Python基础教程之操作MySql数据库
Posted ProChick
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Python基础教程之操作MySql数据库相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1.关于Python操作数据库的概述
- Python所有的数据库接口程序都在一定程度上遵守 Python DB-API 规范。
- DB-API定义了一系列必须的对象和数据库存取方式,以便为各种底层数据库系统和多种多样的数据库接口程序提供一致的访问接口。由于DB-API 为不同的数据库提供了一致的访问接口, 在不同的数据库之间移植代码成为一件轻松的事情。
- 在Python中如果要连接数据库,不管是MySQL、SQL Server、PostgreSQL亦或是SQLite,使用时都是采用游标的方式。
2.一般操作流程
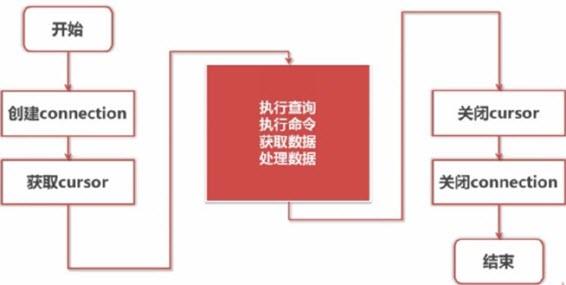
3.安装mysql的操作库
$ pip3 install PyMySQL
4.基本操作
-
创建连接import pymysql # 创建连接方式1 db = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', user='root', password='root', db='test', port=3306) # 创建连接方式2 db = pymysql.connect(dsn='localhost:test', user='root', password='root')-
close()
关闭此connect对象, 关闭后无法再进行操作,除非再次创建连接。
-
cursor()
创建游标对象。一个游标允许用户执行数据库命令和得到查询结果。一个 Python DB-API 游标对象总是扮演游标的角色, 无论数据库是否真正支持游标。也就说,数据库接口程序必须实现游标对象。创建游标对象之后, 你就可以执行查询或其它命令(或者多个查询和多个命令), 也可以从结果集中取出一条或多条记录。
-
commit()
提交当前事务,执行游标对象的所有更新操作。
-
rollback()
取消当前事务,回滚当前游标的所有操作。
-
-
游标操作cursor = db.cursor()- close():关闭此游标对象
- fetchone():得到结果集的下一行
- fetchall():得到结果集中剩下的所有行
- excute(sql[, args]):执行一个数据库查询或命令
- callproc(func[,args]): 调用一个存储过程
-
查询操作import pymysql db = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', user='root', password='root', db='test') cursor = db.cursor() sql = '''select * from t_account''' try: cursor.execute(sql) # 方式1读取结果集 rows = cursor.fetchall() for row in rows: print(row) # 方式2读取结果集 for i in range(cursor.rowcount): result = cursor.fetchone() print(result) except Exception as e: raise e finally: cursor.close() db.close() -
添加操作import pymysql db = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', user='root', password='root', db='test') cursor = db.cursor() sql = '''insert into t_account values(default,'zhangsan','z',100,'张三')''' try: print(cursor.execute(sql)) db.commit() except: db.rollback() finally: cursor.close() db.close() -
修改操作import pymysql db = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', user='root', password='root', db='test') cursor = db.cursor() sql = '''update t_account set realname = '李四' where id = '5' ''' try: print(cursor.execute(sql)) db.commit() except: db.rollback() finally: cursor.close() db.close() -
删除操作import pymysql db = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', user='root', password='root', db='test') cursor = db.cursor() sql = '''delete from t_account where id = '5' ''' try: print(cursor.execute(sql)) db.commit() except: db.rollback() finally: cursor.close() db.close() -
调用存储过程cursor.callproc("存储过程名称") for result in cursor.fetchall(): print(result)
以上是关于Python基础教程之操作MySql数据库的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章