Lambda表达式
Posted Code_BinBin
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Lambda表达式相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
什么是Lambda表达式
Lambda表达式是一个匿名函数,我们可以这样理解Lambda表达式:Lambda是一段可以传递的代码(能够做到将代码像数据一样进行传递)。使用Lambda表达式能够写出更加简洁、灵活的代码。并且,使用Lambda表达式能够使Java的语言表达能力得到提升。
Lambda的优点
- 简单、干净、易读
- 业界要求
- 编写干净、易于维护的代码
- 降低了开发时间和成本
Lambda的缺点
- 代码可读性变差
- 在非并行计算中,很多计算机未必有传统的for性能要求
- 不容易进行调试
为什么使用Lambda 表达式
Lambda 是一个匿名函数,我们可以把Lambda 表达式理解为是一段可以传递的代码(将代码像数据一样进行传递)。使用它可以写出更简洁、更灵活的代码。作为一种更紧凑的代码风格,使Java的语言表达能力得到了提升。
匿名内部类
在介绍如何使用Lambda表达式之前,我们先来看看匿名内部类,例如,我们使用匿名内部类比较两个Integer类型数据的大小。
public void test(){
Comparator<Integer> com = new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return Math.max(o1,o2);
}
};
System.out.println(com.compare(9,2));
}
我们可以发现,这么长的一段代码里面,真正起到作用的只有一句
return Math.max(o1,o2);
于是我们便采用Lambda表达式进行书写
@Test
public void test(){
//没有引入Lambda表达式
Comparator<Integer> com = new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return Math.max(o1,o2);
}
};
System.out.println(com.compare(9,2));
//引入Lambda表达式
Comparator<Integer> coms = (x, y) -> Math.max(x, y);
System.out.println(coms.compare(1,5));
}
这样看起来是不是代码看起来高级了许多
语法格式一:无参数,无返回值
() -> System.out.println(“Hello Lambda!”);
例子:
@Test
public void test1(){
//jdk1.8之前的写法
//jdk 1.7 前,内部类引用外部的局部变量必须是 final
String str = "你是一帅哥";
Runnable r = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run () {
System.out.println(str);
}
};
r.run();
//java8之后的写法
String str1 = "我也是帅哥";
Runnable r1 = () -> System.out.println(str1);
r1.run();
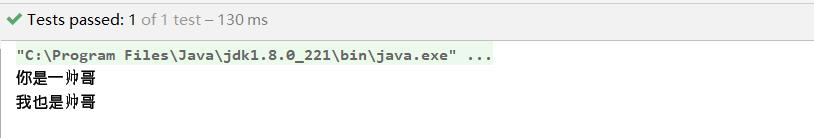
}
结果:
语法格式二:有一个参数,并且无返回值
(x) -> System.out.println(x)
例子:
@Test
public void test2(){
Consumer<String> consumer = (x) -> System.out.println(x);
consumer.accept("这个是只有一个参数,没有返回值的语法");
}
结果:

语法格式三:若只有一个参数,小括号可以省略不写
x -> System.out.println(x)
例子:
@Test
public void test3(){
Consumer<String> consumer = x -> System.out.println(x);
consumer.accept("只有一个参数小括号可以不写");
}
结果:

语法格式四:有两个以上的参数,有返回值,并且 Lambda 体中有多条语句
(x, y) -> {
//执行语句
return [返回值];
};
例子:
@Test
public void test3(){
BiFunction<Integer,Integer,Integer> biFunction = (x,y) -> {
System.out.println("有两个参数以上并且有多条语句");
return x+y;
};
Integer sum = biFunction.apply(1, 2);
System.out.println(sum);
}
结果:

语法格式五:若 Lambda 体中只有一条语句, return 和 大括号都可以省略不写
Comparator com = (x, y) -> Integer.compare(x, y);
例子:
@Test
public void test5 () {
BiFunction<Integer, Integer, Integer> biFunction = ( x, y ) -> x + y;
Integer sum = biFunction.apply(1, 2);
System.out.println(sum);
}
结果:

Lambda 表达式需要“函数式接口”的支持
函数式接口:接口中只有一个抽象方法的接口,称为函数式接口。 可以使用注解 @FunctionalInterface 修饰可以检查是否是函数式接口
什么是函数式(Functional)接口
- 只包含一个抽象方法的接口,称为函数式接口。
- 你可以通过Lambda 表达式来创建该接口的对象。(若Lambda 表达式抛出一个受检异常(即:非运行时异常),那么该异常需要在目标接口的抽象方法上进行声明)。
- 我们可以在一个接口上使用@FunctionalInterface 注解,这样做可以检查它是否是一个函数式接口。同时javadoc 也会包含一条声明,说明这个接口是一个函数式接口。
- 在java.util.function包下定义了Java 8 的丰富的函数式接口
自定义函数接口:
接口:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface MyFunction {
int max(int x,int y);
}
测试类:
@Test
public void test6 () {
MyFunction myFunction=(x,y)-> Math.max(x,y);
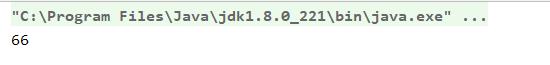
System.out.println(myFunction.max(9,66));
}
结果:
对比常规方法和Lambda表达式
例如,你有一个需求,需要从一众学生中选出年龄在20岁以上的出来
学生类:
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
private int hight;
}
接着,我们存储学生信息
List <Student>studentList=new ArrayList<>();
studentList.add(new Student("znb",20,175));
studentList.add(new Student("lsl",21,182));
studentList.add(new Student("cy",22,172));
studentList.add(new Student("oyj",20,168));
studentList.add(new Student("xm",20,158));
studentList.add(new Student("mm",19,162));
常规遍历
public List<Student> filterStudentByAge(List<Student> list){
List<Student> employees = new ArrayList<>();
for(Studente : list){
if(e.getAge() >= 20){
employees.add(e);
}
}
return Student;
}
使用Stream API
List <Student>studentList=new ArrayList<>();
studentList.add(new Student("znb",20,175));
studentList.add(new Student("lsl",21,182));
studentList.add(new Student("cy",22,172));
studentList.add(new Student("oyj",20,168));
studentList.add(new Student("xm",20,158));
studentList.add(new Student("mm",20,162));
List<Student> studentList1=studentList.stream().sorted((p1,p2)->p1.getAge()-p2.getAge()).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(studentList1);
System.out.println("============================================");
studentList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(Student::getAge).reversed().thenComparing(Student::getName)).forEach( System.out::println);
以上是关于Lambda表达式的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章