iOS之深入解析malloc的底层原理
Posted Forever_wj
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了iOS之深入解析malloc的底层原理相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、前言
- ios 在创建对象的时候,alloc 方法有三个核心部分:cls->instanceSize(计算需要开辟内存的大小),calloc(开辟内存空间),obj->initlnstanceIsa(将 cls 类和 obj 指针关联)。
- 然而 obj = (id)calloc(1, size) 这一段代码所在位置不再是 libObjc4,它定位到了 libmalloc。
- malloc 的流程实质上是 iOS 对象申请内存空间实际的对齐方式是 8 字节对齐。
二、malloc_zone_t 分析
- malloc_zone_t 的结构如下:
typedef struct _malloc_zone_t {
void *reserved1; /* RESERVED FOR CFAllocator DO NOT USE */
void *reserved2; /* RESERVED FOR CFAllocator DO NOT USE */
size_t (* MALLOC_ZONE_FN_PTR(size))(struct _malloc_zone_t *zone, const void *ptr); /* returns the size of a block or 0 if not in this zone; must be fast, especially for negative answers */
void *(* MALLOC_ZONE_FN_PTR(malloc))(struct _malloc_zone_t *zone, size_t size);
void *(* MALLOC_ZONE_FN_PTR(calloc))(struct _malloc_zone_t *zone, size_t num_items, size_t size); /* same as malloc, but block returned is set to zero */
void *(* MALLOC_ZONE_FN_PTR(valloc))(struct _malloc_zone_t *zone, size_t size); /* same as malloc, but block returned is set to zero and is guaranteed to be page aligned */
void (* MALLOC_ZONE_FN_PTR(free))(struct _malloc_zone_t *zone, void *ptr);
void *(* MALLOC_ZONE_FN_PTR(realloc))(struct _malloc_zone_t *zone, void *ptr, size_t size);
void (* MALLOC_ZONE_FN_PTR(destroy))(struct _malloc_zone_t *zone);
const char *zone_name;
unsigned (* MALLOC_ZONE_FN_PTR(batch_malloc))(struct _malloc_zone_t *zone, size_t size, void **results, unsigned num_requested);
struct malloc_introspection_t * MALLOC_INTROSPECT_TBL_PTR(introspect);
unsigned version;
void *(* MALLOC_ZONE_FN_PTR(memalign))(struct _malloc_zone_t *zone, size_t alignment, size_t size);
void (* MALLOC_ZONE_FN_PTR(free_definite_size))(struct _malloc_zone_t *zone, void *ptr, size_t size);
size_t (* MALLOC_ZONE_FN_PTR(pressure_relief))(struct _malloc_zone_t *zone, size_t goal);
boolean_t (* MALLOC_ZONE_FN_PTR(claimed_address))(struct _malloc_zone_t *zone, void *ptr);
} malloc_zone_t;
- malloc_zone_t 是一个非常基础结构,里面包含一堆函数指针,用来存储一堆相关的处理函数的具体实现的地址,例如 malloc、free、realloc 等函数的具体实现。
三、calloc 流程分析
① calloc -> malloc_zone_calloc 流程
- 进入 calloc -> malloc_zone_calloc 源码,实现如下:
void * calloc(size_t num_items, size_t size)
{
void *retval;
retval = malloc_zone_calloc(default_zone, num_items, size);
if (retval == NULL) {
errno = ENOMEM;
}
return retval;
}
- 其中 default_zone 其实是一个“假” zone,同时它也是 malloc_zone_t 类型。
- 它存在的目的就是要引导程序进入一个创建真正的 zone 的流程。
② default_zone
- malloc_zone_calloc 传入的 default_zone,执行 ptr = zone->calloc(zone, num_items, size),如下:
void * malloc_zone_calloc(malloc_zone_t *zone, size_t num_items, size_t size)
{
MALLOC_TRACE(TRACE_calloc | DBG_FUNC_START, (uintptr_t)zone, num_items, size, 0);
void *ptr;
if (malloc_check_start && (malloc_check_counter++ >= malloc_check_start)) {
internal_check();
}
ptr = zone->calloc(zone, num_items, size);
if (malloc_logger) {
malloc_logger(MALLOC_LOG_TYPE_ALLOCATE | MALLOC_LOG_TYPE_HAS_ZONE | MALLOC_LOG_TYPE_CLEARED, (uintptr_t)zone,
(uintptr_t)(num_items * size), 0, (uintptr_t)ptr, 0);
}
MALLOC_TRACE(TRACE_calloc | DBG_FUNC_END, (uintptr_t)zone, num_items, size, (uintptr_t)ptr);
return ptr;
}
- 此时传进来的 zone 的类型是上面 calloc 传入的 default_zone,所以 zone->calloc 的调用实现要看 default_zone 的定义。
③ defaultzone 定义
- defaultzone 定义如下,可以看出 defaultzone->calloc 实际的函数实现为 default_zone_calloc:
static virtual_default_zone_t virtual_default_zone
__attribute__((section("__DATA,__v_zone")))
__attribute__((aligned(PAGE_MAX_SIZE))) = {
NULL,
NULL,
default_zone_size,
default_zone_malloc,
default_zone_calloc,
default_zone_valloc,
default_zone_free,
default_zone_realloc,
default_zone_destroy,
DEFAULT_MALLOC_ZONE_STRING,
default_zone_batch_malloc,
default_zone_batch_free,
&default_zone_introspect,
10,
default_zone_memalign,
default_zone_free_definite_size,
default_zone_pressure_relief,
default_zone_malloc_claimed_address,
};
- 然后引导创建真正的 zone,使用真正的 zone 进行 calloc,如下:
static void *
default_zone_calloc(malloc_zone_t *zone, size_t num_items, size_t size) {
zone = runtime_default_zone();
return zone->calloc(zone, num_items, size);
}
④ zone 分析
- 在创建正在的 zone 时,其实系统是有对应的一套创建策略的,在跟踪 runtime_default_zone 方法后,最终会进入如下调用:
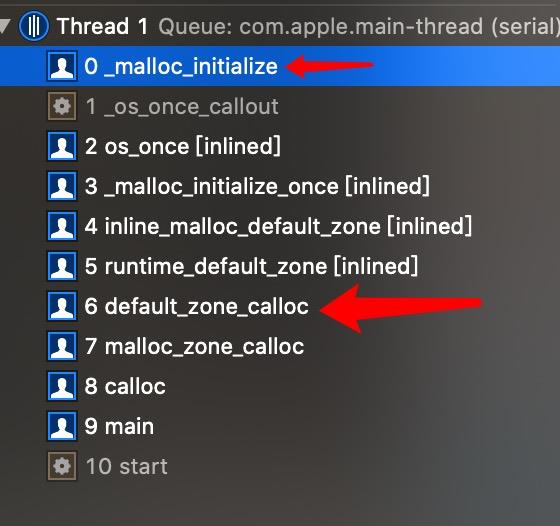
- 继续去源码查看 _malloc_initialize 方法,实现如下:
static void
_malloc_initialize(void *context __unused) {
......
// 创建helper_zone,
malloc_zone_t *helper_zone = create_scalable_zone(0, malloc_debug_flags);
// 创建 nano zone
if (_malloc_engaged_nano == NANO_V2) {
zone = nanov2_create_zone(helper_zone, malloc_debug_flags);
} else if (_malloc_engaged_nano == NANO_V1) {
zone = nano_create_zone(helper_zone, malloc_debug_flags);
}
// 如果上面的if else if 成立,这进入 nonazone
if (zone) {
malloc_zone_register_while_locked(zone);
malloc_zone_register_while_locked(helper_zone);
// Must call malloc_set_zone_name() *after* helper and nano are hooked together.
malloc_set_zone_name(zone, DEFAULT_MALLOC_ZONE_STRING);
malloc_set_zone_name(helper_zone, MALLOC_HELPER_ZONE_STRING);
} else {
// 使用helper_zone分配内存
zone = helper_zone;
malloc_zone_register_while_locked(zone);
malloc_set_zone_name(zone, DEFAULT_MALLOC_ZONE_STRING);
}
// 缓存default_zone
initial_default_zone = zone;
.....
}
- 可以看到,主要执行了以下逻辑:
-
- 创建 helper_zone;
-
- 创建 nano zone;
-
- 如果上面的 if else if 成立,这进入 nonazone;
-
- 使用 helper_zone 分配内存;
-
- 缓存 default_zone。
- 需要注意的是,在这里 zone 会存在两种情况:nanozone_t 和 scalable_zone。
⑤ nanozone_t 分析
- nanozone_t 的定义如下:
typedef struct nano_meta_s {
OSQueueHead slot_LIFO MALLOC_NANO_CACHE_ALIGN;
unsigned int slot_madvised_log_page_count;
volatile uintptr_t slot_current_base_addr;
volatile uintptr_t slot_limit_addr;
volatile size_t slot_objects_mapped;
volatile size_t slot_objects_skipped;
bitarray_t slot_madvised_pages;
// position on cache line distinct from that of slot_LIFO
volatile uintptr_t slot_bump_addr MALLOC_NANO_CACHE_ALIGN;
volatile boolean_t slot_exhausted;
unsigned int slot_bytes;
unsigned int slot_objects;
} *nano_meta_admin_t;
// vm_allocate()'d, so page-aligned to begin with.
typedef struct nanozone_s {
// first page will be given read-only protection
malloc_zone_t basic_zone;
uint8_t pad[PAGE_MAX_SIZE - sizeof(malloc_zone_t)];
// remainder of structure is R/W (contains no function pointers)
// page-aligned
// max: NANO_MAG_SIZE cores x NANO_SLOT_SIZE slots for nano blocks {16 .. 256}
//以Mag、Slot为维度,维护申请的band内存部分 slot 的范围为 1~16
struct nano_meta_s meta_data[NANO_MAG_SIZE][NANO_SLOT_SIZE];//
_malloc_lock_s band_resupply_lock[NANO_MAG_SIZE];
uintptr_t band_max_mapped_baseaddr[NANO_MAG_SIZE];
size_t core_mapped_size[NANO_MAG_SIZE];
unsigned debug_flags;
uintptr_t cookie;
malloc_zone_t *helper_zone;
} nanozone_t;
- 可以看到,nanozone_t 同样是 malloc_zone_t 类型,在nano_create_zone 函数内部会完成对 calloc 等函数的重新赋值。
⑥ nano_create_zone 分析
- nano_create_zone 的实现如下:
malloc_zone_t *
nano_create_zone(malloc_zone_t *helper_zone, unsigned debug_flags)
{
nanozone_t *nanozone;
int i, j;
// 构造nano zone
/* Note: It is important that nano_create_zone resets _malloc_engaged_nano
* if it is unable to enable the nanozone (and chooses not to abort). As
* several functions rely on _malloc_engaged_nano to determine if they
* should manipulate the nanozone, and these should not run if we failed
* to create the zone.
*/
// MALLOC_ASSERT(_malloc_engaged_nano == NANO_V1);
/* get memory for the zone. */
nanozone = nano_common_allocate_based_pages(NANOZONE_PAGED_SIZE, 0, 0, VM_MEMORY_MALLOC, 0);
if (!nanozone) {
_malloc_engaged_nano = NANO_NONE;
return NULL;
}
// 构造对zone 的一些函数进行重新赋值
/* set up the basic_zone portion of the nanozone structure */
nanozone->basic_zone.version = 10;
nanozone->basic_zone.size = (void *)nano_size;
nanozone->basic_zone.malloc = (debug_flags & MALLOC_DO_SCRIBBLE) ? (void *)nano_malloc_scribble : (void *)nano_malloc;
nanozone->basic_zone.calloc = (void *)nano_calloc;
nanozone->basic_zone.valloc = (void *)nano_valloc;
nanozone->basic_zone.free = (debug_flags & MALLOC_DO_SCRIBBLE) ? (void *)nano_free_scribble : (void *)nano_free;
nanozone->basic_zone.realloc = (void *)nano_realloc;
nanozone->basic_zone.destroy = (void *)nano_destroy;
nanozone->basic_zone.batch_malloc = (void *)nano_batch_malloc;
nanozone->basic_zone.batch_free = (void *)nano_batch_free;
nanozone->basic_zone.introspect = (struct malloc_introspection_t *)&nano_introspect;
nanozone->basic_zone.memalign = (void *)nano_memalign;
nanozone->basic_zone.free_definite_size = (debug_flags & MALLOC_DO_SCRIBBLE) ? (void *)nano_free_definite_size_scribble
: (void *)nano_free_definite_size;
nanozone->basic_zone.pressure_relief = (void *)nano_pressure_relief;
nanozone->basic_zone.claimed_address = (void *)nano_claimed_address;
nanozone->basic_zone.reserved1 = 0; /* Set to zero once and for all as required by CFAllocator. */
nanozone->basic_zone.reserved2 = 0; /* Set to zero once and for all as required by CFAllocator. */
mprotect(nanozone, sizeof(nanozone->basic_zone), PROT_READ); /* Prevent overwriting the function pointers in basic_zone. */
/* Nano zone does not support MALLOC_ADD_GUARD_PAGES. */
if (debug_flags & MALLOC_ADD_GUARD_PAGES) {
malloc_report(ASL_LEVEL_INFO, "nano zone does not support guard pages\\n");
debug_flags &= ~MALLOC_ADD_GUARD_PAGES;
}
/* set up the remainder of the nanozone structure */
nanozone->debug_flags = debug_flags;
if (phys_ncpus > sizeof(nanozone->core_mapped_size) /
sizeof(nanozone->core_mapped_size[0])) {
MALLOC_REPORT_FATAL_ERROR(phys_ncpus,
"nanozone abandoned because NCPUS > max magazines.\\n");
}
/* Initialize slot queue heads and resupply locks. */
OSQueueHead q0 = OS_ATOMIC_QUEUE_INIT;
for (i = 0; i < nano_common_max_magazines; ++i) {
_malloc_lock_init(&nanozone->band_resupply_lock[i]);
for (j = 0; j < NANO_SLOT_SIZE; ++j) {
nanozone->meta_data[i][j].slot_LIFO = q0;
}
}
/* Initialize the security token. */
nanozone->cookie = (uintptr_t)malloc_entropy[0] & 0x0000ffffffff0000ULL; // scramble central 32bits with this cookie
nanozone->helper_zone = helper_zone;
return (malloc_zone_t *)nanozone;
}
- 在 nano_create_zone 中主要做了:
-
- 构造 nano zone;
-
- 构造对 zone 的一些函数进行重新赋值;
-
- Nano zone 不支持 MALLOC_ADD_GUARD_PAGES;
-
- 建立其余的 nanozone 结构;
-
- 初始化插槽队列头并重新供应锁;
-
- 初始化安全令牌。
⑦ nano_calloc 分析
- nano_calloc 的实现如下:
static void *
nano_calloc(nanozone_t *nanozone, size_t num_items, size_t size) {
size_t total_bytes;
if (calloc_get_size(num_items, size, 0, &total_bytes)) {
return NULL;
}
// 如果要开辟的空间小于 NANO_MAX_SIZE 则进行nanozone_t的malloc。
if (total_bytes <= NANO_MAX_SIZE) {
void *p = _nano_malloc_check_clear(nanozone, total_bytes, 1);
if (p) {
return p;
} else {
/* FALLTHROUGH to helper zone */
}
}
// 否则就进行helper_zone的流程
malloc_zone_t *zone = (malloc_zone_t *)(nanozone->helper_zone);
return zone->calloc(zone, 1, total_bytes);
}
- nano_calloc 中根据要开辟的空间 total_bytes 的大小,如果小于 NANO_MAX_SIZE 则进行,否则就进行 helper_zone 的流程。
⑧ _nano_malloc_check_clear 分析
- _nano_malloc_check_clear 的实现如下,可以看到使用 nanozone_t 的限制为不超过 256B:
static void *
_nano_malloc_check_clear(nanozone_t *nanozone, size_t size, boolean_t cleared_requested)
{
MALLOC_TRACE(TRACE_nano_malloc, (uintptr_t)nanozone, size, cleared_requested, 0);
void *ptr;
size_t slot_key;
// 获取16字节对齐之后的大小,slot_key非常关键,为slot_bytes/16的值,也是数组的二维下下标
size_t slot_bytes = segregated_size_to_fit(nanozone, size, &slot_key); // Note slot_key is set here
// 根据_os_cpu_number经过运算获取 mag_index(meta_data的一维索引)
mag_index_t mag_index = nano_mag_index(nanozone);
// 确定当前cpu对应的mag和通过size参数计算出来的slot,去对应metadata的链表中取已经被释放过的内存区块缓存
nano_meta_admin_t pMeta = &(nanozone->meta_data[mag_index][slot_key]);
// 检测是否存在已经释放过,可以直接拿来用的内存,已经被释放的内存会缓存在 chained_block_s 链表
// 每一次free。同样会根据 index 和slot 的值回去 pMeta,然后把slot_LIFO的指针指向释放的内存。
ptr = OSAtomicDequeue(&(pMeta->slot_LIFO), offsetof(struct chained_block_s, next));
if (ptr) {
...
// 如果缓存的内存存在,这进行指针地址检查等异常检测,最后返回
// 第一次调用malloc时,不会执行这一块代码。
} else {
// 没有释放过的内存,所以调用函数 获取内存
ptr = segregated_next_block(nanozone, pMeta, slot_bytes, mag_index);
}
if (cleared_requested && ptr) {
memset(ptr, 0, slot_bytes); // TODO: Needs a memory barrier after memset to ensure zeroes land first?
}
return ptr;
}
- _nano_malloc_check_clear 流程分析:
-
- 获取 16 字节对齐之后的大小,slot_key 非常关键,为 slot_bytes/16 的值,也是数组的二维下下标;
-
- 根据 _os_cpu_number 经过运算获取 mag_index ( meta_data 的一维索引);
-
- 确定当前 cpu 对应的 mag 和通过 size 参数计算出来的 slot,去对应 metadata 的链表中取已经被释放过的内存区块缓存;
-
- 检测是否存在已经释放过,可以直接拿来用的内存,已经被释放的内存会缓存在 chained_block_s 链表;
-
- 每一次 free,同样会根据 index 和 slot 的值回去 pMeta,然后把 slot_LIFO 的指针指向释放的内存;
-
- 如果缓存的内存存在,这进行指针地址检查等异常检测,最后返回;
-
- 没有释放过的内存,所以调用函数获取内存。
- 因此,_nano_malloc_check_clear 方法主要是通过 cpu 与 slot 确定 index,从chained_block_s 链表中找出是否存在已经释放过的缓存。如果存在则进行指针检查之后返回,否则进入查询 meta data 或者开辟 band。
⑨ segregated_next_block 分析
- segregated_next_block 实现如下:
static MALLOC_INLINE void *
segregated_next_block(nanozone_t *nanozone, nano_meta_admin_t pMeta, size_t slot_bytes, unsigned int mag_index) {
while (1) {
// 当前这块pMeta可用内存的结束地址
uintptr_t theLimit = pMeta->slot_limit_addr; // Capture the slot limit that bounds slot_bump_addr right now
// 原子的为pMeta->slot_bump_addr添加slot_bytes的长度,偏移到下一个地址
uintptr_t b = OSAtomicAdd64Barrier(slot_bytes, (volatile int64_t *)&(pMeta->slot_bump_addr));
// 减去添加的偏移量,获取当前可以获取的地址
b -= slot_bytes; // Atomic op returned addr of *next* free block. Subtract to get addr for *this* allocation.
if (b < theLimit