JavaWeb学习——JDBC
Posted Johnny*
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了JavaWeb学习——JDBC相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
JDBC
Java Database Connectivity ,可以为多种关系型数据库DBMS 提供统一的访问方式,实现用Java来操作 数据库。
JDBC架构
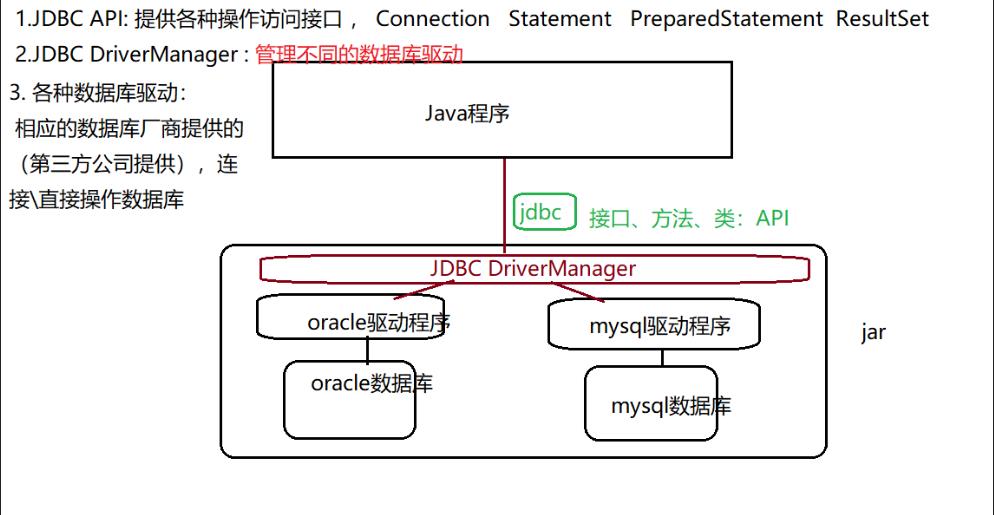
JDBC API
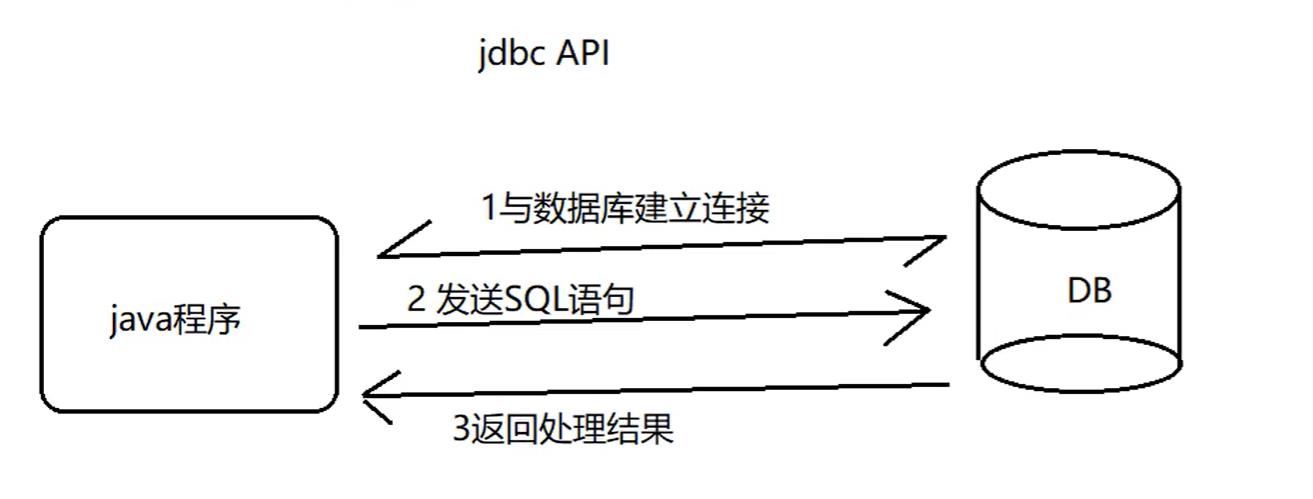
JDBC API主要通过以下类/接口来实现。
| 类/接口 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| DriverManager | 管理JDBC 驱动 |
| Connection | 连接(通过DriverManager产生) |
| Statement | (子类:PreparedStatement,通过Connection对象产生) |
| CallableStatement | 调用数据库的存储过程/存储函数(通过connection产生) |
| Result | 返回的结果集(通过上面的Statement等产生) |
JDBC访问数据库的具体步骤:
- 导入驱动,加载具体的驱动类。mysql 为 “com.mysql.jdbc.Driver”
- 通过DriverManager 获取数据库connection连接对象
- 通过connection对象获得statement对象,该对象执行相应SQL语句
- 处理返回结果集
Connection产生操作数据库的对象
产生Statement 对象, createStatement()
产生PreparedStatement 对象, prepareStatement()
产生CallableStatement对象, prepareCall()
Statement操作数据库
增删改 executeUpdate()
查询 executeQuery()
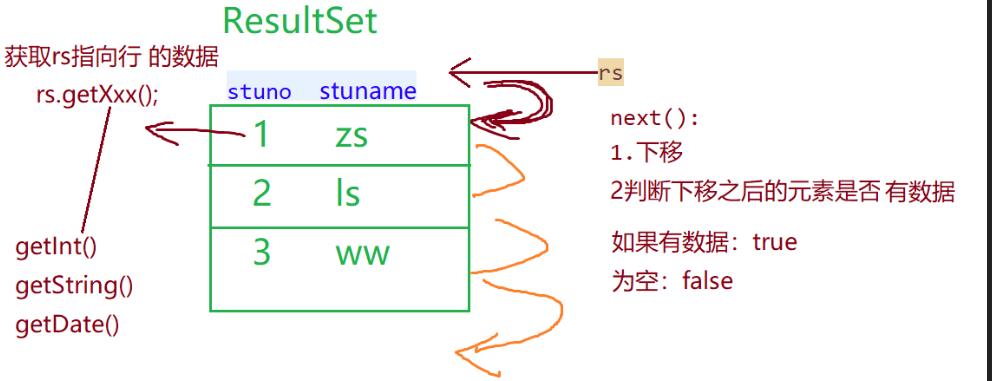
** ResultSet **
next() 光标下移并判断是否有下一条数据
previous() 光标上移并判断是否有上一条数据
getXxx(字段名或位置) 获取具体字段值
PrepareStatement操作数据库
增删改: executeUpdate()
查询: executeQuery()
才外还有赋值操作,setXxx()
数据库驱动
| 数据库 | 驱动jar | 具体驱动类 | 连接字符串 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oracle | ojdbc-x.jar | oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver | jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:ORCL |
| MySQL | mysql-connector-java-x.jar | com.mysql.jdbc.Driver | jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/数据库实例名 |
| SqlServer | sqljdbc-x.jar | com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver | jdbc:microsoft:sqlserver:localhost:1433;databasename=数据库实例名 |
使用statement操作对象
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class JDBCDemoMySQL {
private static final String URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/goodsadmin";
private static final String USERNAME = "用户名";
private static final String PWD = "密码";
public static void update() {// 增删改
Connection connection = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try {
// a.导入驱动,加载具体的驱动类
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");// 加载具体的驱动类
// b.与数据库建立连接
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(URL, USERNAME, PWD);
// c.发送sql,执行(增删改、查)
stmt = connection.createStatement();
String sql = "insert into student values(1,'zs',23,'s1')";
// String sql = "update student set STUNAME='ls' where stuno=1";
// String sql = "delete from student where stuno=1";
// 执行SQL
int count = stmt.executeUpdate(sql); // 返回值表示 增删改 几条数据
// d.处理结果
if (count > 0) {
System.out.println("操作成功!");
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
try {
if(stmt!=null) stmt.close();// 对象.方法
if(connection!=null)connection.close();
}catch(SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void query() {// 查询
Connection connection = null;
Statement st = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(URL, USERNAME, PWD);
st = connection.createStatement();
String sql = "select stuNo, stuName from student";
// 查询结果
rs = st.executeQuery(sql);
// 对结果集内容进行操作
while (rs.next()) {
int no = rs.getInt("stuNo");
String name = rs.getString("stuName");
System.out.println(no + "_ " + name);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (rs != null)
rs.close();
if (st != null)
st.close();
if (connection != null)
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
update() ;
}
}
操作ResultSet 常用API
PreparedStatement
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
public class JDBCPreparedStatementDemo {
private static final String URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/goodsadmin";
private static final String USERNAME = "root";
private static final String PWD = "120329";
public static void update() {// 增删改
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
try {
// a.导入驱动,加载具体的驱动类
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver");// 加载具体的驱动类
// b.与数据库建立连接
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(URL, USERNAME, PWD);
String sql = "insert into student values(?,?,?,?)";
//预编译
pstmt = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setInt(1, 4);
pstmt.setString(2, "sww");
pstmt.setInt(3, 55);
pstmt.setString(4, "s5");
int count = pstmt.executeUpdate();
if(count > 0) System.out.println("操作成功!");
else System.out.println("操作失败!");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
try {
if(pstmt!=null) pstmt.close();// 对象.方法
if(connection!=null)connection.close();
}catch(SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void query() {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null ;
try {
// a.导入驱动,加载具体的驱动类
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver");// 加载具体的驱动类
// b.与数据库建立连接
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(URL, USERNAME, PWD);
// c.发送sql,执行(增删改、【查】)
Scanner input= new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入用户名:");
String name = input.nextLine() ;
System.out.println("请输入密码:");
String pwd = input.nextLine() ;
String sql ="select count(*) from login where uname= ? and upwd =?";
pstmt = connection.prepareStatement(sql) ;
pstmt.setString(1, name);//下标1指定第一个?
pstmt.setString(2, pwd);//2指定第二个?
int count = -1;
if(rs.next()) {
count = rs.getInt(1) ;
}
if(count>0) {
System.out.println("登陆成功!");
}else {
System.out.println("登陆失败!");
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
try {
if(rs!=null) rs.close();
if(pstmt!=null) pstmt.close();// 对象.方法
if(connection!=null)connection.close();
}catch(SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
update() ;
// query() ;
}
}
Statement 与 PreparedStatement区别:
- 安全上
PreparedStatement可有效防止SQL注入。而Statement因为使用字符串拼接会有用户输入语句与SQL语句混合而造成的SQL注入风险。例如:
select count(*) from login where uname=’ “+name+” ’ and upwd =’ “+pwd+” ’
输入用户名: 任意值 ’ or 1=1 –
密码:任意值
select count() from login where uname=’ 任意值 ’ or 1=1 --and upwd =’ “+pwd+” ’
等价于 select count() from login
因此,PreparedStatement比Statement安全
2. PreparedStatement可有效提高性能
因为PreparedStatement有预编译操作,对于批量的相同操作,该语句只需预编译一次,往后无需编译。
例如需要重复增加100条数据
stmt:
String sql =" insert into student(stuno,stuname) values(’"+name+"’, “+age+” ) " ;
for(100)
stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
pstmt:
String sql =" insert into student(stuno,stuname) values(?,?) " ;
pstmt = connection.prepareStatement(sql);//预编译SQL
pstmt.setString(1,name);
pstmt.setInt(2,age);
for( 100){
pstmt.executeUpdate();
}
- 编码更加简便
由于PreparedStatement使用? 占位符,避免了字符串的拼接。
存储过程
CallableStatement 调用存储过程、存储函数。
- connection.prepareCall(参数: 存储过程或存储函数名)获取CallableStatemet对象
参数格式:
存储过程(存储过程无返回值,使用out参数代替): {call 存储过程名(参数 列表) }
存储函数(有返回值return): { ? = call 存储函数名(参数列表)}
cstmt = connection.prepareCall( “…” ) ;
- 通过cstmt.setXxx()处理输入的参数值
- 通过registerOutParameter(……)处理输出参数类型
- cstmt.execute() 执行
- 接受输出值(返回值) cstmt. getXxx()
Mysql 创建存储过程
CREATE DEFINER=`root`@`localhost` PROCEDURE `addTwoNum`(IN `num1` int,IN `num2` int,OUT `res` int)
BEGIN
set res = num1 + num2;
END
Mysql 创建存储函数
CREATE DEFINER=`root`@`localhost` FUNCTION `addTwoNumFun`(`num1` int,`num2` int) RETURNS int(11)
BEGIN
RETURN num1 + num2;
END
import java.sql.CallableStatement;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.sql.Types;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class JDBCCallableStatement {
private static final String URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/goodsadmin";
private static final String USERNAME = "用户名";
private static final String PWD = "密码";
public static void invokeProcedure() {
Connection connection = null;
CallableStatement cstmt = null;
try {
// a.导入驱动,加载具体的驱动类
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");// 加载具体的驱动类
// b.与数据库建立连接
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(URL, USERNAME, PWD);
cstmt = connection.prepareCall("{ call addTwoNum(?,?,?)}");
//输入参数
cstmt.setInt(1, 15);
cstmt.setInt(2, 22);
cstmt.registerOutParameter(3, Types.INTEGER);
cstmt.execute();
int result = cstmt.getInt(3);
System.out.println(result);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
try {
if(cstmt!=null) cstmt.close();// 对象.方法
if(connection!=null)connection.close();
}catch(SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void invokeFunction() {
Connection connection = null;
CallableStatement cstmt = null;
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");// 加载具体的驱动类
// b.与数据库建立连接
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(URL, USERNAME, PWD);
cstmt = connection.prepareCall("{ ?= call addTwoNumFun(?,?)}");
cstmt.setInt(2, 55);
cstmt.setInt(3, 12);
//设置输出参数返回类型
cstmt.registerOutParameter(1, Types.INTEGER);
cstmt.execute();
int result = cstmt.getInt(1) ;//获取计算结果
System.out.println(result);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
try {
if(cstmt!=null) cstmt.close();// 对象.方法
if(connection!=null)connection.close();
}catch(SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// invokeProcedure();
invokeFunction() ;
}
}
JDBC处理大文件
处理TEXT/BLOB类型
处理稍大型数据:
a.存储路径 E:\\JDK_API_zh_CN.CHM
通过JDBC存储文件路径,然后 根据IO操作处理
例如:JDBC将 E:\\JDK_API_zh_CN.CHM 文件 以字符串形式“E:\\JDK_API_zh_CN.CHM”存储到数据库中
获取:1.获取该路径“E:\\JDK_API_zh_CN.CHM” 2.IO
b.
TEXT:大文本数据 (小说->数据)
BLOB:二进制
TEXT:大文本数据 字符流 Reader Writer
存
1.先通过pstmt 的? 代替小说内容 (占位符)
2.再通过pstmt.setCharacterStream(2, reader, (int)file.length()); 将上一步的?替换为 小说流, 注意第三个参数需要是 Int类型
取:
1.通过Reader reader = rs.getCharacterStream(“NOVEL”) ; 将TEXT类型的数据 保存到Reader对象中
2. 将Reader通过Writer输出即可。
blob:二进制 字节流 InputStream OutputStream
与TEXT步骤基本一致,区别:setBinaryStream(…) getBinaryStream(…)
TEXT 大文本文件
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.Reader;
import java.io.Writer;
import java.nio.CharBuffer;
import java.sql.Connection;
import以上是关于JavaWeb学习——JDBC的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章