第2217期typescript4.2新特性
Posted 前端早读课
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了第2217期typescript4.2新特性相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前言
周末愉快。今日前端早读课由苏宁@chao wu授权分享。
正文从这开始~~
2021年2月23日,微软发布了typescript4.2版本,我们来看一下有哪些新的特性
更加智能的保留类型别名
TypeScript可以使用type定义一个类型,用来标识某个变量的类型,并且可以自动推断出赋值后新变量的类型,比如以下代码:
export type BasicPrimitive = number | string | boolean;
export function doStuff(value: BasicPrimitive) {
let x = value;
return x;
}
我们可以将上面的代码粘贴到TS Playground中运行,然后将鼠标hover到变量上,发现ts会自动推断出x变量的类型,如下图所示:
但是我们将代码稍做改造,如下:
export type BasicPrimitive = number | string | boolean;
export function doStuff(value: BasicPrimitive) {
if (Math.random() < 0.5) {
return undefined;
}
return value;
}
此时你猜想一下doStuff函数的返回值的类型,是BasicPrimitive | undefined ?
结果和你想的可能不一样,如下图所示:
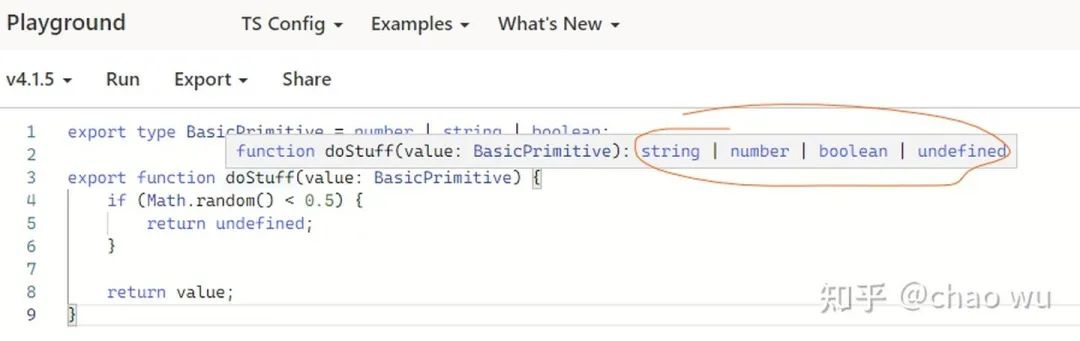
那为什么会这样?
好吧,这与TypeScript如何在内部表示类型有关。当你从一个或多个联合类型创建新的联合类型时,它会将这些类型转成新的扁平化联合类型,但是这样做会丢失原有的类型信息。
在TypeScript 4.2中,内部结构就变得更加智能了,你可以在 TS Playground 中切换编译版本为4.2,你会发现类型推断很完美,如下图所示:
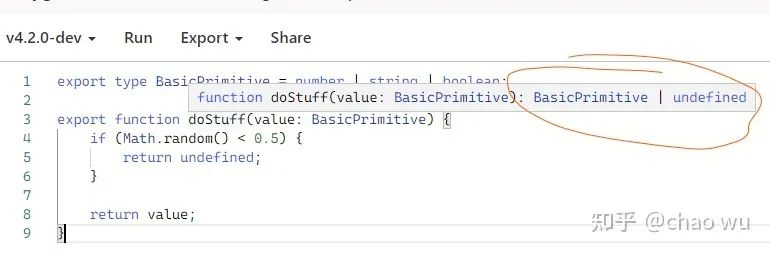
不可跟踪的rest元素
TS中我们可以用元组类型去标识一个数组的类型,例如:
let a: [string, number, boolean] = ['hello world', 10, false];
但是以上写法,元组中参数的个数是固定的,但如果number的数量是不固定的呢?
对TS熟悉的人可能会这么去写:
let a: [string, ...number[], boolean] = ['hello world', 10, false];
但这在4.2以下版本,会报以下错误:
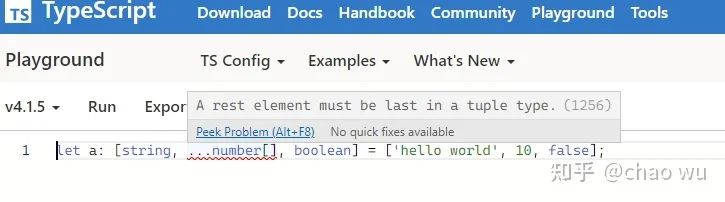
原因就是number的数量是不可预知的,你必须将它放到boolean后面,但这会和我们的代码逻辑产生冲突。而这一切在4.2中会变得很和谐:

值得注意的是,如果你使用的是4.0版本,你可以这样修改你的代码,会发现报错也会消失(但需要注意的是,4.1依然会报错)
type Original = [string, ...number[]];
type NewType = [...Original, boolean, undefined];
let a: NewType = ['hello world', 10, false];
a = ['hello world', 10, 8, 3, false];
更进一步,我们可以用这个特性去定义一个“拥有任意个前导参数,且最后是几个固定类型的参数”,比如:
declare function doStuff(...args: [...names: string[], shouldCapitalize: boolean]): void;
doStuff(/*shouldCapitalize:*/ false)
doStuff("fee", "fi", "fo", "fum", /*shouldCapitalize:*/ true);
虽然rest元素可以处在元组的任意位置,但唯一的限制是“每个元组仅一个rest元素,在rest元素之后不能有其他rest元素”,举个例子:
interface Clown { /*...*/ }
interface Joker { /*...*/ }
let StealersWheel: [...Clown[], "me", ...Joker[]];
// ~~~~~~~~~~ Error!
// A rest element cannot follow another rest element.
let StringsAndMaybeBoolean: [...string[], boolean?];
// ~~~~~~~~ Error!
// An optional element cannot follow a rest element.
--noPropertyAccessFromIndexSignature
有如下代码:
interface Person {
/** 姓名 */
name: string;
/** 通过索引签名去扩充数据字段 */
[x: string]: any;
}
function processOptions(person: Person) {
console.log(`name: ${person.name}, age: ${person.age}`);
}
processOptions({ name: 'jack', age: 22 } as Person);
首先以上代码不会报错。
在代码中,age来自于索引签名,但往往为了区别于已知字段(比如name),用户可能会想让编译器报错,这时你可以在tsconfig.json中设置:
"noPropertyAccessFromIndexSignature": true,
然后重新启动前端项目,即可发现报错
Property 'age' comes from an index signature, so it must be accessed with ['age'].
抽象构造签名
有如下代码:
interface IShape {
getArea(): number;
}
class Shape implements IShape {
getArea() {
return 2;
}
}
function makeSubclassWithArea(Ctor: new () => IShape) {
return class extends Ctor {}
}
let MyShape = makeSubclassWithArea(Shape);
const a = new MyShape();
console.log(a.getArea()); // 2
上述代码功能很简单:
创建子类构造器,比如MyShape通过继承Shape构造器来创建。但是我们想通过抽象类来实现的话,代码可能会变成这样:
abstract class Shape {
// 在子类中去实现该方法
abstract getArea(): number;
}
interface IShape {
getArea(): number;
}
function makeSubclassWithArea(Ctor: new () => IShape) {
return class extends Ctor {
// 实现抽象类中的抽象函数
getArea() {
return 2;
}
}
}
let MyShape = makeSubclassWithArea(Shape);
但是遗憾的是,编译器会报错:
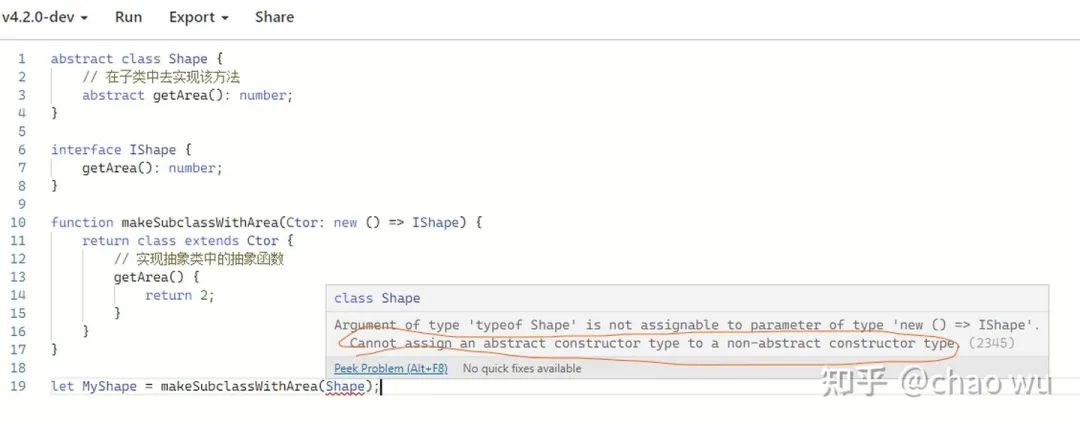
另外,如果使用InstanceType也会报同样的错:
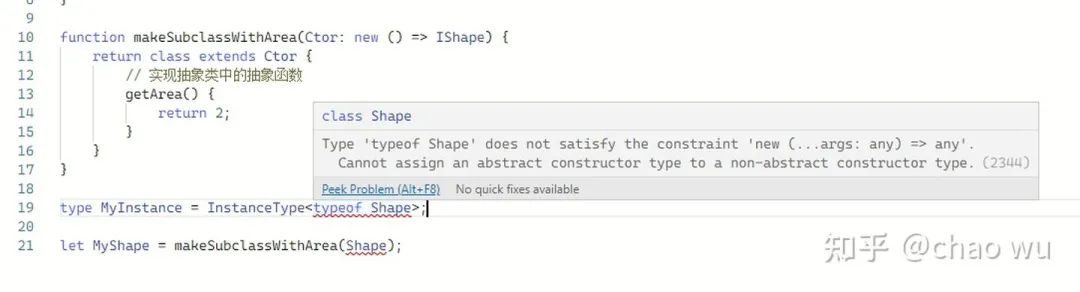
这就是为什么TypeScript 4.2允许您在构造函数签名上指定抽象修饰符。以下是处理方案:
abstract class Shape {
// 在子类中去实现该方法
abstract getArea(): number;
}
type AbstractConstructor<T> = abstract new (...args: any[]) => T;
function makeSubclassWithArea<T extends AbstractConstructor<object>>(Ctor: T) {
abstract class SubClass extends Ctor {
// 实现抽象类中的抽象函数
getArea() {
return 2;
}
}
return SubClass;
}
class SubclassWithArea extends makeSubclassWithArea(Shape) {
customMethod() {
return this.getArea();
}
}
const a = new SubclassWithArea();
console.log(a.getArea()); // 2
console.log('customMethod result:' + a.customMethod()); // customMethod result: 2
使用--explainFiles了解您的项目结构
使用以下指令时,TypeScript编译器将给出一些非常长的输出,关于import信息。
tsc --explainFiles
# 如果全局没安装typescript,使用以下命令
# npx tsc --explainFiles
信息如下(提取自命令行工具):
...
node_modules/typescript/lib/lib.es5.d.ts
Library referenced via 'es5' from file 'node_modules/typescript/lib/lib.es2015.d.ts'
Library referenced via 'es5' from file 'node_modules/typescript/lib/lib.es2015.d.ts'
node_modules/@types/react/jsx-runtime.d.ts
Imported via "react/jsx-runtime" from file 'src/index.tsx' with packageId '@types/react/jsx-runtime.d.ts@17.0.2' to import 'jsx' and 'jsxs' factory functions
node_modules/@types/react/index.d.ts
Imported via 'react' from file 'src/framework/lib/BuryingPoint.tsx' with packageId '@types/react/index.d.ts@17.0.2'
Imported via 'react' from file 'node_modules/antd-mobile/lib/accordion/index.d.ts' with packageId '@types/react/index.d.ts@17.0.2'
Imported via 'react' from file 'node_modules/antd-mobile/lib/action-sheet/index.d.ts' with packageId '@types/react/index.d.ts@17.0.2'
node_modules/@types/react-router/index.d.ts
Imported via 'react-router' from file 'src/framework/routes/route.tsx' with packageId '@types/react-router/index.d.ts@5.1.11'
...
如果你觉得命令行工具中看的不舒服,可以将信息提取到txt或者vscode中
# 提前到txt
npx tsc --explainFiles > expanation.txt
# 提前到vscode
npx tsc --explainFiles | code -
改进逻辑表达式中的未调用函数检查
TypeScript的未调用函数检查现在适用于&&和||表达式。
在strictNullChecks: true下,以下代码现在将会报错。
function shouldDisplayElement(element: Element) {
// ...
return true;
}
function getVisibleItems(elements: Element[]) {
return elements.filter(e => shouldDisplayElement && e.children.length)
// ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
// This condition will always return true since the function is always defined.
// Did you mean to call it instead.
}
解构变量可以明确标记为未使用
# 首先在tsconfig.json中配置noUnusedLocals为true
"noUnusedLocals": true,
以下代码中,_a未被使用(4.2以下版本会报以下错误)
const [_a, b] = [12, 3];
console.log(b); // TS6133: '_a' is declared but its value is never read.
你可能想要的是:告诉TS,以下划线开头的变量表示未使用变量,只负责占位,请不要报错。
此时,你只需要将ts版本升级为4.2即可(这确实是一个很重要的更新)。
但值得注意的是,以下代码,依然会报错:
const [a, b] = [12, 3];
console.log(b); // TS6133: 'a' is declared but its value is never read.
可选属性和字符串索引签名之间的宽松规则
先看一段代码(运行环境: < TS4.2),会报错:
type WesAndersonWatchCount = {
"Fantastic Mr. Fox"?: number;
"The Royal Tenenbaums"?: number;
"Moonrise Kingdom"?: number;
"The Grand Budapest Hotel"?: number;
};
// same as
// type WesAndersonWatchCount = {
// "Fantastic Mr. Fox"?: number | undefined;
// "The Royal Tenenbaums"?: number | undefined;
// "Moonrise Kingdom"?: number | undefined;
// "The Grand Budapest Hotel"?: number | undefined;
// }
declare const wesAndersonWatchCount: WesAndersonWatchCount;
const movieWatchCount: { [key: string]: number } = wesAndersonWatchCount;
// ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ error!
// Type 'WesAndersonWatchCount' is not assignable to type '{ [key: string]: number; }'.
// Property '"Fantastic Mr. Fox"' is incompatible with index signature.
// Type 'number | undefined' is not assignable to type 'number'.
// Type 'undefined' is not assignable to type 'number'. (2322)
然而上面的代码在4.2中是可以通过编译的,但是改造一下:
type WesAndersonWatchCount = { // 删除问号
"Fantastic Mr. Fox": number | undefined;
"The Royal Tenenbaums": number | undefined;
"Moonrise Kingdom": number | undefined;
"The Grand Budapest Hotel": number | undefined;
}
declare const wesAndersonWatchCount: WesAndersonWatchCount;
const movieWatchCount: { [key: string]: number } = wesAndersonWatchCount;
// ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ error!
// Type 'WesAndersonWatchCount' is not assignable to type '{ [key: string]: number; }'.
// Property '"Fantastic Mr. Fox"' is incompatible with index signature.
// Type 'number | undefined' is not assignable to type 'number'.
// Type 'undefined' is not assignable to type 'number'.(2322)
// 以下场景在TypeScript 4.2也会报错
// Type 'undefined' is not assignable to type 'number'
movieWatchCount["It's the Great Pumpkin, Charlie Brown"] = undefined;
。。。其他变化。。。
lib.d.ts 的更新
noImplicitAny错误适用于宽松的yeild表达式:
# 首先设置noImplicitAny为true
"noImplicitAny": true
然后在4.2中运行以下代码:
function* g1() {
const value = yield 1;
// ~~~~~~~
// Error!
// 'yield' expression implicitly results in an 'any' type
// because its containing generator lacks a return-type annotation.
}
function* g2() {
// No error.
// The result of `yield 1` is unused.
yield 1;
}
function* g3() {
// No error.
// `yield 1` is contextually typed by 'string'.
const value: string = yield 1;
}
function* g4(): Generator<number, void, string> {
// No error.
// TypeScript can figure out the type of `yield 1`
// from the explicit return type of `g3`.
const value = yield 1;
}
然而以上代码中g1方法在4.2以下版本不会报错。
in运算符不再允许在右侧使用基本类型
// [< 4.2] The right-hand side of an 'in' expression must be of type 'any', an object type or a type parameter.
"foo" in 42
// [= 4.2] The right-hand side of an 'in' expression must not be a primitive.
"foo" in 42
元组展开限制
TypeScript中可以使用扩展语法(...)来创建新的元组类型。
type NumStr = [number, string];
type NumStrNumStr = [...NumStr, ...NumStr];
但有时,这些元组类型可能会意外增长为巨大的类型,这可能会使类型检查花费很长时间。在4.2版本后,TypeScript设置了限制器以避免执行所有工作。
.d.ts扩展 不能在导入路径中使用
在TypeScript 4.2中,导入路径中包含.d.ts现在是错误的。
// must be changed something like
// - "./foo"
// - "./foo.js"
import { Foo } from "./foo.d.ts";
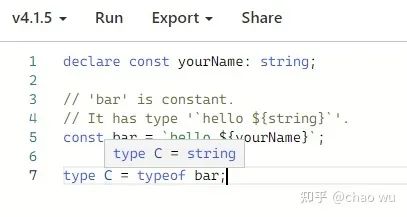
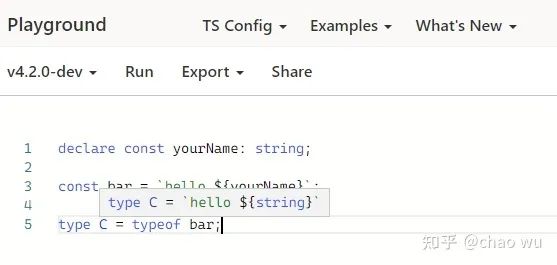
恢复模板字面量推断
declare const yourName: string;
const bar = `hello ${yourName}`;
type C = typeof bar;
下面分别展示的是4.1 和 4.2的不同:
但是如果你只想让此特性生效一次,你可以这样改造:
declare const yourName: string;
const bar = `hello ${yourName}` as const;
const baz = `hello ${yourName}`;
type C = typeof bar; // C -> `hello ${string}`
type D = typeof baz; // D -> string
值得一提的是4.1版本(4.1以下会报错),以下代码效果和4.2一致:
declare const yourName: string;
const bar = `hello ${yourName}` as const;
type C = typeof bar; // C -> `hello ${string}`
为你推荐
欢迎自荐投稿,前端早读课等你来
以上是关于第2217期typescript4.2新特性的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
奇舞周刊第 382 期:ECMAScript 2021 新特征