JSP内置对象
Posted XiaoFanMi
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了JSP内置对象相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
JSP内置对象
在jsp页面中可以不加声明和创建就可以在脚本中使用。
JSP脚本中包含9个内置对象:
1.out向客户端输出
2.request 封装用户请求
3.response 向用户做出响应
4.session 客户和服务器间的会话
5.application 于服务器启动时开始运行,用来存放全局变量,在用户间共享
6.pageContext 用于访问page的各种对象
7.exception 异常
8.config 初始化要用的参数
9.page JSP页面本身
out向客户端输出
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
out.print("aa");
javax.servlet.jsp.JspWriter out1 = pageContext.getOut();
out1.print("aa");
%>
</body>
</html>
JSP内置对象-request/ response
• request是javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest的实例,该对象封装了一次请求,客户端的请求参数都被封装在该对象里。
•response是HttpServletResponse类的实例,response对象包含了响应客户请求的有关信息。
request请求传递对象
•request对象同时也是一个域对象,开发人员通过request对象在实现转发时,把数据通过request对象带给其它web资源处理
–setAttribute(“name”,value)
–getAttribute(“name”)
–removeAttribute(“name”)
创建一个登录表单
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<%out.print(request.getAttribute("msg"));%>
<form action="login " method="post">
账户:<input type="text" name="account" value="" id="acountId"><br>
密码:<input type="password" name="password" value="" id="passwordId"> <br>
<input type="submit" value="登录">
</form>
</body>
</html>
在servlet中进行相应处理
servlet主要用于逻辑处理,处理完之后,将结果交给另一个jsp,由jsp向客户端做出响应
两种解决方法:
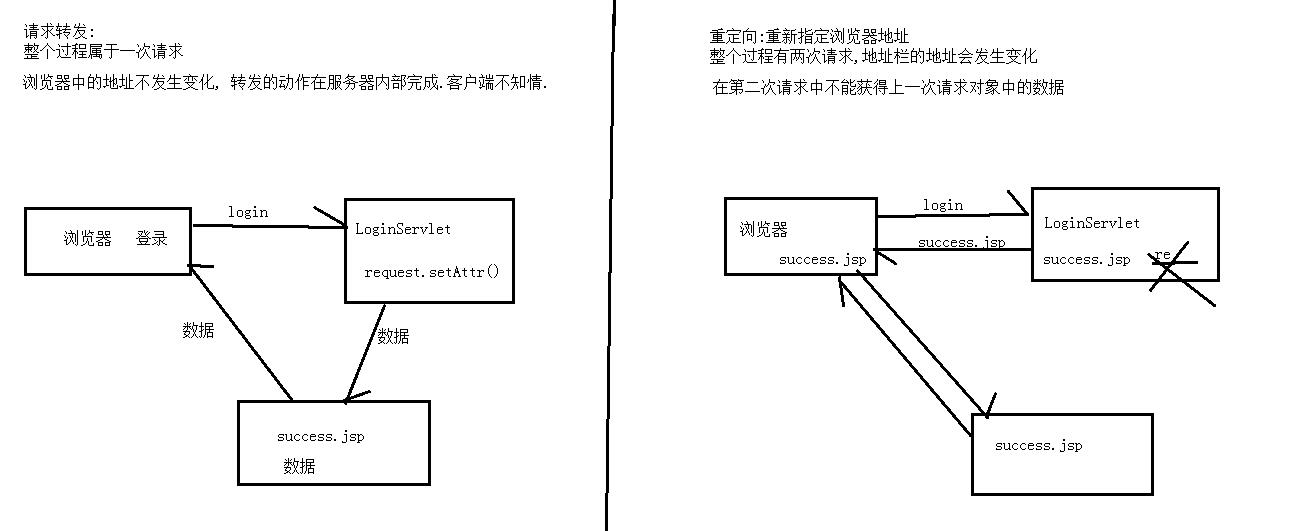
1.使用request进行请求转发
2.使用response进行重定向
import javax.servlet.RequestDispatcher;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebServlet(name = "login",urlPatterns = "/login")
public class servlet_bank extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
req.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
String account = req.getParameter("account");
String password = req.getParameter("password");
if (account.equals("admin") && password.equals("111")){
req.setAttribute("account",account);
RequestDispatcher requestDispatcher = req.getRequestDispatcher("success.jsp");
requestDispatcher.forward(req,resp);
}else{
req.setAttribute("msg","账户或密码错误");
RequestDispatcher requestDispatcher = req.getRequestDispatcher("login.jsp");
requestDispatcher.forward(req,resp);
}
}
}
登陆成功界面
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>欢迎<%out.print(request.getAttribute("account"));%>登录<h1/>
</body>
</html>
response实现请求重定向
• 重定向是指页面重新定位到某个新地址,之前的请求失效,进入一个新的请求,且跳转后浏览器地址栏内容将变为新的指定地址。
• 重定向是通过HttpServletResponse对象的sendRedirect()来实现,该方法相当于浏览器重新发送一个请求
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebServlet(name = "login",urlPatterns = "/login")
public class servlet_bank2 extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
req.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
String account = req.getParameter("account");
String password = req.getParameter("password");
if (account.equals("admin") && password.equals("111")){
req.setAttribute("account",account);
resp.sendRedirect("success.jsp");
}else{
req.setAttribute("msg","账户或密码错误");
resp.sendRedirect("login.jsp");
}
}
}
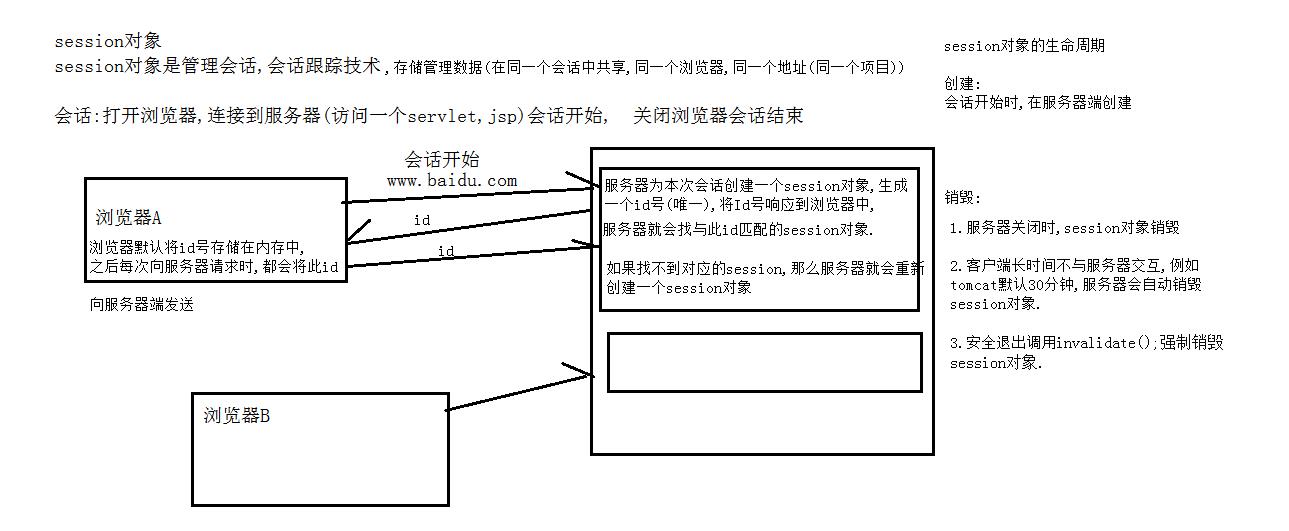
session 客户和服务器间的会话
Session对象是javax.servlet.http.HttpSession的实例
它在第一个JSP页面被装载时自动创建,完成会话期管理。从一个客户打开浏览器并连接到服务器开始,到客户关闭浏览器离开这个服务器结束,被称为一个会话。
**会话:**打开浏览器,链接到服务器,会话开始,关闭浏览器会话结束
Servlet API中,定义了HttpSession接口,用来封装会话对象。
HttpSession是接口,会话对象是Web容器创建的,在Servlet中使用HttpServletRequest中的方法获得会话对象。
–public HttpSession getSession():获取跟当前请求相关的session,如果不存在session,就创建一个新的session对象返回。
JSP文件中使用会话对象的方法
–JSP文件中有内置对象session,可以直接调用HttpSession接口中任意方法
使用session实现会话机制的过程
- 当容器创建一个新的HttpSession对象后,即生成一个随机数,称为会话ID,并将ID值封装成一个名字为JSESSIONID的session,返回给客户端。
- 调用request.getSession方法获得会话对象时,容器先从request中获取JSESSIONID值,根据JSESSIONID值查找到对应的会话对象,返回使用。
- 如果没有获取到JSESSIONID值,认为当前的请求没有相关联的会话对象,重复步骤1
| setAttribute(String key,Object value) | 以key/value的形式保存对象值 |
|---|---|
| getAttribute(String key) | 通过key获取对象值 |
| removeAttribute(String key) | 通过key删除属性 |
| getMaxInactiveInterval() | 获取session的有效非活动时间,以秒为单位 |
| setMaxInactiveInterval (int interval ) | 设置session的最大非活动时间,以秒为单位,超时将被销毁。 |
| getId() | 获取session对象的编号 |
| invalidate() | 设置session对象失效 |
| isNew() | 判断一个session是不是一个新创建的会话对象 |
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebServlet(name = "login",urlPatterns = "/login")
public class servlet_安全退出 extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
req.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
try {
String account = req.getParameter("account");
String password = req.getParameter("password");
if (account.equals("admin") && password.equals("111")){
HttpSession session = req.getSession();//从请求对象中获得与之对应的session
session.setAttribute("account",account);
resp.sendRedirect("success.jsp");
}else{
req.setAttribute("msg","账户或密码错误");
resp.sendRedirect("login.jsp");
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
resp.sendRedirect("500.jsp");//只跳转页面,不进行数据的传输
}
}
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
req.getSession().invalidate();//销毁session
resp.sendRedirect("login.jsp");
}
}
我们可以在统一浏览器同一地址的不同页面中可以获得Session’中的数据
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
<script>
function test() {
var c = confirm("您确定要退出吗");
if (c) {
window.location.replace("login");
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>欢迎<%out.print(session.getAttribute("account"));%>登录<h1/><br/>
<input type="submit" value="安全退出" οnclick=" test()" />
</body>
</html>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
out.print(session.getId()+"<br/>");
out.print(session.isNew()+"<br/>");
String account = (String)request.getAttribute("account");
out.println(account);
%>
</body>
</html>
设置会话时间
- 可以在web.xml中进行配置,修改默认时间。例如,修改为50分钟销毁。
<session-config>
<session-timeout>50</session-timeout>
</session-config>
- 可以使用HttpSession接口中的setMaxIntervalTime设置,以秒为单位,如果参数是负数,表示永远不失效。
例如:将会话的有效时长设置为2小时。
session.setMaxInactiveInterval(26060);
application 于服务器启动时开始运行,用来存放全局变量,在用户间共享
创建一个APP1.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
/*
ServletContext application 在一个应用程序中只要一个servletContext对象
存储整个应用程序共享的数据
在服务器创建
在服务器关闭时销毁
在不同页面,不同浏览器,只要服务器未关闭都可以共享数据
*/
application.setAttribute("name","appname");
out.print(application.getAttribute("name"));
%>
</body>
</html>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
out.print(application.getAttribute("name"));
%>
</body>
</html>
pageContext 用于访问page的各种对象
当前页面上下文,获取当前页面中的数据
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
/*
当前页面上下文,获取当前页面中的数据
*/
pageContext.setAttribute("page","pageName");
out.print(pageContext.getAttribute("page"));
%>
</body>
</html>
另一个页面拿不到数据
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
out.print(pageContext.getAttribute("page"));
%>
</body>
</html>
总结四个内置对象
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
/*
当前页面上下文,获取当前页面中的数据
pageContext.setAttribute("page","pageName");用一个页面
application.setAttribute("app","appName");同一个应用程序
request.setAttribute("req","reqName");同一个请求
session.setAttribute("session","sessionName");同一个会话
*/
pageContext.setAttribute("page","pageName");
application.setAttribute("app","appName");
request.setAttribute("req","reqName");
session.setAttribute("session","sessionName");
out.print(pageContext.getAttribute("page"));
out.print(application.getAttribute("app"));
out.print(request.getAttribute("req"));
out.print(session.getAttribute("session"));
%>
</body>
</html>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
out.print(pageContext.getAttribute("page"));
out.print(application.getAttribute("app"));
out.print(request.getAttribute("req"));
out.print(session.getAttribute("session"));
%>
</body>
</html>
以上是关于JSP内置对象的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章