Linux内核性能架构:perf_event
Posted rtoax
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Linux内核性能架构:perf_event相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目录
http://terenceli.github.io/%E6%8A%80%E6%9C%AF/2020/08/29/perf-arch
组件概述
Linux性能子系统在性能分析中非常有用。以下显示了这篇文章中的perf子系统componenet 。

“ perf”是可用于执行性能分析的用户程序。
仅暴露给用户空间的系统调用perf_event_open返回一个perf事件fd。该系统调用没有glibc包装器。更多信息可以在手册页中阅读。此功能是最复杂的功能之一。
“ perf_event”是内核中的核心结构。性能事件有几种类型,例如跟踪点,软件,硬件。
我们还可以通过perf event fd将eBPF程序附加到trae事件。
抽象层
以下显示了perf的抽象层。
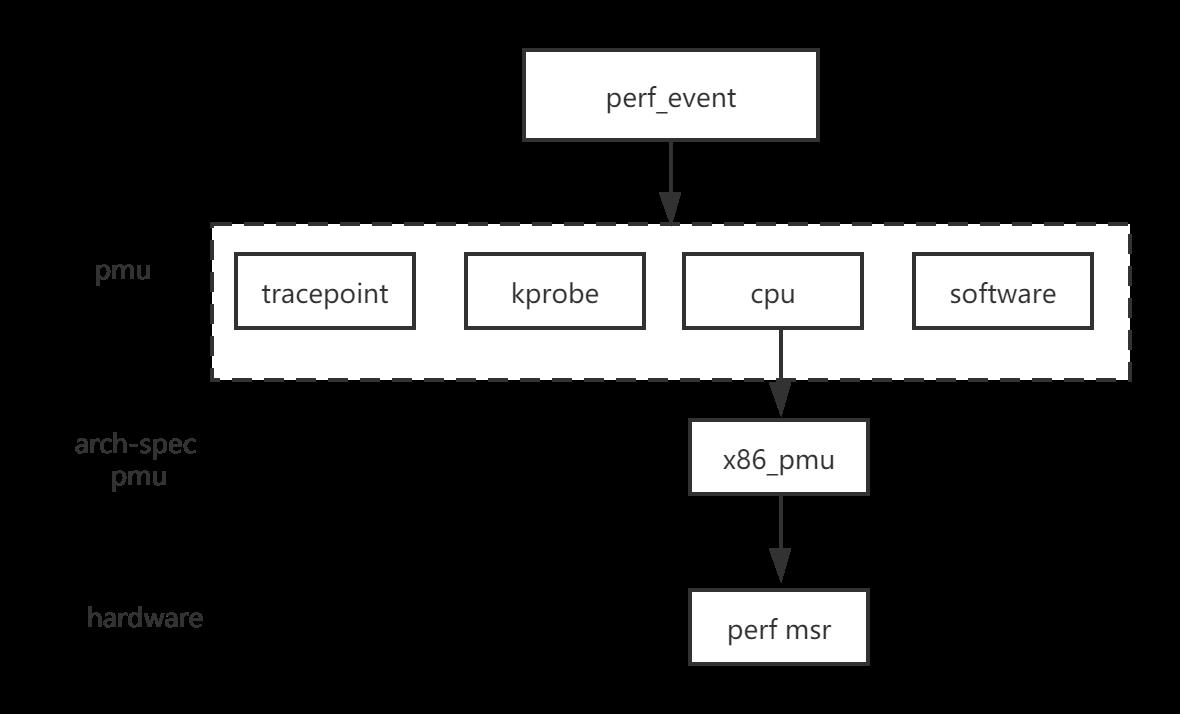
每个类型的性能事件都有一个对应的PMU(性能监视单元)。例如,跟踪点pmu具有以下pmu。
static struct pmu perf_tracepoint = {
.task_ctx_nr = perf_sw_context,
.event_init = perf_tp_event_init,
.add = perf_trace_add,
.del = perf_trace_del,
.start = perf_swevent_start,
.stop = perf_swevent_stop,
.read = perf_swevent_read,
};与硬件相关的PMU具有与arch-spec有关的抽象结构,例如'struct x86_pmu'。与硬件相关的结构将读取/写入性能监视器MSR。
每个PMU都通过调用“ perf_pmu_register”进行注册。
性能事件上下文
性能可以监视cpu相关事件和任务相关事件。他们两个都可以有几个受监视的事件。因此,我们需要一个上下文来连接事件。这是“ perf_event_context”。
有两种上下文,软件和硬件,定义如下:
enum perf_event_task_context {
perf_invalid_context = -1,
perf_hw_context = 0,
perf_sw_context,
perf_nr_task_contexts,
};对于CPU级别,上下文定义为“ perf_cpu_context”,并在“ struct pmu”中定义为percpu变量。
struct pmu {
...
struct perf_cpu_context __percpu *pmu_cpu_context;
};如果PMU是相同类型,则它们将共享一个“ struct perf_cpu_context”。
int perf_pmu_register(struct pmu *pmu, const char *name, int type)
{
int cpu, ret, max = PERF_TYPE_MAX;
mutex_lock(&pmus_lock);
...
pmu->pmu_cpu_context = find_pmu_context(pmu->task_ctx_nr);
if (pmu->pmu_cpu_context)
goto got_cpu_context;
ret = -ENOMEM;
pmu->pmu_cpu_context = alloc_percpu(struct perf_cpu_context);
if (!pmu->pmu_cpu_context)
goto free_dev;
for_each_possible_cpu(cpu) {
struct perf_cpu_context *cpuctx;
cpuctx = per_cpu_ptr(pmu->pmu_cpu_context, cpu);
__perf_event_init_context(&cpuctx->ctx);
lockdep_set_class(&cpuctx->ctx.mutex, &cpuctx_mutex);
lockdep_set_class(&cpuctx->ctx.lock, &cpuctx_lock);
cpuctx->ctx.pmu = pmu;
cpuctx->online = cpumask_test_cpu(cpu, perf_online_mask);
__perf_mux_hrtimer_init(cpuctx, cpu);
cpuctx->heap_size = ARRAY_SIZE(cpuctx->heap_default);
cpuctx->heap = cpuctx->heap_default;
}
...
}下图显示了此帖子中的相关结构。

对于任务级别,“ task_struct”具有如下定义的指针数组:
struct task_struct {
struct perf_event_context *perf_event_ctxp[perf_nr_task_contexts];
};下图显示了相关结构,也来自于该帖子。

CPU在线时将触发CPU级性能事件。但是对于任务级别的perf事件,只能通过运行任务来触发它。“ perf_cpu_context”的task_ctx包含当前正在运行的任务的perf上下文。
性能事件上下文时间表
性能的一项工作是安排任务的perf_event_context的进出时间。
下图显示了与性能相关的任务计划输入和输出功能。
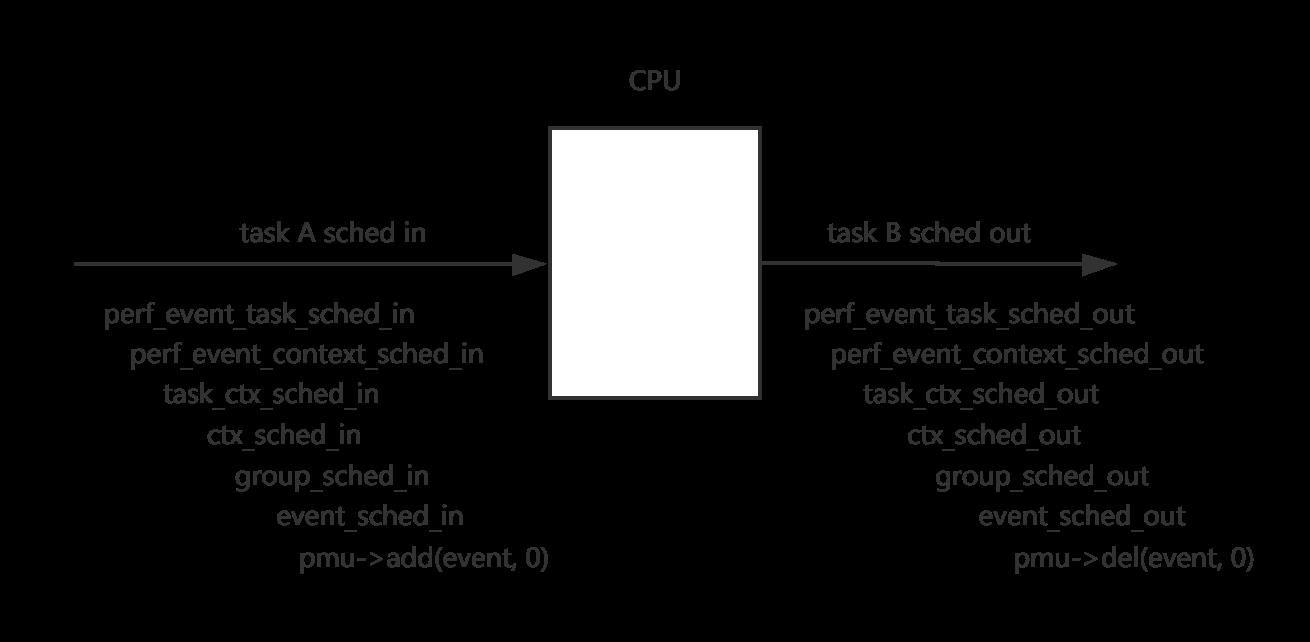
最后,将调用PMU的add和del回调。让我们以跟踪点为例。add回调是“ perf_trace_add”,而del回调是“ perf_trace_add”。
int perf_trace_add(struct perf_event *p_event, int flags)
{
struct trace_event_call *tp_event = p_event->tp_event;
if (!(flags & PERF_EF_START))
p_event->hw.state = PERF_HES_STOPPED;
/*
* If TRACE_REG_PERF_ADD returns false; no custom action was performed
* and we need to take the default action of enqueueing our event on
* the right per-cpu hlist.
*/
if (!tp_event->class->reg(tp_event, TRACE_REG_PERF_ADD, p_event)) {
struct hlist_head __percpu *pcpu_list;
struct hlist_head *list;
pcpu_list = tp_event->perf_events;
if (WARN_ON_ONCE(!pcpu_list))
return -EINVAL;
list = this_cpu_ptr(pcpu_list);
hlist_add_head_rcu(&p_event->hlist_entry, list);
}
return 0;
}
void perf_trace_del(struct perf_event *p_event, int flags)
{
struct trace_event_call *tp_event = p_event->tp_event;
/*
* If TRACE_REG_PERF_DEL returns false; no custom action was performed
* and we need to take the default action of dequeueing our event from
* the right per-cpu hlist.
*/
if (!tp_event->class->reg(tp_event, TRACE_REG_PERF_DEL, p_event))
hlist_del_rcu(&p_event->hlist_entry);
}“ perf_event”将被添加或删除到“ tp_event-> perf_events”列表中。
perf_event_open流
perf_event_open
->perf_copy_attr
->get_unused_fd_flags(fd)
->perf_event_alloc
->perf_init_event
->perf_try_init_event
->pmu->event_init()
->find_get_context
->perf_install_in_context
->__perf_install_in_context
->add_event_to_ctx
->list_add_event
->perf_group_attach
->add_event_to_ctx
->fd_installperf_event_open将调用'pmu-> event_init'来初始化事件。并将perf_event添加到perf_event_context中。
性能跟踪事件
回顾跟踪点PMU的定义。
static struct pmu perf_tracepoint = {
.task_ctx_nr = perf_sw_context,
.event_init = perf_tp_event_init,
.add = perf_trace_add,
.del = perf_trace_del,
.start = perf_swevent_start,
.stop = perf_swevent_stop,
.read = perf_swevent_read,
};让我们尝试看一下perf子系统如何监视跟踪点事件。
性能事件初始化
称为“ perf_tp_event_init”。
perf_tp_event_init
->perf_trace_init
->perf_trace_event_init
->perf_trace_event_reg
->tp_event->class->reg(TRACE_REG_PERF_REGISTER)'perf_trace_init'将找到指定的跟踪点。
“ perf_trace_event_reg”将分配并初始化“ tp_event_perf_events”列表。并使用TRACE_REG_PERF_REGISTER调用“ tp_event-> class-> reg”。
static int perf_trace_event_reg(struct trace_event_call *tp_event,
struct perf_event *p_event)
{
struct hlist_head __percpu *list;
int ret = -ENOMEM;
int cpu;
p_event->tp_event = tp_event;
if (tp_event->perf_refcount++ > 0)
return 0;
list = alloc_percpu(struct hlist_head);
if (!list)
goto fail;
for_each_possible_cpu(cpu)
INIT_HLIST_HEAD(per_cpu_ptr(list, cpu));
tp_event->perf_events = list;
...
ret = tp_event->class->reg(tp_event, TRACE_REG_PERF_REGISTER, NULL);
if (ret)
goto fail;
total_ref_count++;
return 0;
...
}“ tp_event_> class-> reg”回调为“ trace_event_reg”。
int trace_event_reg(struct trace_event_call *call,
enum trace_reg type, void *data)
{
struct trace_event_file *file = data;
WARN_ON(!(call->flags & TRACE_EVENT_FL_TRACEPOINT));
switch (type) {
...
#ifdef CONFIG_PERF_EVENTS
case TRACE_REG_PERF_REGISTER:
return tracepoint_probe_register(call->tp,
call->class->perf_probe,
call);
case TRACE_REG_PERF_UNREGISTER:
tracepoint_probe_unregister(call->tp,
call->class->perf_probe,
call);
return 0;
case TRACE_REG_PERF_OPEN:
case TRACE_REG_PERF_CLOSE:
case TRACE_REG_PERF_ADD:
case TRACE_REG_PERF_DEL:
return 0;
#endif
}
return 0;
}我们可以看到'call-> class-> perf_probe'将被注册到跟踪点。从我的帖子。我们知道这个“ perf_probe”是“ perf_trace _ ## call”。
static notrace void \\
perf_trace_##call(void *__data, proto) \\
{ \\
struct trace_event_call *event_call = __data; \\
struct trace_event_data_offsets_##call __maybe_unused __data_offsets;\\
struct trace_event_raw_##call *entry; \\
struct pt_regs *__regs; \\
u64 __count = 1; \\
struct task_struct *__task = NULL; \\
struct hlist_head *head; \\
int __entry_size; \\
int __data_size; \\
int rctx; \\
\\
__data_size = trace_event_get_offsets_##call(&__data_offsets, args); \\
\\
head = this_cpu_ptr(event_call->perf_events); \\
if (!bpf_prog_array_valid(event_call) && \\
__builtin_constant_p(!__task) && !__task && \\
hlist_empty(head)) \\
return; \\
\\
__entry_size = ALIGN(__data_size + sizeof(*entry) + sizeof(u32),\\
sizeof(u64)); \\
__entry_size -= sizeof(u32); \\
\\
entry = perf_trace_buf_alloc(__entry_size, &__regs, &rctx); \\
if (!entry) \\
return; \\
\\
perf_fetch_caller_regs(__regs); \\
\\
tstruct \\
\\
{ assign; } \\
\\
perf_trace_run_bpf_submit(entry, __entry_size, rctx, \\
event_call, __count, __regs, \\
head, __task); \\
}如果“ event_call-> perf_events”为空,则表示没有任何当前的perf_event添加到该跟踪点。这是'perf_event_open'初始化perf_event时的默认状态。
性能事件添加
在CPU中调度任务时,将调用'pmu-> add',并将'perf_event'链接到'event_call-> perf_events'链接列表。
性能事件
从CPU调度任务后,将调用“ pmu-> del”,并且将从“ event_call-> perf_events”链接列表中删除“ perf_event”。
性能事件触发器
如果'event_call-> perf_events'不为空,则将调用'perf_trace_run_bpf_submit'。如果没有附加eBPF程序,则将调用“ perf_tp_event”。
void perf_tp_event(u16 event_type, u64 count, void *record, int entry_size,
struct pt_regs *regs, struct hlist_head *head, int rctx,
struct task_struct *task)
{
struct perf_sample_data data;
struct perf_event *event;
struct perf_raw_record raw = {
.frag = {
.size = entry_size,
.data = record,
},
};
perf_sample_data_init(&data, 0, 0);
data.raw = &raw;
perf_trace_buf_update(record, event_type);
hlist_for_each_entry_rcu(event, head, hlist_entry) {
if (perf_tp_event_match(event, &data, regs))
perf_swevent_event(event, count, &data, regs);
}
...
perf_swevent_put_recursion_context(rctx);
}对于“ event_call-> perf_events”列表中的每个“ perf_event”。它调用perf_swevent_event触发性能事件。
static void perf_swevent_event(struct perf_event *event, u64 nr,
struct perf_sample_data *data,
struct pt_regs *regs)
{
struct hw_perf_event *hwc = &event->hw;
local64_add(nr, &event->count);
if (!regs)
return;
if (!is_sampling_event(event))
return;
if ((event->attr.sample_type & PERF_SAMPLE_PERIOD) && !event->attr.freq) {
data->period = nr;
return perf_swevent_overflow(event, 1, data, regs);
} else
data->period = event->hw.last_period;
if (nr == 1 && hwc->sample_period == 1 && !event->attr.freq)
return perf_swevent_overflow(event, 1, data, regs);
if (local64_add_negative(nr, &hwc->period_left))
return;
perf_swevent_overflow(event, 0, data, regs);
}'perf_swevent_event'添加'event-> count'。如果事件未采样,则仅返回。Tis是性能计数模式。如果perf_event在样本模式下,则需要复制跟踪点数据。以下是呼叫链。
perf_swevent_overflow
->__perf_event_overflow->event
->overflow_handler(perf_event_output).软件性能事件
软件PMU定义如下:
static struct pmu perf_swevent = {
.task_ctx_nr = perf_sw_context,
.capabilities = PERF_PMU_CAP_NO_NMI,
.event_init = perf_swevent_init,
.add = perf_swevent_add,
.del = perf_swevent_del,
.start = perf_swevent_start,
.stop = perf_swevent_stop,
.read = perf_swevent_read,
};性能事件初始化
“ perf_swevent_init”将被调用。它称为“ swevent_hlist_get”
static int perf_swevent_init(struct perf_event *event)
{
u64 event_id = event->attr.config;
if (event->attr.type != PERF_TYPE_SOFTWARE)
return -ENOENT;
/*
* no branch sampling for software events
*/
if (has_branch_stack(event))
return -EOPNOTSUPP;
switch (event_id) {
case PERF_COUNT_SW_CPU_CLOCK:
case PERF_COUNT_SW_TASK_CLOCK:
return -ENOENT;
default:
break;
}
if (event_id >= PERF_COUNT_SW_MAX)
return -ENOENT;
if (!event->parent) {
int err;
err = swevent_hlist_get();
if (err)
return err;
static_key_slow_inc(&perf_swevent_enabled[event_id]);
event->destroy = sw_perf_event_destroy;
}
return 0;
}这将创建一个percpu'swhash-> swevent_hlist'列表。还要将perf_swevent_enabled [event_id]设置为true。
性能事件添加
'perf_swevent_add'将perf_event添加到percpu哈希列表中。
static int perf_swevent_add(struct perf_event *event, int flags)
{
struct swevent_htable *swhash = this_cpu_ptr(&swevent_htable);
struct hw_perf_event *hwc = &event->hw;
struct hlist_head *head;
if (is_sampling_event(event)) {
hwc->last_period = hwc->sample_period;
perf_swevent_set_period(event);
}
hwc->state = !(flags & PERF_EF_START);
head = find_swevent_head(swhash, event);
if (WARN_ON_ONCE(!head))
return -EINVAL;
hlist_add_head_rcu(&event->hlist_entry, head);
perf_event_update_userpage(event);
return 0;
}性能事件
'perf_swevent_del'从哈希列表中删除。
static void perf_swevent_del(struct perf_event *event, int flags)
{
hlist_del_rcu(&event->hlist_entry);
}性能事件触发器
以任务开关为例。
“ perf_sw_event_sched”将被调用。
static inline void perf_event_task_sched_out(struct task_struct *prev,
struct task_struct *next)
{
perf_sw_event_sched(PERF_COUNT_SW_CONTEXT_SWITCHES, 1, 0);
if (static_branch_unlikely(&perf_sched_events))
__perf_event_task_sched_out(prev, next);
}在perf_event_task_sched_out-> _perf_sw_event-> do_perf_sw_event调用链之后。
static void do_perf_sw_event(enum perf_type_id type, u32 event_id,
u64 nr,
struct perf_sample_data *data,
struct pt_regs *regs)
{
struct swevent_htable *swhash = this_cpu_ptr(&swevent_htable);
struct perf_event *event;
struct hlist_head *head;
rcu_read_lock();
head = find_swevent_head_rcu(swhash, type, event_id);
if (!head)
goto end;
hlist_for_each_entry_rcu(event, head, hlist_entry) {
if (perf_swevent_match(event, type, event_id, data, regs))
perf_swevent_event(event, nr, data, regs);
}
end:
rcu_read_unlock();
}如我们所见,它最终会调用“ perf_swevent_event”来触发事件。
硬件性能事件
硬件PMU之一定义如下:
static struct pmu pmu = {
.pmu_enable = x86_pmu_enable,
.pmu_disable = x86_pmu_disable,
.attr_groups = x86_pmu_attr_groups,
.event_init = x86_pmu_event_init,
.event_mapped = x86_pmu_event_mapped,
.event_unmapped = x86_pmu_event_unmapped,
.add = x86_pmu_add,
.del = x86_pmu_del,
.start = x86_pmu_start,
.stop = x86_pmu_stop,
.read = x86_pmu_read,
.start_txn = x86_pmu_start_txn,
.cancel_txn = x86_pmu_cancel_txn,
.commit_txn = x86_pmu_commit_txn,
.event_idx = x86_pmu_event_idx,
.sched_task = x86_pmu_sched_task,
.task_ctx_size = sizeof(struct x86_perf_task_context),
.swap_task_ctx = x86_pmu_swap_task_ctx,
.check_period = x86_pmu_check_period,
.aux_output_match = x86_pmu_aux_output_match,
};硬件性能事件非常复杂,因为它将与硬件交互。这里不会深入介绍硬件。
性能事件初始化
x86_pmu_event_init
->__x86_pmu_event_init
->x86_reserve_hardware
->x86_pmu.hw_config()
->validate_event此处的“ x86_pmu”是基于arch规范的PMU结构。
性能事件添加
x86_pmu_add->收集事件->-> x86_pmu.schedule_events()-> x86_pmu.add
'collect_events'集
cpuc->event_list[n] = leader;性能事件
x86_pmu_del将删除“ cpuc-> event_list”中的事件。
性能事件触发器
触发硬件事件时,它将触发NMI中断。此处理程序是“ perf_event_nmi_handler”。
static int
perf_event_nmi_handler(unsigned int cmd, struct pt_regs *regs)
{
u64 start_clock;
u64 finish_clock;
int ret;
/*
* All PMUs/events that share this PMI handler should make sure to
* increment active_events for their events.
*/
if (!atomic_read(&active_events))
return NMI_DONE;
start_clock = sched_clock();
ret = x86_pmu.handle_irq(regs);
finish_clock = sched_clock();
perf_sample_event_took(finish_clock - start_clock);
return ret;
}以Taks'x86_pmu.handle_irq'= x86_pmu_handle_irq为例。
for (idx = 0; idx < x86_pmu.num_counters; idx++) {
if (!test_bit(idx, cpuc->active_mask))
continue;
event = cpuc->events[idx];
val = x86_perf_event_update(event);
if (val & (1ULL << (x86_pmu.cntval_bits - 1)))
continue;
/*
* event overflow
*/
handled++;
perf_sample_data_init(&data, 0, event->hw.last_period);
if (!x86_perf_event_set_period(event))
continue;
if (perf_event_overflow(event, &data, regs))
x86_pmu_stop(event, 0);
}在这里,我们可以看到它对“ cpuc”进行了迭代,以查找触发该中断的事件。
以上是关于Linux内核性能架构:perf_event的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章