H264码流解析
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了H264码流解析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
这是一段H264码流,00 00 00 01这是对应forbidden_zero_bit的f(1),接着后面的nal_ref_idc的u(2),这个怎么解呀,有点晕。刚接触不久,nal_unit_type的u(5),后面的profile_idc的u(8)指的是那几个,是多少?
nal_ref_idc的u(2)对应67变成前两位0 1也就是1,nal_unit_type取64接着的5位 10 01 1则组合成19 ,profile_idc的u(8)则是后面的64转化为十进制则是100,level_idc则是0D是13,seq_parameter_set_id的ue(v),则指到AC了,这是哥伦布编码,答案是0,这个是怎么算出来的?
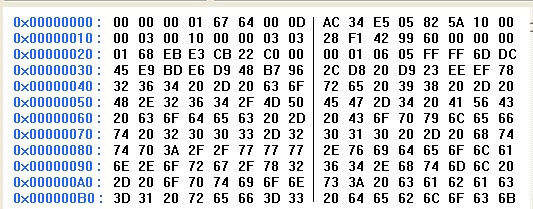
forbidden_zero_bit 是禁止位,应该是第一位即f(1)=0,1为语法有错误
nal_ref_idc是参考级别,代表被其它帧参考情况,u(2)= 11 = 3最(0为无参考,详见规范)
nal_unit_type是该帧的类型,为剩下的5位,u(5)= 0 0111 = 7
目前类型有:
//H264定义的类型 values for nal_unit_type
typedef enum
NALU_TYPE_SLICE = 1,
NALU_TYPE_DPA = 2,
NALU_TYPE_DPB = 3,
NALU_TYPE_DPC = 4,
NALU_TYPE_IDR = 5,
NALU_TYPE_SEI = 6,
NALU_TYPE_SPS = 7,
NALU_TYPE_PPS = 8,
NALU_TYPE_AUD = 9,
NALU_TYPE_EOSEQ = 10,
NALU_TYPE_EOSTREAM = 11,
NALU_TYPE_FILL = 12,
#if (MVC_EXTENSION_ENABLE)
NALU_TYPE_PREFIX = 14,
NALU_TYPE_SUB_SPS = 15,
NALU_TYPE_SLC_EXT = 20,
NALU_TYPE_VDRD = 24 // View and Dependency Representation Delimiter NAL Unit
#endif
NaluType;
可以看出是NALU_TYPE_SPS 即sequence parameter sets
profile_idc的u(8)则是后面的64转化为十进制则是100,
66 Baseline
77 Main
88 Extended
100 High (FRExt)
110 High 10 (FRExt)
122 High 4:2:2 (FRExt)
144 High 4:4:4 (FRExt)
100是High (FRExt)
“level_idc则是0D是13,seq_parameter_set_id的ue(v),则指到AC了,这是哥伦布编码,答案是0,这个是怎么算出来的?“
就不太懂了。互相帮忙吧。本回答被提问者采纳
视音频数据处理入门:H.264视频码流解析
=====================================================
视音频数据处理入门系列文章:
=====================================================
前两篇文章介绍的YUV/RGB处理程序以及PCM处理程序都属于视音频原始数据的处理程序。从本文开始介绍视音频码流的处理程序。本文介绍的程序是视频码流处理程序。视频码流在视频播放器中的位置如下所示。
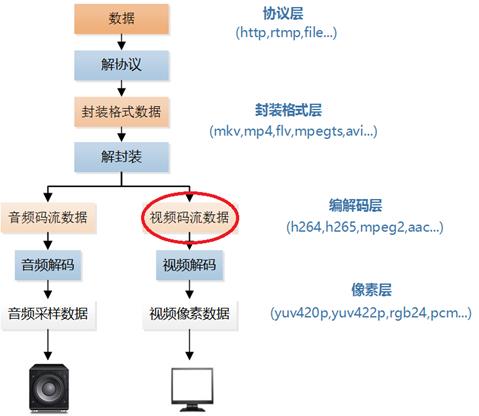
本文中的程序是一个H.264码流解析程序。该程序可以从H.264码流中分析得到它的基本单元NALU,并且可以简单解析NALU首部的字段。通过修改该程序可以实现不同的H.264码流处理功能。
原理
H.264原始码流(又称为“裸流”)是由一个一个的NALU组成的。他们的结构如下图所示。

H.264码流解析的步骤就是首先从码流中搜索0x000001和0x00000001,分离出NALU;然后再分析NALU的各个字段。本文的程序即实现了上述的两个步骤。
代码
整个程序位于simplest_h264_parser()函数中,如下所示。/**
* 最简单的视音频数据处理示例
* Simplest MediaData Test
*
* 雷霄骅 Lei Xiaohua
* leixiaohua1020@126.com
* 中国传媒大学/数字电视技术
* Communication University of China / Digital TV Technology
* http://blog.csdn.net/leixiaohua1020
*
* 本项目包含如下几种视音频测试示例:
* (1)像素数据处理程序。包含RGB和YUV像素格式处理的函数。
* (2)音频采样数据处理程序。包含PCM音频采样格式处理的函数。
* (3)H.264码流分析程序。可以分离并解析NALU。
* (4)AAC码流分析程序。可以分离并解析ADTS帧。
* (5)FLV封装格式分析程序。可以将FLV中的MP3音频码流分离出来。
* (6)UDP-RTP协议分析程序。可以将分析UDP/RTP/MPEG-TS数据包。
*
* This project contains following samples to handling multimedia data:
* (1) Video pixel data handling program. It contains several examples to handle RGB and YUV data.
* (2) Audio sample data handling program. It contains several examples to handle PCM data.
* (3) H.264 stream analysis program. It can parse H.264 bitstream and analysis NALU of stream.
* (4) AAC stream analysis program. It can parse AAC bitstream and analysis ADTS frame of stream.
* (5) FLV format analysis program. It can analysis FLV file and extract MP3 audio stream.
* (6) UDP-RTP protocol analysis program. It can analysis UDP/RTP/MPEG-TS Packet.
*
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
typedef enum {
NALU_TYPE_SLICE = 1,
NALU_TYPE_DPA = 2,
NALU_TYPE_DPB = 3,
NALU_TYPE_DPC = 4,
NALU_TYPE_IDR = 5,
NALU_TYPE_SEI = 6,
NALU_TYPE_SPS = 7,
NALU_TYPE_PPS = 8,
NALU_TYPE_AUD = 9,
NALU_TYPE_EOSEQ = 10,
NALU_TYPE_EOSTREAM = 11,
NALU_TYPE_FILL = 12,
} NaluType;
typedef enum {
NALU_PRIORITY_DISPOSABLE = 0,
NALU_PRIRITY_LOW = 1,
NALU_PRIORITY_HIGH = 2,
NALU_PRIORITY_HIGHEST = 3
} NaluPriority;
typedef struct
{
int startcodeprefix_len; //! 4 for parameter sets and first slice in picture, 3 for everything else (suggested)
unsigned len; //! Length of the NAL unit (Excluding the start code, which does not belong to the NALU)
unsigned max_size; //! Nal Unit Buffer size
int forbidden_bit; //! should be always FALSE
int nal_reference_idc; //! NALU_PRIORITY_xxxx
int nal_unit_type; //! NALU_TYPE_xxxx
char *buf; //! contains the first byte followed by the EBSP
} NALU_t;
FILE *h264bitstream = NULL; //!< the bit stream file
int info2=0, info3=0;
static int FindStartCode2 (unsigned char *Buf){
if(Buf[0]!=0 || Buf[1]!=0 || Buf[2] !=1) return 0; //0x000001?
else return 1;
}
static int FindStartCode3 (unsigned char *Buf){
if(Buf[0]!=0 || Buf[1]!=0 || Buf[2] !=0 || Buf[3] !=1) return 0;//0x00000001?
else return 1;
}
int GetAnnexbNALU (NALU_t *nalu){
int pos = 0;
int StartCodeFound, rewind;
unsigned char *Buf;
if ((Buf = (unsigned char*)calloc (nalu->max_size , sizeof(char))) == NULL)
printf ("GetAnnexbNALU: Could not allocate Buf memory\\n");
nalu->startcodeprefix_len=3;
if (3 != fread (Buf, 1, 3, h264bitstream)){
free(Buf);
return 0;
}
info2 = FindStartCode2 (Buf);
if(info2 != 1) {
if(1 != fread(Buf+3, 1, 1, h264bitstream)){
free(Buf);
return 0;
}
info3 = FindStartCode3 (Buf);
if (info3 != 1){
free(Buf);
return -1;
}
else {
pos = 4;
nalu->startcodeprefix_len = 4;
}
}
else{
nalu->startcodeprefix_len = 3;
pos = 3;
}
StartCodeFound = 0;
info2 = 0;
info3 = 0;
while (!StartCodeFound){
if (feof (h264bitstream)){
nalu->len = (pos-1)-nalu->startcodeprefix_len;
memcpy (nalu->buf, &Buf[nalu->startcodeprefix_len], nalu->len);
nalu->forbidden_bit = nalu->buf[0] & 0x80; //1 bit
nalu->nal_reference_idc = nalu->buf[0] & 0x60; // 2 bit
nalu->nal_unit_type = (nalu->buf[0]) & 0x1f;// 5 bit
free(Buf);
return pos-1;
}
Buf[pos++] = fgetc (h264bitstream);
info3 = FindStartCode3(&Buf[pos-4]);
if(info3 != 1)
info2 = FindStartCode2(&Buf[pos-3]);
StartCodeFound = (info2 == 1 || info3 == 1);
}
// Here, we have found another start code (and read length of startcode bytes more than we should
// have. Hence, go back in the file
rewind = (info3 == 1)? -4 : -3;
if (0 != fseek (h264bitstream, rewind, SEEK_CUR)){
free(Buf);
printf("GetAnnexbNALU: Cannot fseek in the bit stream file");
}
// Here the Start code, the complete NALU, and the next start code is in the Buf.
// The size of Buf is pos, pos+rewind are the number of bytes excluding the next
// start code, and (pos+rewind)-startcodeprefix_len is the size of the NALU excluding the start code
nalu->len = (pos+rewind)-nalu->startcodeprefix_len;
memcpy (nalu->buf, &Buf[nalu->startcodeprefix_len], nalu->len);//
nalu->forbidden_bit = nalu->buf[0] & 0x80; //1 bit
nalu->nal_reference_idc = nalu->buf[0] & 0x60; // 2 bit
nalu->nal_unit_type = (nalu->buf[0]) & 0x1f;// 5 bit
free(Buf);
return (pos+rewind);
}
/**
* Analysis H.264 Bitstream
* @param url Location of input H.264 bitstream file.
*/
int simplest_h264_parser(char *url){
NALU_t *n;
int buffersize=100000;
//FILE *myout=fopen("output_log.txt","wb+");
FILE *myout=stdout;
h264bitstream=fopen(url, "rb+");
if (h264bitstream==NULL){
printf("Open file error\\n");
return 0;
}
n = (NALU_t*)calloc (1, sizeof (NALU_t));
if (n == NULL){
printf("Alloc NALU Error\\n");
return 0;
}
n->max_size=buffersize;
n->buf = (char*)calloc (buffersize, sizeof (char));
if (n->buf == NULL){
free (n);
printf ("AllocNALU: n->buf");
return 0;
}
int data_offset=0;
int nal_num=0;
printf("-----+-------- NALU Table ------+---------+\\n");
printf(" NUM | POS | IDC | TYPE | LEN |\\n");
printf("-----+---------+--------+-------+---------+\\n");
while(!feof(h264bitstream))
{
int data_lenth;
data_lenth=GetAnnexbNALU(n);
char type_str[20]={0};
switch(n->nal_unit_type){
case NALU_TYPE_SLICE:sprintf(type_str,"SLICE");break;
case NALU_TYPE_DPA:sprintf(type_str,"DPA");break;
case NALU_TYPE_DPB:sprintf(type_str,"DPB");break;
case NALU_TYPE_DPC:sprintf(type_str,"DPC");break;
case NALU_TYPE_IDR:sprintf(type_str,"IDR");break;
case NALU_TYPE_SEI:sprintf(type_str,"SEI");break;
case NALU_TYPE_SPS:sprintf(type_str,"SPS");break;
case NALU_TYPE_PPS:sprintf(type_str,"PPS");break;
case NALU_TYPE_AUD:sprintf(type_str,"AUD");break;
case NALU_TYPE_EOSEQ:sprintf(type_str,"EOSEQ");break;
case NALU_TYPE_EOSTREAM:sprintf(type_str,"EOSTREAM");break;
case NALU_TYPE_FILL:sprintf(type_str,"FILL");break;
}
char idc_str[20]={0};
switch(n->nal_reference_idc>>5){
case NALU_PRIORITY_DISPOSABLE:sprintf(idc_str,"DISPOS");break;
case NALU_PRIRITY_LOW:sprintf(idc_str,"LOW");break;
case NALU_PRIORITY_HIGH:sprintf(idc_str,"HIGH");break;
case NALU_PRIORITY_HIGHEST:sprintf(idc_str,"HIGHEST");break;
}
fprintf(myout,"%5d| %8d| %7s| %6s| %8d|\\n",nal_num,data_offset,idc_str,type_str,n->len);
data_offset=data_offset+data_lenth;
nal_num++;
}
//Free
if (n){
if (n->buf){
free(n->buf);
n->buf=NULL;
}
free (n);
}
return 0;
}
上文中的函数调用方法如下所示。
simplest_h264_parser("sintel.h264");结果
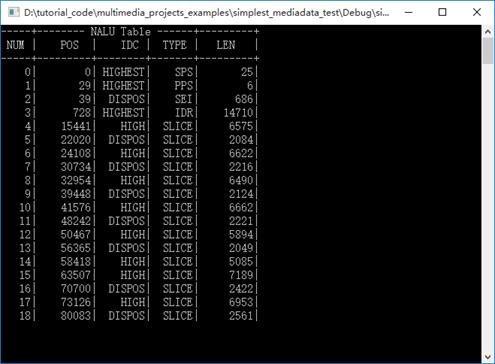
本程序的输入为一个H.264原始码流(裸流)的文件路径,输出为该码流的NALU统计数据,如下图所示。
下载
Simplest mediadata test
SourceForge:https://sourceforge.net/projects/simplest-mediadata-test/
Github:https://github.com/leixiaohua1020/simplest_mediadata_test
开源中国:http://git.oschina.net/leixiaohua1020/simplest_mediadata_test
CSDN下载地址:http://download.csdn.net/detail/leixiaohua1020/9422409
本项目包含如下几种视音频数据解析示例:
(1)像素数据处理程序。包含RGB和YUV像素格式处理的函数。(2)音频采样数据处理程序。包含PCM音频采样格式处理的函数。
(3)H.264码流分析程序。可以分离并解析NALU。
(4)AAC码流分析程序。可以分离并解析ADTS帧。
(5)FLV封装格式分析程序。可以将FLV中的MP3音频码流分离出来。
(6)UDP-RTP协议分析程序。可以将分析UDP/RTP/MPEG-TS数据包。
雷霄骅 (Lei Xiaohua)
leixiaohua1020@126.com
http://blog.csdn.net/leixiaohua1020
以上是关于H264码流解析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章