Springboot-Swagger整合
Posted guardwhy
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Springboot-Swagger整合相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
学习视频: https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1PE411i7CV?p=47
1.1 Swagger基本概念
Swagger官网:https://swagger.io/
前后端分离
- 后端:后端控制层,服务层,数据访问层。
- 前端: 前端控制层、视图层。
- 前后端通过API进行交互,前后端相对独立且松耦合。
- 前后端可以部署在不同的服务器上…
产生的问题
前后端集成联调,前端人员和后端人员无法做到"即使协商,尽早解决",最终导致问题集中爆发。
解决方案:
- 指定schema【计划的提纲】,实时更新最新的API,降低集成的风险。
Swagger
- 号称世界上最流行的API框架。
- Restful Api 文档在线自动生成器,API 文档 与API 定义同步更新。
- 直接运行,在线测试API,支持多种语言 (如:Java,php等)。
1.2 集成Swagger
1、新建一个Springboot项目。
2、添加相关的maven依赖
2.x.x 版本
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.springfox/springfox-swagger2 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.springfox/springfox-swagger-ui -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
3.x.x版本
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.0.0</version>
</dependency>
3、编写对应的controller
package cn.guardwhy.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello")
public String hello(){
return "hello Swagger!!!";
}
}
4、编写一个配置类-SwaggerConfig来配置 Swagger
package cn.guardwhy.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;
@Configuration // 配置类
@EnableSwagger2 // 开启Swagger2的自动配置
public class SwaggerConfig {
}
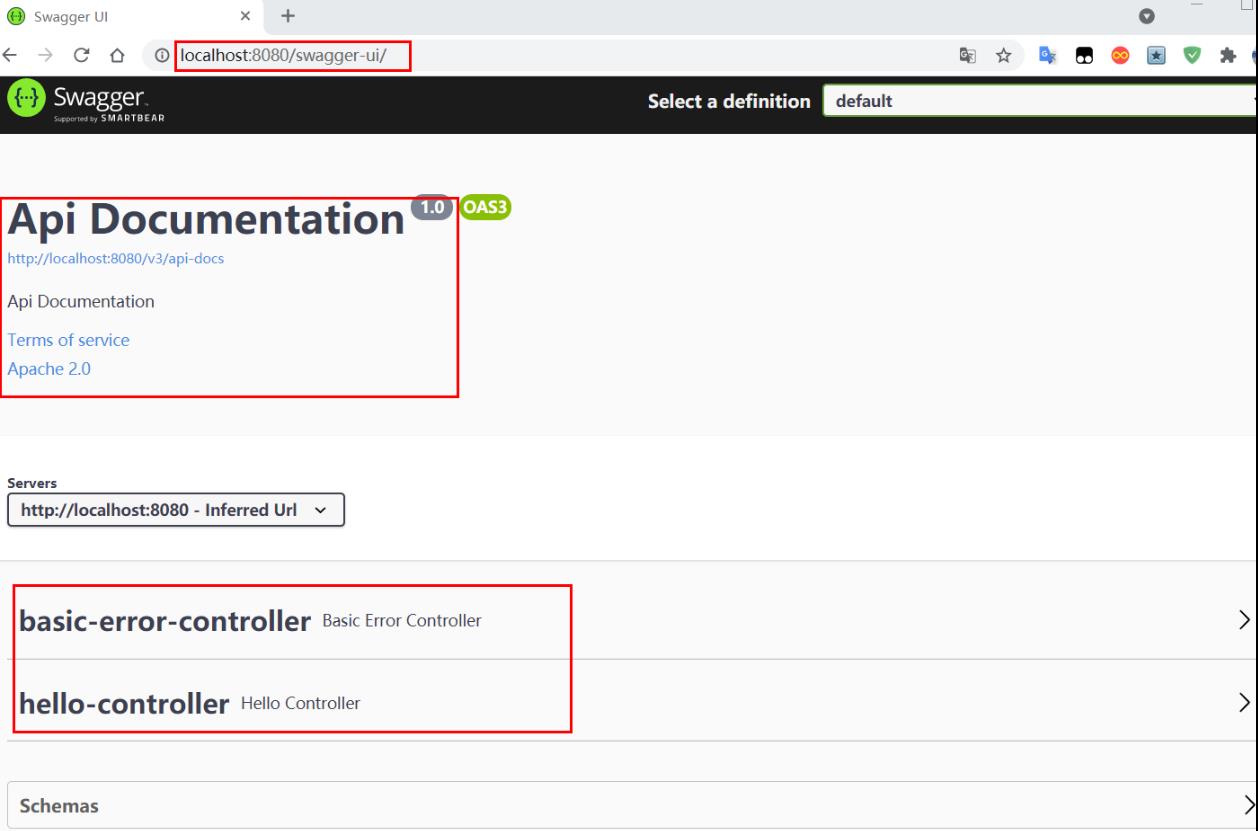
5、启动项目,访问测试。就可以看到swagger界面!!
2.x.x版本: http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html

3.x.x版本: http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui/
1.3 配置Swagger
1、Swagger实例Bean是Docket,通过配置Docket实例来配置Swaggger。
package cn.guardwhy.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType;
import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket;
import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;
@Configuration // 配置类
@EnableSwagger2 // 开启Swagger2的自动配置
public class SwaggerConfig {
// 1.配置了Swagger的Docket的bean实例
@Bean
public Docket docket(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2);
}
}
源码分析

2、可以通过apiInfo()属性配置文档信息
// 2.配置Swagger信息=apiInfo
private ApiInfo apiInfo() {
// 2.1 作者信息
Contact contact = new Contact("guardwhy", "https://home.cnblogs.com/u/Guard9/","hxy1625309592@aliyun.com");
return new ApiInfo(
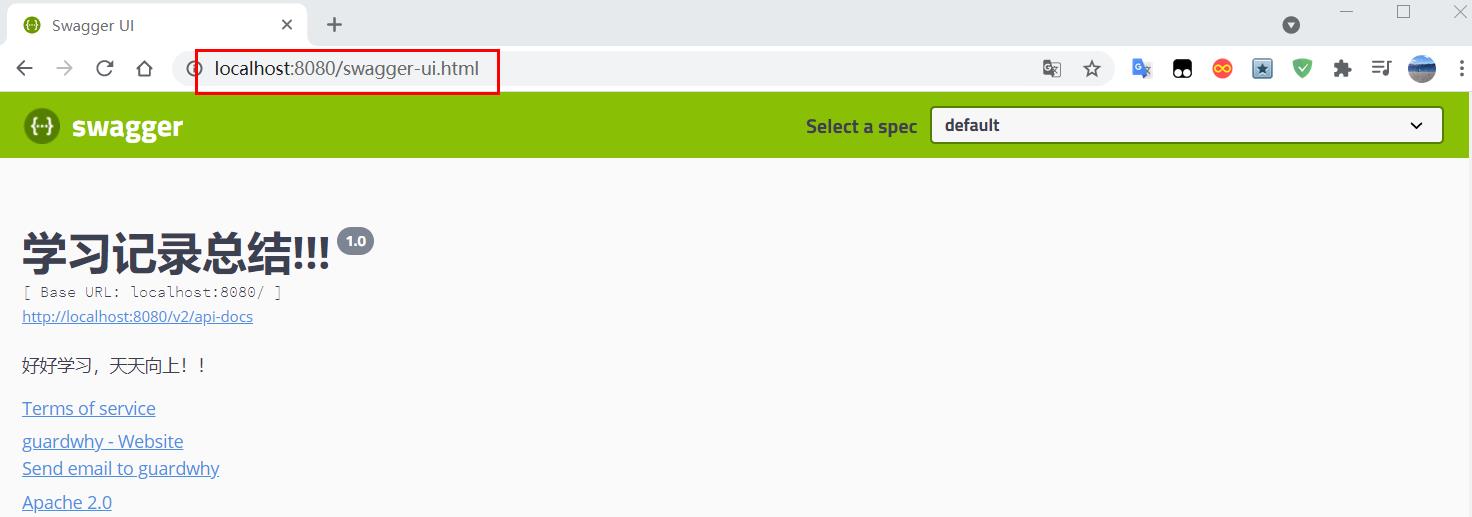
"学习记录总结!!!",
"好好学习,天天向上!!",
"1.0",
"urn:tos",
contact,
"Apache 2.0",
"http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0",
new ArrayList()
);
}
3、Docket 实例关联上 apiInfo()
package cn.guardwhy.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import springfox.documentation.service.ApiInfo;
import springfox.documentation.service.Contact;
import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType;
import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket;
import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;
import java.util.ArrayList;
@Configuration // 配置类
@EnableSwagger2 // 开启Swagger2的自动配置
public class SwaggerConfig {
// 1.配置了Swagger的Docket的bean实例
@Bean
public Docket docket(){
// 1.1 Docket实例关联上 apiInfo()
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).apiInfo(apiInfo());
}
// 2.配置Swagger信息=apiInfo
private ApiInfo apiInfo() {
// 2.1 作者信息
Contact contact = new Contact("guardwhy", "https://home.cnblogs.com/u/Guard9/","hxy1625309592@aliyun.com");
return new ApiInfo(
"学习记录总结!!!",
"好好学习,天天向上!!",
"1.0",
"urn:tos",
contact,
"Apache 2.0",
"http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0",
new ArrayList()
);
}
}
4、重启项目,访问测试!!
1.4 配置扫描接口
1、通过select()方法配置扫描接口
@Bean
public Docket docket(){
// 1.1 Docket实例关联上 apiInfo()
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.select()
// RequestHandlerSelectors,配置要扫描接口的方式
// basePackage:指定要扫描的包
// any():扫描全部
// none():不扫描
// withClassAnnotation:扫描类上的注解,参数是一个注解的反射对象
// withMethodAnnotation:扫描方法上的注解
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("cn.guardwhy.controller"))
.build();
}
2、配置接口扫描过滤
@Bean
public Docket docket(){
// 1.1 Docket实例关联上 apiInfo()
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("cn.guardwhy.controller"))
// 配置如何通过path过滤,即这里只扫描请求以/guardwhy开头的接口
.paths(PathSelectors.ant("/guardwhy/**"))
.build();
}
1.5 配置开关Swagger
1、通过enable()方法配置是否启用swagger,如果是false,swagger将不能在浏览器中访问了。
@Bean
public Docket docket(){
// 1.1 Docket实例关联上 apiInfo()
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.enable(false) // enable是否启动Swagger,如果为False,则Swagger不能再浏览器中的访问!!
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("cn.guardwhy.controller"))
// 配置如何通过path过滤,即这里只扫描请求以/guardwhy开头的接口
.paths(PathSelectors.ant("/guardwhy/**"))
.build();
}
执行结果
2、希望Swagger在生产环境中使用,在发布的时候不使用?
application.properties
spring.profiles.active=dev
application-dev.properties
server.port=8081
application-pro.properties
server.port=8082
SwaggerConfig
@Bean
public Docket docket(Environment environment){
// 1.设置要显示Swagger的环境
Profiles profiles = Profiles.of("dev","test");
// 2.通过environment.acceptsProfiles 判断是否处在自己设定的环境当中
boolean flag = environment.acceptsProfiles(profiles);
System.out.println(flag);
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.enable(flag) // enable是否启动Swagger,如果为False,则Swagger不能再浏览器中的访问!!
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("cn.guardwhy.controller"))
// 配置如何通过path过滤,即这里只扫描请求以/guardwhy开头的接口
.paths(PathSelectors.ant("/guardwhy/**"))
.build();
}
3、启动项目,访问测试 http://localhost:8081/swagger-ui.html
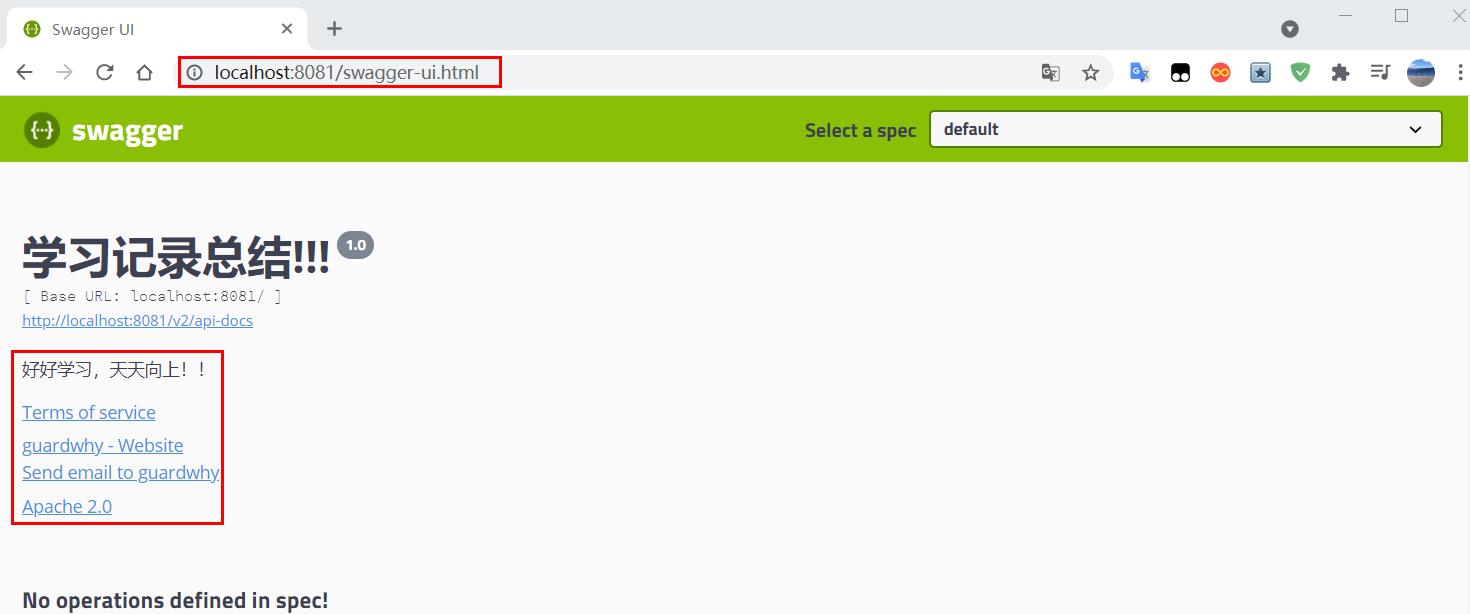
1.6 分组和实体类配置
1.6.1 配置分组
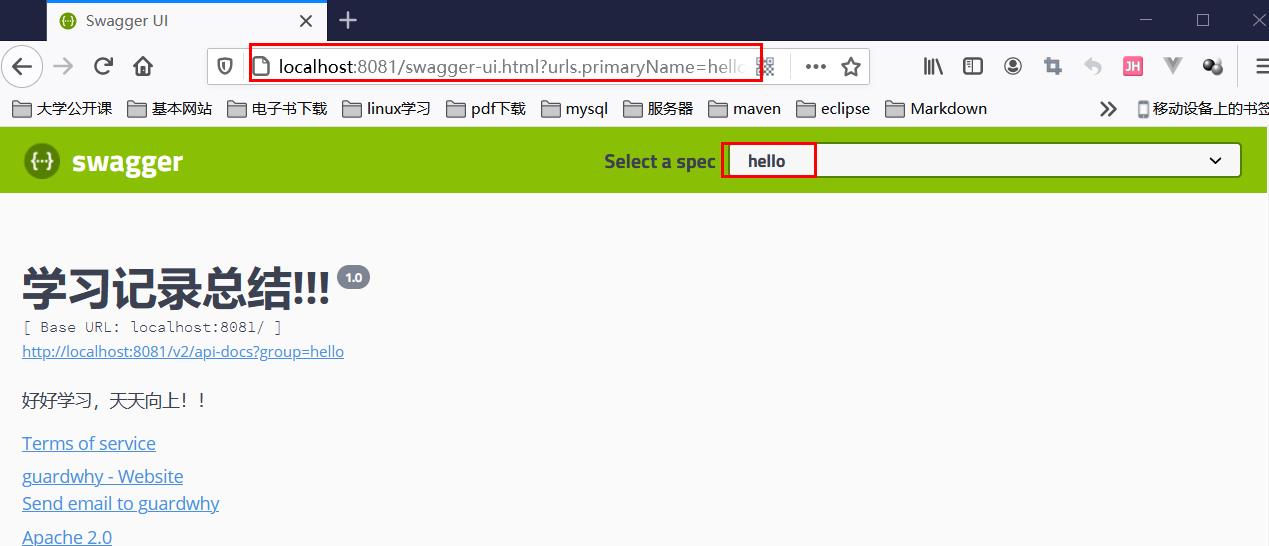
1、如果没有配置分组,默认是default。通过groupName()方法即可配置分组
@Bean
public Docket docket(Environment environment){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.groupName("hello")
.enable(flag) // enable是否启动Swagger,如果为False,则Swagger不能再浏览器中的访问!!
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("cn.guardwhy.controller"))
// 配置如何通过path过滤,即这里只扫描请求以/guardwhy开头的接口
.paths(PathSelectors.ant("/guardwhy/**"))
.build();
}
2、启动项目,查看结果!!!
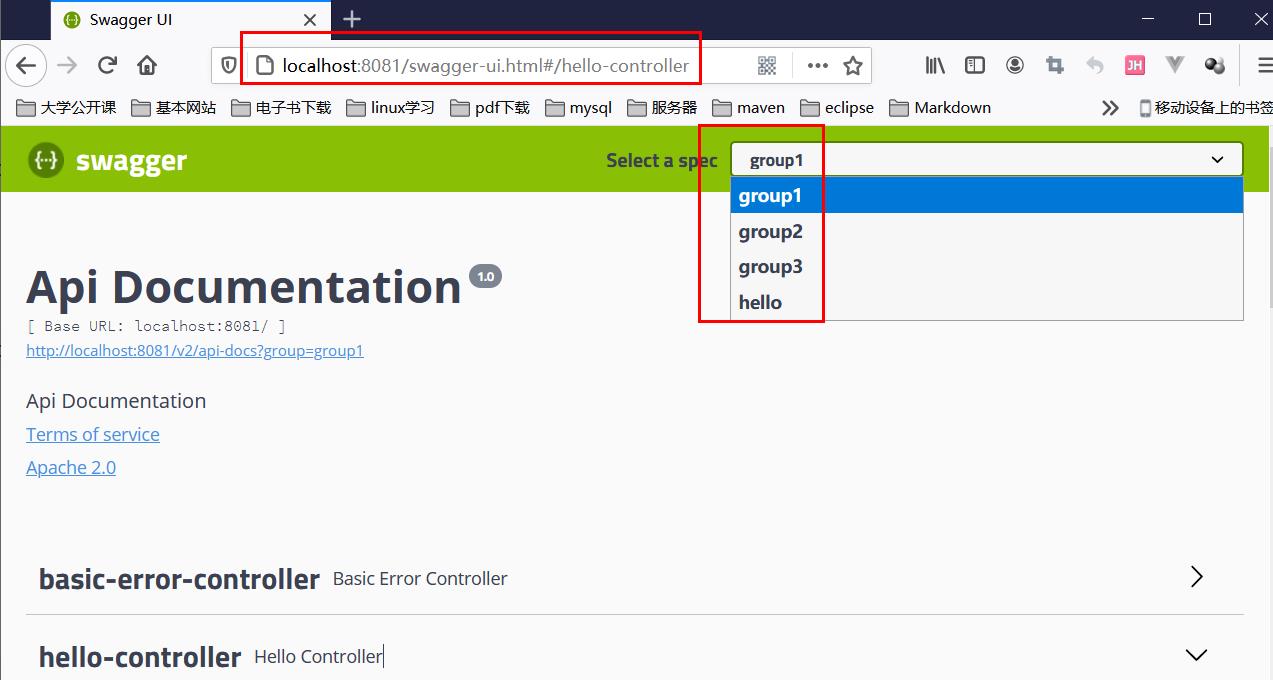
3、配置多个分组只需要配置多个docket。
// 3.配置多个分组
@Bean
public Docket docket1(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("group1");
}
@Bean
public Docket docket2(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("group2");
}
@Bean
public Docket docket3(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("group3");
}
4、重启项目,测试:http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html
1.6.2 实体配置
1、新建一个实体类User类
@ApiModel为类添加注释
@ApiModelProperty为类属性添加注释
package cn.guardwhy.pojo;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModel;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModelProperty;
@ApiModel("用户实体类")
public class User {
@ApiModelProperty("用户名")
public String username;
@ApiModelProperty("密码")
public String password;
}
2、只要这个实体在请求接口的返回值上,都能映射到实体项中
// 只要接口中,返回值存在实体类,它就会扫描到Swagger中
@PostMapping(value = "/user")
public User user(){
return new User();
}
3、重启项目,执行结果!!!

1.6.3 小结
Swagger是个优秀的工具,较于传统的Postman或Curl方式测试接口,使用swagger简直就是傻瓜式操作,不需要额外说明文档。
以上是关于Springboot-Swagger整合的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章