网络编程--03NIO
Posted Anrys
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了网络编程--03NIO相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
网络编程--03 NIO
4.NIO
4.1概述
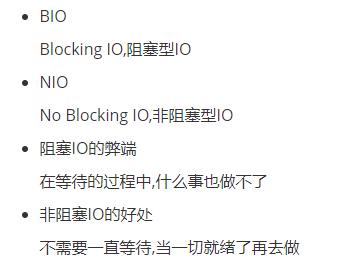
4.2NIO与BIO的区别
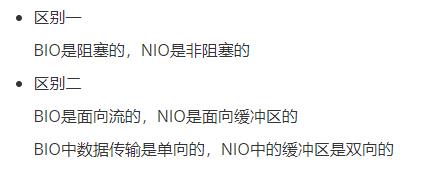
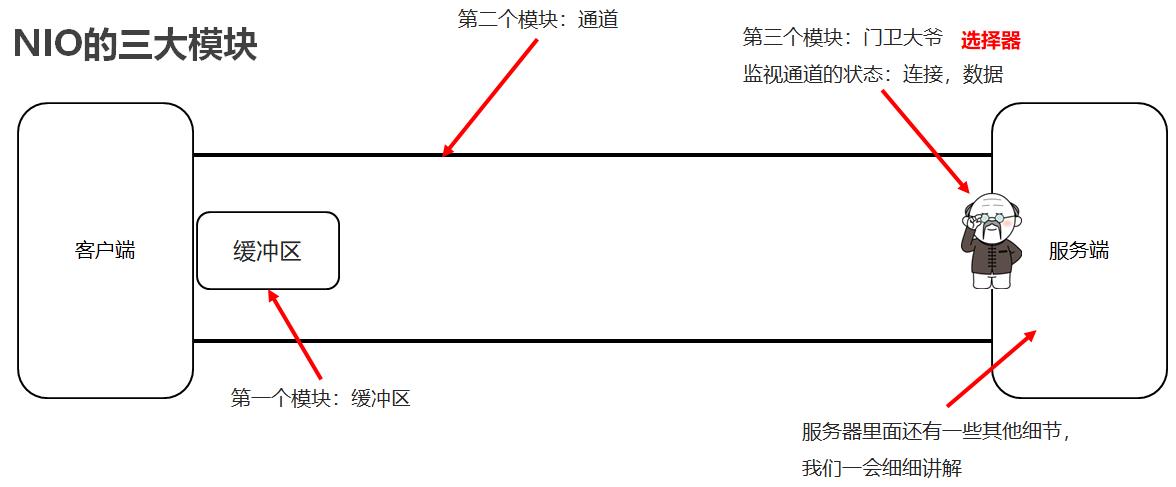
4.3NIO三大模块

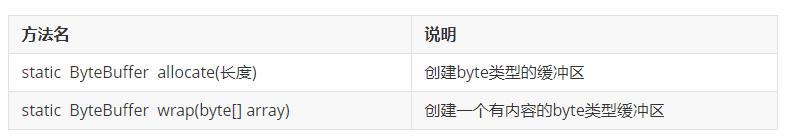
4.4 NIO创建缓冲区对象
方法介绍:
代码:
public class CreateByteBufferDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//method1();
//method2();
ByteBuffer wrap = ByteBuffer.wrap("aaa".getBytes());
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
System.out.println(wrap.get());
}
}
private static void method2() {
byte [] bytes = {97,98,99};
ByteBuffer byteBuffer2 = ByteBuffer.wrap(bytes);
//缓冲区的长度3
//缓冲区里面的内容就是字节数组的内容.
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
System.out.println(byteBuffer2.get());
}
System.out.println(byteBuffer2.get());
}
private static void method1() {
ByteBuffer byteBuffer1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(5);
//get
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println(byteBuffer1.get());
}
System.out.println(byteBuffer1.get());
}
}
4…5NIO缓冲区添加数据应用
方法介绍:
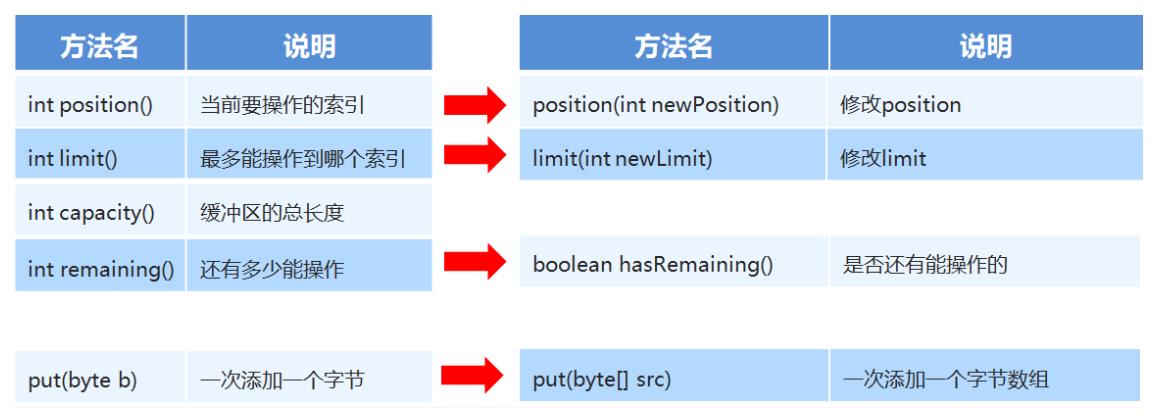
代码:
public class ByteBufferDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// int position() 当前要操作的索引
// int limit() 最多能操作到哪个索引
// int capacity() 缓冲区的总长度
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
System.out.println(byteBuffer.position());//0
System.out.println(byteBuffer.limit());//10
System.out.println(byteBuffer.capacity());//10
// put(byte b) 一次添加一个字节
// byteBuffer.put((byte) 97);
// System.out.println(byteBuffer.position());
// System.out.println(byteBuffer.limit());
// System.out.println(byteBuffer.capacity());
// put(byte[] src) 一次添加一个字节数组
// byteBuffer.put("aaa".getBytes());
// System.out.println(byteBuffer.position());//3
// System.out.println(byteBuffer.limit());//10
// System.out.println(byteBuffer.capacity());//10
// position(int newPosition) 修改position
// byteBuffer.position(1);
// limit(int newLimit) 修改limit
// byteBuffer.limit(5);
// System.out.println(byteBuffer.position());
// System.out.println(byteBuffer.limit());
// System.out.println(byteBuffer.capacity());
// int remaining() 还有多少能操作
// boolean hasRemaining() 是否还有能操作的
byteBuffer.put("0123456789".getBytes());
System.out.println(byteBuffer.remaining());
System.out.println(byteBuffer.hasRemaining());
}
}
4.6缓冲区获取数据
方法介绍:
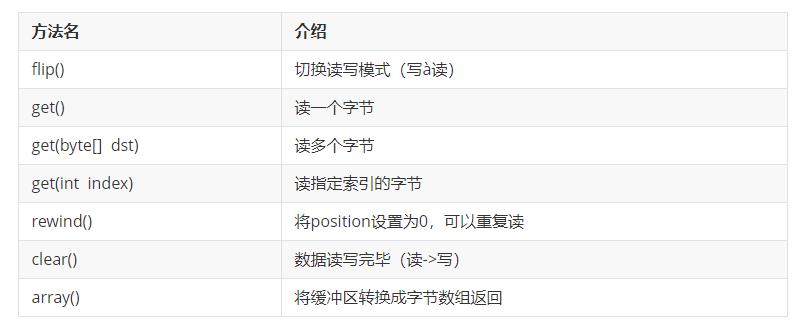
代码示例:
public class ByteBufferDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
byteBuffer.put("abc".getBytes());
// flip() 切换读写模式(写读)
byteBuffer.flip();
// get() 读一个字节
// while(byteBuffer.limit() != byteBuffer.position()){
// System.out.println((char) byteBuffer.get());
// }
for (int i = 0; i < byteBuffer.limit(); i++) {
System.out.println((char) byteBuffer.get());
}
// get(byte[] dst) 读多个字节
// byte [] bytes = new byte[byteBuffer.limit()];
// byteBuffer.get(bytes);
// System.out.println(new String(bytes));
// get(int index) 读指定索引的字节
// System.out.println((char) byteBuffer.get(0));
// rewind() 将position设置为0,可以重复读
// byteBuffer.rewind();
// for (int i = 0; i < byteBuffer.limit(); i++) {
// System.out.println((char) byteBuffer.get());
// }
// clear() 数据读写完毕(读->写)
byteBuffer.clear();
byteBuffer.put("qqq".getBytes());
// array() 将缓冲区转换成字节数组返回
byte[] bytes = byteBuffer.array();
System.out.println(new String(bytes));
}
}
4.7 小结

4.8NIO通道客户端实现

代码:
public class NIOClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.打开通道
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
//2.指定IP和端口号
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",10000));
//3.写出数据
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap("一点寒毛先制".getBytes());
socketChannel.write(byteBuffer);
//4.释放资源
socketChannel.close();
}
}
4.9 NIO通道服务端

代码:
public class Nioserver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1.打开一个服务端通道
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
// 2.绑定对应的端口号
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(10000));
// 3.通道默认是阻塞的,需要设置为非阻塞
//如果传递true 表示通道设置为阻塞通道...默认值
//如果传递false 表示通道设置为非阻塞通道
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 4.此时没有门卫大爷,所以需要经常看一下有没有连接发过来没?
while (true) {
// 5.如果有客户端来连接了,则在服务端通道内部,再创建一个客户端通道,相当于是客户端通道的延伸
//此时已经设置了通道为非阻塞
//所以在调用方法的时候,如果有客户端来连接,那么会创建一个SocketChannel对象.
//如果在调用方法的时候,没有客户端来连接,那么他会返回一个null
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
//System.out.println(socketChannel);
if(socketChannel != null){
// 6.客户端将缓冲区通过通道传递给服务端,就到了这个延伸通道socketChannel里面
// 7.服务端创建一个空的缓冲区装数据并输出
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//获取传递过来的数据,并把他们放到byteBuffer缓冲区中.
//返回值:
//正数: 表示本次读到的有效字节个数.
//0 : 表示本次没有读到有效字节.
//-1 : 表示读到了末尾
int len = socketChannel.read(byteBuffer);
System.out.println(new String(byteBuffer.array(),0,len));
//8.释放资源
socketChannel.close();
}
}
}
}
4.10 NIO通道练习

示例代码:
public class Clinet {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1.打开通道
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
// 2.指定IP和端口号
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",10000));
// 3.写出数据
ByteBuffer byteBuffer1 = ByteBuffer.wrap("吃俺老孙一棒棒".getBytes());
socketChannel.write(byteBuffer1);
// 手动写入结束标记
socketChannel.shutdownOutput();
System.out.println("数据已经写给服务器");
// 4.读取服务器写回的数据
ByteBuffer byteBuffer2 = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int len;
while((len = socketChannel.read(byteBuffer2)) != -1){
byteBuffer2.flip();
System.out.println(new String(byteBuffer2.array(),0,len));
byteBuffer2.clear();
}
// 5.释放资源
socketChannel.close();
}
}
服务端:

代码:
public class Sever {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1,打开一个服务端通道
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
// 2,绑定对应的端口号
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(10000));
// 3,通道默认是阻塞的,需要设置为非阻塞
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 4,此时没有门卫大爷,所以需要经常看一下有没有连接发过来没?
while(true){
// 5,如果有客户端来连接了,则在服务端通道内部,再创建一个客户端通道,相当于是客户端通道的延伸
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
if(socketChannel != null){
System.out.println("此时有客户端来连接了");
// 6,获取客户端传递过来的数据,并把数据放在byteBuffer1这个缓冲区中
ByteBuffer byteBuffer1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//socketChannel.read(byteBuffer1);
int len;
//针对于缓冲区来讲
//如果 从添加数据 ----> 获取数据 flip
//如果 从获取数据 ----> 添加数据 clear
while((len = socketChannel.read(byteBuffer1)) != -1){
byteBuffer1.flip();
System.out.println(new String(byteBuffer1.array(),0,len));
byteBuffer1.clear();
}
System.out.println("接收数据完毕,准备开始往客户端回写数据");
// 7,给客户端回写数据
ByteBuffer byteBuffer2 = ByteBuffer.wrap("哎哟,真疼啊!!!".getBytes());
socketChannel.write(byteBuffer2);
// 8,释放资源
socketChannel.close();
}
}
}
}
4.11NIO通道练习优化

代码:
// 客户端
public class Clinet {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",10000));
ByteBuffer byteBuffer1 = ByteBuffer.wrap("吃俺老孙一棒棒".getBytes());
socketChannel.write(byteBuffer1);
System.out.println("数据已经写给服务器");
ByteBuffer byteBuffer2 = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int len;
while((len = socketChannel.read(byteBuffer2)) != -1){
System.out.println("客户端接收回写数据");
byteBuffer2.flip();
System.out.println(new String(byteBuffer2.array(),0,len));
byteBuffer2.clear();
}
socketChannel.close();
}
}
// 服务端
public class Sever {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(10000));
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
while(true){
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
if(socketChannel != null){
System.out.println("此时有客户端来连接了");
// 将服务端内部获取的客户端通道设置为非阻塞的
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//获取客户端传递过来的数据,并把数据放在byteBuffer1这个缓冲区中
ByteBuffer byteBuffer1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//socketChannel.read(byteBuffer1);
int len;
//针对于缓冲区来讲
//如果 从添加数据 ----> 获取数据 flip
//如果 从获取数据 ----> 添加数据 clear
while((len = socketChannel.read(byteBuffer1)) > 0){
System.out.println("服务端接收发送数据");
byteBuffer1.flip();
System.out.println(new String(byteBuffer1.array(),0,len));
byteBuffer1.clear();
}
System.out.println("接收数据完毕,准备开始往客户端回写数据");
ByteBuffer byteBuffer2 = ByteBuffer.wrap("哎哟,真疼啊!!!".getBytes());
socketChannel.write(byteBuffer2);
socketChannel.close();
}
}
}
}
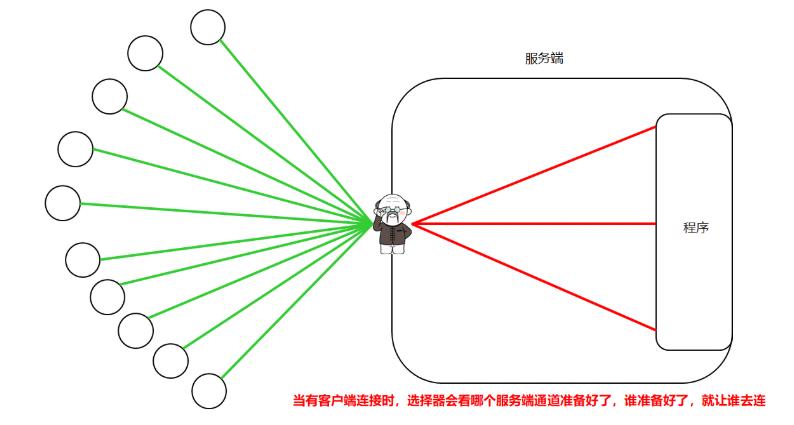
4.12 NIO选择器
选择器可以监视通道的状态,多路复用
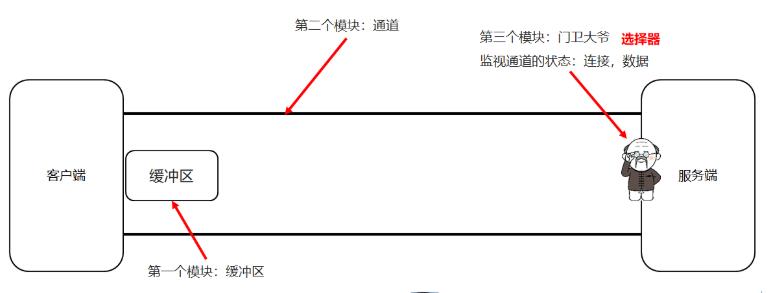
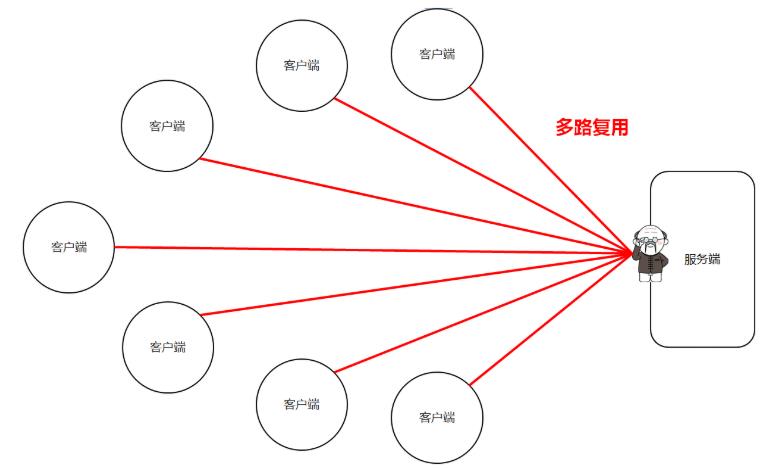

4.13 NIO选择器改写服务端

// 客户端
public class Clinet {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",10000));
ByteBuffer byteBuffer1 = ByteBuffer.wrap("吃俺老孙一棒棒".getBytes());
socketChannel.write(byteBuffer1);
System.out.println("数据已经写给服务器");
ByteBuffer byteBuffer2 = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int len;
while((len = socketChannel.read(byteBuffer2)) != -1){
System.out.println("客户端接收回写数据");
byteBuffer2.flip();
System.out.println(new String(byteBuffer2.array(),0以上是关于网络编程--03NIO的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章