tensorflow 高级函数 where,gather,gather_nd
Posted 炫云云
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了tensorflow 高级函数 where,gather,gather_nd相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
tf.gather
tf.gather(params, indices, …, axis=0)
- 作用: 根据indices从params的指定轴axis索引元素(类似于仅能在指定轴进行一维索引)
- 返回维度: params.shape[:axis] + indices.shape + params.shape[axis + 1:]
data = np.array([[[1, 1, 1], [2, 2, 2]],
[[3, 3, 3], [4, 4, 4]],
[[5, 5, 5], [6, 6, 6]]])
print(data.shape)
(3, 2, 3)
indices = np.array([0,2])
print(indices.shape)
(2,)
example 1
tf.gather(data, indices)
<tf.Tensor: id=7, shape=(2, 2, 3), dtype=int64, numpy=
array([[[1, 1, 1],
[2, 2, 2]],
[[5, 5, 5],
[6, 6, 6]]])>
- axis=0, indices选择0,2, data为(3,2,3)
- 索引出的数组为[[[1, 1, 1],[2, 2, 2]], [[5, 5, 5],[6, 6, 6]]]是data矩阵axis=0轴的第1和第3个数组
- data.shape[:0]=(); indeices.shape=(2,); data.shpe[1:]=(2,3)
- 最后的输出大小为上述3个之和, () + (2,) + (2,3) => (2, 2, 3)
example 2
tf.gather(data, indices, axis=2)
<tf.Tensor: id=12, shape=(3, 2, 2), dtype=int64, numpy=
array([[[1, 1],
[2, 2]],
[[3, 3],
[4, 4]],
[[5, 5],
[6, 6]]])>
- axis=2, indices选择[0,2], data为(3,2,3)
- 索引出的数组为[[[1, 1],[2, 2]], [[3, 3],[4, 4]], [[5, 5],[6, 6]]]是data矩阵axis=2轴的第1和第3个数组
- data.shape[:2]=(3,2); indeices.shape=(2,); data.shpe[2+1:]=()
- 最后的输出大小为上述3个之和, (3,2) + (2,) + (0) => (3, 2, 2)
考虑班级成绩册的例子,假设共有 4个班级,每个班级 35 个学生,8 门科目,保存成绩册的张量 shape 为[4,35,8]。
现在需要收集第 1~2 个班级的成绩册,可以给定需要收集班级的索引号:[0,1],并指定班
级的维度 axis=0,通过 tf.gather 函数收集数据,代码如下:
x = tf.random.uniform([4,35,8],maxval = 100,dtype=tf.int32)
y = tf.gather(x,[0,1],axis=0) # 在班级维度收集第 1~2 号班级成绩册
print(y)
tf.Tensor(
[[[41 76 66 56 26 19 16 94]
[64 5 75 33 20 24 15 76]
[97 19 55 79 47 75 82 97]
[ 2 8 8 66 55 65 14 86]
[41 68 73 43 42 94 63 99]
[45 7 99 9 26 2 18 96]
[ 2 49 19 15 4 56 56 32]
[28 10 48 99 53 32 87 32]
[53 58 27 35 75 58 80 81]
[15 74 14 3 63 48 31 29]
[48 30 0 28 5 75 21 35]
[56 14 57 28 59 16 75 91]
[63 95 52 77 42 34 36 96]
[52 65 68 45 80 14 16 18]
[ 7 45 30 39 79 72 66 0]
[68 96 24 68 2 66 24 9]
[66 23 46 25 45 79 91 49]
[74 95 37 50 11 17 64 36]
[76 89 1 23 80 82 19 62]
[70 43 39 26 75 5 38 62]
[38 79 97 84 23 47 63 31]
[86 12 66 21 45 75 72 30]
[87 41 22 67 0 62 49 80]
[65 51 58 83 82 48 50 0]
[13 6 83 56 90 2 1 14]
[46 41 30 73 84 52 58 68]
[79 74 94 6 76 74 71 31]
[21 21 96 32 20 84 10 91]
[52 34 41 40 79 81 29 69]
[58 58 26 16 23 37 8 75]
[72 26 99 81 19 52 58 13]
[35 50 81 56 69 13 94 1]
[19 19 84 95 56 65 78 35]
[24 0 38 41 41 70 4 35]
[27 26 94 11 16 92 77 20]]
[[68 83 55 87 22 67 12 39]
[18 35 72 49 39 81 79 59]
[30 67 91 56 68 38 13 2]
[72 80 69 13 36 21 84 19]
[52 94 1 6 12 82 31 88]
[38 91 50 31 41 64 29 15]
[23 88 99 77 13 27 11 69]
[96 49 70 35 68 71 10 15]
[46 23 9 44 12 30 17 8]
[81 99 75 60 65 27 85 68]
[79 83 55 83 60 0 76 85]
[50 68 66 29 1 66 80 27]
[13 0 50 24 74 13 7 53]
[47 19 25 5 45 46 88 85]
[76 76 69 67 52 91 99 85]
[14 19 94 10 46 26 92 13]
[32 0 85 77 58 86 12 18]
[ 0 18 87 99 44 62 29 48]
[70 49 86 8 43 18 52 50]
[55 4 17 52 22 86 1 59]
[71 16 30 67 63 44 35 2]
[42 89 82 81 49 28 73 27]
[92 48 42 96 46 5 66 76]
[41 20 86 78 58 97 9 93]
[31 11 4 0 35 40 3 2]
[10 69 91 78 14 22 70 27]
[80 83 3 70 40 60 75 86]
[26 3 50 98 17 54 20 78]
[69 52 94 96 35 69 3 10]
[61 64 57 31 32 4 55 50]
[20 42 81 72 95 77 81 95]
[59 91 4 17 57 48 55 23]
[29 79 34 3 76 88 27 62]
[42 12 25 87 16 71 21 67]
[29 4 44 63 7 45 92 19]]], shape=(2, 35, 8), dtype=int32)
实际上,对于上述需求,通过切片𝑥[: 2]可以更加方便地实现。但是对于不规则的索引方式,比如,需要抽查所有班级的第 1、4、9、12、13、27 号同学的成绩数据,则切片方式
实现起来非常麻烦,而 tf.gather 则是针对于此需求设计的,使用起来更加方便,实现如下:
y = tf.gather(x,[0,3,8,11,12,26],axis = 1)# 收集第 1,4,9,12,13,27 号同学成绩
print(y)
tf.Tensor(
[[[41 76 66 56 26 19 16 94]
[ 2 8 8 66 55 65 14 86]
[53 58 27 35 75 58 80 81]
[56 14 57 28 59 16 75 91]
[63 95 52 77 42 34 36 96]
[79 74 94 6 76 74 71 31]]
[[68 83 55 87 22 67 12 39]
[72 80 69 13 36 21 84 19]
[46 23 9 44 12 30 17 8]
[50 68 66 29 1 66 80 27]
[13 0 50 24 74 13 7 53]
[80 83 3 70 40 60 75 86]]
[[15 29 92 83 17 77 50 96]
[10 94 22 54 22 41 45 31]
[52 85 67 50 84 33 38 54]
[33 10 9 28 23 53 48 10]
[36 81 57 6 37 46 86 91]
[24 40 42 46 34 51 2 84]]
[[11 27 64 59 50 93 58 98]
[62 96 31 62 50 34 77 52]
[59 4 3 83 2 13 26 6]
[63 3 40 0 97 21 61 75]
[25 36 27 34 16 65 52 84]
[48 80 69 6 46 63 32 45]]], shape=(4, 6, 8), dtype=int32)
如果需要收集所有同学的第 3 和第 5 门科目的成绩,则可以指定科目维度 axis=2,实现如
下:
y = tf.gather(x,[2,4],axis = 2)# 收集第 3,5科目的成绩
print(y)
tf.Tensor(
[[[66 26]
[75 20]
[55 47]
[ 8 55]
[73 42]
[99 26]
[19 4]
[48 53]
[27 75]
[14 63]
[ 0 5]
[57 59]
[52 42]
[68 80]
[30 79]
[24 2]
[46 45]
[37 11]
[ 1 80]
[39 75]
[97 23]
[66 45]
[22 0]
[58 82]
[83 90]
[30 84]
[94 76]
[96 20]
[41 79]
[26 23]
[99 19]
[81 69]
[84 56]
[38 41]
[94 16]]
[[55 22]
[72 39]
[91 68]
[69 36]
[ 1 12]
[50 41]
[99 13]
[70 68]
[ 9 12]
[75 65]
[55 60]
[66 1]
[50 74]
[25 45]
[69 52]
[94 46]
[85 58]
[87 44]
[86 43]
[17 22]
[30 63]
[82 49]
[42 46]
[86 58]
[ 4 35]
[91 14]
[ 3 40]
[50 17]
[94 35]
[57 32]
[81 95]
[ 4 57]
[34 76]
[25 16]
[44 7]]
[[92 17]
[ 8 14]
[86 70]
[22 22]
[56 0]
[60 53]
[65 28]
[96 35]
[67 84]
[93 58]
[23 93]
[ 9 23]
[57 37]
[55 2]
[71 33]
[80 63]
[32 70]
[71 7]
[81 86]
[ 4 15]
[17 28]
[93 12]
[26 76]
[85 8]
[16 56]
[89 2]
[42 34]
[96 45]
[41 5]
[67 81]
[62 56]
[32 49]
[79 84]
[16 64]
[79 55]]
[[64 50]
[92 74]
[53 51]
[31 50]
[69 96]
[87 79]
[ 1 90]
[30 15]
[ 3 2]
[84 2]
[40 38]
[40 97]
[27 16]
[30 47]
[36 70]
[69 34]
[39 45]
[17 59]
[ 8 56]
[89 70]
[60 40]
[23 68]
[91 19]
[67 93]
[36 89]
[72 44]
[69 46]
[16 53]
[14 43]
[67 52]
[37 91]
[14 6]
[20 69]
[47 41]
[17 52]]], shape=(4, 35, 2), dtype=int32)
可以看到,tf.gather 非常适合索引号没有规则的场合,其中索引号可以乱序排列,此时收
集的数据也是对应顺序,例如:
a=tf.range(8)
a = tf.reshape(a,[4,2])
tf.gather(a,[3,1,0,2],axis=0)# 收集第 4,2,1,3 号元素
<tf.Tensor: shape=(4, 2), dtype=int32, numpy=
array([[6, 7],
[2, 3],
[0, 1],
[4, 5]])>
我们将问题变得稍微复杂一点。如果希望抽查第[2,3]班级的第[3,4,6,27]号同学的科目
成绩,则可以通过组合多个 tf.gather 实现。首先抽出第[2,3]班级,实现如下:
students = tf.gather(x,[1,2],axis=0) # 收集第 2,3 号班级
再从这 2 个班级的同学中提取对应学生成绩,代码如下:
tf.gather(students,[2,3,5,26],axis=1)
<tf.Tensor: shape=(2, 4, 8), dtype=int32, numpy=
array([[[30, 67, 91, 56, 68, 38, 13, 2],
[72, 80, 69, 13, 36, 21, 84, 19],
[38, 91, 50, 31, 41, 64, 29, 15],
[80, 83, 3, 70, 40, 60, 75, 86]],
[[36, 47, 86, 78, 70, 99, 40, 27],
[10, 94, 22, 54, 22, 41, 45, 31],
[98, 48, 60, 55, 53, 85, 38, 32],
[24, 40, 42, 46, 34, 51, 2, 84]]])>
此时得到这 2 个班级 4 个同学的成绩张量,shape 为[2,4,8]。
我们继续问题进一步复杂化。这次我们希望抽查第 2 个班级的第 2 个同学的所有科
目,第 3 个班级的第 3 个同学的所有科目,第 4 个班级的第 4 个同学的所有科目。那么怎
么实现呢?
可以通过笨方式,一个一个的手动提取数据。首先提取第一个采样点的数据:𝑥[1,1],
可得到 8 门科目的数据向量:
再串行提取第二个采样点的数据:𝑥[2,2],以及第三个采样点的数据𝑥[3,3],最后通过 stack
方式合并采样结果,实现如下:
tf.concat([x[1,1],x[2,2],x[3,3]],axis=0)
tf.stack([x[1,1],x[2,2],x[3,3]],axis=0)
<tf.Tensor: shape=(3, 8), dtype=int32, numpy=
array([[18, 35, 72, 49, 39, 81, 79, 59],
[36, 47, 86, 78, 70, 99, 40, 27],
[62, 96, 31, 62, 50, 34, 77, 52]])>
tf.gather_nd
tf.gather_nd(params, indices, name=None)
- 作用:将params索引为indices指定形状的切片数组中(indices代表索引后的数组形状)
- indices将切片定义为params的前N个维度,其中N = indices.shape [-1]
- 通常要求indices.shape[-1] <= params.rank(可以用np.ndim(params)查看)
- 如果等号成立是在索引具体元素
- 如果等号不成立是在沿params的indices.shape[-1]轴进行切片
- 返回维度: indices.shape[:-1] + params.shape[indices.shape[-1]:]
- 前面的indices.shape[:-1]代表索引后的指定形状
通过 tf.gather_nd 函数,可以通过指定每次采样点的多维坐标来实现采样多个点的目
的。回到上面的挑战,我们希望抽查第 2 个班级的第 2 个同学的所有科目,第 3 个班级的
第 3 个同学的所有科目,第 4 个班级的第 4 个同学的所有科目。那么这 3 个采样点的索引
坐标可以记为:[1,1]、[2,2]、[3,3],我们将这个采样方案合并为一个 List 参数,即
[[1,1],[2,2],[3,3]],通过 tf.gather_nd 函数即可,实现如下:
tf.gather_nd(x,[[1,1],[2,2],[3,3]])
<tf.Tensor: shape=(3, 8), dtype=int32, numpy=
array([[18, 35, 72, 49, 39, 81, 79, 59],
[36, 47, 86, 78, 70, 99, 40, 27],
[62, 96, 31, 62, 50, 34, 77, 52]])>
一般地,在使用 tf.gather_nd 采样多个样本时,例如希望采样𝑖号班级,𝑗个学生,𝑘门
科目的成绩,则可以表达为[. . . ,[𝑖,𝑗, 𝑘], . . .],外层的括号长度为采样样本的个数,内层列表
包含了每个采样点的索引坐标,例如:
tf.gather_nd(x,[[1,1,2],[2,2,3],[3,3,4]])
<tf.Tensor: shape=(3,), dtype=int32, numpy=array([72, 78, 50])>
data = np.array([[[1, 1, 1], [2, 2, 2]],
[[3, 3, 3], [4, 4, 4]],
[[5, 5, 5], [6, 6, 6]]])
print("data is \\n", data)
print("data shape is ",data.shape)
print("data rank is ", np.ndim(data))
data is
[[[1 1 1]
[2 2 2]]
[[3 3 3]
[4 4 4]]
[[5 5 5]
[6 6 6]]]
data shape is (3, 2, 3)
data rank is 3
example 1
indices = np.array([[0, 1], [1, 0]])
print(indices.shape)
(2, 2)
# (indices.shape[-1]=2) < (np.ndim(data)=3), 沿data的axis=2轴切片
tf.gather_nd(data, indices)
<tf.Tensor: id=16, shape=(2, 3), dtype=int64, numpy=
array([[2, 2, 2],
[3, 3, 3]])>
- indices选择[[0, 1], [1, 0]], data为(3,2,3)
- [0,1]的索引过程为选取axis=0的第1个数组得到[[1,1,1],[2,2,2]],
再选取axis=1的第2个数组得到[2,2,2],[1,0]过程同理,最后索引出的是[[2,2,2],[3,3,3]] - indices.shape[:-1]=(2,); indices.shape[-1]=2;
data.shpe[indices.shape[-1]:]=>data.shape[2:]=(3,) - 最后的输出大小为上述2个之和, (2,) + (3,) => (2, 3)
example 2
indices = np.array([[[0, 0, 1], [1, 1, 0]]])
print(indices.shape)
(1, 2, 3)
# (indices.shape[-1]=3) < (np.ndim(data)=3), 取data对应位置的元素
tf.gather_nd(data, indices)
<tf.Tensor: id=20, shape=(1, 2), dtype=int64, numpy=array([[1, 4]])>
- indices选择[[[0, 0, 1], [1, 1, 0]]], data为(3,2,3)
- [0,0,1]的索引过程为选取axis=0的第1个数组得到[[1,1,1],[2,2,2]],
再选取axis=1的第1个数组得到[1,1,1],再取axis=3的第3个数组得到1,[1,1,0]过程同理,最后索引出的是[[1,4]] - indices.shape[:-1]=(1,2); indices.shape[-1]=3;
data.shpe[indices.shape[-1]:]=>data.shape[3:]=() - 最后的输出大小为上述2个之和, (1,2) + () => (1,2)
tf.boolean_mask
除了可以通过给定索引号的方式采样,还可以通过给定掩码(Mask)的方式进行采样。
继续以 shape 为[4,35,8]的成绩册张量为例,这次我们以掩码方式进行数据提取。
考虑在班级维度上进行采样,对这 4 个班级的采样方案的掩码为
m
a
s
k
=
[
T
r
u
e
,
F
a
l
s
e
,
F
a
l
s
e
,
T
r
u
e
]
mask = [True, False, False, True]
mask=[True,False,False,True]
即采样第 1 和第 4 个班级的数据,通过 tf.boolean_mask(x, mask, axis)可以在 axis 轴上根据
mask 方案进行采样,实现为:
tf.boolean_mask(x,mask = [True,False,False,True],axis=0)
<tf.Tensor: shape=(2, 35, 8), dtype=int32, numpy=
array([[[41, 76, 66, 56, 26, 19, 16, 94],
[64, 5, 75, 33, 20, 24, 15, 76],
[97, 19, 55, 79, 47, 75, 82, 97],
[ 2, 8, 8, 66, 55, 65, 14, 86],
[41, 68, 73, 43, 42, 94, 63, 99],
[45, 7, 99, 9, 26, 2, 18, 96],
[ 2, 49, 19, 15, 4, 56, 56, 32],
[28, 10, 48, 99, 53, 32, 87, 32],
[53, 58, 27, 35, 75, 58, 80, 81],
[15, 74, 14, 3, 63, 48, 31, 29],
[48, 30, 0, 28, 5, 75, 21, 35],
[56, 14, 57, 28, 59, 16, 75, 91],
[63, 95, 52, 77, 42, 34, 36, 96],
[52, 65, 68, 45, 80, 14, 16, 18],
[ 7, 45, 30, 39, 79, 72, 66, 0],
[68, 96, 24, 68, 2, 66, 24, 9],
[66, 23, 46, 25, 45, 79, 91, 49],
[74, 95, 37, 50, 11, 17, 64, 36],
[76, 89, 1, 23, 80, 82, 19, 62],
[70, 43, 39, 26, 75, 5, 38, 62],
[38, 79, 97, 84, 23, 47, 63, 31],
[86, 12, 66, 21, 45, 75, 72, 30],
[87, 41, 22, 67, 0, 62, 49, 80],
[65, 51, 58, 83, 82, 48, 50, 0],
[13, 6, 83, 56, 90, 2, 1, 14],
[46, 41, 30, 73, 84, 52, 58, 68],
[79, 74, 94, 6, 76, 74, 71, 31],
[21, 21, 96, 32, 20, 84, 10, 91],
[52, 34, 41, 40, 79, 81, 29, 69],
[58, 58, 26, 16, 23, 37, 8, 75],
[72, 26, 99, 81, 19, 52, 58, 13],
[35, 50, 81, 56, 69, 13, 94, 1],
[19, 19, 84, 95, 56, 65, 78, 35],
[24, 0, 38, 41, 41, 70, 4, 35],
[27, 26, 94, 11, 16, 92, 77, 20]],
[[11, 27, 64, 59, 50, 93, 58, 98],
[50, 18, 92, 75, 74, 3, 81, 19],
[87, 77, 53, 82, 51, 72, 21, 0],
[62, 96, 31, 62, 50, 34, 77, 52],
[86, 26, 69, 35, 96, 81, 70, 99],
[74, 81, 87, 25, 79, 9, 47, 83],
[51, 17, 1, 74, 90, 61, 25, 75],
[17, 90, 30, 41, 15, 28, 34, 46],
[59, 4, 3, 83, 2, 13, 26, 6],
[45, 50, 84, 89, 2, 19, 28, 39],
[ 3, 1, 40, 99, 38, 9, 47, 68],
[63, 3, 40, 0, 97, 21, 61, 75],
[25, 36, 27, 34, 16, 65, 52, 84],
[36, 93, 30, 60, 47, 7, 65, 96],
[76, 44, 36, 42, 70, 36, 1, 68],
[67, 21, 69, 26, 34, 86, 25, 89],
[64, 17, 39, 34, 45, 64, 77, 40],
[77, 93, 17, 11, 59, 86, 60, 13],
[34, 44, 8, 37, 56, 81, 94, 18],
[75, 94, 89, 86, 70, 99, 3, 42],
[28, 7, 60, 88, 40, 14, 50, 2],
[43, 8, 23, 6, 68, 29, 93, 82],
[70, 59, 91, 74, 19, 13, 70, 71],
[97, 31, 67, 88, 93, 64, 64, 98],
[ 6, 6, 36, 64, 89, 54, 90, 8],
[33, 81, 72, 68, 44, 34, 4, 81],
[48, 80, 69, 6, 46, 63, 32, 45],
[18, 95, 16, 15, 53, 36, 92, 87],
[47, 94, 14, 5, 43, 93, 22, 96],
[13, 47, 67, 29, 52, 8, 72, 65],
[78, 52, 37, 78, 91, 42, 17, 34],
[25, 81, 14, 51, 6, 97, 23, 28],
[ 6, 63, 20, 99, 69, 2, 38, 36],
[52, 64, 47, 71, 41, 18, 20, 45],
[29, 87, 17, 47, 52, 6, 80, 75]]])>
注意掩码的长度必须与对应维度的长度一致,如在班级维度上采样,则必须对这 4 个班级是否采样的掩码全部指定,掩码长度为 4。
如果对 8 门科目进行掩码采样,设掩码采样方案为
m
a
s
k
=
[
T
r
u
e
,
F
a
l
s
e
,
F
a
l
s
e
,
T
r
u
e
,
T
r
u
e
,
F
a
l
s
e
,
F
a
l
s
e
,
T
r
u
e
]
mask = [True, False, False, True, True, False, False, True]
mask=[True,False,False,True,True,False,False,True]
即采样第 1、4、5、8 门科目,则可以实现为:
tf.boolean_mask(x,mask=[True,False,False,True,True,False,False,True],axis=2)
<tf.Tensor: shape=(4, 35, 4), dtype=int32, numpy=
array([[[41, 56, 26, 94],
[64, 33, 20, 76],
[97, 79, 47, 97],
[ 2, 66, 55, 86],
[41, 43, 42, 99],
[45, 9, 26, 96],
[ 2, 15, 4, 32],
[28, 99, 53, 32],
[53, 35, 75, 81],
[15, 3, 63, 29],
[48, 28, 5, 35],
[56, 28, 59, 91],
[63, 77, 42, 96],
[52, 45, 80, 18],
[ 7, 39, 79, 0],
[68, 68, 2, 9],
[66, 25, 45, 49],
[74, 50, 11, 36],
[76, 23, 80, 62],
[70, 26, 75, 62],
[38, 84, 23, 31],
[86, 21, 45, 30],
[87, 67, 0, 80],
[65, 83, 82, 0],
[13, 56, 90, 14],
[46, 73, 84, 68],
[79, 6, 76, 31],
[21, 32, 20, 91],
[52, 40, 79, 69],
[58, 16, 23, 75],
[72, 81, 19, 13],
[35, 56, 69, 1],
[19, 95, 56, 35],
[24, 41, 41, 35],
[27, 11, 16, 20]],
[[68, 87, 22, 39],
[18, 49, 39, 59],
[30, 56, 68, 2],
[72, 13, 36, 19],
[52, 6, 12, 88],
[38, 31, 41, 15],
[23, 77, 13, 69],
[96, 35, 68, 15],
[46, 44, 12, 8],
[81, 60, 65, 68],
[79, 83, 60, 85],
[50, 29, 1, 27],
[13, 24, 74, 53],
[47, 5, 45, 85],
[76, 67, 52, 85],
[14, 10, 46, 13],
[32, 77, 58, 18],
[ 0, 99, 44, 48],
[70, 8, 43, 50],
[55, 52, 22, 59],
[71, 67, 63, 2],
[42, 81, 49, 27],
[92, 96, 46, 76],
[41, 78, 58, 93],
[31, 0, 35, 2],
[10, 78, 14, 27],
[80, 70, 40, 86],
[26, 98, 17, 78],
[69, 96, 35, 10],
[61, 31, 32, 50],
[20, 72, 95, 95],
[59, 17, 57, 23],
[29, 3, 76, 62],
[42, 87, 16, 67],
[29, 63, 7, 19]],
[[15, 83, 17, 96],
[49, 96, 14, 16],
[36, 78, 70, 27],
[10, 54, 22, 31],
[81, 93, 0, 96],
[98, 55, 53, 32],
[31, 30, 28, 38],
[77, 71, 35, 34],
[52, 50, 84, 54],
[59, 91, 58, 91],
[82, 46, 93, 86],
[33, 28, 23, 10],
[36, 6, 37, 91],
[56, 14, 2, 65],
[ 0, 14, 33, 85],
[24, 74, 63, 62],
[ 8, 42, 70, 88],
[53, 45, 7, 60],
[68, 68, 86, 3],
[58, 33, 15, 8],
[29, 25, 28, 15],
[96, 33, 12, 31],
[80, 23, 76, 50],
[75, 85, 8, 0],
[29, 67, 56, 58],
[45, 41, 2, 92],
[24, 46, 34, 84],
[68, 10, 45, 67],
[99, 45, 5, 20],
[96, 24, 81, 84],
[86, 66, 56, 12],
[94, 61, 49, 25],
[22, 49, 84, 85],
[69, 71, 64, 50],
[78, 91, 55, 31]],
[[11, 59, 50, 98],
[50, 75, 74, 19],
[87, 82, 51, 0],
[62, 62, 50, 52],
[86, 35, 96, 99],
[74, 25, 79, 83],
[51, 74, 90, 75],
[17, 41, 15, 46],
[59, 83, 2, 6],
[45, 89, 2, 39],
[ 3, 99, 38, 68],
[63, 0, 97, 75],
[25, 34, 16, 84],
[36, 60, 47, 96],
[76, 42, 70, 68],
[67, 26, 34, 89],
[64, 34, 45, 40],
[77, 11, 59, 13],
[34, 37, 56, 18],
[75, 86, 70, 42],
[28, 88, 40, 2],
[43, 6, 68, 82],
[70, 74, 19, 71],
[97, 88, 93, 98],
[ 6, 64, 89, 8],
[33, 68, 44, 81],
[48, 6, 46, 45],
[18, 15, 53, 87],
[47, 5, 43, 96],
[13, 29, 52, 65],
[78, 78, 91, 34],
[25, 51, 6, 28],
[ 6, 99, 69, 36],
[52, 71, 41, 45],
[29, 47, 52, 75]]])>
不难发现,这里的 tf.boolean_mask 的用法其实与 tf.gather 非常类似,只不过一个通过掩码方式采样,一个直接给出索引号采样。
现在我们来考虑与 tf.gather_nd 类似方式的多维掩码采样方式。为了方便演示,我们将班级数量减少到 2 个,学生的数量减少到 3 个,即一个班级只有 3 个学生,shape 为 [2,3,8]。如果希望采样第 1 个班级的第 1~2 号学生,第 2 个班级的第 2~3 号学生,通过tf.gather_nd 可以实现为:
x = tf.random.uniform([2,3,8],maxval=100,dtype=tf.int32)
tf.gather_nd(x,[[0,0],[0,1],[1,1],[1,2]]) # 多维坐标采集
<tf.Tensor: shape=(4, 8), dtype=int32, numpy=
array([[86, 35, 9, 15, 67, 70, 66, 66],
[16, 24, 25, 9, 56, 50, 50, 65],
[96, 67, 92, 47, 97, 58, 88, 76],
[29, 33, 9, 69, 19, 97, 87, 54]])>
共采样 4 个学生的成绩,shape 为[4,8]。
如果用掩码方式,怎么表达呢?如下表 5.2 所示,行为每个班级,列为每个学生,表中数据表达了对应位置的采样情况:
表
5.2
成
绩
册
掩
码
采
样
方
案
表 5.2 成绩册掩码采样方案
表5.2成绩册掩码采样方案
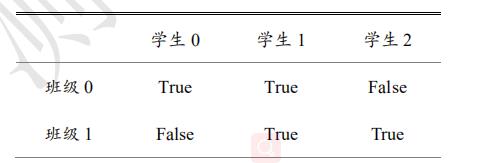
tf.boolean_mask(x,[[True,True,False],[False,True,True]])
<tf.Tensor: shape=(4, 8), dtype=int32, numpy=
array([[86, 35, 9, 15, 67, 70, 66, 66],
[16, 24, 25, 9, 56, 50, 50, 65],
[96, 67, 92, 47, 97, 58, 88, 76],
[29, 33, 9, 69, 19, 97, 87, 54]])>
tf.where()
tf.where(condition, x, y, name)
- 作用: 返回condition为True的元素坐标(x=y=None)
- 返回维度: (num_true, dim_size(condition)
- 其中dim_size为condition的维度
ind = np.array([[[1, 0, 0], [0, 0, 2]],
[[0, 0, 3], [0, 0, 0]],
[[0, 5, 0], [6, 0, 0]]])
print(ind.shape)
tf.where(ind)
(3, 2, 3)
<tf.Tensor: shape=(5, 3), dtype=int64, numpy=
array([[0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 2],
[1, 0, 2],
[2, 0, 1],
[2, 1, 0]], dtype=int64)>
- 上述tf.where操作后返回的矩阵维度是(5,3)
- 其中5是指ind矩阵中有5个元素不为0(即True)
- 返回的[[0, 0, 0],[0, 1, 2],[1, 0, 2],[2, 0, 1],[2, 1, 0]]为对应元素的坐标
- 其中3是指ind矩阵的维度为3
通过 tf.where(cond, a, b)操作可以根据 cond 条件的真假从参数𝑨或𝑩中读取数据,条件判定规则如下:
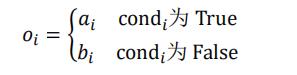
其中 i i i 为张量的元素索引,返回的张量大小与 A A A 和 B \\boldsymbol{B} B 一致,当对应位置的 c o n d i cond_{i} condi 为 True, o i o_{i} oi 从 a i a_{i} ai 中复制数据; 当对应位置的 c o n d i cond_{i} con