learning to see in the dark: 弱光场景下基于相机底层信号的图像处理
Posted MrCharles
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了learning to see in the dark: 弱光场景下基于相机底层信号的图像处理相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Chen, C., Chen, Q., Xu, J., & Koltun, V. (2018). Learning to see in the dark. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (pp. 3291-3300).
针对以往的黑暗条件下图像处理的一些挑战,特别是短曝光的图像没有对应的ground truth的问题,该文提出了一个数据集,有一些列的短曝光的图像,同时给一个长曝光的图像作为GT。
然后作者利用CNN,直接在传感器信号上做处理,也就是输入传感器原始的信号到CNN,来进行图像处理,得到清晰的,降噪的图像。
we introduce a dataset of raw short-exposure low-light images, with corresponding long-exposure reference images.
Using the presented dataset, we develop a pipeline for processing low-light images, based on end-to-end training of a fully convolutional network.
The network operates directly on raw sensor data and replaces much of the traditional image processing pipeline, which tends to perform poorly on such data.
需要了解一点名词解释吧:
signal-to-noise ratio (SNR):
PSNR 的公式很容易搜到。峰值信噪比经常用作图像压缩等领域中信号重建质量的测量方法,它常简单地通过均方差(MSE)进行定义。两个m×n单色图像I和K,如果一个为另外一个的噪声近似,那么它们的的均方差定义为:
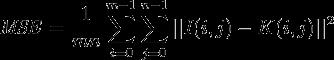
峰值信噪比定义为:

SNR
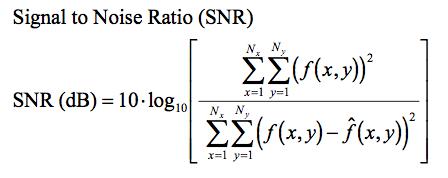
有一种方法可以近似估计图像信噪比,即信号与噪声的方差之比。首先计算图像所有象素的局部方差,将局部方差的最大值认为是信号方差,最小值是噪声方差,求出它们的比值,再转成dB数,最后用经验公式修正,具体参数请参看“反卷积与信号复原(邹谋炎)”。s/n叫做信噪比。由于在实际使用中S与N的比值太大,故常取其分贝数(db)。分贝与信噪比的关系为 : db=10lg(s/n)
以下是英文的notes
Related works:
Image denoising
Image denoising: Many approaches: total variation, wavelet-domain processing, sparse coding, nuclear norm minimization, and 3D transform-domain filtering (BM3D)
But they based on specific image priors such as smoothness, sparsity, low rank,
or self-similarity.
deep networks: stacked sparse denoising auto-encoders, MLP, CNN,
Unfortunately, most existing methods have been evaluated on synthetic data, such as images with added Gaussian or salt&pepper noise.
Joint denoising and demosaicing using NN.
But these methods have been evaluated on synthetic Bayer patterns and synthetic noise, rather than real images
multiple-image denoising has also been considered, bcz more information
But these pipelines can be elaborate, involving reference image selection (‘lucky imaging’) and dense correspondence estimation across images.
Low-light image enhancement
- histogram equalization
- gamma correction
- more global analysis and processing (wavelet transform,Retinex model)
- illumination map estimation
But they do not explicitly model image noise and typically apply off-the-shelf denoising as a postprocess
datasets
there is no public dataset with raw low-light images and corresponding ground truth
See-in-the-Dark Dataset
The number of distinct long-exposure reference images in SID is 424.
the Sony camera has a full-frame Bayer sensor
the Fuji camera has an APS-C X-Trans sensor
The resolution is 4240×2832 for Sony and 6000×4000 for the Fuji images.
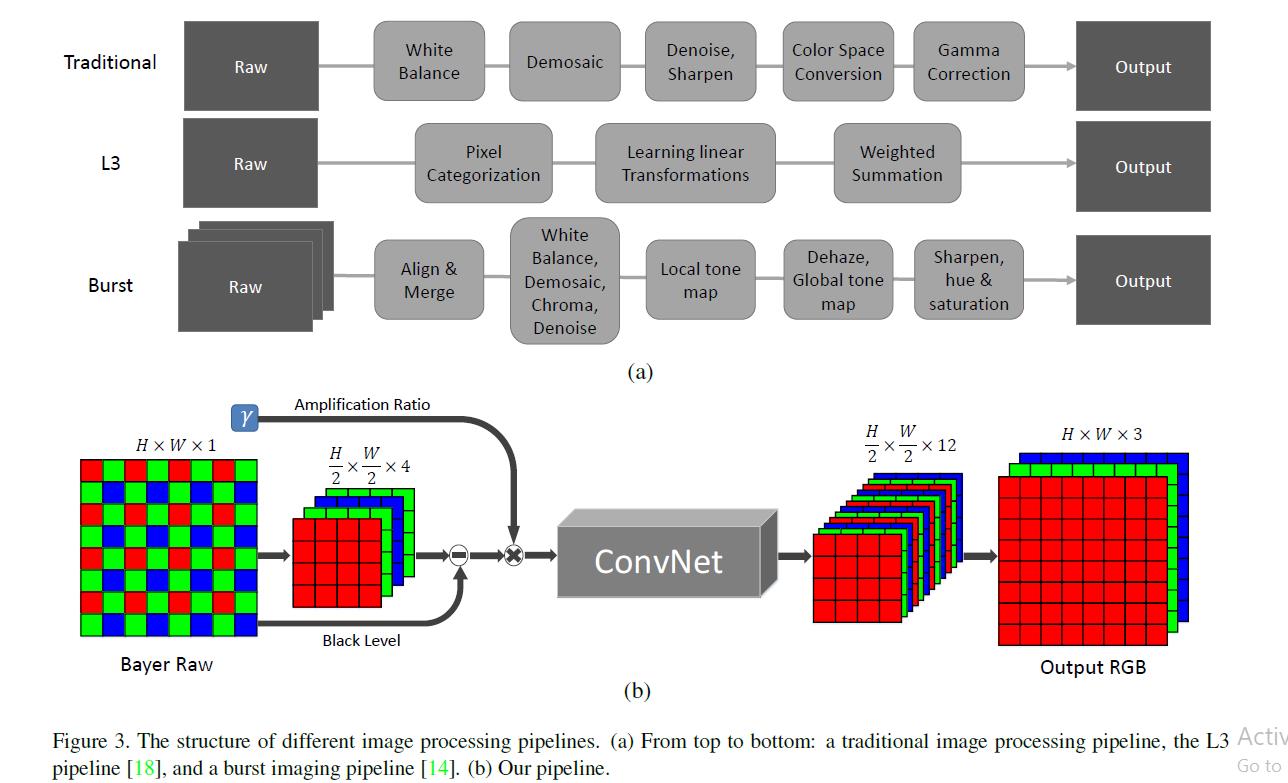
Methods
Bayer arrays H*W*1
pack the input into four channels `H/2W/24
X-Trans arrays: 6×6 blocks
pack it into 9 channels instead of 36 channels by exchanging adjacent elements
subtract the black level and scale the data (X100,X300…)
fed into a FCNN. The output is a 12-channel image with half the spatial resolution
For CNN:
- a multi-scale context aggregation network (CAN) recently used for fast image processing
- and a U-net
why this two ya?
- we did not find these beneficial in our setting, possibly because our input and output are represented in different color spaces
- memory consumption: we have chosen architectures that can process a full-resolution image (e.g., at 4240×2832 or 6000×4000 resolution) in GPU memory.
Experiments
Qualitative
Compared with traditional pipeline:
- traditional one not effectively handle the noise and color bias
- denoise post-hoc A small noise level setting may leave perceptually significant noise in the image, while a large level may over-smooth.
- burst denoising: taking the per-pixel median for a sequence of 8 images.
Qualitative results on smartphone images.
We expect that best results will be obtained when a dedicated network is trained for a specific camera sensor
But not true la. We have applied a model trained on the Sony subset of SID to images captured by an iPhone 6s smartphone, which also has a Bayer filter array and 14-bit raw data. Shows good.
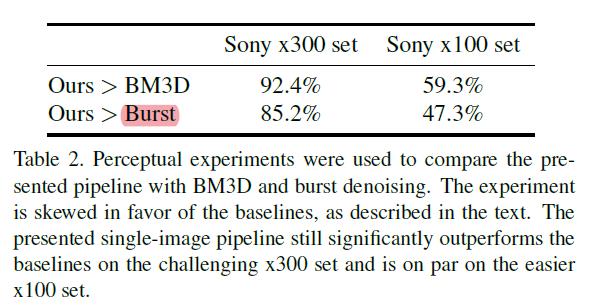
作者提出的框架,在x300上表现就好,从人眼去看的话。
quantitative experimets
Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR) and Structural SIMilarity (SSIM)
Stretched references can not
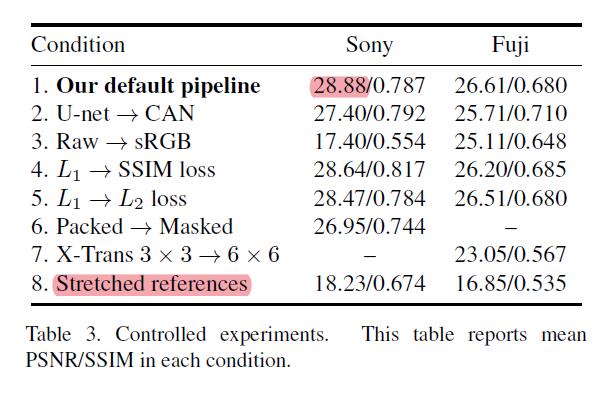
作者给出一系列分析:
默认的是最好的。骨架改成CAN,并不会提升明显。不从raw,从sRGB,效果会变差很多。这是很显然的。因为你是从传感器最初的信号来的嘛。
更改损失函数没有多大差别。然后Stretched references在这个文章里面始终没有做到。
讨论
那么其实还有很多可以做:
- 作者提出的数据集可以用来尝试不同的方法
- 作者只是使用了简单的CNN,但是他的处理的时间效率依然很慢
- 生成的图片依然有一些artfect,瑕疵之类的。其实他的网络还是要更加强大才行。
- 我们可以根据他的数据集,使用更加强大的网络去做,使用以下transfer learning,说不定可以更好的结果
- 作者也提出HDR tone mapping 没有尝试,相机HDR是趋势,黑暗场景下的HDR是非常具有研究意义的。
Charles@tcl research 2021-05-18
以上是关于learning to see in the dark: 弱光场景下基于相机底层信号的图像处理的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章