开发成长之路(14)-- 小项目:视频点播器服务端(放码过来)
Posted 看,未来
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了开发成长之路(14)-- 小项目:视频点播器服务端(放码过来)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
系列教程一览
开发成长之路(1)-- C语言从入门到开发(入门篇一)
开发成长之路(2)-- C语言从入门到开发(函数与定制输入输出控制函数)
开发成长之路(3)-- C语言从入门到开发(讲明白指针和引用,链表很难吗?)
开发成长之路(4)-- C语言从入门到开发(距离开发,还差这一篇)
开发成长之路(5)-- C语言从入门到开发(仿ATM机项目,我写的第一个项目)
开发成长之路(6)-- C++从入门到开发(C++入门不难)
开发成长之路(6)-- C++从入门到开发(C++知名库:STL入门·容器(一))
开发成长之路(7)-- C++从入门到开发(C++知名库:STL入门·容器(二))
开发成长之路(8)-- C++从入门到开发(C++知名库:STL入门·容器(三))
开发成长之路(9)-- C++从入门到开发(C++知名库:STL入门·空间配置器)
开发成长之路(10)-- C++从入门到开发(C++知名库:STL入门·算法)
开发成长之路(11)-- STL常用函数大集合
开发成长之路(12)-- Linux网络服务端编程(通识篇之熟悉操作环境)
开发成长之路(13)-- Linux网络服务端编程(通识篇)
“看,未来”的个人简介
朋友们大家好,我是“看,未来”,最近跟CSDN头部大佬们学了这一招,听说挺受用的,我也来试试。
本系列主要面向想要走开发路线,又不知从何学起的大学生。
我本人也是在大一的时候就去参加了培训,后来又自学了一段时间,在这期间,我觉得更重要的是跟行业内的前辈们请教,这比培训来的实在多了。
网页右侧有我的个人微信二维码,如果对学习有困惑的小伙伴可以扫我,知无不言,言无不尽,欢迎来聊。
项目需求分析
我先简单的放一张架构图吧
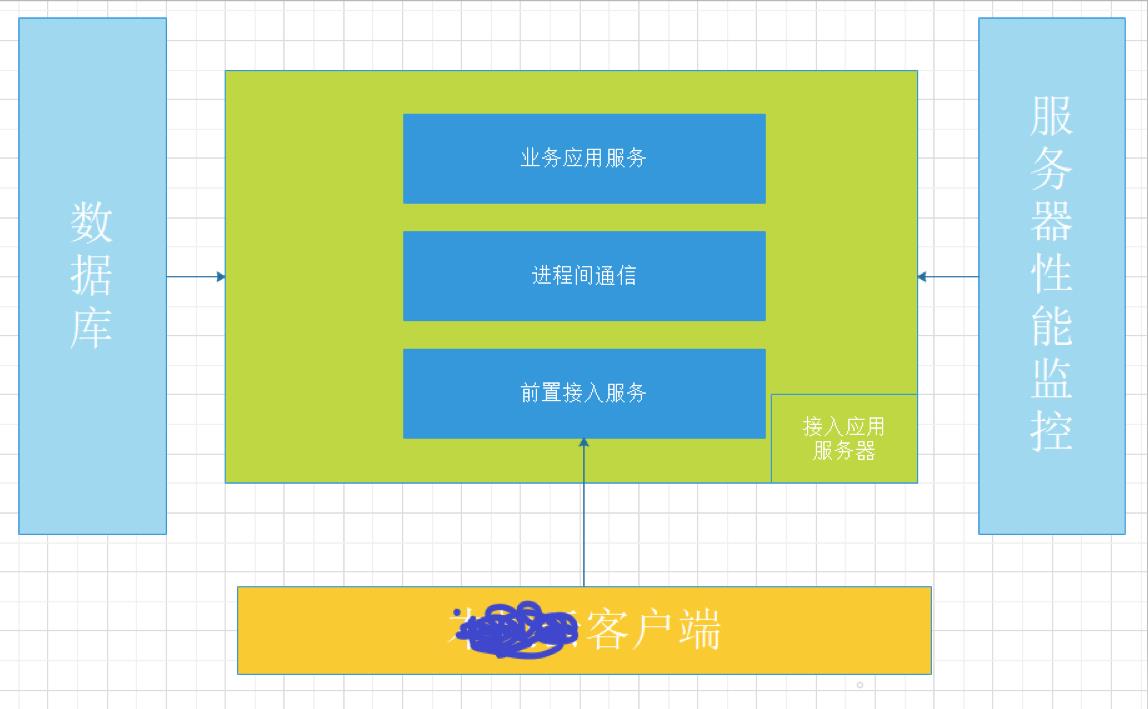
这次这个小项目分为 前置服务器、后置服务器、进程间通信、数据库通信、性能检测、日志六个模块。
前置服务器:
使用epoll+socket模式,实现大量并发连接的快速处理。并接收通讯数据包,判断是否该传入后置服务器(心跳包就地抛弃)
进程间通信:
shm共享内存
后置服务器:
线程池处理业务、解压包模块内置、数据库连接查询、数据包协议
数据库通信:
sqlite3、mysql选一个
性能检测:
单用户单业务、单用户多业务、多用户单业务、多用户多业务。
日志:
记录运行过程的日常日志、记录故障的故障日志。
业务分类:
连接、登录、注册、查询视频、查询历史记录、请求播放、退出连接
时间安排:20天周期。三天需求分析、三天demo测试、八天代码编写、四天联调、两天优化代码与文档撰写。
放码过来
很长的啊,我稍微放几个比较重要的出来。
有需要参照的小伙伴可以扫右侧我的微信找我拿,没思路也可以找我聊。
线程池.cpp
#include "e_pthread_pool.h"
E_PThread_Pool::E_PThread_Pool(unsigned int max,unsigned int min,unsigned int wait)
{
//配置基本参数
count = 0;
waitcount = 0;
mincount = min;
maxcount = max;
waitsec = wait;
Stop = false;
//上锁,创建一定数量的线程作为初始线程池
cond.lock();
for (unsigned i = 0; i < mincount; i++)
{
createThread();
}
cond.unlock();
}
E_PThread_Pool::~E_PThread_Pool()
{
destroyThread();
}
void E_PThread_Pool::addTask(Task *task)
{
if (Stop) //线程池是否停止工作
{
return;
}
//向任务队列中添加新任务
taskCond.lock();
taskList.push_back(task);
taskCond.unlock();
cond.lock();
if(waitcount)//需要注意这里的waitcount配置
{
if(count < maxcount)
{
createThread();
}
cond.signal();
}
else if(count < maxcount)
{
createThread();
}
cond.unlock();
}
void E_PThread_Pool::createThread()
{
pthread_t tid;
int ret = pthread_create(&tid, NULL, taskThread, (void *)this);
if (ret < 0)
{
perror("pthread create error");
}
else
{
count++;
}
}
//线程池创建一定数量的线程
void E_PThread_Pool::start(unsigned NumCreate)
{
cond.lock();
for (unsigned i = 0; i < NumCreate && i < maxcount-2; i++) //这里为什么是减2
{
createThread();
}
cond.unlock();
}
// 工作线程
void * E_PThread_Pool::taskThread(void *arg)
{
pthread_detach(pthread_self()); //设置自分离
E_PThread_Pool *pool=(E_PThread_Pool *)arg;
while(1)
{
pool->cond.lock();
//如果没有工作线程在等待
if (pool->taskList.empty())
{
if(pool->Stop)
{
pool->count--;
pool->cond.unlock();
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
pool->waitcount++;
bool bSignal = pool->cond.timewait(pool->waitsec); //新任务等待被唤醒
pool->waitcount--;
// 删除无用线程
if (!bSignal && pool->count > pool->mincount)
{
pool->count--;
pool->cond.unlock();
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
}
pool->cond.unlock();
//如果有工作线程在等待
if (!pool->taskList.empty())
{
//获取一个工作线程并执行
pool->taskCond.lock();
Task *t = pool->taskList.front();
pool->taskList.pop_front(); //移除工作线程
pool->taskCond.unlock();
t->run(); //任务开始
delete t;
}
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void E_PThread_Pool::destroyThread()
{
printf("destroy?\\n");
#if 0 //等待所有线程执行完毕
list_task::iterator it = taskList.begin();
for (; it! = taskList.end(); it++)
{
Task *t = *it;
delete t;
t = NULL;
}
taskList.clear();
#endif
Stop = true;
while (count > 0)
{
cond.lock();
cond.broadcast();
cond.unlock();
// 等待所有线程执行完毕
sleep(1);
}
}
shm共享内存.cpp
#include "f_shm.h"
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/sem.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
typedef struct shmhead_st
{
int shmid; // 共享内存ID
unsigned int blksize; // 块大小
unsigned int blocks; // 总块数
unsigned int rd_index; // 读索引
unsigned int wr_index; // 写索引
//必须放在共享内存内部才行
sem_t sem_mutex; // 用来互斥用的信号量
sem_t sem_full; // 用来控制共享内存是否满的信号量
sem_t sem_empty; // 用来控制共享内存是否空的信号量
}shmhead_t;
F_Shm::F_Shm(key_t key, int blksize, int blocks)
{
this->open_shm(key, blksize, blocks);
}
F_Shm::F_Shm()
{
shmhead = NULL;
payload = NULL;
open = false;
}
F_Shm::~F_Shm()
{
this->close_shm();
}
//返回头地址
bool F_Shm::creat_shm(key_t key, int blksize, int blocks)
{
int shmid = 0;
//1. 查看是否已经存在共享内存,如果有则删除旧的
shmid = shmget(key, 0, 0);
if (shmid != -1)
{
shmctl(shmid, IPC_RMID, NULL); // 删除已经存在的共享内存
}
//2. 创建共享内存
shmid = shmget(key, sizeof(shmhead_t) + blksize*blocks, 0666 | IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL);
if(shmid == -1)
{
ERR_EXIT("shmget");
}
printf("Create shmid=%d size=%u \\n", shmid, sizeof(shmhead_t) + blksize*blocks);
//3.连接共享内存
shmhead = shmat(shmid, (void*)0, 0); //连接共享内存
if(shmhead == (void*)-1)
{
ERR_EXIT("shmat");
}
memset(shmhead, 0, sizeof(shmhead_t) + blksize*blocks); //初始化
//4. 初始化共享内存信息
shmhead_t * pHead = (shmhead_t *)(shmhead);
pHead->shmid = shmid; //共享内存shmid
pHead->blksize = blksize; //共享信息写入
pHead->blocks = blocks; //写入每块大小
pHead->rd_index = 0; //一开始位置都是第一块
pHead->wr_index = 0; //
sem_init(&pHead->sem_mutex, 1, 1); // 第一个1表示可以跨进程共享,第二个1表示初始值
sem_init(&pHead->sem_empty, 1, 0); // 第一个1表示可以跨进程共享,第二个0表示初始值
sem_init(&pHead->sem_full, 1, blocks);// 第一个1表示可以跨进程共享,第二个blocks表示初始值
//5. 填充控制共享内存的信息
payload = (char *)(pHead + 1); //实际负载起始位置
open = true;
return true;
}
void F_Shm::dsy_shm()
{
shmhead_t *pHead = (shmhead_t *)shmhead;
int shmid = pHead->shmid;
//删除信号量
sem_destroy (&pHead->sem_full);
sem_destroy (&pHead->sem_empty);
sem_destroy (&pHead->sem_mutex);
shmdt(shmhead); //共享内存脱离
//销毁共享内存
if(shmctl(shmid, IPC_RMID, 0) == -1) //删除共享内存
{
printf("Delete shmid=%d \\n", shmid);
ERR_EXIT("shmctl rm");
}
shmhead = NULL;
payload = NULL;
open = false;
}
void F_Shm::Destroy(key_t key)
{
int shmid = 0;
//1. 查看是否已经存在共享内存,如果有则删除旧的
shmid = shmget(key, 0, 0);
if (shmid != -1)
{
printf("Delete shmid=%d \\n", shmid);
shmctl(shmid, IPC_RMID, NULL); // 删除已经存在的共享内存
}
}
//返回头地址
bool F_Shm::open_shm(key_t key, int blksize, int blocks)
{
int shmid;
this->close_shm();
//1. 查看是否已经存在共享内存,如果有则删除旧的
shmid = shmget(key, 0, 0);
if (shmid == -1)
{
return this->creat_shm(key, blksize, blocks);
}
//2.连接共享内存
shmhead = shmat(shmid, (void*)0, 0); //连接共享内存
if(shmhead == (void*)-1)
{
ERR_EXIT("shmat");
}
printf("Open shmid=%d size=%u \\n", shmid, sizeof(shmhead_t) + blksize*blocks);
//3. 填充控制共享内存的信息
payload = (char *)((shmhead_t *)shmhead + 1); //实际负载起始位置
open = true;
return true;
}
//关闭共享内存
void F_Shm::close_shm(void)
{
if(open)
{
shmdt(shmhead); //共享内存脱离
shmhead = NULL;
payload = NULL;
open = false;
}
}
void F_Shm::write_into_shm(const void *buf)
{
shmhead_t *pHead = (shmhead_t *)shmhead;
sem_wait(&pHead->sem_full); //是否有资源写? 可用写资源-1
sem_wait(&pHead->sem_mutex); //是否有人正在写?
printf("write to shm[%d] index %d \\n", pHead->shmid, pHead->rd_index);
memcpy(payload + (pHead->wr_index) * (pHead->blksize), buf, pHead->blksize);
pHead->wr_index = (pHead->wr_index+1) % (pHead->blocks); //写位置偏移
sem_post(&pHead->sem_mutex); //解除互斥
sem_post(&pHead->sem_empty); //可用读资源+1
}
void F_Shm::read_from_shm(void *buf)
{
shmhead_t *pHead = (shmhead_t *)shmhead;
sem_wait(&pHead->sem_empty); //检测写资源是否可用
printf("read from shm[%d] index %d \\n", pHead->shmid, pHead->rd_index);
memcpy(buf, payload + (pHead->rd_index) * (pHead->blksize), pHead->blksize);
//读位置偏移
pHead->rd_index = (pHead->rd_index+1) % (pHead->blocks);
sem_post(&pHead->sem_full); //增加可写资源
}
协议包包头.h
#ifndef I_PACKET_PUBLIC_H
#define I_PACKET_PUBLIC_H
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAX_LEN 256
/************接入层数据包头************/
typedef struct packet_header_st
{
int fd;//用于前后端通信即目标客户端fd(服务器用到)
int funcId; // 功能号
//登录包0x01,注册包0x02,找回密码0x03,心跳包0x04
//客户端上传视频点播请求功能0x10 客户端上传视频点播时长功能0x11
//播放历史请求包0x20
//请求视频列表0x30
int optid; // 操作码:请求0x00 和 应答0x01
int usrlenth;// 包体的长度
int packet_seq; //包序号
int packet_sum; //包总数
char以上是关于开发成长之路(14)-- 小项目:视频点播器服务端(放码过来)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
开发成长之路(13)-- Linux网络服务端编程(通识篇)
开发成长之路(13)-- Linux网络服务端编程(通识篇)
开发成长之路(12)-- Linux网络服务端编程(通识篇之熟悉操作环境)