Unix/Linux 编程:网络编程之 内存池
Posted sesiria
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Unix/Linux 编程:网络编程之 内存池相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一,内存池的原理
1. 什么是内存池?
服务器程序或者需要长时间运行处理业务的程序在整个生命过程中可能需要频繁的调用malloc/free 或者(new /delete)
但是由于每个内存块的大小以及生命周期不是统一的,尤其是高并发的服务器程序在执行一段时间以后可能会在某个空间内产生大量小块而又无法释放的内存块。这就是内存碎片的产生。
比如下面这张图:
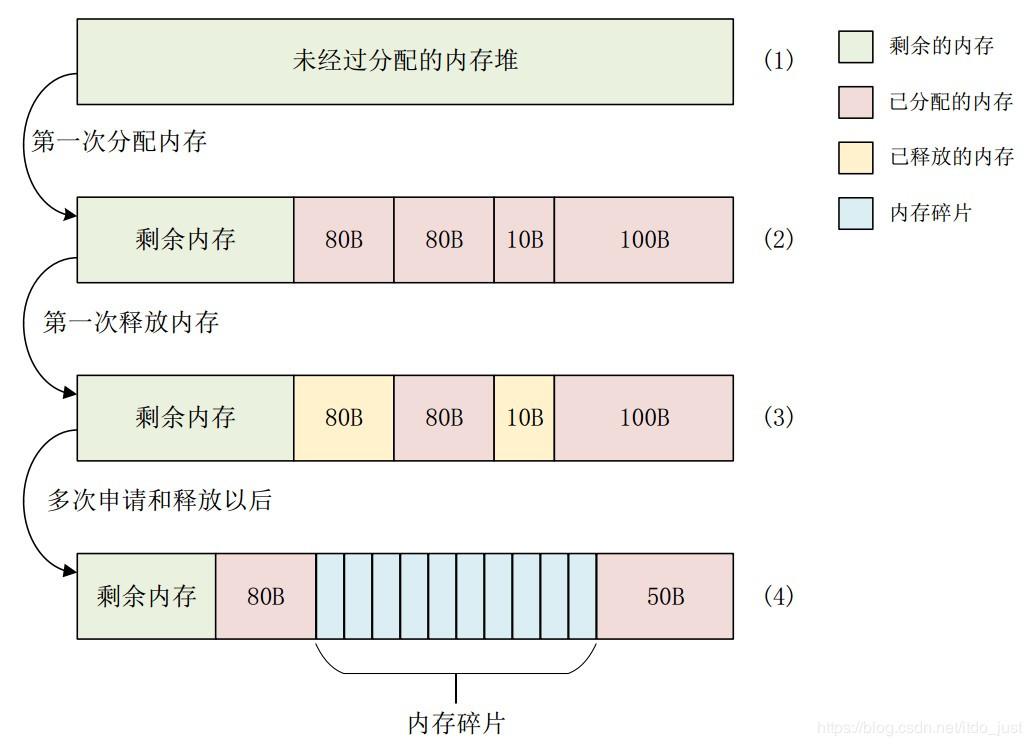
可以看到在多次申请和释放以后,内存中产生了大量小块但是又无法被继续申请的碎片块。这会导致内存实际使用效率的降低。
那么有什么解决方法呢?
将程序中需要实际使用小块的内存集中在一个地方进行管理,等到需要释放的时候直接释放整个内存块,而不是去对每次小块的内存都进行释放。
而大块的内存块则按正常的逻辑申请和释放。
内存池就是一种解决内存碎片的内存管理技术。
2. 内存池的结构
首先内存池也能够像系统申请内存,比如使用malloc或者sbrk。
但是内存池本身不直接申请小块的内存,而是直接申请大块的内存,通常是一个页,比如4K。
(虽然malloc函数内部通常也是以页为单位进行申请,但是malloc函数会通过遍历其内部的链表对每次申请和释放都进行操作)但内存池对于小块内存采取的措施是要么合并回收,或者仅做标记最后一次释放整个页。
二,内存池的应用
内存池主要用于频繁需要申请加释放小块文件的场合。通过自己管理内存区块,整块申请,自己管理,最后整块释放的方式来达到减小内存碎片的目的。
但不是所有的情况都适合内存池,一般内存池适用于 快速申请,快速释放的场合。如果有些内存区块需要长时间驻留于内存,那么用内存池显然并不能很好的处理这种业务情况。(因为内存池需要等到小块内存完全没任何使用以后才释放整块。如果整块内存中有一些内存需要长时间主流于系统,那么这种情况就不太适用。(静态存储区可能会更合适)
三,基于连接的简单的内存池的实现
以下将实现一个简单的内存池,基于连接业务。比如服务器处理每个连接的适合,当accept创建clientfd以后则给每个连接创建内存池。
后续该连接使用的内存块从内存池中分配。当连接断开以后则释放整个内存池。
首先数据结构定义:
内存池的基本结构是两条链表:
一条存储小区块内存,以页为单位(通常是4K或者8K),
另一条存储大块内存,通常大于一个页(4K或者8K以上)
1. 数据结构定义:
小块内存块结构体:
// define the memory pool block less thant 4K
struct mp_node_s {
unsigned char* end; // end of the block
unsigned char* last; // point to the current used.
struct mp_node_s* next; // linklist
int failed;
};大块内存块结构体:
// define the memory pool block large than 4K
struct mp_large_s {
struct mp_large_s* next;
void* alloc;
};注意:内存池向内核实际申请内存的最小单位以页为单位,因此这些结构体也全部存储在这些页内存中。
2. 接口定义:
//=============function declaration==============
struct mp_pool_s* mp_create(int size);
void* mp_alloc(struct mp_pool_s* pool, int size);
void* mp_calloc(struct mp_pool_s* pool, int size);
void mp_destory_pool(struct mp_pool_s* pool);
void mp_free(struct mp_pool_s* pool, void* p);
//=============function definition===============分别是:
1)创建内存池
2)申请内存
3)申请内存块,并设置值为0
4)销毁内存池
5)释放内存块
3. 内存池代码的具体实现:
/**
* File name: memorypool.c
* Author: sesiria 2021-05-05
* A Implementation of memory pool.
*
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define PAGE_SIZE 4096
#define MP_ALIGNMENT 16
#define FAILED_TIMES 4 // number of tries to search from the current block.
//===============start of declaration==============
// define the memory pool block large than 4K
struct mp_large_s {
struct mp_large_s* next;
void* alloc;
};
// define the memory pool block less thant 4K
struct mp_node_s {
unsigned char* end; // end of the block
unsigned char* last; // point to the current used.
struct mp_node_s* next; // linklist
int failed;
};
// the memory pool object
struct mp_pool_s {
struct mp_large_s* large; // point to the first node of the large blocks linklist.
struct mp_node_s* head; // point to the first node of the small blocks linklist.
struct mp_node_s* current; // point to the current node of the small(less thant 4K) block
};
//===============end of declaration==============
//=============function declaration==============
struct mp_pool_s* mp_create_pool(int size);
void mp_destory_pool(struct mp_pool_s* pool);
void mp_reset_pool(struct mp_pool_s* pool);
void* mp_alloc(struct mp_pool_s* pool, int size);
void* mp_calloc(struct mp_pool_s* pool, int size);
void mp_free(struct mp_pool_s* pool, void* p);
//=============function definition===============
// the input size is the size of the memory block node.
// 1 page_size
struct mp_pool_s* mp_create_pool(int size) {
struct mp_pool_s* p;
int ret = posix_memalign(&p, MP_ALIGNMENT, size + sizeof(struct mp_pool_s) + sizeof(struct mp_node_s));
if (ret != 0) {
perror("memory alloc error!\\n");
return NULL;
}
p->large = NULL;
p->current = p->head = (unsigned char*)p + sizeof(struct mp_pool_s);
p->head->last = (unsigned char*)p + sizeof(struct mp_pool_s) + sizeof(struct mp_node_s);
p->head->end = p->head->last + size;
p->head->failed = 0;
return p;
}
// destory
void mp_destory_pool(struct mp_pool_s* pool) {
if (pool == NULL)
return;
// free large list.
struct mp_large_s* l;
for (l = pool->large; l; l = l->next) {
if (l->alloc) {
free(l->alloc);
}
}
// free node.
struct mp_node_s* h, * n;
h = pool->head->next;
while (h) {
n = h->next;
free(h);
h = n;
}
free(pool);
}
// reset the memory pool
// will free all the large blocks but keep the small blocks.
void mp_reset_pool(struct mp_pool_s* pool) {
struct mp_node_s* h;
struct mp_large_s* l;
for (l = pool->large; l; l = l->next) {
if (l->alloc) {
free(l->alloc);
}
}
pool->large = NULL;
for (h = pool->head; h; h = h->next) {
h->last = (unsigned char*)h + sizeof(struct mp_node_s);
h->failed = 0;
}
}
// alloc the memory block with size > PAGE-size - sizeof(struct mp_node_s)
void* mp_alloc_large(struct mp_pool_s* pool, int size) {
unsigned char* m;
int ret = posix_memalign(&m, MP_ALIGNMENT, size);
if (ret != 0) {
perror("alloc memory error!\\n");
return NULL;
}
struct mp_large_s* large;
for (large = pool->large; large; large = large->next) {
if (large->alloc == NULL) {
large->alloc = m;
return m;
}
}
large = (struct m_large_s*)mp_alloc(pool, sizeof(struct mp_large_s));
large->alloc = m;
large->next = pool->large;
pool->large = large;
return m;
}
// alloc the memory block with size <= PAGE-size - sizeof(struct mp_node_s)
void* mp_alloc_block(struct mp_pool_s* pool, int size) {
unsigned char* m;
int ret = posix_memalign(&m, MP_ALIGNMENT, PAGE_SIZE);
if (ret != 0) {
perror("memory alloc error!\\n");
return NULL;
}
struct mp_node_s* new_node = (struct mp_node_s*)m;
new_node->end = m + PAGE_SIZE;
new_node->next = NULL;
new_node->last = m + sizeof(struct mp_node_s) + size;
struct mp_node_s* p, * current = pool->current;
for (p = current; p->next; p = p->next) {
if (p->failed++ > FAILED_TIMES) {
current = p->next;
}
}
p->next = new_node; // insert the new node into the linklist
pool->current = current ? current : new_node;
return m + sizeof(struct mp_node_s);
}
// alloc
void* mp_alloc(struct mp_pool_s* pool, int size) {
if (size <= 0) return NULL;
if (size > PAGE_SIZE - sizeof(struct mp_node_s)) { // large
return mp_alloc_large(pool, size);
}
else {
// we could alloc the memory in the current block
struct mp_node_s* p = pool->current;
unsigned char* m = p->last;
if (p->end - m >= size) {
p->last = m + size;
return m;
}
else {
return mp_alloc_block(pool, size);
}
}
}
// calloc
void* mp_calloc(struct mp_pool_s* pool, int size)
{
void* p = mp_alloc(pool, size);
if (p == NULL) {
perror("memory alloc error!\\n");
return p;
}
memset(p, 0, size);
return p;
}
// free memory block.
// we only need to free the large block.
// the small block will be released when the disconnection is occured.
void mp_free(struct mp_pool_s* pool, void* p) {
// search from the large block.
struct mp_large_s* l;
for (l = pool->large; l; l = l->next) {
if (p == l->alloc) {
free(l->alloc);
l->alloc = NULL;
return;
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
int size = 1 << 12;
struct mp_pool_s* p = mp_create_pool(size);
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
void* mp = mp_alloc(p, 512);
mp_free(p, mp);
}
//printf("mp_create_pool: %ld\\n", p->max);
//printf("mp_align(123, 32): %d, mp_align(17, 32): %d\\n", mp_align(24, 32), mp_align(17, 32));
//printf("mp_align_ptr(p->current, 32): %lx, p->current: %lx, mp_align(p->large, 32): %lx, p->large: %lx\\n", mp_align_ptr(p->current, 32), p->current, mp_align_ptr(p->large, 32), p->large);
int j = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
char* pp = mp_calloc(p, 32);
for (j = 0; j < 32; j++) {
if (pp[j]) {
printf("calloc wrong\\n");
}
printf("calloc success\\n");
}
}
printf("mp_reset_pool\\n");
// alloc large blocks.
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
void* l = mp_alloc(p, 8192);
mp_free(p, l);
}
mp_reset_pool(p);
printf("mp_destory_pool\\n");
for (i = 0; i < 58; i++) {
mp_alloc(p, 256);
}
mp_destory_pool(p);
return 0;
}
以上是关于Unix/Linux 编程:网络编程之 内存池的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章