重链剖分求LCA
Posted PushyTao
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了重链剖分求LCA相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
题目链接
倍增做法求LCA 在 这篇博客中有提到
题目描述
如题,给定一棵有根多叉树,请求出指定两个点直接最近的公共祖先。
输入格式
第一行包含三个正整数 N,M,SN,M,S,分别表示树的结点个数、询问的个数和树根结点的序号。
接下来 N-1N−1 行每行包含两个正整数 x, yx,y,表示 xx 结点和 yy 结点之间有一条直接连接的边(数据保证可以构成树)。
接下来 MM 行每行包含两个正整数 a, ba,b,表示询问 aa 结点和 bb 结点的最近公共祖先。
输出格式
输出包含 MM 行,每行包含一个正整数,依次为每一个询问的结果。
输入输出
样例 1
输入
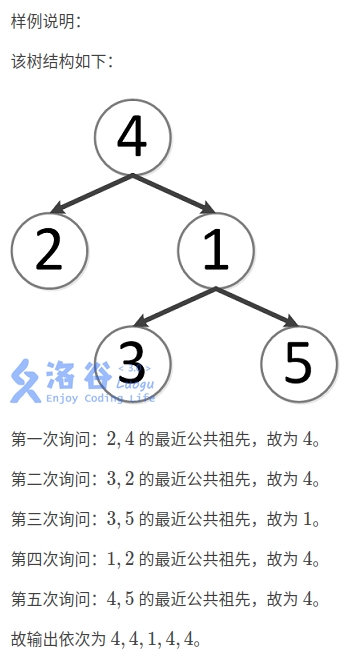
5 5 4
3 1
2 4
5 1
1 4
2 4
3 2
3 5
1 2
4 5
输出
4
4
1
4
4
说明/提示
对于 30% 的数据,N≤10,M≤10。
对于 70% 的数据,N≤10000,M≤10000。
对于 100% 的数据,N≤500000,M≤500000。
int lca(int u,int v) {
while(top[u] != top[v]) {
if(dep[top[u]] < dep[top[v]]) swap(u,v);
u = fa[top[u]];
}
if(dep[u] < dep[v]) return u;
else return v;
}
对于要求树上两个点u,v的lca,(当两个点不在一条重链上的时候)我们可以每次先让链头深depth比较大的点进行移动,不在一条重链上直接将top更深的节点跳到链头的父节点u = fa[top[u]]; ,当两个点在一条重链上的时候,从深度的角度来看,深度比较小的就应该是祖先节点
int n,m,rt;
struct node {
int to;
int nex;
} e[maxn];
int head[maxn],cnt;
void init() {
for(int i=0; i<maxn; i++) head[i] = -1;
cnt = 0;
}
void add(int u,int v) {
e[cnt].to = v;
e[cnt].nex = head[u];
head[u] = cnt ++;
}
int fa[maxn],siz[maxn],son[maxn],dep[maxn],top[maxn];
void dfs1(int x) {
siz[x] = 1;
dep[x] = dep[fa[x]] + 1;
for(int i=head[x]; ~i; i=e[i].nex) {
int to = e[i].to;
// fa[to] = x;
if(to != fa[x]) {
fa[to] = x;
dfs1(to);
siz[x] += siz[to];
if(siz[to] > siz[son[x]]) son[x] = to;
}
}
}
void dfs2(int rt,int tp) {
top[rt] = tp;
if(son[rt]) dfs2(son[rt],tp);
for(int i = head[rt]; ~i; i = e[i].nex) {
int to = e[i].to;
if(to != fa[rt] && to != son[rt]) dfs2(to,to);
}
}
int lca(int u,int v) {
while(top[u] != top[v]) {
if(dep[top[u]] < dep[top[v]]) swap(u,v);
u = fa[top[u]];
}
if(dep[u] < dep[v]) return u;
else return v;
}
int main() {
cin >> n >> m >> rt;
init();
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int u=read,v=read;
add(u,v);
add(v,u);
}
dfs1(rt);
dfs2(rt,rt);
while(m --) {
int u=read,v=read;
cout<<lca(u,v)<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
以上是关于重链剖分求LCA的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章