基于梯度方向极化变换和聚类算法的图像主特征直线检测
Posted 踟蹰横渡口,彳亍上滩舟。
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了基于梯度方向极化变换和聚类算法的图像主特征直线检测相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
基于梯度方向、极化变换和聚类算法的图像主特征直线检测
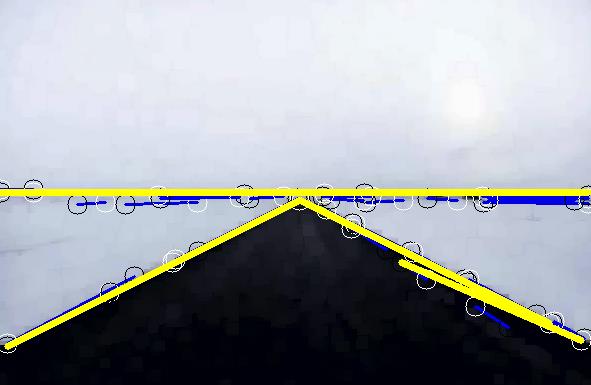
基于机器学习和图像处理的直线检测
代码主要思路:
1)借助类LSD直线检测,提取图像各个方向梯度;
2)对像素中的各个梯度方向做极化变换;
3)对计划变换后的结果进行聚类运算;
4)对聚类运算结果,选取topK,进行极化反变换;
5)对结果进行腐蚀+膨胀+滤波,进行结果整合;
6)可根据图像的长度、斜率等进行配置筛选和去重。
代码结果以及下载地址:下载地址
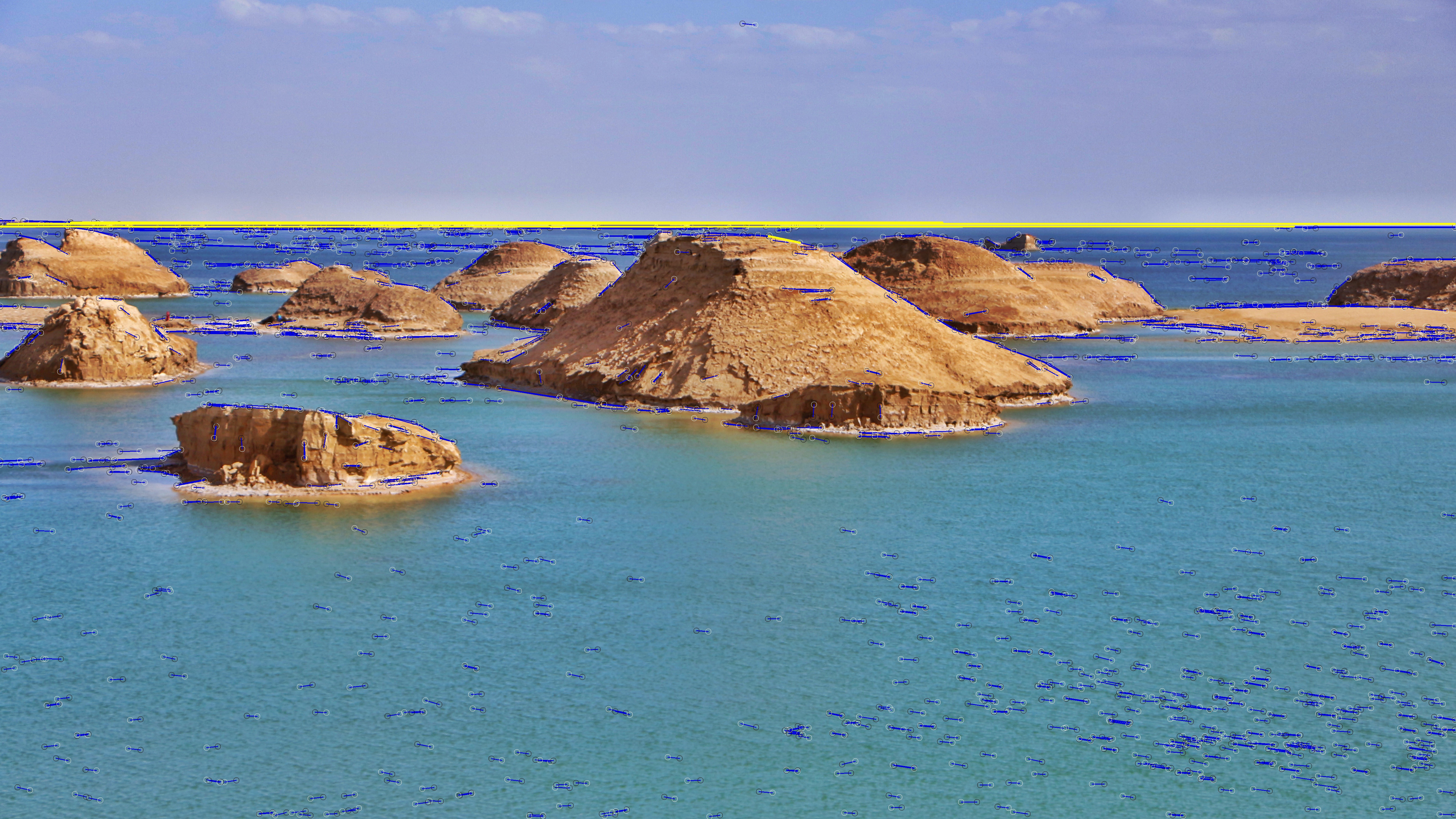
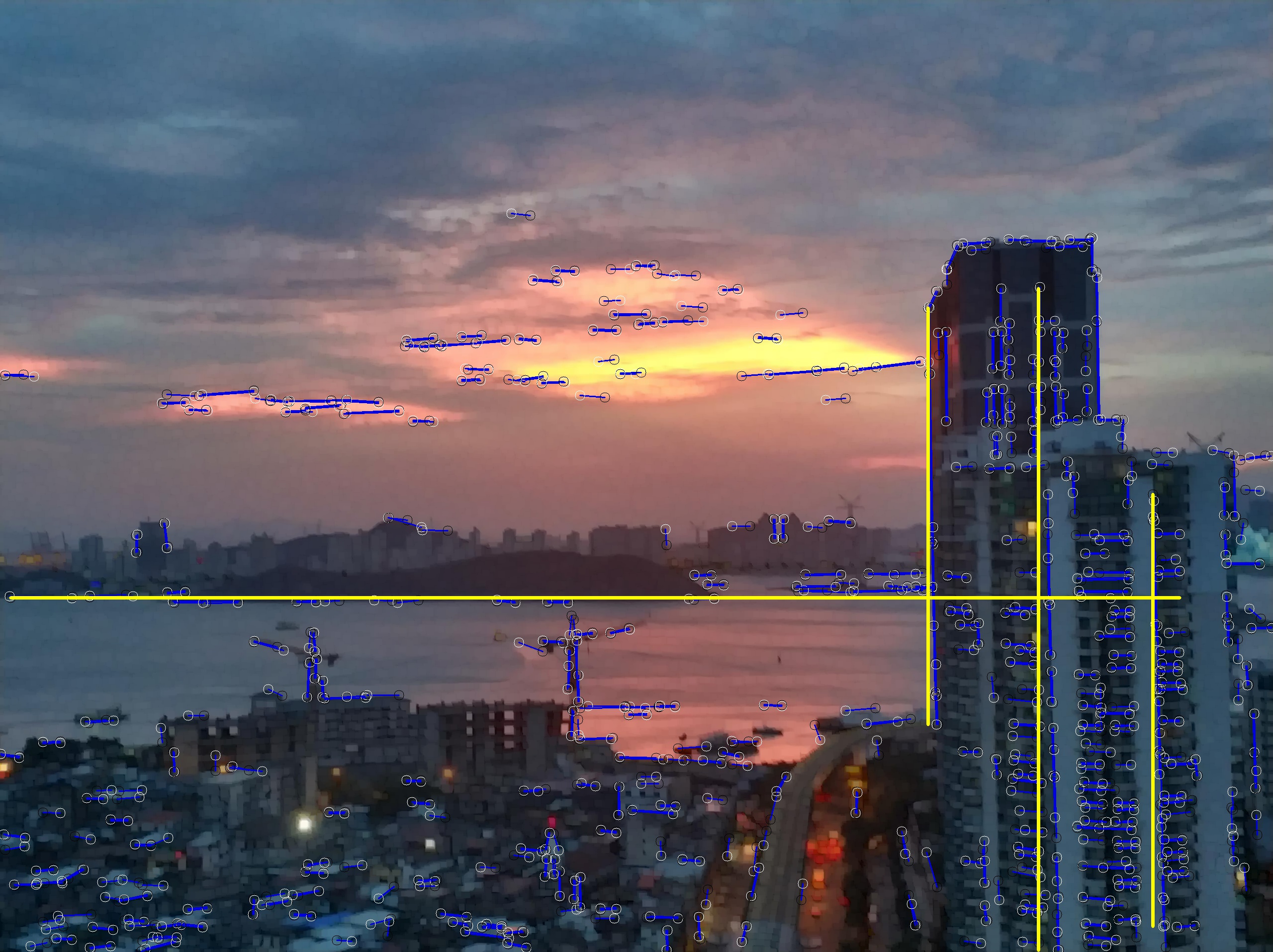
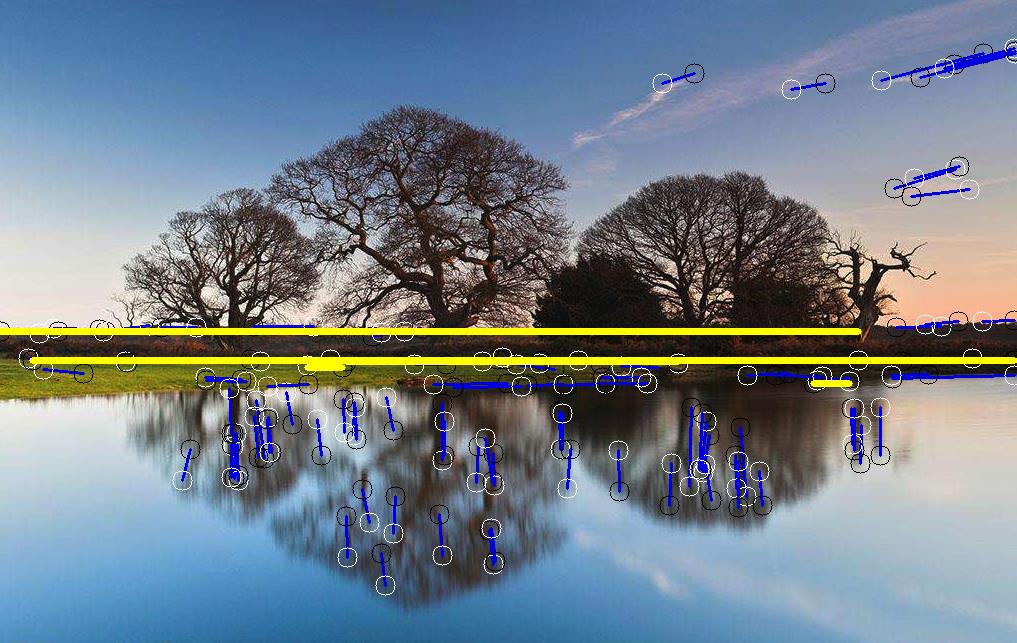
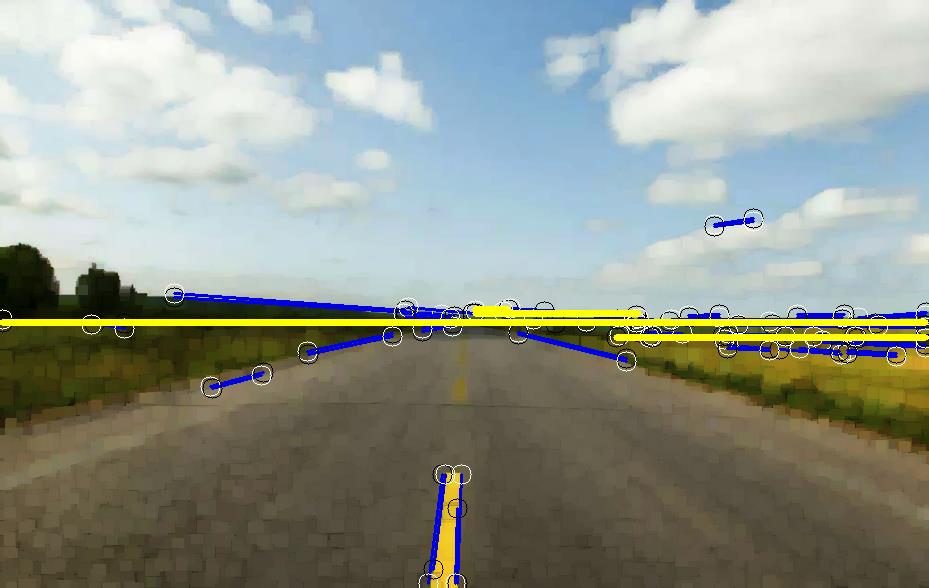





主函数代码
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include "lsd.h"
#include <fstream>
#include <math.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <Cstring>
#include <io.h>
#include<numeric>
#define PI 3.1415926
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
typedef struct {
image_double imgDouble;
Mat imgSrc, imgPro;
}imageInfo;
void listFiles(const char * dir);
imageInfo imageProcess(char * DIR, double scale);
int lineLengthThreshold(ntuple_list LS, double scale);
vector<float> getPolarLine(vector<float> p);
void connectLine(Mat imgPlot, vector<float> decarTopX0, vector<float> decarTopY0,
vector<float> decarTopX1, vector<float> decarTopY1);
void HighPassFilterSobel(const Mat& image, Mat& result);
void main()
{
//生成图像索引
char dir[20] = "images\\\\";
listFiles(dir);
ifstream imageIndex;
imageIndex.open("imageIndex.txt");
const int LINE = 200;
char str[LINE];
while (imageIndex.getline(str, LINE)) {
char DIR[260] = "images\\\\";
strcat_s(DIR, str);
double scale = 0.8;
imageInfo imgInfo = imageProcess(DIR, scale);
image_double image = imgInfo.imgDouble;
Mat img = imgInfo.imgPro;
Mat imgPlot = imgInfo.imgSrc;
imshow("imgPlot", imgPlot);
ntuple_list ls0 = lsd(image);
cout << "ls0->size:" << ls0->size << endl;
int binNum = 60;
vector<double> disNum(binNum, 0);
double binLength = img.rows / binNum;
//设置直线筛选长度
int lineThreshold = lineLengthThreshold(ls0, scale);
cout << "lineThreshold:" << lineThreshold << endl;
//将笛卡尔坐标系点转到极坐标系
vector<float> polarR, polarTheta, decarPointLocX0,
decarPointLocY0, decarPointLocX1, decarPointLocY1;
vector<float> indexStep;//记录累加的步长
for (int i = 0; i < ls0->size; i++) {
ls0->values[5 * i + 0] = (int)(ls0->values[5 * i + 0] / scale);
ls0->values[5 * i + 1] = (int)(ls0->values[5 * i + 1] / scale);
ls0->values[5 * i + 2] = (int)(ls0->values[5 * i + 2] / scale);
ls0->values[5 * i + 3] = (int)(ls0->values[5 * i + 3] / scale);
int x0 = ls0->values[5 * i + 0];
int y0 = ls0->values[5 * i + 1];
int x1 = ls0->values[5 * i + 2];
int y1 = ls0->values[5 * i + 3];
//线长筛选并记录
float lineLength = sqrt((x1 - x0)*(x1 - x0) + (y1 - y0)*(y1 - y0));
if (lineLength < lineThreshold) {
continue;
}
//边缘筛选
int xTemp = img.cols - 10;
int yTemp = img.rows - 10;
if ((x0 < 10 && x1 < 10) || (x0 > xTemp && x1 > xTemp) || (y0 < 10 && y1 < 10) || (y0 > yTemp && y1 > yTemp)) {
continue;
}
Point pp0 = Point(x0, y0);
Point pp1 = Point(x1, y1);
line(img, pp0, pp1, Scalar(225, 0, 0), 2, 4);
circle(img, pp0, 10, Scalar(0, 0, 0));
circle(img, pp1, 10, Scalar(255, 255, 255));
float tempIndexStep = lineLength / lineThreshold;
//cout << "indexStep:" << tempIndexStep << endl;
indexStep.push_back(tempIndexStep);
decarPointLocX0.push_back(x0);
decarPointLocY0.push_back(y0);
decarPointLocX1.push_back(x1);
decarPointLocY1.push_back(y1);
//统一坐标系并记录
vector<float> decarPoint;
int x0Point = x0 - img.cols / 2;
int y0Point = img.rows / 2 - y0;
int x1Point = x1 - img.cols / 2;
int y1Point = img.rows / 2 - y1;
decarPoint.push_back(x0Point);
decarPoint.push_back(y0Point);
decarPoint.push_back(x1Point);
decarPoint.push_back(y1Point);
//获取极坐标并记录
vector<float> polarPoint = getPolarLine(decarPoint);
polarR.push_back(polarPoint[0]);
polarTheta.push_back(polarPoint[1]);
}
float rThreshold = 15;
float thetaThreshold = 0.1;
//寻找各个值的聚类统计数量
int totalLine = polarR.size();
cout << "totalLine:" << totalLine << endl;
vector<float> index(totalLine, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < totalLine; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < totalLine; j++) {
if (i == j) {
continue;
}
float subpolarR = abs(polarR[i] - polarR[j]);
float subpolarTheta = abs(polarTheta[i] - polarTheta[j]);
if (subpolarR < rThreshold && subpolarTheta < thetaThreshold) {
if (indexStep[j] != 0)
index[i] = index[i] + indexStep[j];
else
index[i]++;
}
}
}
//寻找聚类区域最多的点的索引TOP1
vector<float>::iterator maxIndex = max_element(index.begin(), index.end());
cout << "------------------------------" << endl;
cout << "max:" << *maxIndex << endl;
int maxInd = distance(index.begin(), maxIndex);
cout << "maxInd:" << maxInd << endl;
//存储聚类最多点的坐标并画线TOP1
vector<float> decarTop1X0, decarTop1Y0, decarTop1X1, decarTop1Y1;
vector<int> setLabel(totalLine, 0);//0:该点未使用;1:该点已使用
for (int i = 0; i < totalLine; i++) {
float subpolarR = abs(polarR[i] - polarR[maxInd]);
float subpolarTheta = abs(polarTheta[i] - polarTheta[maxInd]);
if (subpolarR < rThreshold && subpolarTheta < thetaThreshold) {
decarTop1X0.push_back(decarPointLocX0[i]);
decarTop1Y0.push_back(decarPointLocY0[i]);
decarTop1X1.push_back(decarPointLocX1[i]);
decarTop1Y1.push_back(decarPointLocY1[i]);
setLabel[i] = 1;
Point pp0 = Point(decarPointLocX0[i], decarPointLocY0[i]);
Point pp1 = Point(decarPointLocX1[i], decarPointLocY1[i]);
//line(imgPlot, pp0, pp1, Scalar(255, 0, 0), 3, 4);
}
}
connectLine(imgPlot, decarTop1X0, decarTop1Y0, decarTop1X1, decarTop1Y1);
//寻找聚类区域第二多的点的索引TOP2
int usedPointTop2 = 0;
vector<float> secondIndex(totalLine, 0);//剔除第一大的元素后的存储位置
for (int i = 0; i < totalLine; i++) {
if (setLabel[i] == 0) {
secondIndex[i] = index[i];
usedPointTop2++;
}
else
secondIndex[i] = 0;
//cout << secondIndex[i] << "-";
}
if (usedPointTop2 < 4) {
continue;
}
//cout << endl;
vector<float>::iterator secondMaxIndex = max_element(secondIndex.begin(), secondIndex.end());
cout << "------------------------------" << endl;
cout << "secondMax:" << *secondMaxIndex << endl;
int secondMaxInd = distance(secondIndex.begin(), secondMaxIndex);
cout << "secondMaxInd:" << secondMaxInd << endl;
//存储聚类第二多点的坐标并画线TOP2
vector<float> decarTop2X0, decarTop2Y0, decarTop2X1, decarTop2Y1;
for (int i = 0; i < totalLine; i++) {
float subpolarR = abs(polarR[i] - polarR[secondMaxInd]);
float subpolarTheta = abs(polarTheta[i] - polarTheta[secondMaxInd]);
if (subpolarR < rThreshold && subpolarTheta < thetaThreshold && setLabel[i] == 0) {
decarTop2X0.push_back(decarPointLocX0[i]);
decarTop2Y0.push_back(decarPointLocY0[i]);
decarTop2X1.push_back(decarPointLocX1[i]);
decarTop2Y1.push_back(decarPointLocY1[i]);
Point pp0 = Point(decarPointLocX0[i], decarPointLocY0[i]);
Point pp1 = Point(decarPointLocX1[i], decarPointLocY1[i]);
setLabel[i] = 1;
//line(imgPlot, pp0, pp1, Scalar(0, 255, 0), 3, 4);
}
}
connectLine(imgPlot, decarTop2X0, decarTop2Y0, decarTop2X1, decarTop2Y1);
//寻找聚类区域第三多的点的索引TOP3
int usedPointTop3 = 0;
vector<float> thirdIndex(totalLine, 0);//剔除第一大和第二大的元素后的存储位置
for (int i = 0; i < totalLine; i++) {
if (setLabel[i] == 0) {
thirdIndex[i] = secondIndex[i];
usedPointTop3++;
}
else
thirdIndex[i] = 0;
//cout << thirdIndex[i] << "-";
}
//cout << endl;
if (usedPointTop3 < 4) {
continue;
}
vector<float>::iterator thirdMaxIndex = max_element(thirdIndex.begin(), thirdIndex.end());
cout << "------------------------------" << endl;
cout << "thirdMax:" << *thirdMaxIndex << endl;
int thirdMaxInd = distance(thirdIndex.begin(), thirdMaxIndex);
cout << "thirdMaxInd:" << thirdMaxInd << endl;
//存储聚类第三多点的坐标并画线TOP3
vector<float> decarTop3X0, decarTop3Y0, decarTop3X1, decarTop3Y1;
for (int i = 0; i < totalLine; i++) {
float subpolarR = abs(polarR[i] - polarR[thirdMaxInd]);
float subpolarTheta = abs(polarTheta[i] - polarTheta[thirdMaxInd]);
if (subpolarR < rThreshold && subpolarTheta < thetaThreshold && setLabel[i] == 0) {
decarTop3X0.push_back(decarPointLocX0[i]);
decarTop3Y0.push_back(decarPointLocY0[i]);
decarTop3X1.push_back(decarPointLocX1[i]);
decarTop3Y1.push_back(decarPointLocY1[i]);
Point pp0 = Point(decarPointLocX0[i], decarPointLocY0[i]);
Point pp1 = Point(decarPointLocX1[i], decarPointLocY1[i]);
setLabel[i] = 1;
//line(imgPlot, pp0, pp1, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 3, 4);
}
}
connectLine(imgPlot, decarTop3X0, decarTop3Y0, decarTop3X1, decarTop3Y1);
//寻找聚类区域第四多的点的索引TOP4
int usedPointTop4 = 0;
vector<float> fourthIndex(totalLine, 0);//剔除第一大的元素后的存储位置
for (int i = 0; i < t以上是关于基于梯度方向极化变换和聚类算法的图像主特征直线检测的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章