浅谈@KafkaListener工作流程
Posted 敲代码的小小酥
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了浅谈@KafkaListener工作流程相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前述
在kafka提供的原生java客户端中,消费者采用while(true){…}的方式进行消息拉取。这一点理解起来还是比较容易的。而用SpringBoot集成Kafka后,我们使用了SpringBoot提供的@KafkaListener注解,去监听消息。这让我不禁产生疑惑:消息是怎么监听过来的呢?怎么实现监听的呢?带着疑问,花费了我一天的时间,去探索其中的原理。由于水平有限,只是探索到了重要的几个步骤,没有探索出来其来龙去脉。下面记录一下这一整天的探索流程。
一、探索过程
首先,对于Spring项目而言,一切的一切,都起源于配置,所以,先看有关Kafka消费者在SpringBoot中的配置,如下:
@Configuration
@EnableKafka
public class KafkaConsumerConfig {
@Value("${kafka.consumer.servers}")
private String servers;
@Value("${kafka.consumer.enable.auto.commit}")
private boolean enableAutoCommit;
@Value("${kafka.consumer.session.timeout}")
private String sessionTimeout;
@Value("${kafka.consumer.auto.commit.interval}")
private String autoCommitInterval;
@Value("${kafka.consumer.group.id}")
private String groupId;
@Value("${kafka.consumer.auto.offset.reset}")
private String autoOffsetReset;
@Value("${kafka.consumer.concurrency}")
private int concurrency;
@Autowired
ConsumerRebalanceListener consumerRebalanceListener;
public Map<String, Object> consumerConfigsAck() {
Map<String, Object> propsMap = new HashMap<>();
propsMap.put(ConsumerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, servers);
propsMap.put(ConsumerConfig.ENABLE_AUTO_COMMIT_CONFIG, false);
propsMap.put(ConsumerConfig.KEY_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringDeserializer.class);
propsMap.put(ConsumerConfig.VALUE_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringDeserializer.class);
propsMap.put(ConsumerConfig.GROUP_ID_CONFIG, groupId);
return propsMap;
}
public ConsumerFactory<String, String> consumerFactoryAck() {
return new DefaultKafkaConsumerFactory<>(consumerConfigsAck());
}
@Bean("listenerAck")
public ConsumerListenerAck listenerAck() {
return new ConsumerListenerAck();
}
@Bean("factoryAck")
public KafkaListenerContainerFactory<ConcurrentMessageListenerContainer<String, String>>
kafkaListenerContainerFactoryAck() {
ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactory<String, String> factory
= new ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactory<>();
factory.setConsumerFactory(consumerFactoryAck());
factory.setConcurrency(concurrency);
factory.getContainerProperties().setPollTimeout(1500);
factory.getContainerProperties().setAckMode(ContainerProperties.AckMode.MANUAL);
factory.getContainerProperties().setConsumerRebalanceListener(consumerRebalanceListener);
return factory;
}
}
- 猜想1.观察者模式实现
进行猜想和分析。首先,我们猜想,@KafkaListener是一个监听器,监听到Consumer获取到对象,然后获取这些信息,采用的是观察者模式(观察者模式)。由观察者模式的实现思路我们可以知道,Consumer中,要维护一个监听器列表,当Consumer监听到消息时,调用监听器列表中监听器的监听方法,讲消息传递给监听器。按照这个猜想,我们来看Consumer对象。
在上面的配置中,配置了ConsumerFactory消费者工厂,顾名思义,消费者工厂肯定是生产消费者对象的。我们可以看到ConsumerFactory工厂中定义了创建消费者对象的方法,如下:
public interface ConsumerFactory<K, V> {
/**
* Create a consumer with the group id and client id as configured in the properties.
* @return the consumer.
*/
default Consumer<K, V> createConsumer() {
return createConsumer(null);
}
/**
* Create a consumer, appending the suffix to the {@code client.id} property,
* if present.
* @param clientIdSuffix the suffix.
* @return the consumer.
* @since 1.3
*/
default Consumer<K, V> createConsumer(@Nullable String clientIdSuffix) {
return createConsumer(null, clientIdSuffix);
}
/**
* Create a consumer with an explicit group id; in addition, the
* client id suffix is appended to the {@code client.id} property, if both
* are present.
* @param groupId the group id.
* @param clientIdSuffix the suffix.
* @return the consumer.
* @since 1.3
*/
default Consumer<K, V> createConsumer(@Nullable String groupId, @Nullable String clientIdSuffix) {
return createConsumer(groupId, null, clientIdSuffix);
}
/**
* Create a consumer with an explicit group id; in addition, the
* client id suffix is appended to the clientIdPrefix which overrides the
* {@code client.id} property, if present.
* @param groupId the group id.
* @param clientIdPrefix the prefix.
* @param clientIdSuffix the suffix.
* @return the consumer.
* @since 2.1.1
*/
Consumer<K, V> createConsumer(@Nullable String groupId, @Nullable String clientIdPrefix,
@Nullable String clientIdSuffix);
/**
* Create a consumer with an explicit group id; in addition, the
* client id suffix is appended to the clientIdPrefix which overrides the
* {@code client.id} property, if present. In addition, consumer properties can
* be overridden if the factory implementation supports it.
* @param groupId the group id.
* @param clientIdPrefix the prefix.
* @param clientIdSuffix the suffix.
* @param properties the properties to override.
* @return the consumer.
* @since 2.2.4
*/
default Consumer<K, V> createConsumer(@Nullable String groupId, @Nullable String clientIdPrefix,
@Nullable String clientIdSuffix, @Nullable Properties properties) {
return createConsumer(groupId, clientIdPrefix, clientIdSuffix);
}
/**
* Return true if consumers created by this factory use auto commit.
* @return true if auto commit.
*/
boolean isAutoCommit();
/**
* Return an unmodifiable reference to the configuration map for this factory.
* Useful for cloning to make a similar factory.
* @return the configs.
* @since 2.0
*/
default Map<String, Object> getConfigurationProperties() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("'getConfigurationProperties()' is not supported");
}
/**
* Return the configured key deserializer (if provided as an object instead
* of a class name in the properties).
* @return the deserializer.
* @since 2.0
*/
@Nullable
default Deserializer<K> getKeyDeserializer() {
return null;
}
/**
* Return the configured value deserializer (if provided as an object instead
* of a class name in the properties).
* @return the deserializer.
* @since 2.0
*/
@Nullable
default Deserializer<V> getValueDeserializer() {
return null;
}
}
那么我们看Consumer,它也是一个接口,是kafka定义的接口,我们找其实现类,如下:
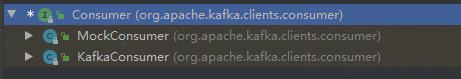
两个实现类,用的肯定是KafkaConsumer,所以我们看KafkaConsumer的源码,查找里面的Listener列表。KafkaConsumer是一个庞大的类,定义了很多东西,我们不可能全部看完,只找重点,直接搜"listener"关键字,在导包的地方,我们可以搜出来两个listeners的字眼:
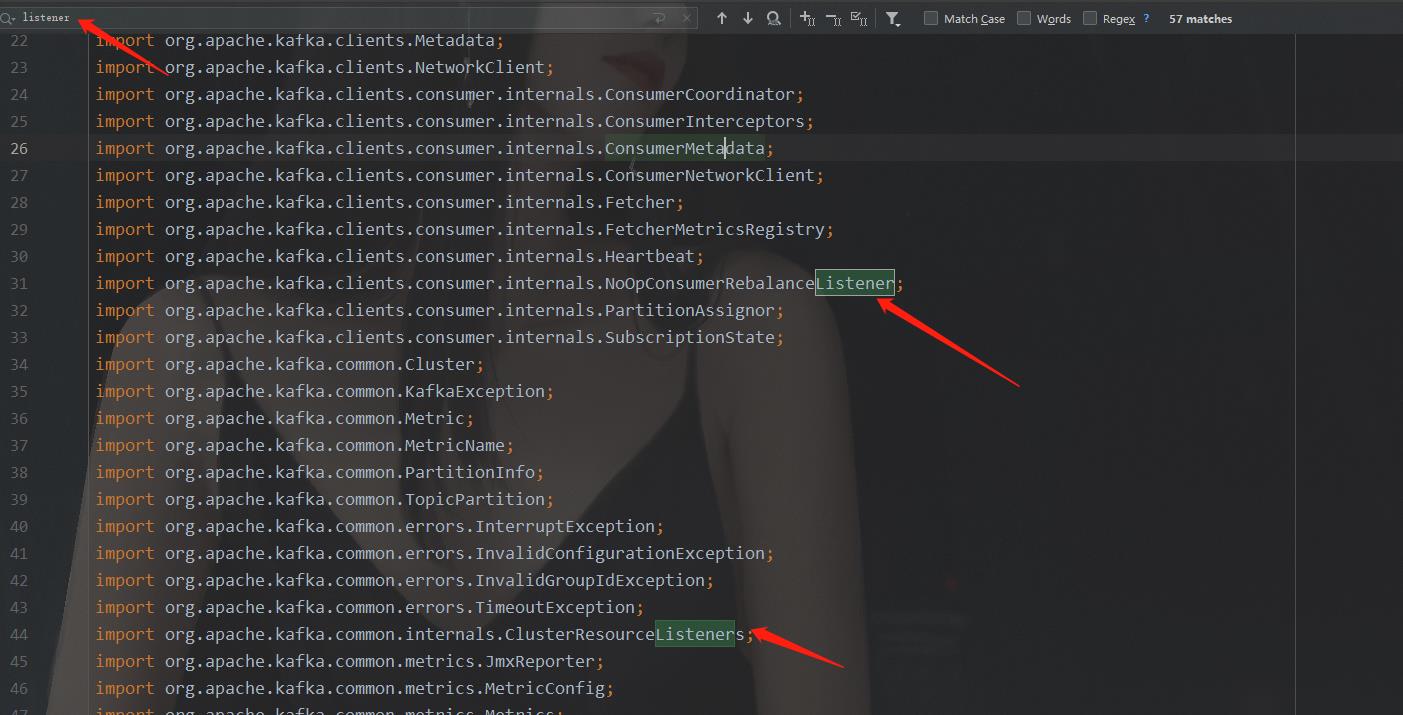
这说明,KafkaConsumer类里用到了这两个listeners相关的类,我们一个一个看。
首先看NoOpConsumerRebalanceListener源码,它实现了ConsumerRebalanceListener接口,是一个分区再均衡监听器,这明显与消息接收的监听器不一样,所以,这个listener不是我们要找的原理。
public class NoOpConsumerRebalanceListener implements ConsumerRebalanceListener {
@Override
public void onPartitionsAssigned(Collection<TopicPartition> partitions) {}
@Override
public void onPartitionsRevoked(Collection<TopicPartition> partitions) {}
}
然后,再看ClusterResourceListeners,看其字面意思,是一个Listener的集合,这不正好就是我们按照观察者模式思路要找的监听器集合吗?心里激动的一批,点开其源码进行查看:
public class ClusterResourceListeners {
private final List<ClusterResourceListener> clusterResourceListeners;
public ClusterResourceListeners() {
this.clusterResourceListeners = new ArrayList<>();
}
/**
* Add only if the candidate implements {@link ClusterResourceListener}.
* @param candidate Object which might implement {@link ClusterResourceListener}
*/
public void maybeAdd(Object candidate) {
if (candidate instanceof ClusterResourceListener) {
clusterResourceListeners.add((ClusterResourceListener) candidate);
}
}
/**
* Add all items who implement {@link ClusterResourceListener} from the list.
* @param candidateList List of objects which might implement {@link ClusterResourceListener}
*/
public void maybeAddAll(List<?> candidateList) {
for (Object candidate : candidateList) {
this.maybeAdd(candidate);
}
}
/**
* Send the updated cluster metadata to all {@link ClusterResourceListener}.
* @param cluster Cluster metadata
*/
public void onUpdate(ClusterResource cluster) {
for (ClusterResourceListener clusterResourceListener : clusterResourceListeners) {
clusterResourceListener.onUpdate(cluster);
}
}
}
可以看到,ClusterResourceListeners内部维护了一个ClusterResourceListener列表,观察者模式的思路越来越清晰,我们看ClusterResourceListener的源码:
public interface ClusterResourceListener {
/**
* A callback method that a user can implement to get updates for {@link ClusterResource}.
* @param clusterResource cluster metadata
*/
void onUpdate(ClusterResource clusterResource);
}
里面的onUpdate方法实锤了,这就是观察者模式。我们的思路似乎得到了证实。那它是怎么实现消息发到ClusterResourceListener 里的呢,具体实现是什么呢?我们要找ClusterResourceListener 的实现类去看。搜索ClusterResourceListener 的实现类发现,尼玛,居然没有实现类:
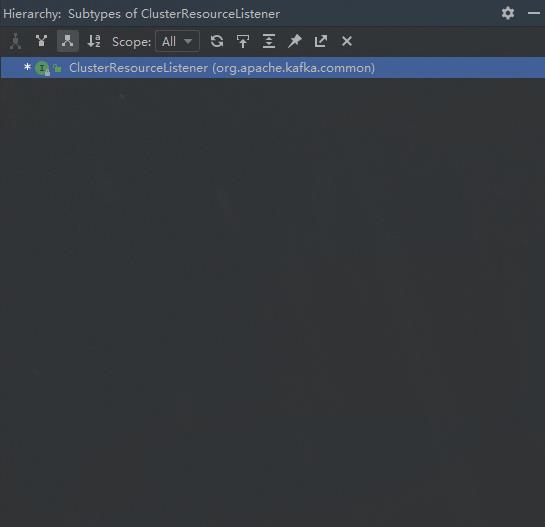
再看ClusterResourceListener源码的注释,第一句就说明了情况:
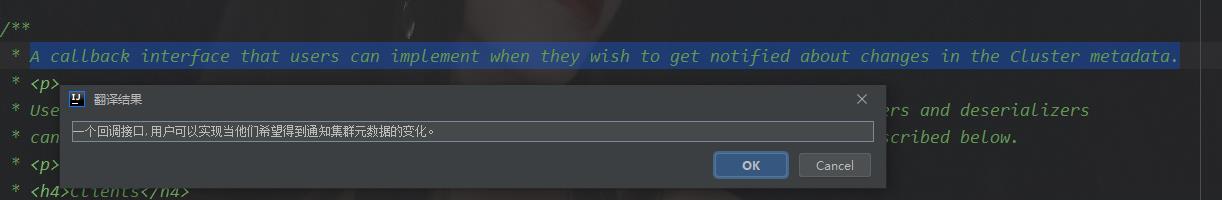
由注释可知,此接口是为用户留出来的接口,可以利用该接口在接收数据时做一些事情。而@KafkaListener监听的消息,并不是用的此接口。
至此,观察者模式思想实现@KafkaListener的猜想失败了。KafkaConsumer里是利用了观察者模式,但并不是利用在了@KafkaListener上面。继续猜想。
- 猜想2:SpringBoot与Kafka消费者的配置中入手
从KafkaConsumer类入手失败了,那只能转换思路了,既然不是KafkaConsumer接收到消息后主动往监听器里推,那就是其他地方调用了KafkaConsumer的poll()方法,拉取来数据,然后再往监听器里塞。
上面说到,一切的一切,都从配置开始,我们分析Kafka消费者在SpringBoot中的配置,请查看上面的配置代码。分析可以得知,最终配置的属性也好,对象也好,就集中到了KafkaListenerContainerFactory里,如下图:
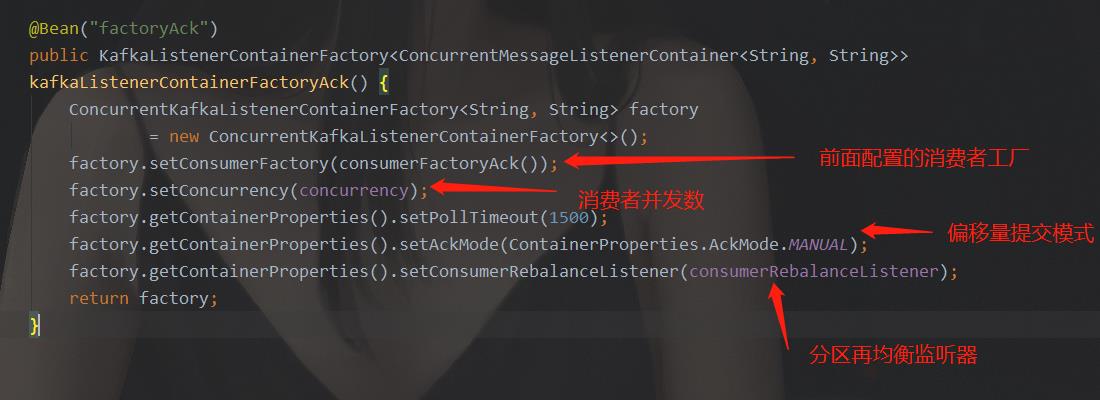
所以,我们猜想,这个类,是Kafka工作的一个核心类。我们又知道,spring中的配置,是项目在初始化的时候用来加载用的,所以,在项目启动过程中,只是初始化一些工厂实例,并填充实例的一些属性。而真正的接收消息,塞入监听,这些逻辑,肯定不在初始化的逻辑中。所以,虽然我们找到了核心类,但是还需要猜测核心类中的核心流程。
我们看KafkaListenerContainerFactory的源码:
/**
* Factory for {@link MessageListenerContainer}s.
*
* @param <C> the {@link MessageListenerContainer} implementation type.
*
* @author Stephane Nicoll
* @author Gary Russell
*
* @see KafkaListenerEndpoint
*/
public interface KafkaListenerContainerFactory<C extends MessageListenerContainer> {
/**
* Create a {@link MessageListenerContainer} for the given {@link KafkaListenerEndpoint}.
* Containers created using this method are added to the listener endpoint registry.
* @param endpoint the endpoint to configure
* @return the created container
*/
C createListenerContainer(KafkaListenerEndpoint endpoint);
/**
* Create and configure a container without a listener; used to create containers that
* are not used for KafkaListener annotations. Containers created using this method
* are not added to the listener endpoint registry.
* @param topicPartitions the topicPartitions to assign.
* @deprecated in favor of {@link #createContainer(TopicPartitionOffset[])}.
* @return the container.
* @since 2.2
*/
@Deprecated
C createContainer(Collection<org.springframework.kafka.support.TopicPartitionInitialOffset> topicPartitions);
/**
* Create and configure a container without a listener; used to create containers that
* are not used for KafkaListener annotations. Containers created using this method
* are not added to the listener endpoint registry.
* @param topicPartitions the topicPartitions to assign.
* @return the container.
* @since 2.3
*/
C createContainer(TopicPartitionOffset... topicPartitions);
/**
* Create and configure a container without a listener; used to create containers that
* are not used for KafkaListener annotations. Containers created using this method
* are not added to the listener endpoint registry.
* @param topics the topics.
* @return the container.
* @since 2.2
*/
C createContainer(String... topics);
/**
* Create and configure a container without a listener; used to create containers that
* are not used for KafkaListener annotations. Containers created using this method
* are not added to the listener endpoint registry.
* @param topicPattern the topicPattern.
* @return the container.
* @since 2.2
*/
C createContainer(Pattern topicPattern);
}
可以看到,该工厂是生产MessageListenerContainer对象的工厂,所以,我们猜测,核心流程,就在MessageListenerContainer对象里定义的。
MessageListenerContainer是一个接口,我们看其源码注释:
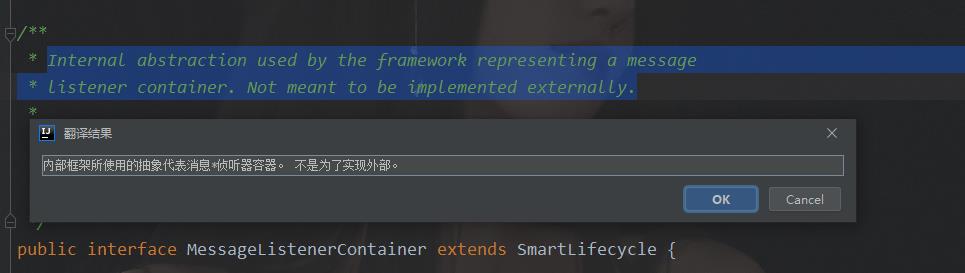
由注释可以看到,其是内部使用的一个监听器接口,这符合我们预期的逻辑,因为消息的监听是框架内部自身实现的,我们没有做任何操作,只是定义了@KafkaListener下面的方法。
我们看MessageListenerContainer的实现类都有哪些:
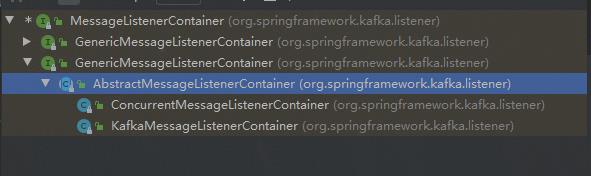
可以看到,下面有一个抽象类,抽象类下又有两个实现类。我们看ConcurrentMessageListenerContainer类的源码:(因为我们采用的是多消费者并发模式,这个类字眼明显是并发消息的监听器,所以看这个类)。
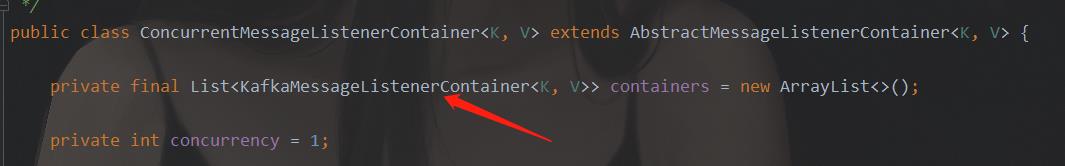
通过上图的源码可知,ConcurrentMessageListenerContainer中又定义了另一个实现类KafkaMessageListenerContainer的集合。所以这两个类其实是有交互的。那么我们如何找这个类中我们想要的方法呢?上面我们提到,现在我们的猜想是这个类去调用KafkaConsumer的poll方法,获得消息后再传入@KafkaListener定义的监听器中,所以,我们在ConcurrentMessageListenerContainer中搜索“consumer”字样,看都在哪里应用了。
通过搜索可知,ConcurrentMessageListenerContainer类中,有consumerFactory的使用,下面截图是使用处:
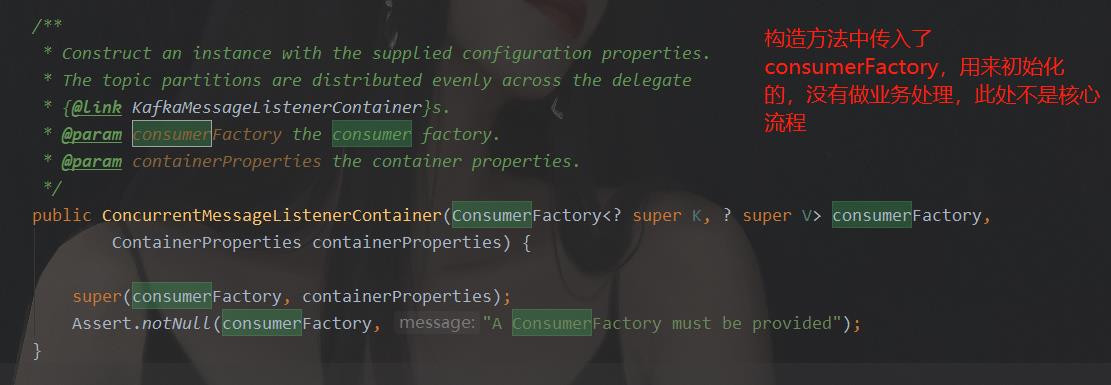
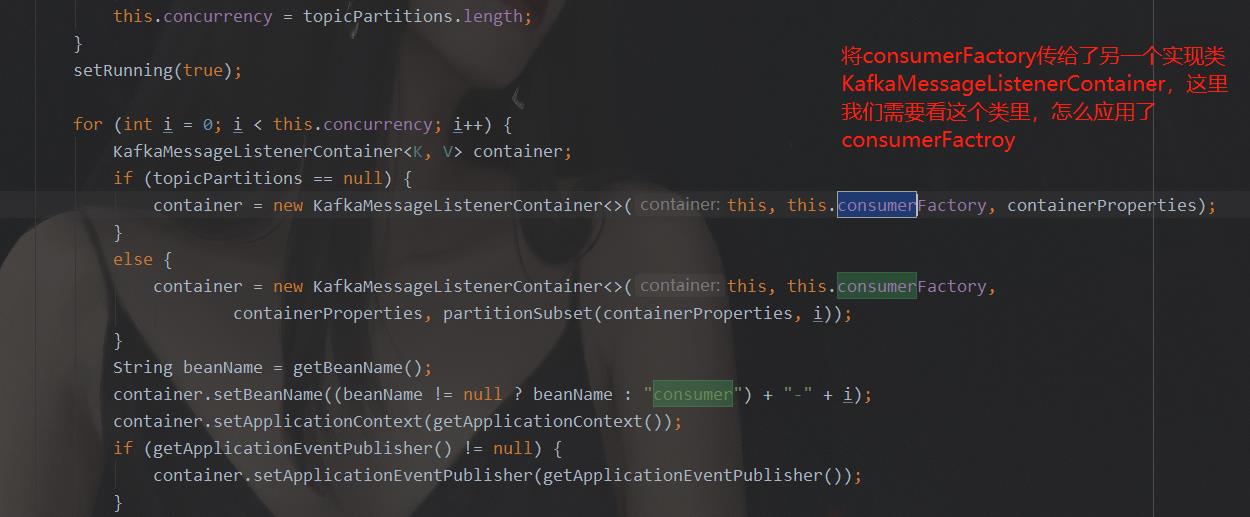
ConcurrentMessageListenerContainer类只有这两个地方应用到了cosumerFactory。所以,我们要看KafkaMessageListenerContainer类中,如何应用的consumerFactory。
打开KafkaMessageListenerContainer的源码,搜索关键字"consumer", 可以发现,里面的“consumer”字眼很多,排查起来很困难。那我们再分析,核心流程肯定是调用consumer的poll方法,获得消息,才能给监听器。所以,我们搜索"poll("关键字,搜索这个关键字,我们找到了关键的流程所在:
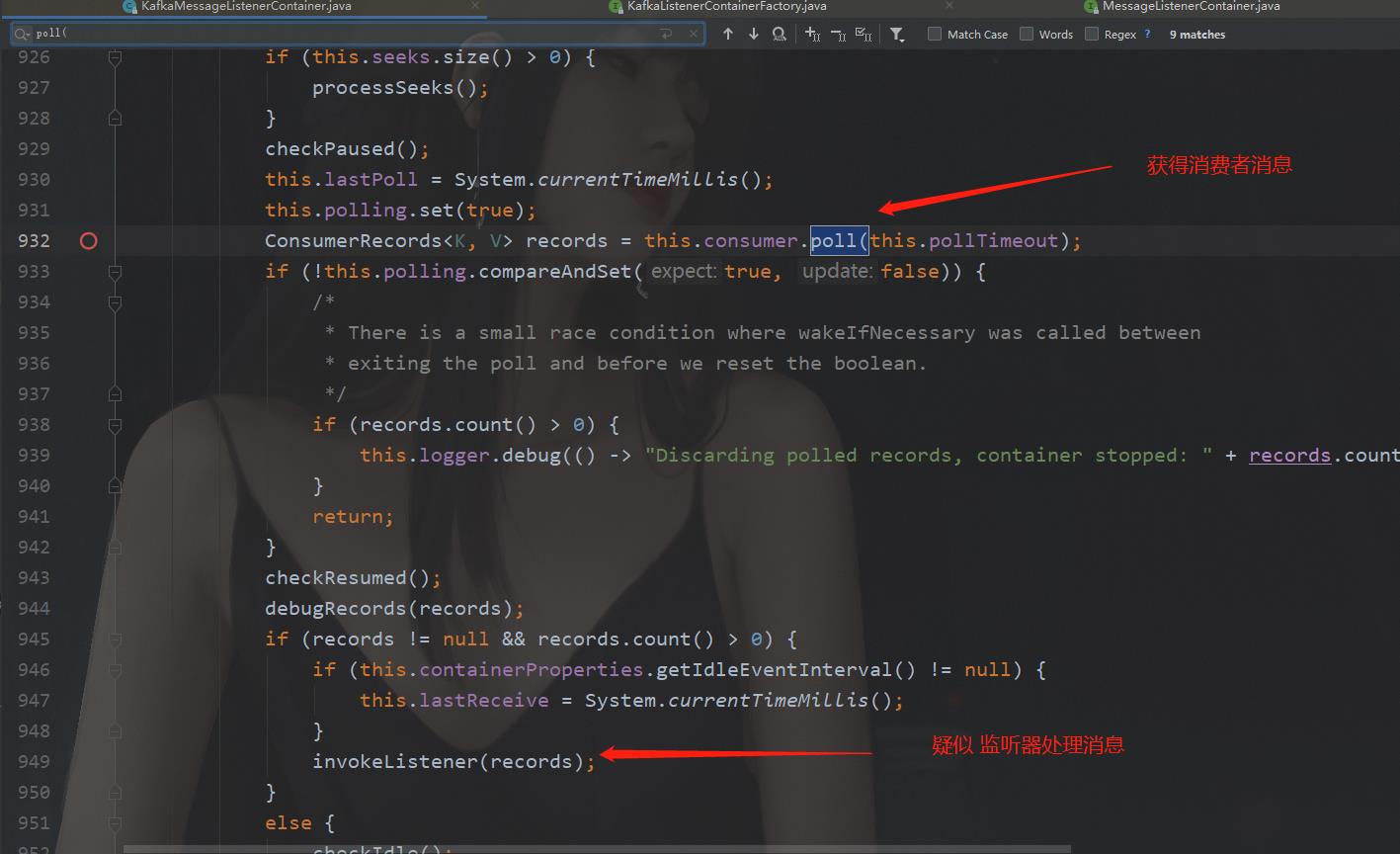
下面我们查看invokeListener方法,求证是否是我们要找的逻辑,源码如下:
private void invokeListener(final ConsumerRecords<K, V> records) {
if (this.isBatchListener) {
invokeBatchListener(records);
}
else {
invokeRecordListener(records);
}
}
这里,我们选择单条的处理invokeRecordListener方法(其实选哪个都行,一个是单条,一个是批量,本质逻辑是一样的):
private void invokeRecordListener(final ConsumerRecords<K, V> records) {
if (this.transactionTemplate != null) {
invokeRecordListenerInTx(records);
}
else {
doInvokeWithRecords(records);
}
}
然后,选doInvokeWithRecords方法,查看源码:
private void doInvokeWithRecords(final ConsumerRecords<K, V> records) {
Iterator<ConsumerRecord<K, V>> iterator = records.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
final ConsumerRecord<K, V> record = iterator.next();
this.logger.trace(() -> "Processing " + record);
doInvokeRecordListener(record, null, iterator);
if (this.nackSleep >= 0) {
handleNack(records, record);
break;
}
}
}
这里,再找到关键步骤doInvokeRecordListener方法,查看其源码,(不再一一罗列),然后,在进入下一个关键步骤invokeOnMessage,查看源码,然后,再进入关键步骤doInvokeOnMessage查看源码,这里,进入了关键步骤,我们分析一下其源码:
private void doInvokeOnMessage(final ConsumerRecord<K, V> recordArg) {
ConsumerRecord<K, V> record = recordArg;
if (this.recordInterceptor != null) {
record = this.recordInterceptor.intercept(record);
}
if (record == null) {
this.logger.debug(() -> "RecordInterceptor returned null, skipping: " + recordArg);
}
else {
switch (this.listenerType) {
case ACKNOWLEDGING_CONSUMER_AWARE:
this.listener.onMessage(record,
this.isAnyManualAck
? new ConsumerAcknowledgment(record)
: null, this.consumer);
break;
case CONSUMER_AWARE:
this.listener.onMessage(record, this.consumer);
break;
case ACKNOWLEDGING:
this.listener.onMessage(record,
this.isAnyManualAck
? new ConsumerAcknowledgment(record)
: null);
break;
case SIMPLE:
this.listener.onMessage(record);
break;
}
}
}
上面我们可以看到,不同类型的listener,调用了不同类型listener的onmessage方法。而onmessage方法,是GenericMessageListener接口定义的。我们查看GenericMessageListener的实现类,去找onmessage的实现方法,
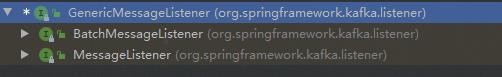
可以看到,有两个大的实现类,一个是Batch的,一个是单条的,这正好和上面的单条处理和批量处理相对应,我们看单条处理的类:
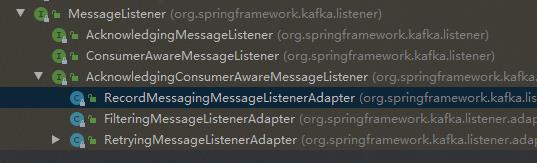
最终选定RecordMessagingMessageListenerAdapter作为分析对象。因为从字面意思上看这个类最合适。我们看其onmessage方法的注释:
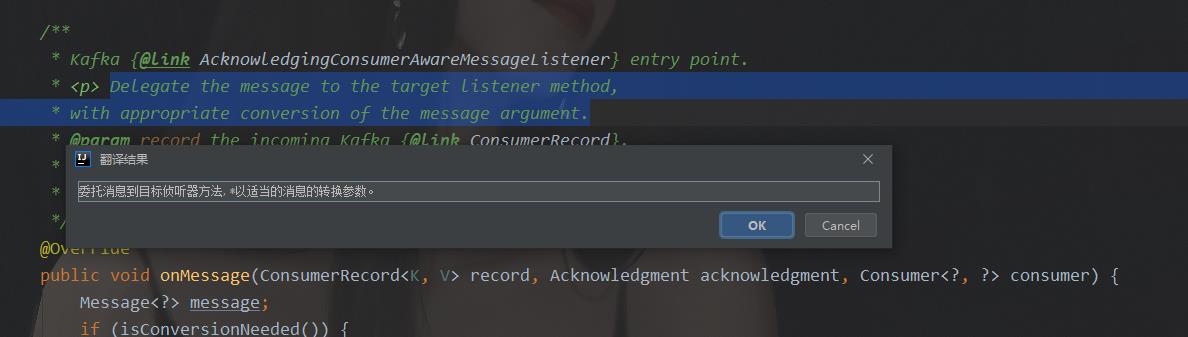
从注释来看,这里就是将消息传给监听器的入口。我们看其源码:
public void onMessage(ConsumerRecord<K, V> record, Acknowledgment acknowledgment, Consumer<?, ?> consumer) {
Message<?> message;
if (isConversionNeeded()) {
message = toMessagingMessage(record, acknowledgment, consumer);
}
else {
message = NULL_MESSAGE;
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Processing [" + message + "]");
}
try {
Object result = invokeHandler(record, acknowledgment, message, consumer);
if (result != null) {
handleResult(result, record, message);
}
}
catch (ListenerExecutionFailedException e) { // NOSONAR ex flow control
if (this.errorHandler != null) {
try {
if (message.equals(NULL_MESSAGE)) {
message = new GenericMessage<>(record);
}
Object result = this.errorHandler.handleError(message, e, consumer);
if (result != null) {
handleResult(result, record, message);
}
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new ListenerExecutionFailedException(createMessagingErrorMessage(// NOSONAR stack trace loss
"Listener error handler threw an exception for the incoming message",
message.getPayload()), ex);
}
}
else {
throw e;
}
}
}
关键步骤是
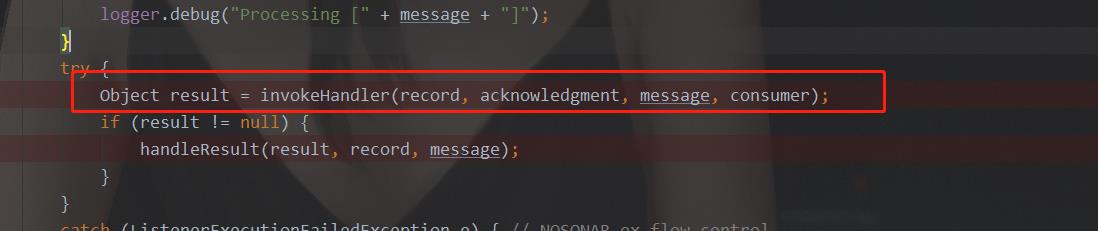
点进去看其源码:
protected final Object invokeHandler(Object data, Acknowledgment acknowledgment, Message<?> message,
Consumer<?, ?>以上是关于浅谈@KafkaListener工作流程的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章