终结全网!手写Netty面试题答案
Posted JavaEdge.
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了终结全网!手写Netty面试题答案相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1 最原始架构
一个线程负责处理连接、读写等各种请求。
创建一个线程,注册到 Selector,将 serversocketchannel 注册到Selector
selectionKey 里就有具体的事件

对应代码
package io.netty.example.helloworld;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.spi.SelectorProvider;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* @author JavaEdge
* @date 2021/5/17
*/
public class Nioserver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 创建一个 ServerSocketChannel
ServerSocketChannel serverChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
// 设置为非阻塞模式
serverChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 创建一个事件查询器
Selector selector = SelectorProvider.provider().openSelector();
// 把 ServerSocketChannel 注册到 selector,并且感兴趣 OP_ACCEPT 事件
serverChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
while (true) {
// 阻塞方法,等待系统有I/O事件发生
int eventNum = selector.select();
System.out.println("系统发生IO事件 数量->" + eventNum);
Set<SelectionKey> keySet = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterable = keySet.iterator();
while (iterable.hasNext()) {
// 拿到该 key
SelectionKey key = iterable.next();
// 拿到后就移除它,否则后面遍历还会重复拿到它
iterable.remove();
// 连接事件
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
ServerSocketChannel ssc = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
// 接受客户端的连接,一个 SocketChannel 代表一个TCP连接
SocketChannel socketChannel = ssc.accept();
// 把SocketChannel设置为非阻塞模式
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
System.out.println("服务器接受了一个新的连接 " + socketChannel.getRemoteAddress());
}
}
}
}
}
package io.netty.example.helloworld;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.spi.SelectorProvider;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @author JavaEdge
* @date 2021/5/17
*/
public class NioServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//创建一个ServerSocket
ServerSocketChannel serverChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8089));
//设置为非阻塞模式
serverChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 创建一个事件查询器
Selector selector = SelectorProvider.provider().openSelector();
// 把 ServerSocketChannel 注册到事件查询器上,并且感兴趣 OP_ACCEPT 事件
serverChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
//
// //创建一组事件查询器
// EventLoopGroup eventLoopGroup = new EventLoopGroup();
while (true) {
// 阻塞方法,等待系统有I/O事件发生
int eventNum = selector.select();
System.out.println("系统发生IO事件 数量->" + eventNum);
Set<SelectionKey> keySet = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterable = keySet.iterator();
while (iterable.hasNext()) {
// 拿到该 key
SelectionKey key = iterable.next();
// 拿到后就移除它,否则后面遍历还会重复拿到它
iterable.remove();
// 连接事件
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
// 因为只有 ServerSocketChannel 有接收事件,所以可直接强转
ServerSocketChannel ssc = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
// 接受客户端的连接,一个 SocketChannel 代表一个TCP连接
// 事件如果发生了,就肯定有新的连接
SocketChannel socketChannel = ssc.accept();
// 把SocketChannel设置为非阻塞模式
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
System.out.println("服务器接受了一个新的连接 " + socketChannel.getRemoteAddress());
// 把SocketChannel注册到Selector,并关注OP_READ事件
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
// eventLoopGroup.register(socketChannel, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
// 可读事件
if (key.isReadable()) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
try {
int readNum = socketChannel.read(buffer);
if (readNum == -1) {
System.out.println("读取结束,关闭 socket");
key.channel();
socketChannel.close();
break;
}
// 将Buffer从写模式切到读模式
buffer.flip();
byte[] bytes = new byte[readNum];
buffer.get(bytes, 0, readNum);
System.out.println(new String(bytes));
/* byte[] response = "client hello".getBytes();
// 清理了才可以重新使用
buffer.clear();
buffer.put(response);
buffer.flip();
// 该方法非阻塞的,如果此时无法写入也不会阻塞在此,而是直接返回 0 了
socketChannel.write(buffer);
*/
// 在 key 上附加一个对象
key.attach("hello client".getBytes());
// 把 key 关注的事件切换为写
key.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("读取时发生异常,关闭 socket");
// 取消 key
key.channel();
}
}
if (key.isWritable()) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
// 可写时再将那个对象拿出来
byte[] bytes = (byte[]) key.attachment();
key.attach(null);
System.out.println("可写事件发生 写入消息" + Arrays.toString(bytes));
if (bytes != null) {
socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(bytes));
}
// 写完后,就不需要写了,就切换为读事件 如果不写该行代码就会死循环
// key.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
}
}
}
}
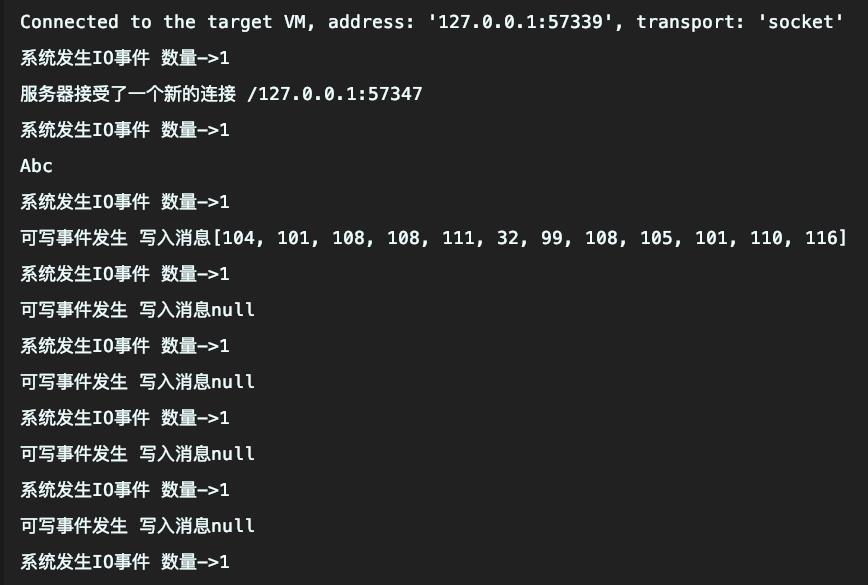
2 接收请求单独处理
- 架构图

2.1 死锁案例
package io.netty.example.helloworld;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.spi.SelectorProvider;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* @author JavaEdge
* @date 2021/5/17
*/
public class NioServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 创建一个ServerSocket
ServerSocketChannel serverChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8089));
// 设置为非阻塞模式
serverChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 创建一个事件查询器
Selector selector = SelectorProvider.provider().openSelector();
// 把 ServerSocketChannel 注册到事件查询器上,并且感兴趣 OP_ACCEPT 事件
serverChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
EventLoop eventLoop = new EventLoop();
while (true) {
// 阻塞方法,等待系统有I/O事件发生
int eventNum = selector.select();
System.out.println("系统发生IO事件 数量->" + eventNum);
Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> keyIterator = selectedKeys.iterator();
while (keyIterator.hasNext()) {
// 拿到该 key
SelectionKey key = keyIterator.next();
// 拿到后就移除它,否则后面遍历还会重复拿到它
keyIterator.remove();
// 只需处理【连接事件】 a connection was accepted by a ServerSocketChannel.
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
// 因为只有 ServerSocketChannel 有接收事件,所以可直接强转
ServerSocketChannel ssc = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
// 接受客户端的连接,一个 SocketChannel 代表一个TCP连接
// 事件如果发生了,就肯定有新的连接
SocketChannel socketChannel = ssc.accept();
// 把SocketChannel设置为非阻塞模式
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
System.out.println("服务器接受了一个新的连接 " + socketChannel.getRemoteAddress());
// 把SocketChannel注册到Selector,并关注OP_READ事件
// socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
eventLoop.register(socketChannel, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
}
}
}
}
package io.netty.example.helloworld;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.ClosedChannelException;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.spi.SelectorProvider;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* @author JavaEdge
* @date 2021/5/25
*/
public class EventLoop implements Runnable {
private Selector selector;
private Thread thread;
public EventLoop() throws IOException {
this.selector = SelectorProvider.provider().openSelector();
this.thread = new Thread(this);
this.thread.start();
}
/**
* 把 channel 注册到 事件查询器
*/
public void register(SocketChannel channel, int keyOps) throws ClosedChannelException {
channel.register(selector, keyOps);
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (!Thread.interrupted()) {
try {
// 阻塞方法,等待系统有 I/0 事件产生
int eventNum = selector.select();
System.out.println("系统发生IO事件 数量->" + eventNum);
Set<SelectionKey> keySet = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterable = keySet.iterator();
while (iterable.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iterable.next();
iterable.remove();
// 可读事件
if (key.isReadable()) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
try {
int readNum = socketChannel.read(buffer);
if (readNum == -1) {
System.out.println("读取结束,关闭 socket");
key.channel();
socketChannel.close();
break;
}
// 将Buffer从写模式切到读模式
buffer.flip();
byte[] bytes = new byte[readNum];以上是关于终结全网!手写Netty面试题答案的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章