Vue全家桶之前后端交互
Posted 前端加油
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Vue全家桶之前后端交互相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Vue全家桶之前后端交互
文章目录
1. 前后端交互模式
前后端交互:前端页面通过工具调用后端接口,拿到数据库中的数据,然后在做前端页面的渲染。
什么是前端? 什么是后端? 什么是数据库?

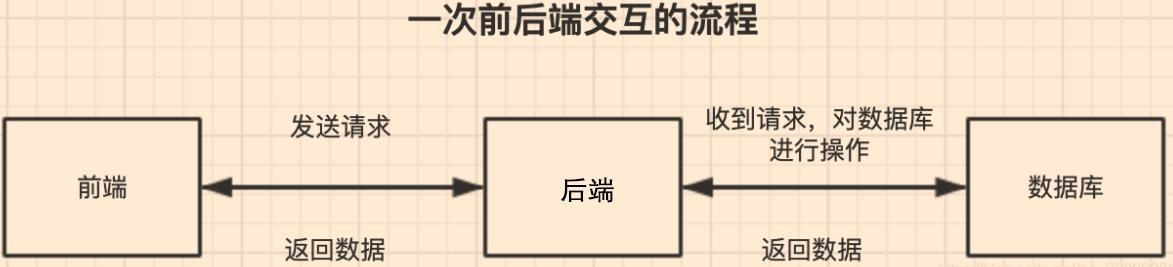
1.1 前端调用后端接口的方式
- 原生ajax
- 基于jQuery的ajax
- fetch
- axios
1.2 URL地址格式
1.传统形式的URL
-
格式:schema://host:port/path?query#fragment
- schema:协议。例如http,https,ftp等
- host:域名或者IP地址
- port:端口,http默认端口80,可以省略
- @path:路径,例如/abc/a/b/c
- query:查询参数,例如uname=lisi&age=120
- fragment:锚点(哈希Hash),用于定位页面的某个位置
-
符合规则的URL
http://www.itcast.cn
http://www.itcast.cn/java/web
http://www.itcast.cn/java/web?flag=1
http://www.itcast.cn/java/web?flag=1#function
2.Restful形式的URL
-
HTTP请求方式
GET 查询
POST 添加
PUT 修改
DELETE 删除 -
符合规则的URL地址
http://www.hello.com/books GET
http://www.hello.com/books POST
http://www.hello.com/books/123 PUT
http://www.hello.com/books/123 DELETE
2. Promise用法
2.1 异步调用
-
异步场景
① 定时任务
② Ajax
③ 事件函数
-
多次异步调用的依赖分析
- 多次异步调用的结果顺序不确定
- 异步调用结果如果存在依赖需要嵌套,嵌套太多会形成回调地狱
回调地狱:一个异步请求套着一个异步请求,一个异步请求依赖于另一个的执行结果,使用回调的方式相互嵌套,代码可读性低、编写费劲、不方便后期维护
2.2 Promise概述
Promise :ES6引入的异步编程的新解决方案,语法是一个构造函数 ,用来封装异步操作并可以获取其成功或失败的结果. resolve和reject两个参数用于处理成功和失败两种情况,并通过p.then获取处理结果
Promise 中的异步体现在then和catch中,所以写在 Promise 中的代码是被当做同步任务立即执行的。
//手写一个promise模板
var promise = new Promise((resolve,reject) => {
if (操作成功) {
resolve(value)
} else {
reject(error)
}
})
promise.then(function (value) {
// success
},function (error) {
// failure
})
//先输出 `promise1`,然后执行 `resolve`,将 `promise2` 分配到微任务队列。
new Promise(function (resolve) {
console.log("promise1");
resolve();
}).then(function () {
console.log("promise2");
});
Promise对象有三种状态:初始化pending 成功fulfilled 失败rejected
-
Promise 就是一个对象,用来表示并传递异步操作的最终结果
-
Promise {: PromiseResult} PromiseState:状态 PromiseResult:返回值
-
Promise 最主要的交互方式:将回调函数传入 then 方法来获得最终结果或出错原因
-
Promise 代码书写上的表现:以“链式调用”代替回调函数层层嵌套(回调地狱)p.then().then()
使用Promise主要有以下`好处`: -
可以避免多层异步调用嵌套问题(回调地狱)
-
Promise对象提供了简洁的API,使得控制异步操作更加容易
//02-Promise基本使用.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type='text/javascript'>
var p = new Promise( (resolve, reject) =>{
//这里用于实现异步任务
setTimeout(function () {
var flag = true;
if (flag) {
//正常情况
resolve('hello')
} else {
//异常情况
reject('出错了')
}
}, 1000)
});
p.then(function (value) {
console.log(value);
},
function (error) {
console.log(error);
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
2.3 基于Promise处理Ajax请求
1.Promise封装原生Ajax
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
function queryData(url) {
return new Promise( (resolve, reject) =>{
//原生请求
//1.创建Ajax对象
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
//2.初始化
xhr.open('get', url);
//3.发送请求
xhr.send()
//4.绑定事件,处理响应结果
xhr.onreadystatechange = function () {
//判断状态
if (xhr.readyState == 4) {
//判断响应状态码200-299
if (xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status <= 299) {
//成功
resolve(xhr.response)
} else {
//失败
reject(xhr.status)
}
}
}
})
};
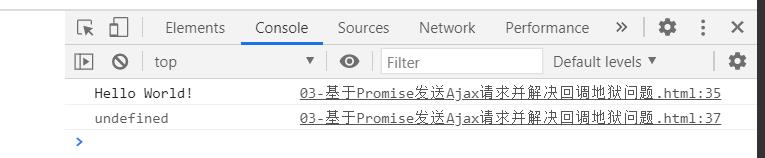
queryData('http://localhost:3000/data')
.then(function (value) {
console.log(value);
}).then(function (error) {
console.log(error);
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
//index.js
//引入express框架
const express = require('express')
//创建网站服务器
const app = express()
//引入接收post请求参数第三方包 `body-parser`。
const bodyParser = require('body-parser')
// 处理静态资源
//app.use 匹配所有的请求方式,可以直接传入请求处理函数,代表接收所有的请求。
app.use(express.static('public'))
// 处理参数
app.use(bodyParser.json());
// 配置body-parser模块
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({
extended: false
}));
// 设置允许跨域访问该服务
app.all('*', function (req, res, next) {
res.header("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "*");
res.header('Access-Control-Allow-Methods', 'PUT, GET, POST, DELETE, OPTIONS');
res.header("Access-Control-Allow-Headers", "X-Requested-With");
res.header('Access-Control-Allow-Headers', 'Content-Type');
res.header('Access-Control-Allow-Headers', 'mytoken');
next();
});
// 路由
//中间件示例
//app.get('请求路径', '处理函数') // 接收并处理get请求
//当客户端以get方式访问/data路由
app.get('/data', (req, res) => {
//对客户端做出响应
res.send('Hello World!')
})
app.get('/data1', (req, res) => {
setTimeout(function () {
res.send('Hello TOM!')
}, 1000);
})
app.get('/data2', (req, res) => {
res.send('Hello JERRY!')
})
// 启动监听
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('服务器启动成功')
})
2.发送多个ajax请求并保证顺序
queryData('http://localhost:3000/data')
.then(function(data){
console.log(data)
return queryData('http://localhost:3000/data1');
})
.then(function(data){
console.log(data);
return queryData('http://localhost:3000/data2');
})
.then(function(data){
console.log(data)
});

2.4 then参数中的函数返回值
1.返回Promise实例对象
返回的该实例对象会调用下一个then,得到上一步的处理结果
2.返回普通值
返回的普通值会直接传递给下一个then,通过then参数中函数的参数接收该值
queryData('http://localhost:3000/data')
.then(function(data){
return queryData('http://localhost:3000/data1');
})
.then(function(data){
//返回Promise实例对象
return new Promise(function(resolve, reject){
setTimeout(function(){
resolve(123);
},1000)
});
})
// 返回的该实例对象会调用下一个then
.then(function(data){
console.log(data)//123
})
queryData('http://localhost:3000/data')
.then(function(data){
return queryData('http://localhost:3000/data1');
})
//返回普通值
.then(function(data){
return 'hello';
})
//回的普通值会直接传递给下一个then,通过then参数中函数的参数接收该值
.then(function(data){
console.log(data)//hello
})
2.5 Promise常用的API
1.实例方法
- p.then()得到异步任务的正确结果
- p.catch()获取异常信息
- p.finally()成功与否都会执行
//p.then()得到异步任务的正确结果
.then(function(data){
console.log(data)
})
//p.catch()获取异常信息
.catch(function(data){
console.log(data)
})
//p.finally()成功与否都会执行
.finally(function(){
console.log('finished')
});
2.对象方法
- Promise.all()并发处理多个异步任务,所有任务都执行完成才能得到结果
- Promise.race()并发处理多个异步任务,只要有一个任务完成就能得到结果
Promise.all([p1, p2, p3]).then(function (result) {
console.log(result)
})
Promise.race([p1, p2, p3]).then(function (result) {
console.log(result)
})
3. 接口调用-fetch用法
3.1 fetch概述
1.基本特性
- 更加简单的数据获取方式,功能更强大、更灵活,可以看做是
ajax的升级版 - 基于Promise实现
2.语法结构
//通过fetchAPI调用接口,通过then获取数据
fetch(url).then(fn2)
.then(fn3)
...
.catch(fn)
3.2 fetch的基本用法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
fetch("http://localhost:3000/fdata")
.then(function (data) {
// text()方法属于fetchAPI的一部分,它返回一个Promise实例对象,用于获取后台返回的数据
return data.text();
})
.then(function (data) {
console.log(data);
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
//路由
app.get('/fdata', (req, res) => {
res.send('Hello Fetch!')
})
3.3 fetch请求参数
1.常用配置选项
- method(String):HTTP请求方法,默认为GET(GET,POST,PUT,DELETE增删改查)
- body(String):HTTP的请求参数
- headers(Object):HTTP的请求头,默认为{ }
fetch('/abc",{
method:'get'
}).then(data=>(
return data.text();
1).then(ret=>{
//注意这里得到的才是最终的数据
console.log(ret);
};
2.GET请求方式的参数传递
// GET参数传递-传统URL
fetch('http://localhost:3000/books?id=123', {
//默认为get可以不添加
method: 'get'
})
.then(function(data){
return data.text();
}).then(function(data){
console.log(data)
});
// GET参数传递-restful形式的URL 通过/传递参数
fetch('http://localhost:3000/books/456', {
method: 'get'
})
.then(function(data){
return data.text();
}).then(function(data){
console.log(data)
});
//路由
app.get('/books', (req, res) => {
//req.query获取get 请求方式
res.send('传统的URL传递参数!' + req.query.id)
})
//id为占位符,表示当前路由要接受一个id作为参数
//req.param适用于restful风格url中的参数的解析
app.get('/books/:id', (req, res) => {
res.send('Restful形式的URL传递参数!' + req.params.id)
})
3.DELETE请求方式的参数传递
// DELETE请求方式参数传递
fetch('http://localhost:3000/books/789', {
method: 'delete'
})
.then(function(data){
return data.text();
}).then(function(data){
console.log(data)
});
//路由
app.delete('/books/:id', (req, res) => {
res.send('DELETE请求传递参数!' + req.params.id)
})
4.POST请求方式的参数传递
// POST请求传参
fetch('http://localhost:3000/books', {
method: 'post',
body: 'uname=lisi&pwd=123',
headers: {
//传统格式数据
'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'
}
})
.then(function(data){
return data.text();
}).then(function(data){
console.log(data)
});
// POST请求传参
fetch('http://localhost:3000/books', {
method: 'post',
//转换为JSON字符串
body: JSON.stringify({
uname: '张三',
pwd: '456'
}),
headers: {
//json格式数据
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
}
})
.then(function(data){
return data.text();
}).then(function(data){
console.log(data)
});
//路由
app.post('/books', (