洪水覆盖算法(Flood Fill):颜色填充
Posted ZSYL
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了洪水覆盖算法(Flood Fill):颜色填充相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Flood Fill
Basic 概念
洪水填充(Flood fill)算法:从一个起始节点开始把附近与其连通的节点提取出或填充成不同颜色颜色,直到封闭区域内的所有节点都被处理过为止,是从一个区域中提取若干个连通的点与其他相邻区域区分开(或分别染成不同颜色)的经典算法。
因为其思路类似洪水从一个区域扩散到所有能到达的区域而得名。
在GNU Go和扫雷中,Flood Fill算法被用来计算需要被清除的区域。
相关参数
洪水填充算法接受三个参数:
起始节点,目标节点特征和针对提取对象要执行的处理。
实现方式
目前有许多实现方式,基本上都显式的或隐式的使用了队列或者栈。
洪水填充算法实现最常见有四邻域填充法(不考虑对角线方向的节点),八邻域填充法(考虑对角线方向的节点),基于扫描线填充方法。
根据实现又可以分为递归与非递归(基于栈)。
最简单的实现方法是采用深度优先搜索的递归方法,也可以采用广度优先搜索的迭代来实现。
基于递归实现的泛洪填充算法有个致命的缺点,就是对于大的区域填充时可能导致栈溢出错误,
基于扫描线的算法实现了一种非递归的洪水填充算法。
除提出连通区域外,还可以应用于计算从某一节点开始,到可能到达其他所有节点的距离。
比如解决像走迷宫这类的问题。
请参考博客:超详解的迷宫问题
FloodFill算法的运用非常广泛,其中突出的是画图的“倒色”。
FloodFill的原理十分简单,就是把一个点x的所有相邻的点都涂上x点的颜色,一直填充下去,直到这个区域内所有的点都被填充完为止。
典型例题
颜色填充
题目描述:
编写函数,实现许多图片编辑软件都支持的「颜色填充」功能。待填充的图像用二维数组 image 表示,元素为初始颜色值。初始坐标点的行坐标为 sr 列坐标为 sc。需要填充的新颜色为 newColor。
周围区域是指颜色相同且在上、下、左、右四个方向上存在相连情况的若干元素。
请用新颜色填充初始坐标点的周围区域,并返回填充后的图像。
DFS
class Solution {
// orientation 四个方向
static int[] orient = {0, -1, 0, 1, 0}; // orientation 方向
public int[][] floodFill(int[][] image, int sr, int sc, int newColor) {
// 无需替换
if (image[sr][sc] == newColor)
return image;
// 起始颜色
int oldColor = image[sr][sc];
// 边界问题 m行,n列
int m = image.length;
int n = image[0].length;
dfs(image, sr, sc, m, n, oldColor, newColor);
return image;
}
// 深度搜索
public void dfs(int[][] image, int x, int y, int m, int n, int oldColor, int newColor) {
if (x < 0 || y < 0 || x == m || y == n || image[x][y] != oldColor)
return;
image[x][y] = newColor;
// 遍历四个方向
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
dfs(image, x + orient[i], y + orient[i+1], m, n, oldColor, newColor);
}
}
}
BFS
class Solution {
public int[][] floodFill(int[][] image, int sr, int sc, int newColor) {
// 无需替换
if (image[sr][sc] == newColor)
return image;
// 起始颜色
int oldImg = image[sr][sc];
// 获取队列
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
// 初始化起始点
queue.offer(new int[]{sr,sc});
image[sr][sc] = newColor;
// 边界问题
int n = image.length;
int m = image[0].length;
// orientation 四个方向
int[] orient = {0, -1, 0, 1, 0}; // orientation 方向
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
// 获取当前位置
int[] x = queue.poll();
// 遍历四个方向
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int xx = x[0] + orient[i];
int yy = x[1] + orient[i+1];
if (xx<0||yy<0||xx==n||yy==m||image[xx][yy]!=oldImg)
continue;
// 覆盖颜色,并加入队列中
image[xx][yy] = newColor;
queue.offer(new int[]{xx, yy});
}
}
return image;
}
}
贪吃蛇大作战
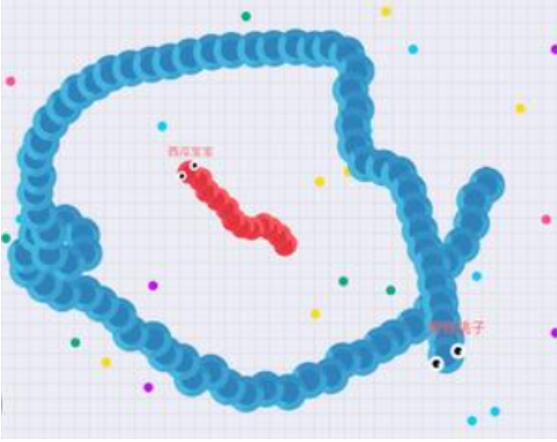
题目描述:
游戏“贪吃蛇大作战”中,如果玩家A被玩家B包围,那么玩家A将会慢性死亡。如图的红蛇已经被蓝蛇所包围,只能原地等着被吃,而每条蛇围起来的区域,叫做“禁区”。
现在给你某时刻游戏的地图方阵,‘1’表示蛇,‘0’表示空地,请你将所有的禁区(蛇身不算)用‘2’标记出来(边界不算禁区,具体看样例)。
输入:
第一行输入一个整数n(1 <= n <= 50)表示矩阵的大小。
接下来输入一个由‘0’和‘1’构成的n * n方阵。
输出:
输出一个n * n的方阵,表示最终地图。
样例输入:
10
0000000000
0001111000
0001001000
0001001000
0001111000
0000000000
0000000000
0000000111
0000000100
0000000100
样例输出:
0000000000
0001111000
0001221000
0001221000
0001111000
0000000000
0000000000
0000000111
0000000100
0000000100
BFS
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
static int n;
static char[][] matrix;
static boolean[][] vis;
static int[] orient = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner((System.in));
n = sc.nextInt();
// 初始化矩阵和标记数组,默认是 false,true:代表洪水已覆盖
matrix = new char[n][n];
vis = new boolean[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
matrix[i] = sc.next().toCharArray();
}
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
// 边界 开始发洪水
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (matrix[0][i] == '0') {
vis[0][i] = true;
queue.offer(new int[]{0, i});
}
if (matrix[n-1][i] == '0') {
vis[n-1][i] = true;
queue.offer(new int[]{n-1, i});
}
if (matrix[i][0] == '0') {
vis[i][0] = true;
queue.offer(new int[]{i, 0});
}
if (matrix[i][n-1] == '0') {
vis[i][n-1] = true;
queue.offer(new int[]{i, n-1});
}
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] x = queue.poll();
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int i = x[0] + orient[k];
int j = x[1] + orient[k+1];
if (i < 0 || j < 0 || i == n || j == n || vis[i][j] || matrix[i][j] == '1')
continue;
vis[i][j] = true;
queue.offer(new int[]{i, j});
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (vis[i][j] || matrix[i][j] == '1')
System.out.print(matrix[i][j]);
else
System.out.print(2);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
DFS
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
static int n; // 矩阵大小
static char[][] matrix; // 矩阵
static boolean[][] vis; // 标记数组
static int[] orient = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}; // 四个方向
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner((System.in));
n = sc.nextInt();
// 初始化矩阵和标记数组,默认是 false,true:代表洪水已覆盖
matrix = new char[n][n];
vis = new boolean[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
matrix[i] = sc.next().toCharArray();
}
// for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// Arrays.fill(vis[i], false);
// }
// 边界 0开始 发洪水
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (matrix[0][i] == '0')
dfs(0, i);
if (matrix[n-1][i] == '0')
dfs(n-1, i);
if (matrix[i][0] == '0')
dfs(i, 0);
if (matrix[i][n-1] == '0')
dfs(i, n-1);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (vis[i][j] || matrix[i][j] == '1')
System.out.print(matrix[i][j]);
else
System.out.print(2);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
// 深度优先搜索
public static void dfs(int x, int y) {
// 边界处理,或者已经访问 则返回
if (x < 0 || y < 0 || x == n || y == n || vis[x][y] || matrix[x][y] == '1')
return;
vis[x][y] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
dfs(x+orient[i], y+orient[i+1]);
}
}
}
参考博客 Link
感谢
努力
加油
小猪梦想变大牛
(* ̄︶ ̄)
以上是关于洪水覆盖算法(Flood Fill):颜色填充的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章