Spring boot JPA
Posted xiaoduup
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Spring boot JPA相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
Spring boot JPA
上一节 Spring boot mybatis
源码
JPA简介
Spring Data JPA为Java Persistence API(JPA)提供了存储库支持。它简化了需要访问JPA数据源的应用程序的开发。
市面上最常见的是hibernate, spring JPA 大部分也沿用了hibernate 的一些实现。使用上更方便,开箱即用。
springboot 整合JPA
- 添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.47</version>
</dependency>
- 配置文件
配置好datasouce 和 jpa的一些配置
spring:
application:
name: jap-demo
# 配置数据源
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mytest?useSSL=false&charsetEncoding=utf8
username: root
password: 123456
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jpa:
hibernate:
# 是否自动创建表结构, 等同于 hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto
ddl-auto: create-drop
# naming:
# physical-strategy: org.springframework.boot.orm.jpa.hibernate.SpringPhysicalNamingStrategy
# 打印sql
show-sql: true
properties:
# 格式化 sql
hibernate:
format_sql: true
logging:
level:
## 打印sql参数,记得日志级别一定设置为 trace
org.hibernate.type.descriptor.sql.BasicBinder: trace
jpa 的一些配置,有很大一部分使用hibernate。
- 代码示例
-
创建实体类
-
沿用Java Persistence API 进行实体类创建和声明, 创建 productEntity 实体;
@Table 对应了数据库表
@entity 标注为数据库表对应的实体
@Id 表明为 id自动
@Column(length = 32) 表字段的映射和设置
@Table(name = "t_product")
@Entity(name = "product")
public class ProductEntity {
@Id
@Column(length = 32)
private String pId;
@Column(length = 255, nullable = false)
private String pName;
@Column(nullable = false)
private Long price;
@Column
private Date scDate;
开启repository
@EnableJpaRepositories(basePackages = {"com.xiaodu.jpa.repository"})
定义repository接口
jpa 默认提供的 repository 的继承树
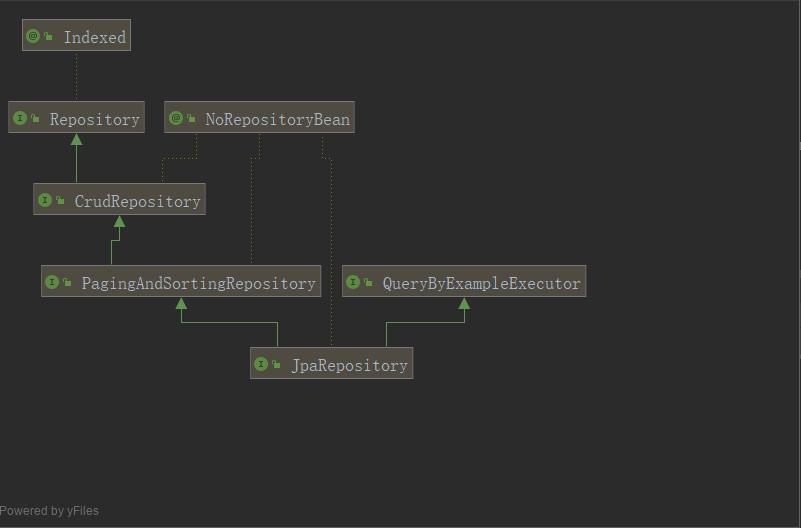
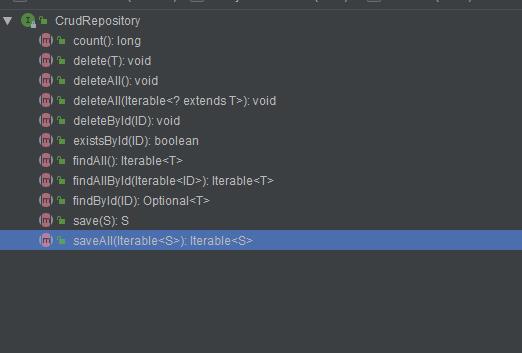
CrudRepository: 提供了增删改查功能的方法
PagingAndSortingRepository: 提供了分页和排序功能
QueryByExampleExecutor: 提供了使用 Example 构建查询条件
JpaRepository: 集成了上面所有的 功能; 所以我们一般继承JapRepository 即可
使用 CurdRepository
@Repository // 可加可不加,我们已经使用EnableJpaRepositories(basePackages = {"com.xiaodu.jpa.repository"})扫描
public interface ProductRepository extends CrudRepository<ProductEntity, String> {}
crudRepository 内置方法使用
private void testCrudRepository() {
ProductEntity p = new ProductEntity();
p.setPrice(199900L);
p.setpName("xiaomi 11");
p.setScDate(new Date());
String id = UUID.randomUUID().toString().replaceAll("-", "");
p.setpId(id);
// 添加
productRepository.save(p);
// 查询
Optional<ProductEntity> byId = productRepository.findById(id);
// count
long count = productRepository.count();
// 修改
p.setPrice(299900L);
productRepository.save(p);
// 删除
// productRepository.deleteById(id);
}
curd 提供的所有方法
使用 PagingAndSortingRepository
PagingAndSortingRepository 提供的方法 增加参数 pageable 和 sort
@Repository
public interface ProductRepository extends PagingAndSortingRepository<ProductEntity, String> {}
使用示例
private void testPagingAndSortingRepository() {
// 排序
productRepository.findAll(Sort.by(Sort.Order.desc("scDate")));
// 分页加排序
productRepository.findAll(PageRequest.of(1, 5, Sort.by(Sort.Order.desc("scDate"))));
}
使用 JpaRepository 和 QueryByExampleExecutor
JpaRepository 提供了PagingAndSortingRepository 和crudRepository 的所有方法 ,所以和上面的示例一样;
这里主要说明下 QueryByExampleExecutor 的使用
(JpaRepository 继承了 QueryByExampleExecutor )
public interface ProductRepository extends
/*CrudRepository*/
/*PagingAndSortingRepository*/
JpaRepository<ProductEntity, String> {}
QueryByExampleExecutor示例代码
使用ExampleMatcher 构建 条件Example;
如下示例:通过 Example 进行构建简单的查询条件 和使用ExampleMatcher模糊查询
private void testJpaRepository() {
//test QueryByExampleExecutor; 使用Example 构建条件
//Example 只能对 string 类型进行匹配查询,并且是有限的; 使用上了解即可
ProductEntity p = new ProductEntity();
p.setPrice(199900L);
p.setpName("xiaoMi");
// where price = ? and p_name = ?
List<ProductEntity> productEntities = productRepository.findAll(Example.of(p));
// 使用ExampleMatcher 构建like; where price = 199900 or p_name like ? escape ?
ExampleMatcher exampleMatcher = ExampleMatcher.matchingAny()
.withMatcher("pName", ExampleMatcher.GenericPropertyMatchers.contains());
List<ProductEntity> productList = productRepository.findAll(Example.of(p, exampleMatcher));
}
自定义查询方法
JPA 可以通过解析方法名来生产sql语句,并不需要任何实现只需要方法命名按照jpa规范和关键字命名即可。
使用示例
例如在 repository 接口中声明方法
// 批量查询,p_name like {#pName} and price >= #{price}
List<ProductEntity> findAllByPNameLikeAndPriceGreaterThanEqual(String pName, Long price);
若想分页或排序只需要在参数中添加Pageable分页 或者 Sort 排序
List findAllByPNameLikeAndPriceGreaterThanEqual(String pName, Long price, Pageable pageable);
注意:参数Sort和Pageable不能为null。如果不想应用任何排序或分页,请使用Sort.unsorted()和Pageable.unpaged()
限制查询结果
返回值可以使用Streamable 代替集合;也可使用java 8 的充当返回值。 甚至可以使用异步查询,使用 Future, completableFure,ListenableFuture 充当返回值进行异步查询;
具体请参考jpa 官方文档。
@Async
Future<User> findByFirstname(String firstname);
查询方法关键字和修饰符
| 关键字 | 方法样例 | 生成的jpsql样例 |
|---|---|---|
| Distinct | findDistinctByLastnameAndFirstname | select distinct … where x.lastname = ?1 and x.firstname = ?2 |
| And | findByLastnameAndFirstname | … where x.lastname = ?1 and x.firstname = ?2 |
| Or | findByLastnameOrFirstname | … where x.lastname = ?1 or x.firstname = ?2 |
| Is, Equals | findByFirstname,findByFirstnameIs,findByFirstnameEquals | … where x.firstname = ?1 |
| Between | findByStartDateBetween | … where x.startDate between ?1 and ?2 |
| LessThan | findByAgeLessThan | … where x.age < ?1 |
| LessThanEqual | findByAgeLessThanEqual | … where x.age <= ?1 |
| GreaterThan | findByAgeGreaterThan | … where x.age > ?1 |
| GreaterThanEqual | findByAgeGreaterThanEqual | … where x.age >= ?1 |
| After | findByStartDateAfter | … where x.startDate > ?1 |
| Before | findByStartDateBefore | … where x.startDate < ?1 |
| IsNull, Null | findByAge(Is)Null | … where x.age is null |
| IsNotNull, NotNull | findByAge(Is)NotNull | … where x.age not null |
| Like | findByFirstnameLike | … where x.firstname like ?1 |
| NotLike | findByFirstnameNotLike | … where x.firstname not like ?1 |
| StartingWith | findByFirstnameStartingWith | … where x.firstname like ?1(参数附后%) |
| EndingWith | findByFirstnameEndingWith | … where x.firstname like ?1(参数加前缀%) |
| Containing | findByFirstnameContaining | … where x.firstname like ?1(参数绑定在中%) |
| OrderBy | findByAgeOrderByLastnameDesc | … where x.age = ?1 order by x.lastname desc |
| Not | findByLastnameNot | … where x.lastname <> ?1 |
| In | findByAgeIn(Collection ages) | … where x.age in ?1 |
| NotIn | findByAgeNotIn(Collection ages) | … where x.age not in ?1 |
| True | findByActiveTrue() | … where x.active = true |
| False | findByActiveFalse() | … where x.active = false |
| IgnoreCase | findByFirstnameIgnoreCase | … where UPPER(x.firstname) = UPPER(?1) |
使用 Specification 进行复杂条件构建
Specification 提供了 比Example 更丰富的复杂查询条件的构建. 如果是复杂sql 还是不太直观。
首先我们要继承 JpaSpecificationExecutor
@Repository
public interface ProductRepository extends
/*CrudRepository*/
/*PagingAndSortingRepository*/
JpaRepository<ProductEntity, String>,
JpaSpecificationExecutor<ProductEntity> {}
使用示例
ProductEntity p = new ProductEntity();
p.setpName("xiaomi");
p.setPrice(1000L);
List<ProductEntity> all = productRepository.findAll(Specification.where((root, query, criteriaBuilder) -> {
Predicate pName = criteriaBuilder.like(root.get("pName"), "%" + p.getpName() + "%");
return criteriaBuilder.and(pName, criteriaBuilder.or(criteriaBuilder.lessThan(root.get("price"), 29900L),
criteriaBuilder.greaterThan(root.get("price"), p.getPrice())));
}));
/*
* select
* productent0_.p_id as p_id1_0_,
* productent0_.p_name as p_name2_0_,
* productent0_.price as price3_0_,
* productent0_.sc_date as sc_date4_0_
* from
* t_product productent0_
* where
* (
* productent0_.p_name like '%xiaomi%'
* )
* and (
* productent0_.price<29900
* or productent0_.price>1000
* )
*/
需要分页的话 需要添加参数 pageable ,排序加sort
// 分页查询
productRepository.findAll((root, query, cb) -> {
Path<String> pName = root.get("pName");
Path<Long> price = root.get("price");
return cb.and(cb.or(cb.greaterThan(price, 199900L), cb.lessThan(price, 399900L)), cb.like(pName, "%xiaomi%"));
}, PageRequest.of(1, 5));
/*
* select
* productent0_.p_id as p_id1_0_,
* productent0_.p_name as p_name2_0_,
* productent0_.price as price3_0_,
* productent0_.sc_date as sc_date4_0_
* from
* t_product productent0_
* where
* (
* productent0_.price>199900
* or productent0_.price<399900
* )
* and (
* productent0_.p_name like ?
* ) limit ?, ?
*/
使用@Query
有时候需要更直观的显示出sql, 我们也可以使用@query注解来编写sql语句
hql 和参数占位
// hql 语句 表名即实体名若用了@Entity 指定则是@Entity指定的名称
@Query("select p from product p")
List<ProductEntity> selectAll();
// hql 带参数; 使用 ?index 进行占位符
@Query("select p from product p where p.price = ?1")
List<ProductEntity> selectByPrice(Long price);
// hql 使用 :field 参数占位符
@Query("select p from product p where p.price = :price")
List<ProductEntity> selectByPrice2(@Param("price") Long price);
sql 和参数占位
默认都是使用的 hql 语句,若使用 原生的 需要指定nativeQuery = true
// 使用原生sqlsql
@Query(value = "select * from t_product", nativeQuery = true)
List<ProductEntity> selectAlls();
// 使用 ?index 接收参数
@Query(value = "select * from t_product where p_name = ?1", nativeQuery = true)
List<ProductEntity> selectByName(String pName);
// 使用 :field 接收
@Query(value = "select * from t_product where p_name = :pName", nativeQuery = true)
List<ProductEntity> selectByName2(@Param("pName") String pName);
分页
分页和排序一样,传递 pageable, 或者 sort
// 分页查询, 需要传递 pageable
@Query("select p from product p where p.price = :price")
Page<ProductEntity> pageByPrice(@Param("price") Long price, Pageable pageable);
对象参数
若参数是一个对象,则使用 :#{#obj.field} 占位,可使用 @param 指定
// 接收对象 使用 :#{#field} 接收
@Query(value = "select * from t_product where p_name = :#{#product.pName}", nativeQuery = true)
List<ProductEntity> selectByName3(@Param("product") ProductEntity productEntity);
执行updpate ,insert, delte 语句,需要使用@Modifying 修饰,并且需要添加事务@Transactional
// 执行update insert delete 语句,需要加上@Modifying 和 @Transactional 语句
@Transactional(timeout = 10)
@Query("update product set pName = :#{#productEntity.pName} where pId = :#{#productEntity.pId}")
@Modifying
int updateProductNameById(@Param("productEntity") ProductEntity productEntity);
多表关联查询
jpa 多表关联查询, 第一种方式可以使用一个 实体类包含所查询的参数,然后使用 @query 进行查询 ;这个比较简单;
实体封装了所有查询的数据, @query 返回锁查询的字段信息
我们使用注解方式
-
@OneToOne
- 一对一关系映射 @OneToMany
- 一对多关系映射 @ManyToOne
- 多对一关系映射 @ManyToMany
- 多对多关系映射
我们使用 order 订单 和 product 产品 进行关系映射示例; 一个订单包含多个商品 oneToMany,多个商品可以在一个订单中ManyToOne 。
orderEntity 中我们声明关系; oneToMany 声明这是一对多的关系,casade 级联的策略,fetch 声明获取是懒加载还是立即查询加载;
@JoinColumn 声明和 product 之前的外键关联, 项目启动后生成的product 会有外键order_no 和 order中的order_no 外键关联
@OneToMany(cascade = CascadeType.ALL, fetch = FetchType.EAGER)
// 外键关联,会在 product 表中生产order_no字段;
@JoinColumn(name = "orderNo", referencedColumnName = "orderNo")
private Set<ProductEntity> productEntities;
我们还可以采取中间表的方式建立关系
@JoinTable; name 指定了中间表,会自动创建中间表; joinColumns 指定了 order 和中间表的关联键, inverseJoinColumns
指定了 中间表和 product 之前的关联键
@OneToMany(cascade = CascadeType.ALL, fetch = FetchType.EAGER)
// 会自动创建中间表 order_product,通过 joinColumns 中关联了自己的orderNo
// 和中间表的orderNo(referencedColumnName引用自己的那个字段)
// 通过inverseJoinColumns 关联了 中间表和关联的Product 表的字段关系
@JoinTable(name = "order_product", joinColumns = {@JoinColumn(name = "orderNo", referencedColumnName = "orderNo")},
inverseJoinColumns = {@JoinColumn(name = "pId", referencedColumnName = "pId")})
private Set<ProductEntity> productEntities;
同样若product也需要查询order 信息;则在product 中指定关系
@ManyToOne
@JoinTable(name = "order_product", joinColumns = {@JoinColumn(name = "pId", referencedColumnName = "pId")},
inverseJoinColumns = {@JoinColumn(name = "orderNo", referencedColumnName = "orderNo")})
private OrderEntity orderEntity;
使用 Querydsl 进行复杂查询
JPA提供的条件查询豆太过于复杂也不太好看。我们可以使用Querydsl 进行复杂查询;
querydsl官网
使用示例
- 添加依赖
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.querydsl/querydsl-jpa -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.querydsl</groupId>
<artifactId>querydsl-jpa</artifactId>
<version>4.1.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.querydsl</groupId>
<artifactId>querydsl-apt</artifactId>
<version>4.1.4</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
- 添加插件
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>com.mysema.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>apt-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.1.3</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>process</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<outputDirectory>target/generated-sources/java</outputDirectory>
<processor>com.querydsl.apt.jpa.JPAAnnotationProcessor</processor>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
添加完插件后 maven compiler 下 ;编译下项目,会生成实体对应的 Q实体;
- 代码示例
private void testQuerydsl() {
JPAQueryFactory jpaQueryFactory = new JPAQueryFactory(entityManager);
// querydsl 生成的QProductEntity
QProductEntity productEntity = QProductEntity.productEntity;
ProductEntity xiaomi = jpaQueryFactory.selectFrom(productEntity)
.where(productEntity.pName.eq("xiaomi")
.spring boot系列spring boot 配置spring data jpa (查询方法)
Spring Boot (十五): Spring Boot + Jpa + Thymeleaf 增删改查示例
初入spring boot(五 )Spring Data JPA