Linux练习_进程间信号练习
Posted Leslie X徐
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Linux练习_进程间信号练习相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
进程练习
例题1
- 要求:创建一对父子进程,子进程通过ctrl+c结束,父进程回收完子进程资源后,再次按ctrl+c结束父进程
- 分析:父进程先忽略信号,接收到子进程结束的信号后再打开接受信号
/*
* signal.c
*要求:子进程通过ctrl+c结束,父进程回收完子进程资源后,再次按ctrl+c结束父进程
*
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <wait.h>
void sig_handler(int signum)
{
if(signum==SIGINT){
printf("回收进程\\n");
exit(0);
}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
pid_t pid;
pid = fork();
if(pid<0){perror("fork error");exit(1);}
else if(pid==0){ //child process
printf("pid: %d,ppid: %d\\n", getpid(),getppid());
while(1)signal(SIGINT, sig_handler); //子进程等待ctrl+c信号
}
else {
signal(SIGINT,SIG_IGN); //屏蔽ctrl+c信号
wait(0); //等待子线程结束
while(1)signal(SIGINT, sig_handler); //父进程等待ctrl+c信号
}
}
例题2
描述:
- 创建2个.c文件,每个.c文件中各有一对父子进程,这四个进程分别称为A,a,B,b进程
要求: - a进程通过ctrl+c结束后,向b进程发送信号,表示a结束;
- b进程接收到a的信号后立即结束;
- B进程接收到b进程结束信号后,回收b资源,并且向A发送信号;
- A进程接收到B进程的信号后,回收a进程的资源,然后A结束。
所有过程要求有完善的printf提示
关于AaBb4个进程,若有数据交互情况,使用文件IO实现。
- 使用C标准文件IO编写
- A进程程序:
/*
* A进程.c
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int Apid=0;
int bpid=0;
void sig_handler(int signum)
{
if(signum==SIGINT){
kill(bpid,SIGINT);
printf("a end\\n");
exit(0);
}
if(signum==SIGQUIT){
wait(0);
printf("all end\\n");
exit(0);
}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int res = fork();
if(res>0){
//A
Apid = getpid();
signal(SIGINT,SIG_IGN);
signal(SIGQUIT,sig_handler);
FILE* fp = fopen("./A.txt","w");
fwrite(&Apid,4,1,fp);
fclose(fp);
}
else {
//a
signal(SIGINT,sig_handler);
FILE* fp=0;
while(fp==0){//手动写同步逻辑
fp = fopen("./b.txt","r");
}
fread(&bpid,4,1,fp);
fclose(fp);
}
while(1);
return 0;
}
- B进程程序:
/*
* B进程.c
*
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int bpid=0;
int Apid=0;
void sig_handler(int signum)
{
if(signum==SIGINT){
printf("b end\\n");
exit(0);
}
if(signum==SIGCHLD){
FILE* fp = fopen("./A.txt","r");
fread(&Apid,4,1,fp);
fclose(fp);
kill(Apid,SIGQUIT);
printf("B end\\n");
wait(0);
exit(0);
}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int res = fork();
if(res>0){
//B
signal(SIGCHLD,sig_handler);
}
else{
//b
signal(SIGINT,sig_handler);
bpid = getpid();
FILE* fp = fopen("./b.txt","w");
fwrite(&bpid,4,1,fp);
fclose(fp);
}
while(1);
return 0;
}
- 使用FIFO命名管道
-
信号框图:
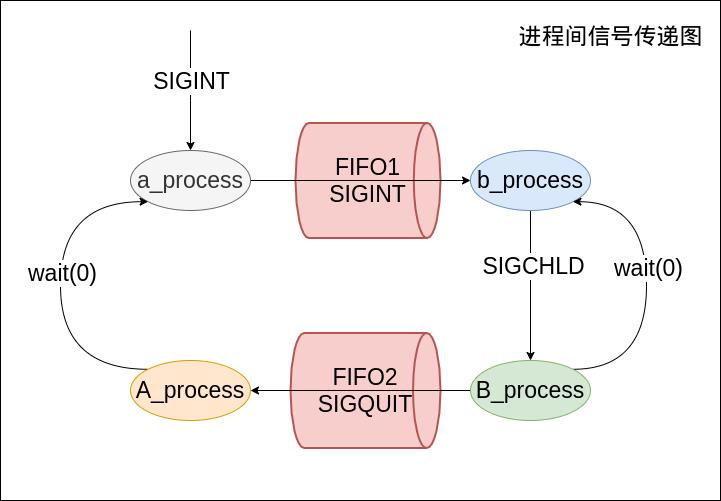
-
A进程程序:
/*
* A进程.c
*
*
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int Apid=0;
int bpid=0;
int fifofdrd,fifofdwr;
void sig_handler(int signum)
{
if(signum==SIGINT){
kill(bpid,SIGINT);
printf("a end\\n");
exit(0);
}
if(signum==SIGQUIT){
wait(0);
remove("my_fifob");
remove("my_fifoA");
printf("all end\\n");
exit(0);
}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
mkfifo("my_fifob",0666);
mkfifo("my_fifoA",0666);
fifofdrd = open("my_fifob",O_RDONLY);
fifofdwr = open("my_fifoA",O_WRONLY);
int res = fork();
if(res>0){
//A
Apid = getpid();
signal(SIGINT,SIG_IGN);
signal(SIGQUIT,sig_handler);
write(fifofdwr,&Apid,sizeof(int));
close(fifofdwr);
}
else {
//a
signal(SIGINT,sig_handler);
read(fifofdrd,&bpid,sizeof(int));
close(fifofdrd);
}
while(1);
return 0;
}
- B进程程序
/*
* B进程.c
*
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int bpid=0;
int Apid=0;
int fifofdrd,fifofdwr;
void sig_handler(int signum)
{
if(signum==SIGINT){
printf("b end\\n");
exit(0);
}
if(signum==SIGCHLD){
read(fifofdrd,&Apid,sizeof(int));
close(fifofdrd);
kill(Apid,SIGQUIT);
printf("B end\\n");
wait(0);
exit(0);
}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
mkfifo("my_fifob",0666);
mkfifo("my_fifoA",0666);
fifofdwr = open("my_fifob",O_WRONLY);
fifofdrd = open("my_fifoA",O_RDONLY);
int res = fork();
if(res>0){
//B
signal(SIGCHLD,sig_handler);
}
else{
//b
signal(SIGINT,sig_handler);
bpid = getpid();
write(fifofdwr,&bpid,sizeof(int));
close(fifofdwr);
}
while(1);
return 0;
}
- alarm
要求:使用alarm,每2秒打印输出
框图: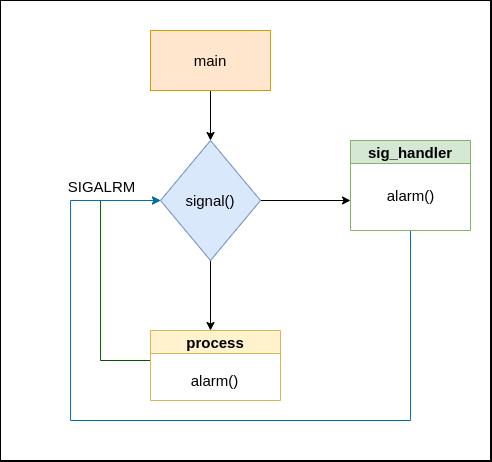
代码:
/*
* alarm信号.c
*
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void handler(int signum)
{
if(signum==SIGALRM){
printf("2s end\\n");
alarm(2);
}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
signal(SIGALRM,handler);
alarm(2);
while(1);
return 0;
}
- pipe
- 要求:
- 创建一个子进程,在其中获取当前工作路径并打印。
- 运用获取的路径,在路径下创建文件1.txt
- 使用信号SIGALRM间隔1秒向文件1.txt写入"Hello"
- 按下ctrl+c结束子进程。
- 父进程打印"Child process end"结束。
/*
* pipe.c
* 创建一个子进程,在其中获取当前工作路径并打印。
* 运用获取的路径,在路径下创建文件1.txt
* 使用信号SIGALRM间隔1秒向文件1.txt写入"Hello"
* 按下ctrl+c结束子进程。
* 父进程打印"Child process end"结束。
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
FILE* fp;
void sig_handler(int signum)
{
if(signum==SIGALRM)
{
printf("Hello\\n");
fprintf(fp,"Hello\\n");
alarm(1);
}
if(signum==SIGINT)
{
fclose(fp);
exit(0);
}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
pid_t cpid = fork();
if(cpid<0){perror("child process error");exit(1);}
if(cpid==0){
printf("Child process start\\n");
fp=popen("pwd","r");
char path[127];
fgets(path,sizeof(path),fp);
printf("%s",path);
path[strlen(path)-1]='\\0';
pclose(fp);
strcat(path,"/1.txt");
printf("%s",path);
fp=fopen(path,"w");
alarm(1);
while(1){
signal(SIGALRM,sig_handler);
signal(SIGINT,sig_handler);
}
}
if(cpid>0){
signal(SIGINT,SIG_IGN);
wait(0);
printf("Child process end\\n");
fclose(fp);
exit(0);
}
return 0;
}
输出:
pi@raspberrypi:~/haitong-learning/Linux/homework/管道练习 $ ./pipe
Child process start
/home/pi/haitong-learning/Linux/homework/管道练习
/home/pi/haitong-learning/Linux/homework/管道练习/1.txtHello
Hello
Hello
Hello
Hello
^C
Child process end
pi@raspberrypi:~/haitong-learning/Linux/homework/管道练习 $
- FIFO
- 要求:
- 实现两个程序mysignal,mycontrol
- mycontrol给mysignal发送SIGINT信号,控制mysignal在屏幕打印"Hello"字符串
- 在mysignal发送SIGQUIT(按ctl+)则两个程序都关闭。
- 分析:使用FIFO进行进程间的通信,获取对方的PID,然后使用kill传送信号
- 代码:
mysignal程序:
/*
* mysignal.c
*
*/
#include <sys/stat.h> //包含mkfifo
#include <sys/types.h> //pid_t
#include <fcntl.h> //包含O_REONLY
#include <signal.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int sigpid,ctlpid;
int fdwr,fdrd;
char* toctl = "toctl_fifo";
char* tosig = "tosig_fifo";
void sig_handler(int signum)
{
if(signum==SIGINT){
printf("Hello\\n");
}
if(signum==SIGQUIT){
kill(ctlpid,SIGQUIT);
printf("\\nmysignal process end\\n");
remove(toctl);
remove(tosig);
exit(0);
}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
printf("按ctl+\\\\退出\\n");
int sigpid = getpid();
printf("sigpid:%d\\n",sigpid);
mkfifo(toctl,0666);
fdwr = open(toctl,O_WRONLY);
write(fdwr,&sigpid,sizeof(int));
close(fdwr);
mkfifo(tosig,0666);
fdrd = open(tosig,O_RDONLY);
read(fdrd,&ctlpid,sizeof(int));
printf("ctlpid:%d\\n",ctlpid);
close(fdrd);
while(1){
signal(SIGQUIT,sig_handler);
signal(SIGINT,sig_handler);
}
return 0;
}
mycontrol程序:
/*
* mycontrol.c
*
*/
#include <sys/stat.h> //包含mkfifo
#include <sys/types.h> //pid_t
#include <fcntl.h> //包含O_REONLY
#include <signal.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int ctlpid,sigpid;
int fdrd,fdwr;
char* toctl = "toctl_fifo";
char* tosig = "tosig_fifo"