this指针.类文件的分离,静态数据成员
Posted Respect@
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了this指针.类文件的分离,静态数据成员相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一级目录
demo1
Human::Human(int age, int salary) {
cout << "调用自定义的构造函数" << endl;
this->age = age; //this是一个特殊的指针,指向这个对象本身
this->salary = salary;
name = "无名";
addr = new char[64];
strcpy_s(addr, 64, "China");
}
说明:在类的静态成员函数【后续学习】中,不能使用this指针!
demo2
#include <iostream>
#include <Windows.h>
#include <string>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
// 定义一个“人类”
class Human {
public:
Human();
Human(int age, int salary);
......
int getAge() const;
const Human* compare1(const Human *);
private:
string name = "Unknown";
int age = 28;
int salary;
char *addr;
};
int Human::getAge() const {
return age;
}
const Human* Human::compare1(const Human * other) {
if (age > other->age) {
return this; //没有创建新的对象
}
else {
return other;
}
}
int main(void) {
Human h1(25, 30000);
Human h2(18, 8000);
cout << h1.compare1(&h2)->getAge() << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
demo3
......
class Human {
public:
Human();
Human(int age, int salary);
int getAge() const;
const Human* compare1(const Human *);
const Human& compare2(const Human&);
private:
string name = "Unknown";
int age = 28;
int salary;
char *addr;
};
......
const Human& Human::compare2(const Human& other) {
if (age > other.age) {
return *this; //访问该对象本身的引用,而不是创建一个新的对象
}
else {
return other;
}
}
int main(void) {
Human h1(25, 30000);
Human h2(18, 8000);
cout << h1.compare2(h2).getAge() << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
类文件的分离
实际开发中,类的定义保存在头文件中,比如Human.h【类的声明文件】(C++PrimerPlus)
类的成员函数的具体实现,保存在.cpp文件中,比如Human.cpp【类的方法文件】(C++PrimerPlus)
其他文件,如果需要使用这个类,就包含这个类的头文件。
静态数据成员
需求分析:
需要获取总的人数,如何实现?
只能使用一个全局变量,然后在构造函数中对这个全局变量进行修改(加1)
缺点:使用全局变量不方便,破坏程序的封装性。
解决方案:
使用类的静态成员。
定义:
Human.h
class Human {
public:
......
int getCount();
private:
string name = "Unknown";
int age = 28;
......
// 类的静态成员
static int count;
};
初始化:
Human.cpp
#include "Human.h"
// 初始化类的静态成员
int Human::count = 0;
......
Human::Human() {
cout << "调用构造函数:" << this << endl;
name = "无名氏";
age = 18;
salary = 30000;
addr = new char[ADDR_LEN];
strcpy_s(addr, ADDR_LEN, "China");
count++;
}
// 类的普通成员函数,可以直接访问静态成员(可读可写)
int Human::getCount() {
return count;
}
main.cpp
#include "Human.h"
int main(void) {
Human h1;
cout << h1.getCount() << endl;
Human h2;
cout << h1.getCount() << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
对于非const的类静态成员,只能在类的实现文件中初始化。
const类静态成员,可以在类内设置初始值,也可以在类的实现文件中设置初始值。(但是不要同时在这两个地方初始化,只能初始化1次)
Human.h
#pragma once
......
class Human {
public:
......
static int getCount();
......
};
Human.cpp
......
//静态方法的实现,不能加static
int Human::getCount() {
// 静态方法中,不能访问实例成员(普通的数据成员)
// cout << age;
// 静态方法中,不能访问this指针
// 因为this指针是属于实例对象的
// cout << this;
//静态方法中,只能访问静态数据成员
return count;
}
......
main.cpp
void test() {
cout << "总人数: ";
// ??? 没有可用的对象来访问getCount()
// 直接通过类名来访问静态方法!
// 用法:类名::静态方法
cout << Human::getCount();
}
int main(void) {
Human h1, h2;
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
说明:
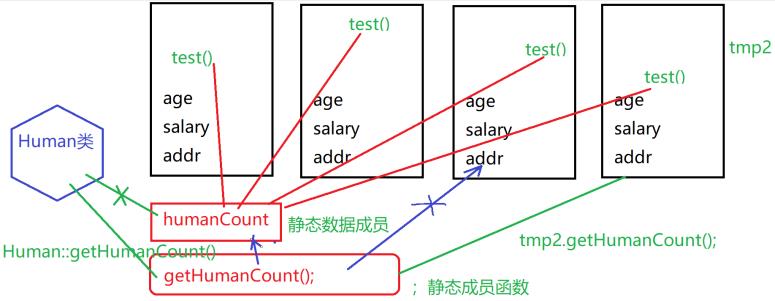
静态成员函数
对象可以直接访问静态成员函数
类可以直接访问静态成员函数(Human::getHumanCount())
在类的静态成员函数(类的静态方法)内部,不能直接访问this指针和对象的数据成员!
在类的静态成员函数(类的静态方法)内部,只能访问类的数据成员
const数据成员
需求分析:
怎样表示人的“血型”?
血型可以修改吗?
解决方案:
把血型定义为const数据类型(常量数据成员)
const数据成员的初始化方式:
1.使用类内值(C++11支持)
2.使用构造函数的初始化列表
(如果同时使用这两种方式,以初始化列表中的值为最终初始化结果)
注意: 不能在构造函数或其他成员函数内,对const成员赋值!
Demo
Human.h
#pragma once
......
class Human {
public:
......
private:
......
const string bloodType;
};
Human.cpp
// 使用初始化列表,对const数据成员初始化
Human::Human():bloodType("未知") {
......
//在成员函数内,不能对const数据成员赋值
//bloodType = "未知血型";
count++;
}
void Human::description() const {
cout << "age:" << age
<< " name:" << name
<< " salary:" << salary
<< " addr:" << addr
<< " bloodType:" << bloodType << endl; //其他成员函数可以“读”const变量
}
Main.cpp
int main(void) {
Human h1;
h1.description();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
const成员函数
需求分析:
const的Human对象,不能调用普通的成员函数。
分析:
C++认为,const(常量)对象,如果允许去调用普通的成员函数,而这个成员函数内部可能会修改这个对象的数据成员!而这讲导致const对象不再是const对象!
【类比】:专一男就是const对象,撩妹方法,就是普通的成员函数,如果允许专一男调去撩妹,那么专一男,也就不专一了!
解决方案:
如果一个成员函数内部,不会修改任何数据成员,就把它定义为const成员函数。
const成员函数内,不能修改任何数据成员!
C++的成员函数设置建议:
如果一个对象的成员函数,不会修改任何数据成员,那么就强烈:
把这个成员函数,定义为const成员函数!
以上是关于this指针.类文件的分离,静态数据成员的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章