线程的应用--生产者与消费者模型
Posted 李憨憨_
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了线程的应用--生产者与消费者模型相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
生产者与消费者模型
生产者与消费者模型: 一种非常典型的设计模式.设计模式: 大佬们针对典型的应用场景设计的解决方案;
应用场景: 有大量数据产生以及进行处理的场景;
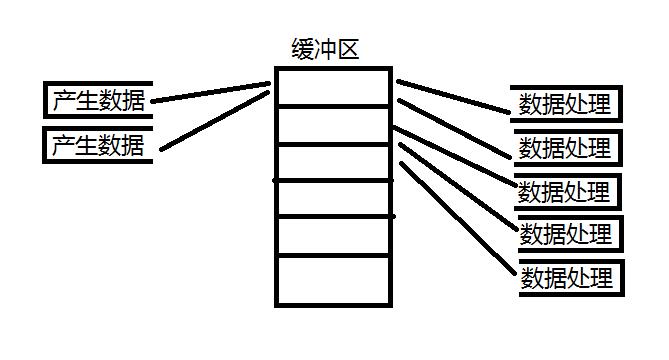
优势: 解耦合, 支持忙闲不均, 支持并发
生产者与消费者模型的实现
实现: 2种角色的线程(一个入队数据, 一个出队数据) + 线程安全的队列(阻塞队列)线程安全:
生产者与生产者: 互斥
消费者与消费者: 互斥
生产者与消费者: 同步 + 互斥
线程安全的阻塞队列的实现
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <queue>
3 #include <pthread.h>
4 #include <stdio.h>
5 #define MAX_QUEUE 5
6 using namespace std;
7
8 class BlockQueue{
9 private:
10 int _capacity;//容量
11 queue<int> _queue;
12 pthread_mutex_t _mutex;
13 pthread_cond_t _cond_pro;
14 pthread_cond_t _cond_cus;
15 public:
16 BlockQueue(int cap = MAX_QUEUE)
17 :_capacity(cap)
18 {
19 pthread_mutex_init(&_mutex,NULL);
20 pthread_cond_init(&_cond_pro,NULL);
21 pthread_cond_init(&_cond_cus,NULL);
22 }
23 ~BlockQueue()
24 {
25 pthread_mutex_destroy(&_mutex);
26 pthread_cond_destroy(&_cond_pro);
27 pthread_cond_destroy(&_cond_cus);
28
29 }
30 bool Push(int data)
31 {
32 pthread_mutex_lock(&_mutex);
33 while(_queue.size() == _capacity){
34 pthread_cond_wait(&_cond_pro, &_mutex);
35 }
36 _queue.push(data);
37 pthread_cond_signal(&_cond_cus);
38 pthread_mutex_unlock(&_mutex);
39 return true;
40 }
41 bool Pop(int* data)
42 {
43 pthread_mutex_lock(&_mutex);
44 while(_queue.empty()){
45 pthread_cond_wait(&_cond_cus, &_mutex);
46 }
47 *data = _queue.front();
48 _queue.pop();
49 pthread_cond_signal(&_cond_pro);
50 pthread_mutex_unlock(&_mutex);
51 return true;
52 }
53 };
54
55 void *productor(void *arg)
56 {
57 BlockQueue *q = (BlockQueue *)arg;
58 int i = 0;
59 while(1){
60 q->Push(i);
61 printf("%p-push data:%d\\n", pthread_self(), i++);
62 }
63 return NULL;
64 }
65 void *customer(void *arg)
66 {
67 BlockQueue *q = (BlockQueue *)arg;
68 while(1){
69 int data;
70 q->Pop(&data);
74 }
75 int main()
76 {
77 BlockQueue q;
78 int count = 4, ret;
79 pthread_t ptid[4], ctid[4];
80 int i;
81 for(i = 0;i < count;i++){
82 ret = pthread_create(&ptid[i],NULL, productor, &q);
83 if(ret != 0){
84 printf("thread create error\\n");
85 return -1;
86 }
87 }
88 for(i = 0;i < count;i++){
89 ret = pthread_create(&ctid[i],NULL, customer, &q);
90 if(ret != 0){
91 printf("thread create error\\n");
92 return -1;
93 }
94 }
95 for(i = 0; i < count; i++){
96 pthread_join(ptid[i],NULL);
97 pthread_join(ctid[i],NULL);
98 }
99 return 0;
100 }
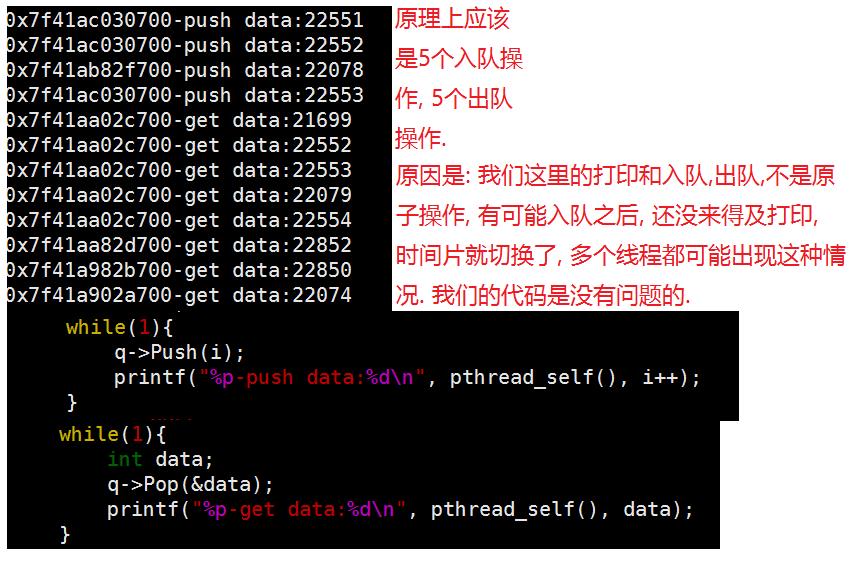
注: 最关键的地方就是BlockQueue(线程安全的阻塞队列)的实现
以上是关于线程的应用--生产者与消费者模型的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章