synchronizedLock接口Condition接口读写锁及ReentrantLock(重入锁) 特性及使用
Posted 小艾路西里
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了synchronizedLock接口Condition接口读写锁及ReentrantLock(重入锁) 特性及使用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. synchronized
synchronized是为了实现线程同步而存在的
在java中,实现线程同步可以使用 synchronized关键字,用于在方法前修饰,添加了synchronized关键字,线程在执行的时候就不会被其他线程抢夺
这是因为每个Java 对象都有一个内置锁,内置锁会保护使用 synchronized 关键字修饰的方法,线程要调用该方法就必须先获得锁,否则就处于阻塞状态
(1) synchronized的3种使用方式
① 修饰实例方法,给调用方法的对象实例加锁
② 修饰静态方法,相当于是给类加锁
③ 修饰代码块,需要指定加锁对象,对给定对象加锁
① 修饰实例方法
class Visitor{
public synchronized void visit(){ // 修饰实例方法
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"正在访问,将持续1秒");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); //线程休眠1秒
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("1秒结束了,"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"执行结束");
}
}
public class TestLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Visitor visitor = new Visitor(); //生成一个Visitor实例
new Thread(()->{
visitor.visit();
}, "线程1").start();
new Thread(()->{
visitor.visit();
},"线程2").start();
}
}

注意,上面只存在一个visitor实例,如果是下面这种写法,synchronized就不会起作用
public class TestLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Visitor visitor = new Visitor(); //生成一个Visitor实例
Visitor visitor1 = new Visitor(); //生成第二个Visitor实例
new Thread(()->{
visitor.visit();
}, "线程1").start();
new Thread(()->{
visitor1.visit();
},"线程2").start();
}
}

② 修饰静态方法
class Visitor{
public static synchronized void staticVisit(){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"正在访问,将持续1秒");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); //线程休眠1秒
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("1秒结束了,"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"执行结束");
}
}
public class TestLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(()->{
Visitor.staticVisit();
}, "线程1").start();
new Thread(()->{
Visitor.staticVisit();
},"线程2").start();
}
}

下面这种写法,和①不同,调用两个不同实例对象的方法synchronized也会起作用,这就是因为静态方法是给类加锁,而至于多少个实例对象,也只有一个Class
public class TestLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Visitor visitor = new Visitor();
Visitor visitor1 = new Visitor();
new Thread(()->{
visitor.staticVisit();
}, "线程1").start();
new Thread(()->{
visitor1.staticVisit();
},"线程2").start();
}
}
③ 修饰代码块
class Visitor{
public void testVisit(Visitor visitor){
if(visitor!=null){ // 如果传入了Visitor的实例化对象
synchronized (visitor){ // 给实例化对象上锁
System.out.println("此时synchronized锁定的是类的实例化对象");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"正在执行");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"正在休眠1秒种");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"执行结束");
System.out.println("======");
}
}
else {
synchronized (Visitor.class){ //给类上锁
System.out.println("此时synchronized锁定的是类");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"正在执行");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"正在休眠1秒种");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"执行结束");
System.out.println("======");
}
}
}
}
public class TestLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Visitor visitor = new Visitor();
// Visitor visitor1 = new Visitor();
new Thread(()->{
Visitor.testVisit(visitor);
},"线程1").start();
new Thread(()->{
Visitor.testVisit(visitor);
},"线程2").start();
}
}
public class TestLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Visitor visitor = new Visitor();
Visitor visitor1 = new Visitor();
new Thread(()->{
visitor.testVisit(null);
},"线程1").start();
new Thread(()->{
visitor1.testVisit(null);
},"线程2").start();
}
}

(2) synchronized加锁方式中断线程的方法
java提供的中断线程的方法
public void Thread.interrupt();//中断线程
public boolean Thread.isInterrupted();//判断线程是否被中断
public static boolean Thread.interrupted();//判断是否被中断并清除当前中断状态(静态方法)
interrupt() 方法的使用
interrupt()其实并没有终止线程,只是将线程的中断标记位设置为了true
如果想让线程停止执行任务,可以在重写run方法中用循环判断中断标记位,如下示例
public class MyThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
int i=0;
while(!isInterrupted()){
i++;
System.out.println(i+"---myThread is running");
}
System.out.println("线程任务结束");
}
}
public class TestThread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread myThread = new MyThread();
myThread.start();
System.out.println(myThread.getState());//打印线程的状态
myThread.interrupt(); //中断线程(将中断标记位设为true)
System.out.println(myThread.isInterrupted()); //打印标记位
System.out.println(myThread.getState()); //打印中断后的状态
}
}

2. Lock接口(显式锁)
Lock接口和synchronized类似,都是为了实现线程同步而存在的锁,不过Lock需要手动加锁和释放
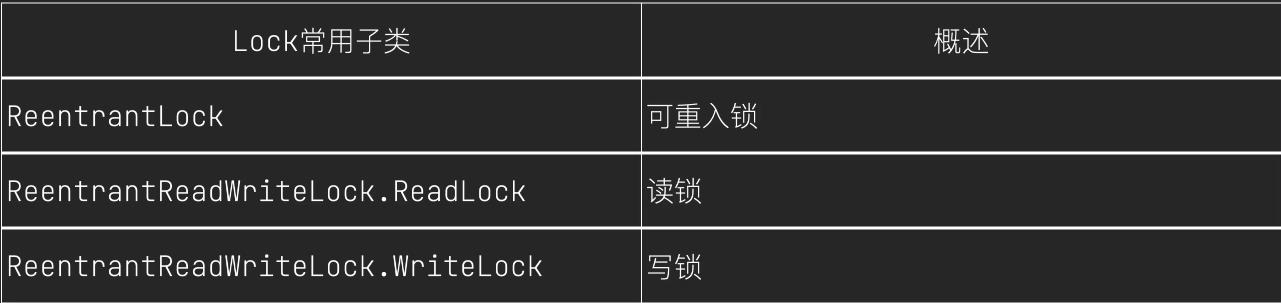
(1) Lock接口的常用实现类
(2) Lock接口的方法
| 方法名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| void lock() | 获取锁 |
| void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException | 可中断获取锁,会响应interrupt()方法并抛出异常 |
| boolean tryLock() | 尝试非阻塞的获取锁,获取成功返回true,否则返回true |
| boolean tryLock(long time,TimeUnit unit) hrows InterruptedException | 设置获取锁的超时时间,获取成功返回true,被中断或时间结束返回false |
| void unlock() | 释放锁 |
| Condition newCondition() | 生成一个Condition对象,用于实现Lock锁的等待唤醒机制 |
(3) Condition 接口
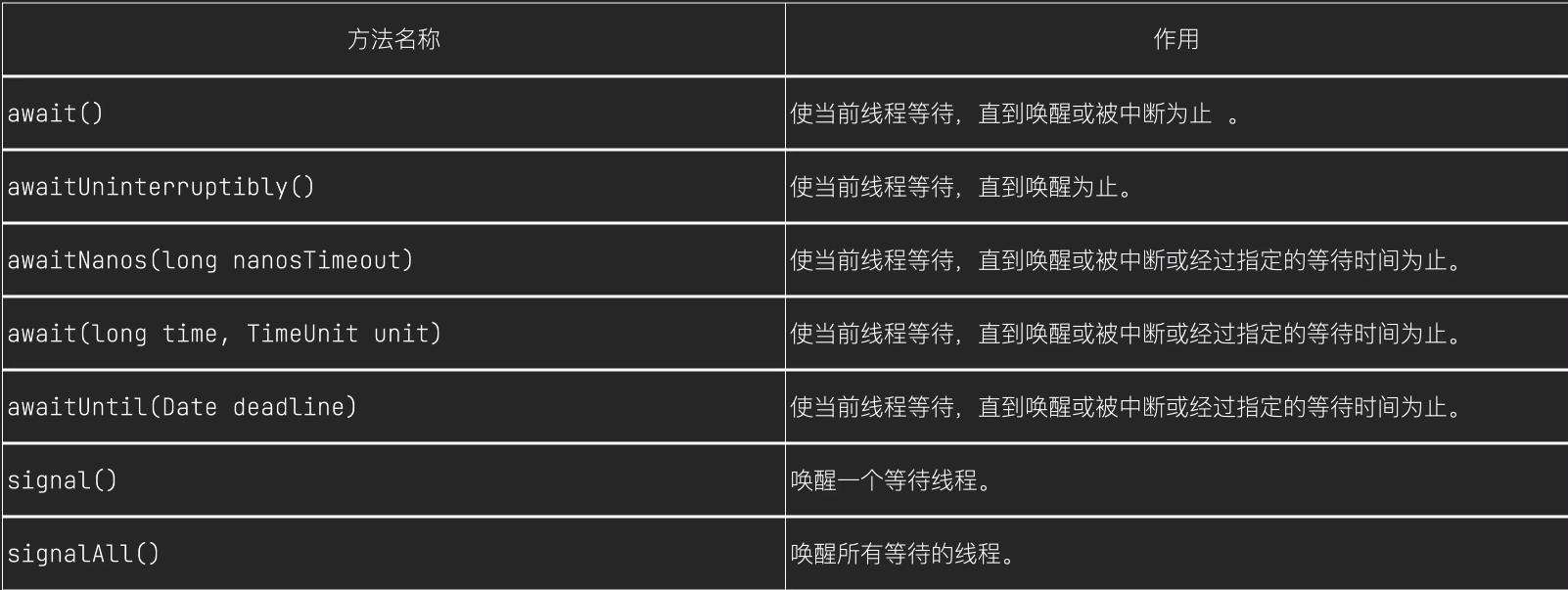
Condition接口提供了类似Object的监视器方法,与Lock配合可以实现等待唤醒机制
Condition 接口的方法
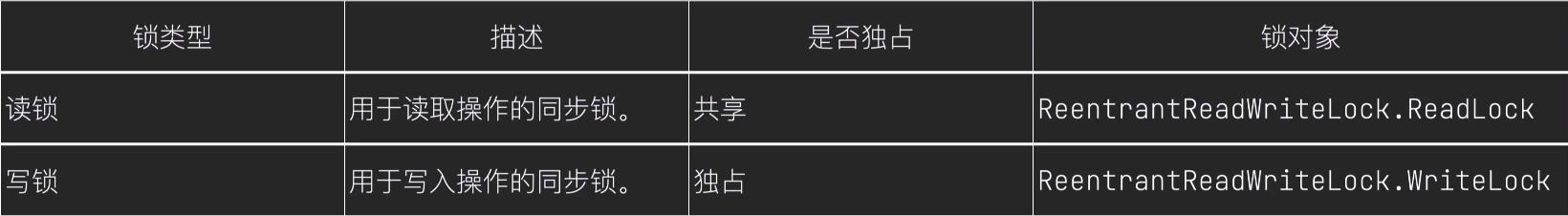
(4) 读写锁
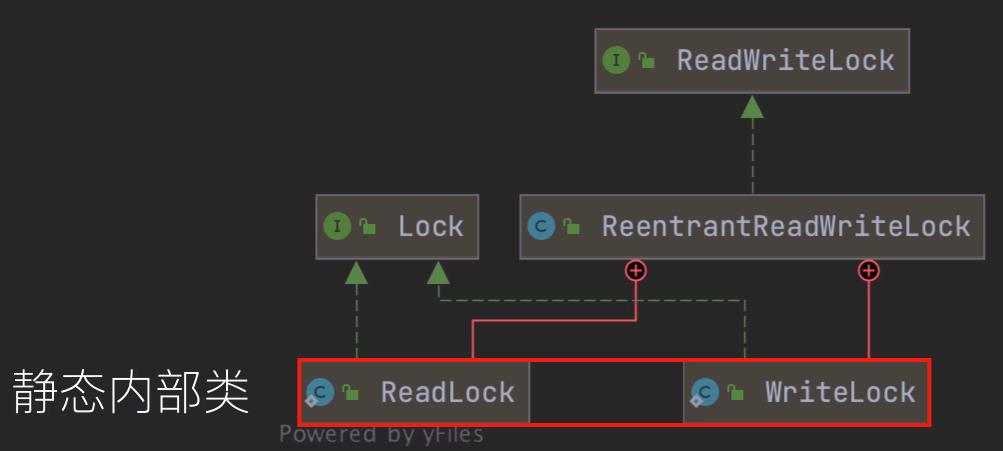
读写锁的UML类图
ReadWriteLock是独立于Lock的一个接口,ReentreantReadWriteLock是该接口的实现类,ReadLock(读锁)、WriteLock(写锁)是该实现类的静态内部类,且都实现了Lock接口
读写锁的使用示例
class Visitor{
//读锁和写锁都需要从ReentrantReadWriteLock对象中获取
private ReadWriteLock readWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock(true);
public Lock readLock = readWriteLock.readLock(); //获得写锁
public Lock writeLock = readWriteLock.writeLock(); //获得读锁
public void readVisit(){ //使用读锁执行任务
this.readLock.lock(); //添加读锁
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"获得了读锁,开始执行任务,且马上休眠1秒");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
this.readLock.unlock();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"任务结束,释放了读锁");
}
}
public void writeVisit(){ //使用写锁执行任务
this.writeLock.lock(); //添加写锁
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"获得了写锁,开始执行任务,且马上休眠1秒");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
this.writeLock.unlock();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"任务结束,释放了写锁");
}
}
}
public class TestLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Visitor visitor = new Visitor();
new Thread(()->{
visitor.readVisit();
},"线程1").start();
new Thread(()->{
visitor.readVisit();
},"线程2").start();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
new Thread(()->{
visitor.writeVisit();
},"线程3").start();
new Thread(()->{
visitor.writeVisit();
},"线程4").start();
}
}

从结果可以看出,读锁可以共享(同步完成任务),而写锁不能共享
3. ReentrantLock(重入锁)
ReentrantLock是Lock(显式锁)接口下的一个实现类,也是使用频率最高的锁
补充:JUC工具包
Lock是JUC工具包java.util.concurrent里的接口,JUC也称为Java并发编程工具包,是Java 官方提供的一套专门用来处理并发编程的工具集合(接口+类)
(1) 使用ReentrantLock实现线程同步
public class TestLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Account account = new Account();
new Thread(()->{
account.visit();
},"线程1").start();
new Thread(()->{
account.visit();
},"线程2").start();