pytorch 图像分类
Posted 东东就是我
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了pytorch 图像分类相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
pytorch 图像分类
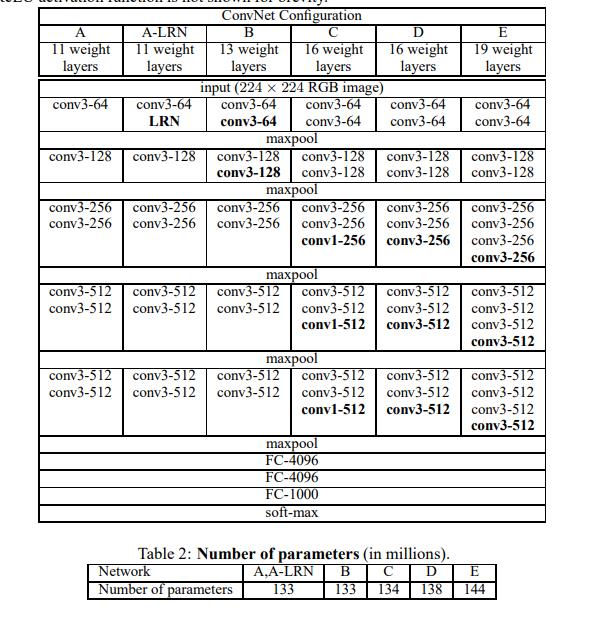
1.VGG
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1409.1556v6.pdf
import torch.nn as nn
cfg = {
'A' : [64, 'M', 128, 'M', 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 'M'],
'B' : [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 'M'],
'D' : [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 'M'],
'E' : [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 512, 'M']
}
class VGG(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,features,num_class=100):
super().__init__()
self.features=features
self.classifier=nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(512,4096),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Dropout(),
nn.Linear(4096,4096),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Dropout(),
nn.Linear(4096,num_class)
)
def forward(self,x):
output=self.features(x)
output=output.view(output.size()[0],-1)
output=self.classifier(output)
return output
def make_layers(cfg,batch_norm=False):
layers=[]
input_channel=3
for l in cfg:
if l=='M':
layers+=[nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2,stride=2)]
continue
layers+=[nn.Conv2d(input_channel,l,kernel_size=3,padding=1)]
if batch_norm:
layers+=[nn.BatchNorm2d(l)]
layers+=[nn.ReLU(inplace=True)]
input_channel=l
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def vgg11_bn():
return VGG(make_layers(cfg['A'], batch_norm=True))
def vgg13_bn():
return VGG(make_layers(cfg['B'], batch_norm=True))
def vgg16_bn():
return VGG(make_layers(cfg['D'], batch_norm=True))
def vgg19_bn():
return VGG(make_layers(cfg['E'], batch_norm=True))
1.bn层计算
https://blog.csdn.net/ChaoFeiLi/article/details/108950522
我理解就是把一个batch中数据归一化,使得训练的数据符合相同的分布。
求数据的均值和方差,然后对每个通道的数据计算后,使得数据满足均值为0方差为1的分布。
但是如果一个batch中每个数据都一样,这样不能代表所有数据的分布,会产生误差。比如batch很小的情况(图像分割)
好处就是:使数据远离激活函数的饱和区,加快速度
batch norm的作用: BatchNorm就是在深度神经网络训练过程中使得每一层神经网络的输入保持相同分布的。
2.relu层
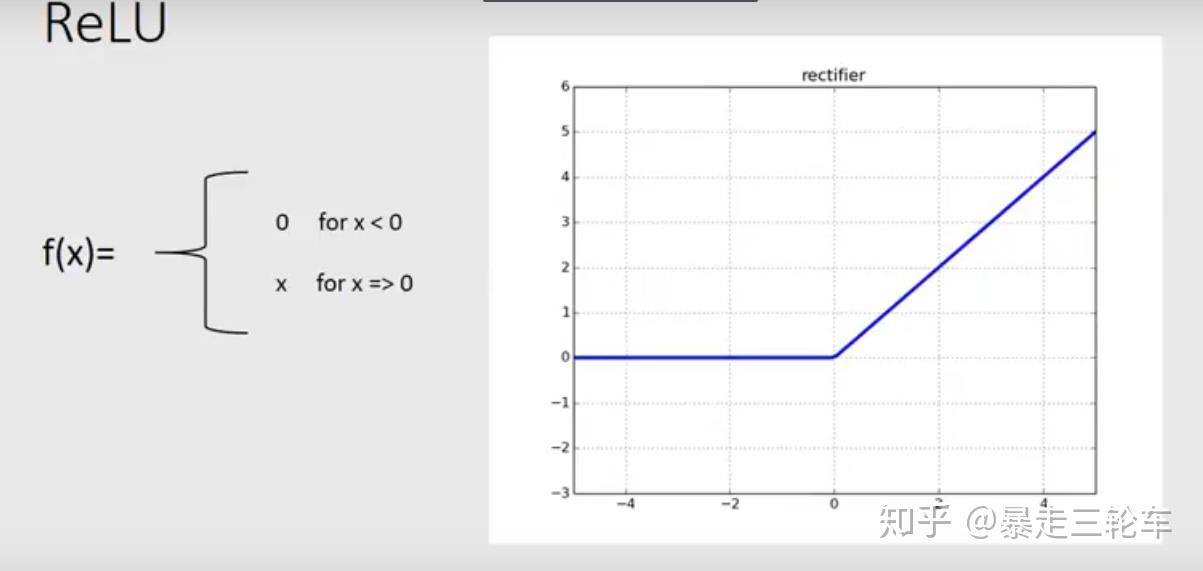
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/46255482
ReLU输出就很稳定,因为他z>0区间就是一个线性函数!不存在sigmoid的梯度消失的问题。
另一个ReLU很给力的地方就是稀疏度问题。就是我们希望每个神经元都能最大化的发挥它筛选的作用,符合某一个特征的中间值,使劲儿放大;不符合的,一刀切掉。
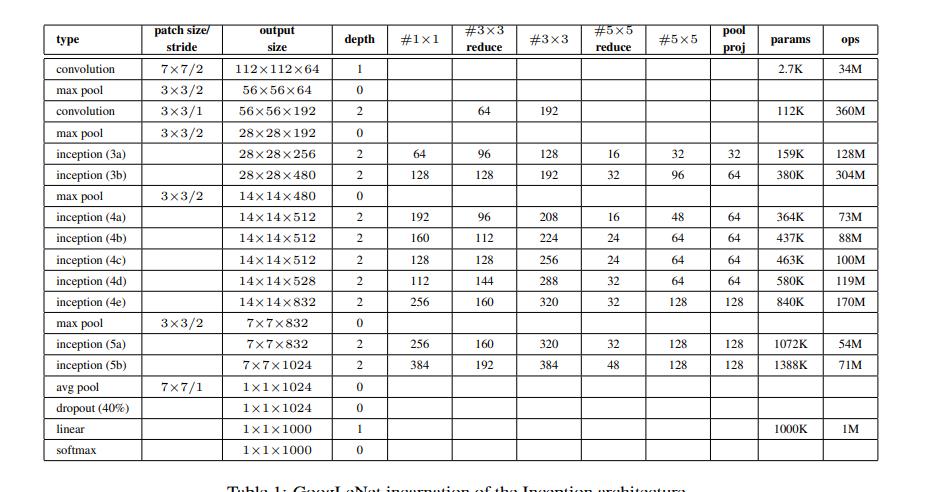
2.Googlenet
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1409.4842v1.pdf
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
class Inception(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,input_channels,n1x1,n3x3_reduce,n3x3,n5x5_reduce,n5x5,pool_proj):
super(Inception, self).__init__()
#1x1conv branch
self.b1=nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(input_channels,n1x1,kernel_size=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(n1x1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
#1x1 ->3x3
self.b2=nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(input_channels,n3x3_reduce,kernel_size=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(n3x3_reduce),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(n3x3_reduce,n3x3,kernel_size=3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(n3x3),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
# #1x1->5x5
# self.b3=nn.Sequential(
# nn.Conv2d(input_channels,n5x5_reduce,kernel_size=1),
# nn.BatchNorm2d(n5x5_reduce),
# nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
# nn.Conv2d(n5x5_reduce,n5x5,kernel_size=5),
# nn.BatchNorm2d(n5x5),
# nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
# )
#1x1->5x5 使用2个3x3
self.b3=nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(input_channels,n5x5_reduce,kernel_size=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(n5x5_reduce),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(n5x5_reduce,n5x5,kernel_size=3,padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(n5x5,n5x5),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(n5x5,n5x5,kernel_size=3,padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(n5x5),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
)
self.b4=nn.Sequential(
nn.MaxPool2d(3,stride=1,padding=1),
nn.Conv2d(input_channels,pool_proj,kernel_size=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(pool_proj),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
def forward(self,x):
return torch.cat([self.b1(x),self.b2(x),self.b3(x),self.b4(x)],dim=1)
class GoogleNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,num_class=100):
super(GoogleNet, self).__init__()
self.prelayer=nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3,64,kernel_size=3,padding=1,bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(64,64,kernel_size=3,padding=1,bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(64,192,kernel_size=3,padding=1,bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(192),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
)
self.a3=Inception(192,64,96,128,16,32,32)
self.b3=Inception(256,128,128,192,32,96,64)
self.maxpool=nn.MaxPool2d(3,stride=2,padding=1)
self.a4=Inception(480,192,96,208,16,48,64)
self.b4=Inception(512,160,112,224,24,64,64)
self.c4=Inception(512,128,128,256,24,64,64)
self.d4=Inception(512,112,144,288,32,64,64)
self.e4=Inception(528,256,160,320,32,128,128)
self.a5=Inception(832,256,160,320,32,128,128)
self.b5=Inception(832,384,192,384,48,128,128)
#input feature size 8*8*1024
self.avgpool=nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1,1))
self.dropout=nn.Dropout2d(p=0.4)
self.linear=nn.Linear(1024,num_class)
def forward(self,x):
x=self.prelayer(x)
x=self.maxpool(x)
x=self.a3(x)
x=self.b3(x)
x=self.maxpool(x)
x=self.a4(x)
x=self.b4(x)
x=self.c4(x)
x=self.d4(x)
x=self.e4(x)
x=self.maxpool(x)
x=self.a5(x)
x=self.b5(x)
x=self.avgpool(x)
x=self.dropout(x)
x=x.view(x.size()[0],-1)
x=self.linear(x)
return x
def googlenet():
return GoogleNet()
print(googlenet())
1.nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d
只用给出输出数据的大小,自适应的给出核的大小和步长。
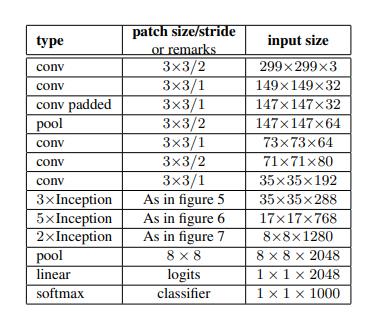
3.InceptionV3
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1512.00567v3.pdf
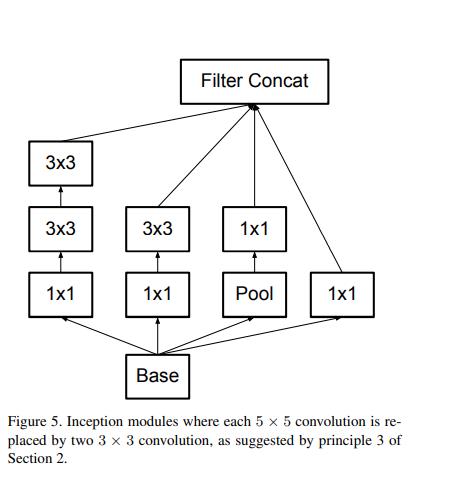
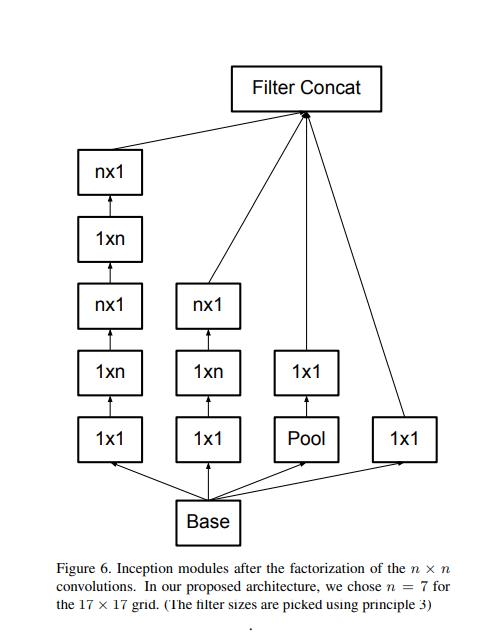
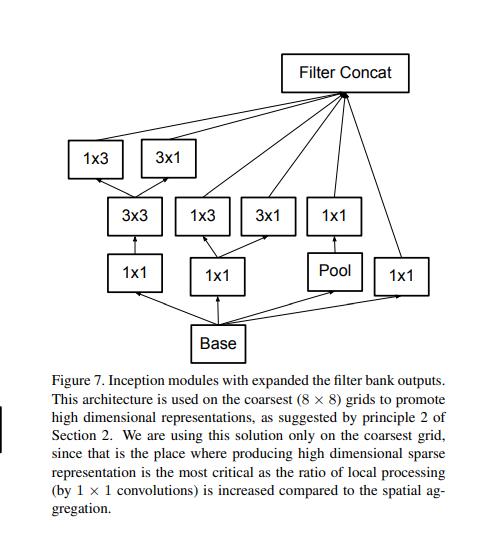
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class BasicConv2d(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_channels, output_channels, **kwargs):
super(BasicConv2d, self).__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(input_channels, output_channels, bias=False, **kwargs)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(output_channels)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.bn(x)
x = self.relu(x)
return x
class InceptionA(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_channels, pool_features):
super(InceptionA, self).__init__()
self.branch1x1 = BasicConv2d(input_channels, 64, kernel_size=1)
self.branch3x3 = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv2d(input_channels, 64, kernel_size=1),
BasicConv2d(64, 96, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
BasicConv2d(96, 96, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
)
self.branch5x5 = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv2d(input_channels, 48, kernel_size=1),
BasicConv2d(48, 64, kernel_size=5, padding=2)
)
self.branchpool = nn.Sequential(
nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
BasicConv2d(input_channels, pool_features, kernel_size=1) # todo size大小改变
)
def forward(self, x):
branch1x1 = self.branch1x1(x)
branch5x5 = self.branch5x5(x)
branch3x3 = self.branch3x3(x)
branchpool = self.branchpool(x)
outputs = [branch1x1, branch5x5, branch3x3, branchpool]
return torch.cat(outputs, 1)
class InceptionB(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_channels):
super(InceptionB, self).__init__()
self.branch3x3 = BasicConv2d(input_channels, 384, kernel_size=3, stride=2)
self.branch3x3stack = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv2d(input_channels, 64, kernel_size=1),
BasicConv2d(64, 96, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
BasicConv2d(96, 96, kernel_size=3, stride=2)
)
self.branchpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2)
def forward(self, x):
branch3x3 = self.branch3x3(x)
branch3x3stack = self.branch3x3stack(x)
branchpool = self.branchpool(x)
outputs = [branch3x3, branch3x3stack, branchpool]
return torch.cat(outputs, 1)
class InceptionC(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_channels, channels_7x7):
super(InceptionC, self).__init__()
self.branch1x1 = BasicConv2d(input_channels, 192, kernel_size=1)
c7 = channels_7x7
self.branch7x7 = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv2d(input_channels, c7, kernel_size=1),
BasicConv2d(c7, 192, kernel_size=(1, 7), padding=(0, 3