SQL常用操作
Posted LL.LEBRON
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了SQL常用操作相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
数据库常用操作
1.数据定义
(1)SQL的数据定义语句
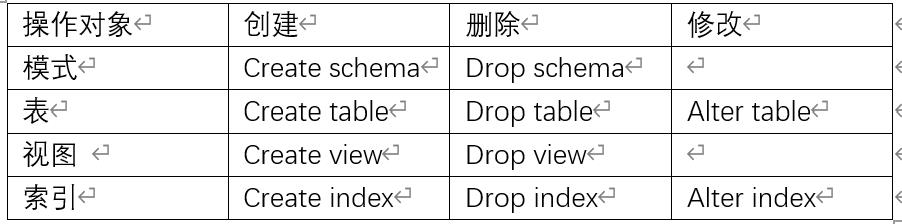
(2)模式的定义与删除
-
定义模式
create schema<模式名> authorization<用户名>; #注意:如果没有指定<模式名>,那么<模式名>隐含为<用户名>。 -
删除模式
drop schema<模式名><cascade|restrict>; #注:其中cascade和restrict两者必选其一。选择了cascade(级联),表示在删除模式的同时把该模式中所有的数据库对象全部删除;选择了restrict(限制),表示如果该模式中已经定义了下属的数据库对象(如表,视图等),则拒绝该删除语句的执行。只有该模式中没有任何下属的对象时才能执行drop schema语句。
(3)基本表的定义,删除与修改
-
定义基本表
create table tableName (<列名><数据类型>[列级完整性约束条件]...) -
修改基本表
-
添加列
alter table tableName add <列名><数据类型>[完整性约束] -
删除列
alter table tableName drop <列名> [restrict|cascade]
-
-
删除基本表
drop table tableName [restrict|cascade]
(4)索引的建立与删除
2.数据查询
(1)数据查询一般格式select
select all|distinct 目标表达式
from 表名或视图名
where 条件表达式
group by 列名 having 条件表达式
order by 列名 asc|desc
(2)基本操作
-
order by
排序:
- asc:升序(默认)
- desc:降序
#例: #查询全体学生的情况,查询结果按所在系的系号升序排序,同一系中的学生按年龄降序排序。 select * from student order by dept_name,stu_age desc; -
group by
group by 子句将查询结果按某一列或多列的值分组,值相等的作为一组。
分组后聚集函数将作用于每一个组,即每一个组都有一个函数值。注意
- group by 子句出现在 where 子句之后,order by 子句之前。
- 除了汇总字段外,select语句中的每一字段都必须在 group by 子句中给出。
- NULL的行会单独分为一组。
- 大多数 SQL 实现不支持 group by 列具有可变长度的数据类型。
#例1: #查询平均成绩大于等于90的学生学号和平均成绩 select stu_id,avg(grade) from student group by stu_id having avg(grade)>=90; #例2: #查询选修了三门以上课程的学生学号 select stu_id from student group by stu_id having count(*)>3; -
distinct
相同值只会出现一次。它作用于所有列,也就是说所有列的值都相同才算相同。
select distinct col1,col2... from tableName; -
limit
限制返回的行数。可以有两个参数,第一个参数为起始行,从 0 开始;第二个参数为返回的总行数。
select * from tableName limit num; select * from tableName limit num1,num2;
(3)连接查询
-
内连接(等值连接)
-
自连接
-
自然连接
-
外连接
(4)嵌套查询
-
在SQL语言中,一个select-from-where语句称为一个查询块。将一个查询块嵌套在另一个查询块的where子句或having短语条件中的查询称为嵌套查询。例
select sname /*外层查询或父查询*/ from student where sno in (select sno /*内查询或子查询*/ from sc where cno='2'); -
注意:子查询的select语句不能使用order by 语句,order by子句只能对最终查询结果排序。
-
带有in谓词的子查询:
子查询的查询条件不依赖父查询,称为不相关子查询。
子查询的查询条件依赖于父查询,称为相关子查询。#例1:查询与“小皮皮"在同一个系学习的学生。 select * from student where dept_name in (select dept_name from student where stu_name='小皮皮'); #例2:查询选修了课程名为“信息系统”的学生学号和姓名。 select stu_id,stu_name from student where stu_id in (select stu_id from takes where cour_id in (select cour_id from course where cour_name='信息系统' )); -
带有比较运算符的子查询
#例:找出每一个学生超过他自己选修课程平均成绩的课程号。 select cour_id,stu_id from takes A where grade>= (select avg(grade) from takes B where A.stu_id=B.stu_id); -
带有any(some)或all谓词的子查询
#例1:查询非计算机科学系中比计算机科学系任意一个学生年龄小的学生姓名和年龄。 select stu_name,stu_age from student where stu_age<any(select stu_age from student where dept_name='计算机科学') and dept_name<>'计算机科学'; -
带有exists谓词的子查询
带有exists谓词的子查询不返回任何数据,只产生逻辑真值“true"或逻辑假值”false“。
使用存在量词exists后,若内层查询结果非空,则外层的where子句返回真值,否则返回假值。
使用exists引出的子查询,目标表达式通常都用*。
#例2:查询所有选修了1号课程的学生姓名。 select stu_name from student where exists in ( select * from takes where stu_id=student.stu_id and cour_id='1'); #例2:查询选修了全部课程的学生姓名。 select stu_name from student where not exists (select * from course where not exists (select * from takes where stu_id=student.stu_id and cour_id=course.cour_id));
(5)集合查询
集合操作主要包括并操作union,交操作intersect和差操作except。
注意参加集合操作的各查询结果的列数必须相同,对应项的数据类型也必须相同。
#例1:查询计算机科学系的学生及年龄不大于19岁的学生。
select *
from student
where stu_age<=19
union
select *
from student
where dept_name='计算机科学系';
#例2:查询计算机科学系的学生与年龄不大于19岁的学生的交集。
select *
from student
where stu_age<=19
intersect
select *
from student
where dept_name='计算机科学系';
#例3:查询计算机科学系的学生与年龄不大于19岁的学生的差集。
select *
from student
where stu_age<=19
except
select *
from student
where dept_name='计算机科学系';
3.数据更新
(1)insert 插入数据
-
普通插入
insert into tableName(col1,col2...) value( value1,value2...) -
插入其他表的数据
insert into tableName(col1,col2...) select col1,col2 from tableName1; -
将一个表的内容插入到一个新表
create table newTable as select * from tableName;
(2)update 修改数据
update tableName
set 列名=表达式,...
where 条件
(3)delete 删除数据
delete
from tableName
where 条件
4.视图
视图是虚拟的表,本身不包含数据,也就不能对其进行索引操作。对视图的操作和对普通表的操作一样。
视图的优点:
- 简化复杂的 SQL 操作,比如复杂的连接;
- 只使用实际表的一部分数据;
- 通过只给用户访问视图的权限,保证数据的安全性;
- 更改数据格式和表示。
create view viewName(colName1,colName2...)
as <子查询>
[check with option];
#表示对视图进行update,insert,delete操作时要保证更新,插入或删除的行满足视图定义中的谓词条件(即子查询中的条件表达式)。
5.授权与收回
(1)grant
grant 权限...
on 对象类型,对象 名...
to 用户...
with grant option;
(2)revoke
revoke 权限...
on 对象类型,对象名...
from 用户...
(3)role
-
角色的创建
create role 角色名 -
给角色授权
grant 权限... on 对象类型,对象名 to 角色名... -
将一个角色授予其他的角色或用户
grant 角色... to 角色/用户... with admin option -
角色权限的收回
revoke 权限... on 对象类型,对象名 from 角色...
6.函数
(1)聚集函数
#聚集函数
count(*) #统计元组个数
count(distinct|all colName) #统计一列中值的个数
sum(distinct|all colName) #统计一列值的总和
avg(distinct|all colName) #计算一列值的平均值
max(distinct|all colName) #求一列值中的最大值
min(distinct|all colName) #求一列值中的最小值
#distinct 表示在计算时要取消指定列中的重复值。
注意
-
avg()会忽略NULL行。
-
使用distinct可以汇总不同的值。
select avg(distinct colName) as avgCol from tableName;
(2)时间和日期处理
| 函 数 | 说 明 |
|---|---|
| adddate() | 增加一个日期(天、周等) |
| addtime() | 增加一个时间(时、分等) |
| curdate() | 返回当前日期 |
| curtime() | 返回当前时间 |
| date() | 返回日期时间的日期部分 |
| datediff() | 计算两个日期之差 |
| date_add() | 高度灵活的日期运算函数 |
| date_format() | 返回一个格式化的日期或时间串 |
| day() | 返回一个日期的天数部分 |
| dayofweek() | 对于一个日期,返回对应的星期几 |
| hour() | 返回一个时间的小时部分 |
| minute() | 返回一个时间的分钟部分 |
| month() | 返回一个日期的月份部分 |
| now() | 返回当前日期和时间 |
| second() | 返回一个时间的秒部分 |
| time() | 返回一个日期时间的时间部分 |
| year() | 返回一个日期的年份部分 |
(3)数值处理
| 函数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| sin() | 正弦 |
| cos() | 余弦 |
| tan() | 正切 |
| abs() | 绝对值 |
| sort() | 平方根 |
| mod() | 余数 |
| exp() | 指数 |
| pi() | 圆周率 |
| rand() | 随机数 |
以上是关于SQL常用操作的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章