Java特性理解
Posted 之墨_
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java特性理解相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
让我们一起通过分析一下以下实例及其运行结果,加深我们对Java特性的理解
一:父类与子类继承
Father f1 = newSon(); // 这就叫upcasting (向上转型)
(向上转型(upcasting)、向下转型(downcasting)
1。父类引用指向子类对象,而子类引用不能指向父类对象。
2。把子类对象直接赋给父类引用叫upcasting向上转型,向上转型不用强制转换。
如:Father f1 = new Son();
3。把指向子类对象的父类引用赋给子类引用叫向下转型(downcasting),要强制转换。
例子1:
1. class Base {
2. public void method(){
3. System.out.print ("Base method");
4. }
5. }
6. class Child extends Base{
7. public void methodB(){
8. System.out.print ("Child methodB");
9. }
10 }
11 class Sample {
12 public static void main(String[] args) {
13 Base base= new Child();
14 base.methodB();
15 }
16 }
这个例子中
Base base= new Child();为向上转型,向上转型只能够调用子类重写的方法,子类独有的方法在父类中根本没有定义,所以父类无法找到子类独有的方法。
所以代码会报错base.methodB();无法运行
例子2:
class ParentClass {
int a = 1;
static { System.out.println("父类静态语句块"); }
public ParentClass() {
System.out.println("这是父类的构造方法。"); }
}
class ChildClass extends ParentClass {
int a;
static { System.out.println("子类静态语句块"); }
public ChildClass() {
System.out.println("这是子类的构造方法。"); }
}
public class ConstructorTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ChildClass cc = new ChildClass();
System.out.println(cc.a);
}}
类中的静态块会在整个类加载过程中的初始化阶段执行,而不是在类加载过程中的加载阶段执行,所以上述代码中因为
new了一个子类对象,所以将会先加载子类和父类中的静态代码块,在执行构造方法的输出语句
输出结果为:
父类静态语句块
子类静态语句块
这是父类的构造方法
这是子类的构造方法
0
二: 内存模型
- 在Java中,以下程序编译运行后,请画出pt1和pt2的内存模型。
public class Test {
int x, y;
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test pt1, pt2;
pt1 = new Test(3, 3);
pt2 = new Test(4, 4);
}
}
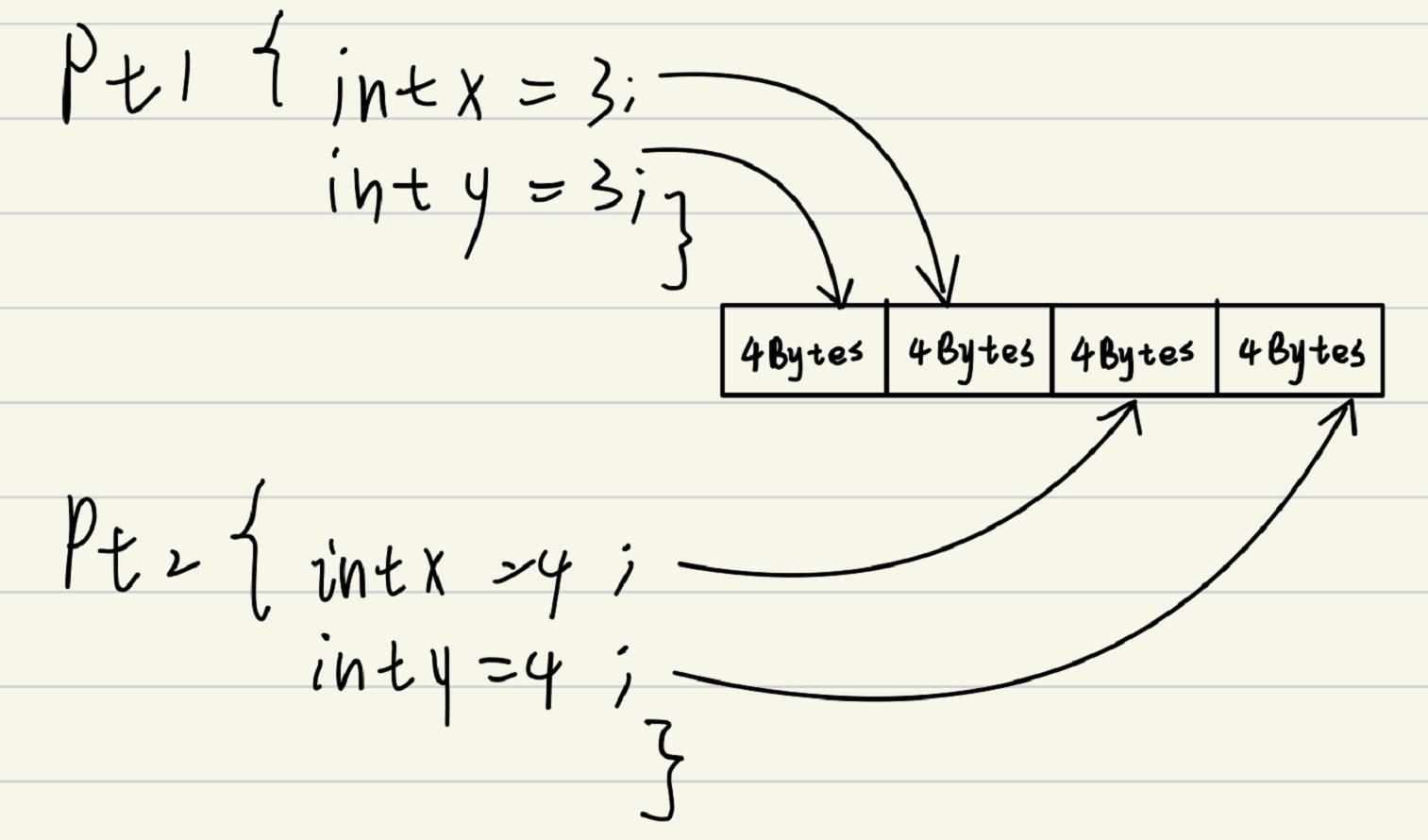
三:线程问题
public class Example extends Thread{
public void run(){
System.out.print("run1");
try{
Thread.sleep(100);
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.print("run2");
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Example example=new Example();
example.run();
System.out.print("main");
}
}
输出 run1run2main 输出run1后停留 100ms 再输出run2main
四:try-catch-finally语句判断
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入数字:");
try {
int num = input.nextInt();
if (num < 1 || num > 4) {
throw new Exception("必须在1-4之间!");
}
} catch (InputMismatchException e) {
System.out.println("InputMismatchException");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}finally{
System.out.println("finally");
}
}
}
输入 -1 时,输出结果为:
请输入数字:-1
必须在1-4之间!
finally
五:for循环语句判断
public class Demo{
public static void main(String args[]){
int count=0;
int num=0;
for(int i=0;i<=100;i++,count++) {
num=num+i;
count = num;
}
System.out.println("num ="+num);
System.out.println("count="+count);
}
}
输出结果:(因为for循环中第三个语句在一次循环结束后执行)
num = 5050
count = 5051
以上是关于Java特性理解的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章