python 文本文件数据处理
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了python 文本文件数据处理相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
请问:怎么把a.txt中相同的set或者setenv合并起来(相同值忽略),若path1中含有mnt的换成$mntpath且生成一行独立的行,结果输出到b.txt
a.txt:
set value1 /usr
set value1 /sys
set value1 /sys
set value2 /asd
set value2 /xyz
set value2 /xyz
setenv path1 /usr/lib:/usr/abc
setenv path1 /usr/asd
setenv path2 /usr
setenv path2 $path2:/abc
setenv path2 $path2:/aaa
setenv path1 $path1:/mnt/abc:/mnt/xyz
setenv path1 $path1:/mnt/ccc:/mnt/ddd
b.txt:
set value1 "/usr:/sys"
set value2 "/asd:/xyz"
setenv path1 "/usr/lib:/usr/abc:/usr/asd"
setenv path2 "/usr:/abc:/aaa"
setenv path1 "$path1:/$mntpath/abc:/$mntpath/xyz:/$mntpath/ccc:/$mntpath/ddd"
由于不知道怎么以code形式或以附件形式发布,所以只能这么贴了。
分隔日志文件存为小文件
#coding:utf-8
#file: FileSplit.py
import os,os.path,time
def FileSplit(sourceFile, targetFolder):
sFile = open(sourceFile, 'r')
number = 100000 #每个小文件中保存100000条数据
dataLine = sFile.readline()
tempData = [] #缓存列表
fileNum = 1
if not os.path.isdir(targetFolder): #如果目标目录不存在,则创建
os.mkdir(targetFolder)
while dataLine: #有数据
for row in range(number):
tempData.append(dataLine) #将一行数据添加到列表中
dataLine = sFile.readline()
if not dataLine :
break
tFilename = os.path.join(targetFolder,os.path.split(sourceFile)[1] + str(fileNum) + ".txt")
tFile = open(tFilename, 'a+') #创建小文件
tFile.writelines(tempData) #将列表保存到文件中
tFile.close()
tempData = [] #清空缓存列表
print(tFilename + " 创建于: " + str(time.ctime()))
fileNum += 1 #文件编号
sFile.close()
if __name__ == "__main__" :
FileSplit("access.log","access")
分类汇总小文件:
#coding:utf-8
#file: Map.py
import os,os.path,re
def Map(sourceFile, targetFolder):
sFile = open(sourceFile, 'r')
dataLine = sFile.readline()
tempData = #缓存列表
if not os.path.isdir(targetFolder): #如果目标目录不存在,则创建
os.mkdir(targetFolder)
while dataLine: #有数据
p_re = re.compile(r'(GET|POST)\\s(.*?)\\sHTTP/1.[01]',re.IGNORECASE) #用正则表达式解析数据
match = p_re.findall(dataLine)
if match:
visitUrl = match[0][1]
if visitUrl in tempData:
tempData[visitUrl] += 1
else:
tempData[visitUrl] = 1
dataLine = sFile.readline() #读入下一行数据
sFile.close()
tList = []
for key,value in sorted(tempData.items(),key = lambda k:k[1],reverse = True):
tList.append(key + " " + str(value) + '\\n')
tFilename = os.path.join(targetFolder,os.path.split(sourceFile)[1] + "_map.txt")
tFile = open(tFilename, 'a+') #创建小文件
tFile.writelines(tList) #将列表保存到文件中
tFile.close()
if __name__ == "__main__" :
Map("access\\\\access.log1.txt","access")
Map("access\\\\access.log2.txt","access")
Map("access\\\\access.log3.txt","access")
3. 再次将多个文件分类汇总为一个文件。
#coding:utf-8
#file: Reduce.py
import os,os.path,re
def Reduce(sourceFolder, targetFile):
tempData = #缓存列表
p_re = re.compile(r'(.*?)(\\d1,$)',re.IGNORECASE) #用正则表达式解析数据
for root,dirs,files in os.walk(sourceFolder):
for fil in files:
if fil.endswith('_map.txt'): #是reduce文件
sFile = open(os.path.abspath(os.path.join(root,fil)), 'r')
dataLine = sFile.readline()
while dataLine: #有数据
subdata = p_re.findall(dataLine) #用空格分割数据
#print(subdata[0][0]," ",subdata[0][1])
if subdata[0][0] in tempData:
tempData[subdata[0][0]] += int(subdata[0][1])
else:
tempData[subdata[0][0]] = int(subdata[0][1])
dataLine = sFile.readline() #读入下一行数据
sFile.close()
tList = []
for key,value in sorted(tempData.items(),key = lambda k:k[1],reverse = True):
tList.append(key + " " + str(value) + '\\n')
tFilename = os.path.join(sourceFolder,targetFile + "_reduce.txt")
tFile = open(tFilename, 'a+') #创建小文件
tFile.writelines(tList) #将列表保存到文件中
tFile.close()
if __name__ == "__main__" :
Reduce("access","access")
参考技术Apython处理文本文件内容数据,下面是具体的案例,代码如下:
#读取一个文本文件之后得到里面出现最多的关键字from time import time
from operator import itemgetter
def test():
# 取 10 个,有需要可以修改, 及定义读取的文件 test.txt
iList = 10
strFileName = 'test.txt'
count =
for word in open(strFileName).read().split():
if count.has_key(word):
count[word] = count[word] + 1
else:
count[word] = 1
print sorted(count.iteritems( ), key=itemgetter(1), reverse=True)[0:iList]
python处理文本文件数据中的正则表达式用法,字符串替换方法:
#1、替换所有匹配的子串#用newstring替换subject中所有与正则表达式regex匹配的子串
result = re.sub(regex, newstring, subject)
#2、替换所有匹配的子串(使用正则表达式对象)
reobj = re.compile(regex)
result = reobj.sub(newstring, subject) 参考技术B #!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
def zhidao_560604345(infile, outfile):
reader = open(infile, 'r')
set_dict =
setenv_dict =
while True:
line = reader.readline()
if len(line) == 0:
break
a, b, c = line.strip().split(maxsplit=2)
if a == 'set':
if not b in set_dict:
set_dict[b] = set()
set_dict[b].add(c.strip())
elif a == 'setenv':
if not b in setenv_dict:
setenv_dict[b] = set()
setenv_dict[b].update(c.strip().split(':'))
reader.close()
buff = []
for k, v in set_dict.items():
buff.append('set %s "%s"' % (k, ':'.join(list(v))))
for k, v in setenv_dict.items():
tmp = []
for item in list(v):
if item == '$' + k:
pass
elif item.startswith('/mnt/'):
tmp.append('mntpath/' + item[5:])
else:
tmp.append(item)
tmp.sort()
buff.append('setenv %s "%s"' % (k, ':'.join(tmp)))
writer = open(outfile, 'w')
writer.write('\\n'.join(buff))
writer.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
zhidao_560604345('zhidao_560604345.input', 'zhidao_560604345.output')
运行结果:
set value2 "/asd:/xyz"set value1 "/usr:/sys"
setenv path2 "/aaa:/abc:/usr"
setenv path1 "/usr/abc:/usr/asd:/usr/lib:mntpath/abc:mntpath/ccc:mntpath/ddd:mntpath/xyz"本回答被提问者采纳
python读取文本文件数据
本文要点刚要:
(一)读文本文件格式的数据函数:read_csv,read_table
1.读不同分隔符的文本文件,用参数sep
2.读无字段名(表头)的文本文件 ,用参数names
3.为文本文件制定索引,用index_col
4.跳行读取文本文件,用skiprows
5.数据太大时需要逐块读取文本数据用chunksize进行分块。
(二)将数据写成文本文件格式函数:to_csv
范例如下:
(一)读取文本文件格式的数据集
1.read_csv和read_table的区别:
#read_csv默认读取用逗号分隔符的文件,不需要用sep来指定分隔符
import pandas as pd
pd.read_csv(\'C:\\\\Users\\\\xiaoxiaodexiao\\\\pythonlianxi\\\\test0424\\\\data.csv\')

#read_csv如果读的是用非逗号分隔符的文件,必须要用sep指定分割符,不然读出来的是原文件的样子,数据没被分割开
import pandas as pd
pd.read_csv(\'C:\\\\Users\\\\xiaoxiaodexiao\\\\pythonlianxi\\\\test0424\\\\data.txt\')
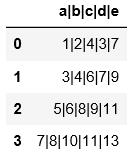
#与上面的例子可以对比一下区别
import pandas as pd
pd.read_csv(\'C:\\\\Users\\\\xiaoxiaodexiao\\\\pythonlianxi\\\\test0424\\\\data.txt\',sep=\'|\')
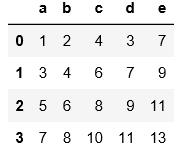
#read_table读取文件时必须要用sep来指定分隔符,否则读出来的数据是原始文件,没有分割开。
import pandas as pd
pd.read_table(\'C:\\\\Users\\\\xiaoxiaodexiao\\\\pythonlianxi\\\\test0424\\\\data.csv\')
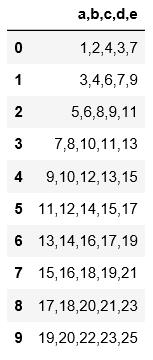
#read_table读取数据必须指定分隔符
import pandas as pd
pd.read_table(\'C:\\\\Users\\\\xiaoxiaodexiao\\\\pythonlianxi\\\\test0424\\\\data.txt\',sep=\'|\')
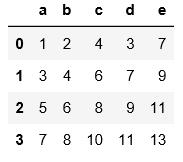
2.读取文本文件时不用header和names指定表头时,默认第一行为表头
#用header=None表示数据集没有表头,会默认用阿拉伯数字填充表头和索引
pd.read_table(\'C:\\\\Users\\\\xiaoxiaodexiao\\\\pythonlianxi\\\\test0424\\\\data.txt\',sep=\'|\',header=None)

#用names可以自定义表头
pd.read_table(\'C:\\\\Users\\\\xiaoxiaodexiao\\\\pythonlianxi\\\\test0424\\\\data.txt\',sep=\'|\',
names=[\'x1\',\'x2\',\'x3\',\'x4\',\'x5\'])

3.默认用阿拉伯数字指定索引;用index_col指定某一列作为索引
names=[\'x1\',\'x2\',\'x3\',\'x4\',\'x0\']
pd.read_table(\'C:\\\\Users\\\\xiaoxiaodexiao\\\\pythonlianxi\\\\test0424\\\\data.txt\',sep=\'|\',
names=names,index_col=\'x0\')

4.以下示例是用skiprows将hello对应的行跳过后读取其他行数据,不管首行是否作为表头,都是将表头作为第0行开始数
可以对比一下三个例子的区别进行理解
pd.read_csv(\'C:\\\\Users\\\\xiaoxiaodexiao\\\\pythonlianxi\\\\test0424\\\\data1.txt\')
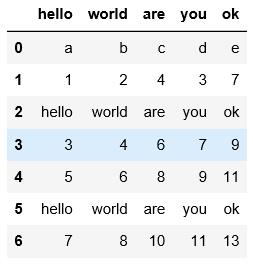
names=[\'x1\',\'x2\',\'x3\',\'x4\',\'x0\']
pd.read_csv(\'C:\\\\Users\\\\xiaoxiaodexiao\\\\pythonlianxi\\\\test0424\\\\data1.txt\',names=names,
skiprows=[0,3,6])
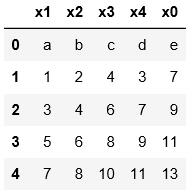
pd.read_csv(\'C:\\\\Users\\\\xiaoxiaodexiao\\\\pythonlianxi\\\\test0424\\\\data1.txt\',
skiprows=[0,3,6])

pd.read_csv(\'C:\\\\Users\\\\xiaoxiaodexiao\\\\pythonlianxi\\\\test0424\\\\data1.txt\',header=None,
skiprows=[0,3,6])
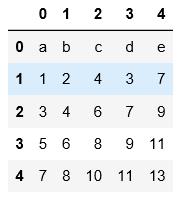
5.分块读取,data1.txt中总共8行数据,按照每块3行来分,会读3次,第一次3行,第二次3行,第三次1行数据进行读取。
注意这里在分块的时候跟跳行读取不同的是,表头没作为第一行进行分块读取,可通过一下两个例子对比进行理解。
chunker = pd.read_csv(\'C:\\\\Users\\\\xiaoxiaodexiao\\\\pythonlianxi\\\\test0424\\\\data1.txt\',chunksize=3)
for m in chunker:
print(len(m))
print m

chunker = pd.read_csv(\'C:\\\\Users\\\\xiaoxiaodexiao\\\\pythonlianxi\\\\test0424\\\\data1.txt\',header=None,
chunksize=3)
for m in chunker:
print(len(m))
print m

(二)将数据写入文本格式用to_csv
以data.txt为例,注意写出文件时,将索引也写入了
data=pd.read_table(\'C:\\\\Users\\\\xiaoxiaodexiao\\\\pythonlianxi\\\\test0424\\\\data.txt\',sep=\'|\')
print data

#可以用index=False禁止索引的写入。
data=pd.read_table(\'C:\\\\Users\\\\xiaoxiaodexiao\\\\pythonlianxi\\\\test0424\\\\data.txt\',sep=\'|\')
data.to_csv(\'C:\\\\Users\\\\xiaoxiaodexiao\\\\pythonlianxi\\\\test0424\\\\outdata.txt\',sep=\'!\',index=False)

#可以用columns指定写入的列
data=pd.read_table(\'C:\\\\Users\\\\xiaoxiaodexiao\\\\pythonlianxi\\\\test0424\\\\data.txt\',sep=\'|\')
data.to_csv(\'C:\\\\Users\\\\xiaoxiaodexiao\\\\pythonlianxi\\\\test0424\\\\outdata2.txt\',sep=\',\',index=False,
columns=[\'a\',\'c\',\'d\'])

以上是关于python 文本文件数据处理的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章