判奇环,和连通块数目。
如何判奇环,在一个连通块中,如果相邻结点有(deep[i] - deep[j])%2==0,两个结点的深度差值为偶数,则有奇环,因为相邻距离为1,加上他们到所在的连通块起点距离为偶数,则是奇环。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <algorithm>
#include <map>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <bitset>
using namespace std;
#define _for(i,a,b) for(int i=(a) ;i<=(b) ;i++)
#define _rep(i,a,b) for(int i=(a) ;i>=(b) ;i--)
#define mst(v,s) memset(v,s,sizeof(v))
#define pb push_back
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
#define int long long
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
#define lson p<<1,l,mid
#define rson p<<1|1,mid+1,r
#define ls p<<1
#define rs p<<1|1
typedef long long ll;
const int N=1e5+10;
int n,m;
bool boo;//是否有奇环
struct ty
{
int t,next;
}edge[N<<1];
int tot,head[N];
void addedge(int x ,int y)
{
edge[++tot].t=y;
edge[tot].next=head[x];
head[x]=tot;
}
int v[N];
void dfs(int x)
{
for(int i=head[x] ;i!=0 ;i=edge[i].next)
{
int y = edge[i].t;
if( v[y] )
{
if((v[y]-v[x])%2==0) boo=1;
//到深度差为偶数则存在奇环
}
else
{
v[y]= v[x] + 1;
dfs(y);
}
}
return;
}
void solve()
{
int cnt=0;
_for(i,1,n)
{
if( !v[i] )
{
v[i]=1;
cnt++;//连通块数
dfs(i);
}
}
cnt--;
if( boo ) cout<<cnt<<endl;//有奇环的话
else cout<<cnt+1<<endl;
}
signed main()
{
///!!!
// freopen("data.txt","r",stdin);
// !!!
IOS;
cin>>n>>m;
_for(i,1,m)
{
int x,y;
cin>>x>>y;
addedge(x,y);addedge(y,x);
}
solve();
}
以上是关于NC52275 图的遍历的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章