JavaScript数据结构与算法 - 树
Posted 友人A ㅤ
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了JavaScript数据结构与算法 - 树相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. 树数据结构
- 树是一种分层数据的抽象模型
- 树是一种非顺序的数据结构
- 树对于存储需要快速查找的数据非常有用
常见例子:如公司的组织架构图
树结构:
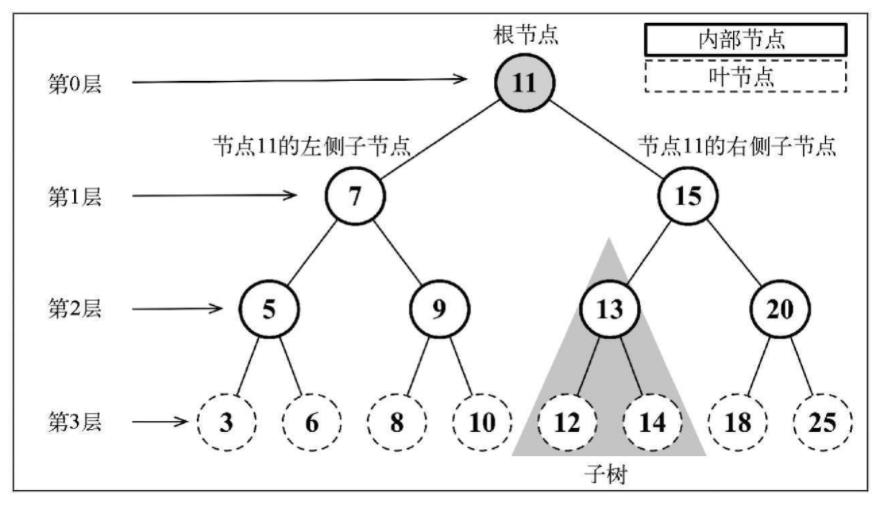
2. 二叉树和二叉搜索树
二叉树: 只能有左右两个子节点
二叉搜索树: 二叉树的一种,但是只允许在左侧节点存储(比父节点)小的值,在右侧节点存储(比父节点)大的值(如上面的图)
2.1 创建BinarySearchTree类
创建Node类来表示二叉搜索树中的每个节点:
class Node {
constructor(key) {
// 节点值,就是下图的键
this.key = key;
// 左侧子节点
this.left = null;
// 右侧子节点
this.right = null;
}
toString() {
return `${this.key}`;
}
}
组织方式:
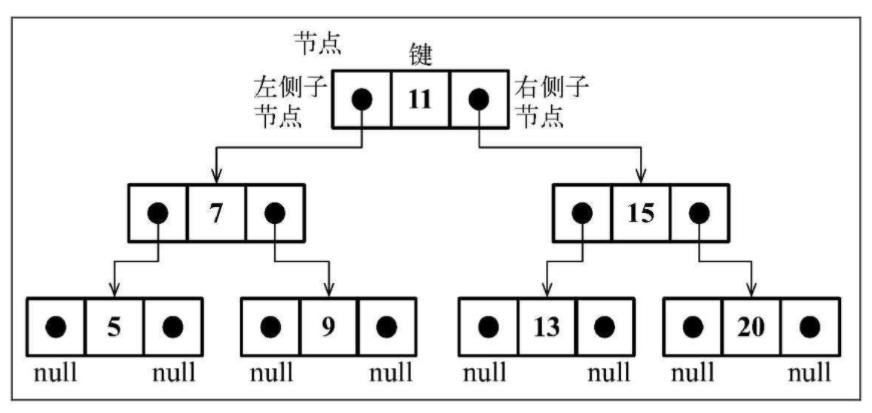
声明BinarySearchTree类的基本结构:
- 这里需要先引入Compare和defaultCompare方法;
const Compare = {
LESS_THAN: -1,
BIGGER_THAN: 1,
EQUALS: 0
};
function defaultCompare(a, b) {
if (a === b) {
return Compare.EQUALS;
}
return a < b ? Compare.LESS_THAN : Compare.BIGGER_THAN;
}
- 声明BinarySearchTree类的基本结构:
class BinarySearchTree {
constructor(compareFn = defaultCompare) {
// 用来比较节点值
this.compareFn = compareFn;
// Node类型的根节点
this.root = null;
}
}
常用方法:
- insert(key):向树中插入一个新的键
- search(key):在树中查找一个键。如果节点存在,则返回true;如果不存在,则返回false
- inOrderTraverse():通过中序遍历方式遍历所有节点
- preOrderTraverse():通过先序遍历方式遍历所有节点
- postOrderTraverse():通过后序遍历方式遍历所有节点
- min():返回树中最小的值/键
- max():返回树中最大的值/键
- remove(key):从树中移除某个键
3.2 向二叉搜索树中插入一个键
- 向树插入一个新键的算法的第一部分
insert(key) {
// 验证是否为特殊情况,即要插入的节点是不是第一个节点
if (this.root === null) {
// 创建一个Node类的实例并将它赋值给root属性来讲root指向新节点
this.root = new Node(key);
}
// 将节点添加到根节点以外的位置,需要借助辅助方法
else {
this.insertNode(this.root, key);
}
}
- 在节点添加到根节点以外的位置的辅助方法
insertNode(node, key) {
// 如果新节点的键小于当前节点的键,需要检查当前节点的左侧子节点
if (this.compareFn(key, node.key) === Compare.LESS_THAN) {
// 如果没有左侧子节点,就插入新节点
if (node.left == null) {
node.left = new Node(key);
}
// 如果有左侧子节点,就递归调用insertNode方法,继续找到树的下一层
else {
this.insertNode(node.left, key);
}
}
// 如果新节点的键大于当前节点的键
else {
// 如果没有右侧子节点,就插入新节点
if (node.right == null) {
node.right = new Node(key);
}
// 如果有右侧子节点,就递归调用insertNode方法,继续找到树的下一层
else {
this.insertNode(node.right, key);
}
}
}
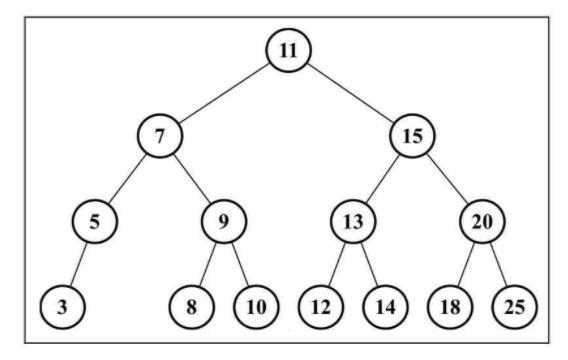
执行下面代码:
const tree = new BinarySearchTree();
tree.insert(11);
// 插入元素
tree.insert(7);
tree.insert(15);
tree.insert(5);
tree.insert(3);
tree.insert(9);
tree.insert(8);
tree.insert(10);
tree.insert(13);
tree.insert(12);
tree.insert(14);
tree.insert(20);
tree.insert(18);
tree.insert(25);
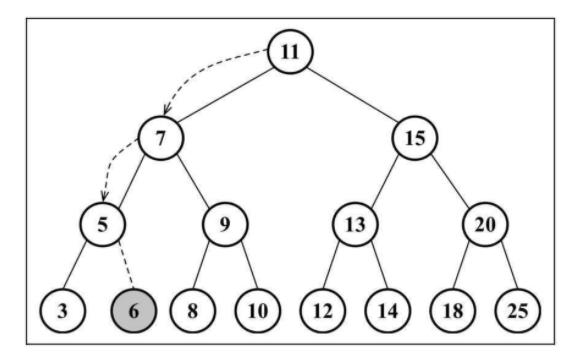
如果插入一个新元素6
tree.insert(6);
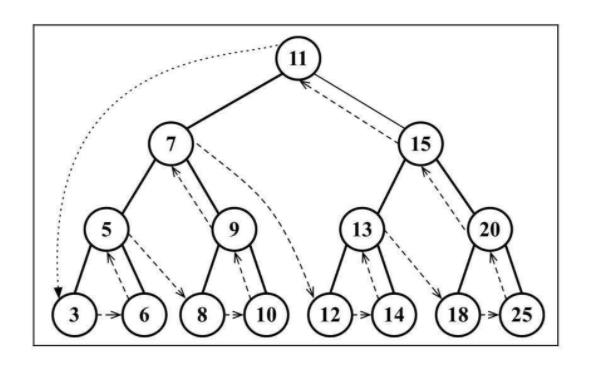
3. 树的遍历
访问树的三种方式:中序、先序和后序。
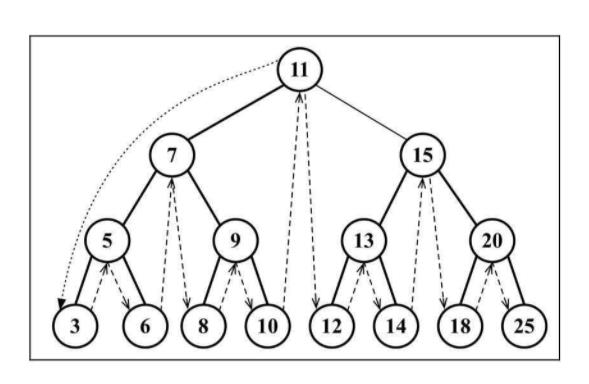
3.1 中序遍历
中序遍历是一种以上行顺序访问BST所有节点的遍历方式,也就是以从最小到最大的顺序访问所有节点。
inOrderTraverse(callback) {
// 接收一个节点和对应的回调函数作为参数
this.inOrderTraverseNode(this.root, callback);
}
inOrderTraverseNode(node, callback) {
// 先检查以参数形式传入的节点是否为null,这是停止递归继续执行的判断条件
if (node != null) {
// 调用相同的函数来访问左侧子节点
this.inOrderTraverseNode(node.left, callback);
// 对根节点进行操作
callback(node.key);
// 再访问右侧子节点
this.inOrderTraverseNode(node.right, callback);
}
}
执行方法:
const printNode = (value) => console.log(value);
tree.inOrderTraverse(printNode);
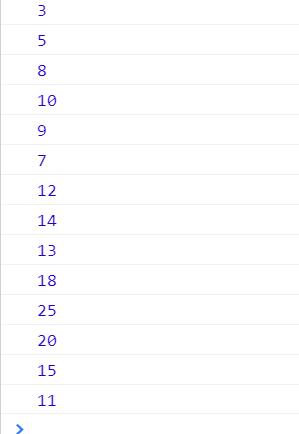
输出结果:
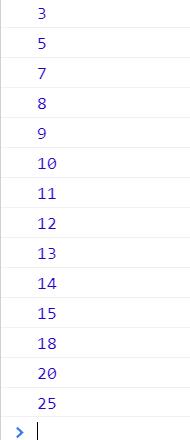
访问路径图:
3.2 先序遍历
先序遍历是以优先于后代节点的顺序访问每个节点的。先序遍历的一种应用是打印一个结构化的文档。
preOrderTraverse(callback) {
this.preOrderTraverseNode(this.root, callback);
}
preOrderTraverseNode(node, callback) {
if (node != null) {
// 先访问节点本身
callback(node.key);
// 再访问左侧节点
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.left, callback);
// 最后是右侧节点
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.right, callback);
}
}
输出结果:
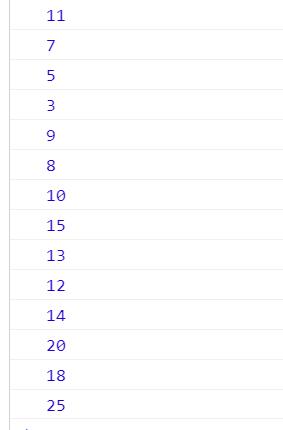
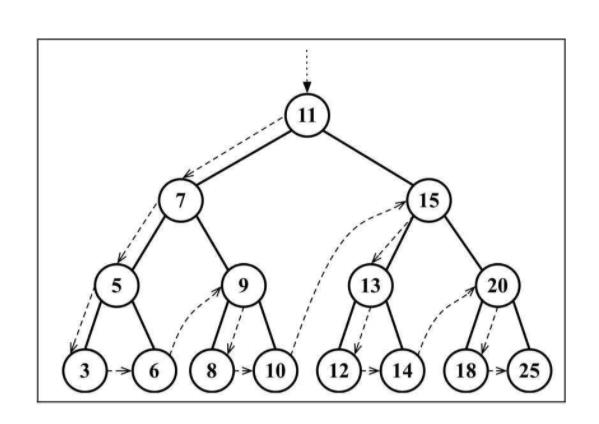
3.3 后序遍历
postOrderTraverse(callback) {
this.postOrderTraverseNode(this.root, callback);
}
postOrderTraverseNode(node, callback) {
if (node != null) {
// 先访问左侧子节点
this.postOrderTraverseNode(node.left, callback);
// 然后访问右侧子节点
this.postOrderTraverseNode(node.right, callback);
// 最后访问根节点
callback(node.key);
}
}
输出结果:
4. 搜索树中的值
4.1 搜索最小值和最大值
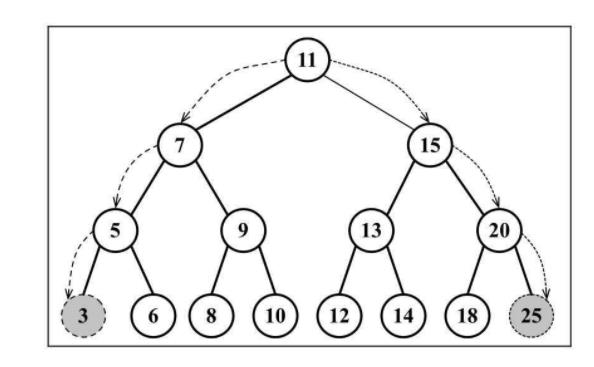
- 搜索最小值:
min() {
// 在调用minNode方法的时候传入树的根节点
return this.minNode(this.root);
}
minNode(node) {
let current = node;
// 遍历树的左边,直到找到树的最下层(最左端)
while (current != null && current.left != null) {
current = current.left;
}
return current;
}
- 搜索最大值:
max() {
return this.maxNode(this.root);
}
maxNode(node) {
let current = node;
// 沿着树的右边进行遍历,直到找到最右端的节点
while (current != null && current.right != null) {
current = current.right;
}
return current;
}
因此,对于寻找最小值,总是沿着树的左边;而对于寻找最大值,总是沿着树的右边。
4.2 搜索一个特定的值
search(key) {
return this.searchNode(this.root, key);
};
// 用来寻找一棵树或其任意子树中的一个特定的值
searchNode(node, key) {
// 检验传入的node是否合法
if (node == null) {
return false;
}
// 要找的键比当前的节点小,则继续在左侧的子树上搜索
if (this.compareFn(key, node.key) === Compare.LESS_THAN) {
return this.searchNode(node.left, key);
}
// 要找的键比当前的节点大,从右侧子节点开始继续搜索
else if (this.compareFn(key, node.key) === Compare.BIGGER_THAN) {
return this.searchNode(node.right, key);
}
// 要找的键和当前节点相等
else {
return true;
}
}
测试方法:
console.log(tree.search(1) ? 'found' : 'not found'); // not found
console.log(tree.search(8) ? 'found' : 'not found'); // found
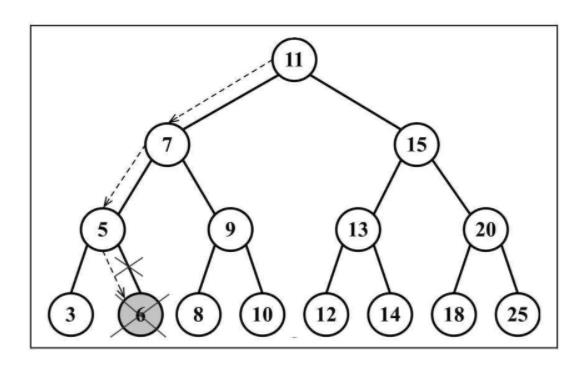
4.3 移除一个元素
remove(key) {
return this.removeNode(this.root, key);
}
removeNode(node, key) {
// 如果正在检测的节点为null,说明键不存在于树中
if (node == null) {
return false;
}
// 如果要找的键比当前节点的值小,就沿树的左边找下一个节点
if (this.compareFn(key, node.key) === Compare.LESS_THAN) {
node.left = this.removeNode(node.left, key);
return node;
}
// 如果要找的键比当前节点的值大,就沿树的右边找下一个节点
else if (this.compareFn(key, node.key) === Compare.BIGGER_THAN) {
node.right = this.removeNode(node.right, key);
return node;
}
// 找到了要找的键
else {
// 第一种情况:移除一个叶节点
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) { // 该节点是一个没有左侧或右侧子节点的叶节点
node = null;
return node;
}
// 第二种情况:移除一个有左侧或右侧子节点的节点
if (node.left == null) { // 如果这个节点没有左侧子节点
// 把对它的引用改为对它右侧子节点的引用
node = node.right;
return node;
} else if (node.right == null) { // 如果这个节点没有右侧子节点
// 把对它的引用改为对它左侧子节点的引用
node = node.left;
return node;
}
// 第三种情况:移除有两个字节点的节点
// 找到要移除的节点后,需要找到它右边子树中最小的节点
const aux = this.minNode(node.right);
// 用它右侧子树中最小节点的键去更新这个节点的值
node.key = aux.key;
// 继续把右侧子树中的最小节点移除
node.right = this.removeNode(node.right, aux.key);
// 向它的父节点返回更新后节点的引用
return node;
}
}
第一种情况:
第二种情况:
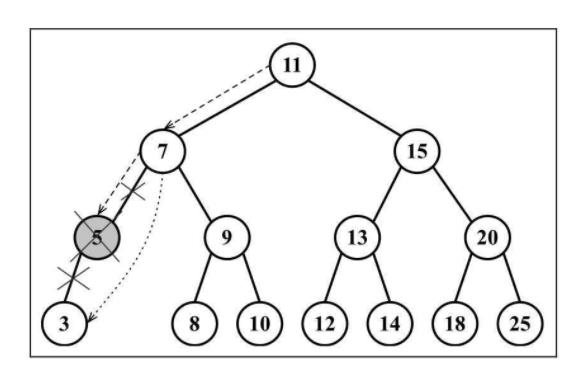
第三种情况:
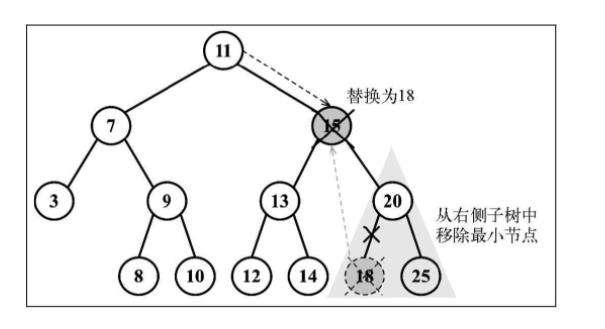
5. 自平衡树
问题:BST存在一个问题,取决于你添加的节点数,树的一条边可能会非常深;也就是说,树的一条分支会有很多层,而其他的分支却只有几层。
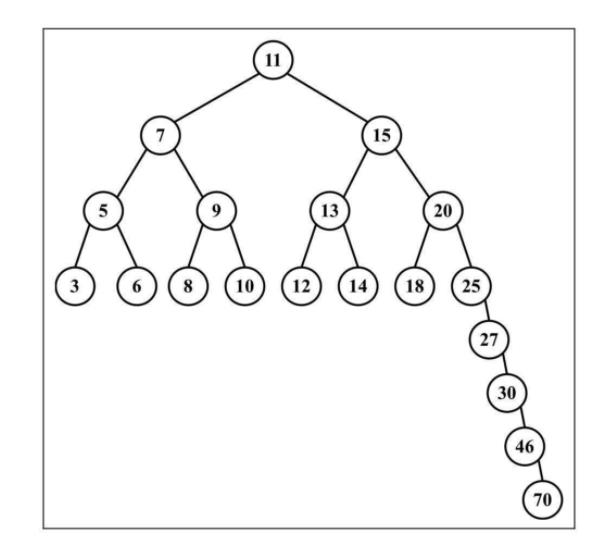
解决:尽可能尝试转换为完全树(Adelson-Velskii-Landi)是一种自平衡二叉搜索树,意思是任何一个节点左右两侧子树的高度之差最多为1。
5.1 AVL树
- AVL树是一种自平衡树。
- 添加或移除节点时,AVL树会尝试保持自平衡。
- 任意一个节点(不论深度)的左子树和右子树高度最多相差1。
- 添加或移除节点时,AVL树会尽可能尝试转换为完全树。
创建AVLTree类:
class AVLTree extends BinarySearchTree {
constructor(compareFn = defaultCompare) {
super(compareFn);
this.compareFn = compareFn;
this.root = null;
}
}
AVL树是一个BST,可以扩展BST类,只需要覆盖用来维持AVL树平衡的方法,也就是insert、insertNode和removeNode方法。所有其他的BST方法将会被AVLTree类继承。
1. 节点的高度和平衡因子
节点的高度是从节点到其任意子节点的边的最大值
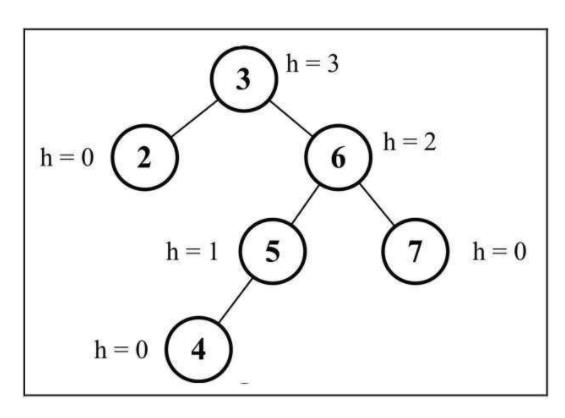
计算节点高度:
getNodeHeight(node) {
if (node == null) {
return -1;
}
// 对每个节点计算右子树高度和左子树高度之间的差值,如果结果不是0,1或-1这三个值之一,则需要AVL树
return Math.max(
this.getNodeHeight(node.left), this.getNodeHeight(node.right)
) + 1;
}
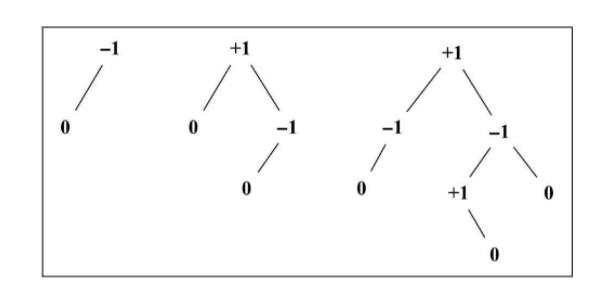
遵循计算一个节点的平衡因子并返回其值:
getBalanceFactor(node) {
const heightDifference = this.getNodeHeight(node.left) - this.getNodeHeight(node.right);
switch (heightDifference) {
case -2:
return BalanceFactor.UNBALANCED_RIGHT;
case -1:
return BalanceFactor.SLIGHTLY_UNBALANCED_RIGHT;
case 1:
return BalanceFactor.SLIGHTLY_UNBALANCED_LEFT;
case 2:
return BalanceFactor.UNBALANCED_LEFT;
default:
return BalanceFactor.BALANCED;
}
}
为了避免直接在代码中处理平衡因子的数值,创建一个用来作为计数器的javascript常量:
const BalanceFactor = {
UNBALANCED_RIGHT: 1,
SLIGHTLY_UNBALANCED_RIGHT: 2,
BALANCED: 3,
SLIGHTLY_UNBALANCED_LEFT: 4,
UNBALANCED_LEFT: 5
}
2 平衡操作 - AVL旋转
在对AVL树添加或移除节点后,需要计算节点的高度并验证树是否需要进行平衡。
向AVL树插入节点时,可以执行单旋转或双旋转两种平衡操作。
有以下四种场景:
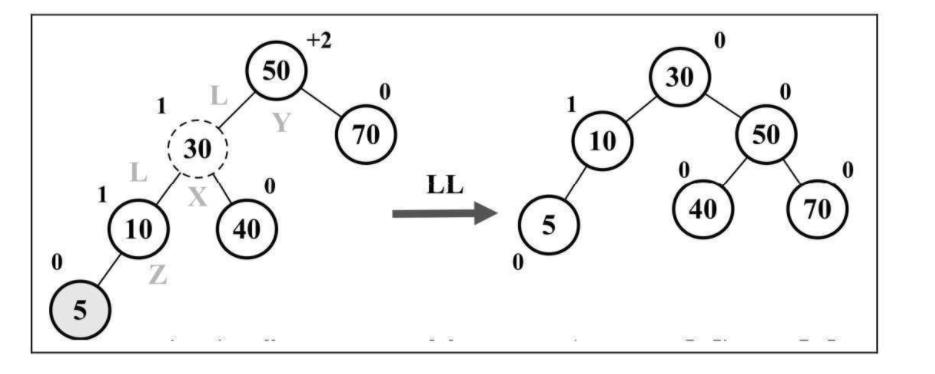
- 左 - 左(LL): 向右的单旋转
这种情况出现于节点的左侧子节点的高度大于右侧子节点的高度时,并且左侧子节点也是平衡或左侧较重的。
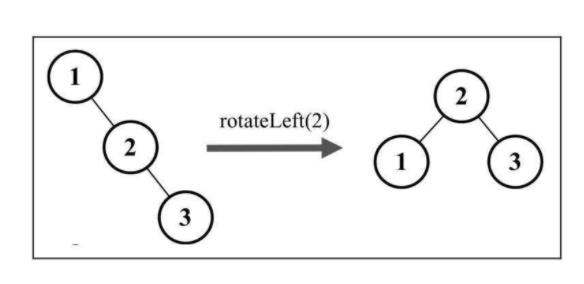
rotationLL(node) {
// 与平衡操作相关节点有X,Y和Z,将节点X置于节点Y(平衡因子为+2)所在的位置
// 节点X的左子树保持不变
const tmp = node.left;
// 将节点Y的左子节点置为节点X的右子节点Z
node.left = tmp.right;
// 将节点X的右子节点置为节点Y
tmp.right = node;
return tmp;
}
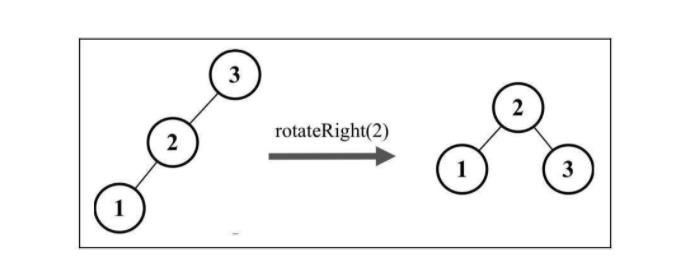
- 右 - 右(RR): 向左的单旋转
右-右的情况和左-左的情况相反。它出现于右侧子节点的高度大于左侧子节点的高度,并且右侧子节点也是平衡或右侧较重的。
rotationRR(node) {
// 与平衡操作相关的节点有三个(X、Y、Z),将节点X置于节点Y(平衡因子为-2)所在的位置
// 节点X的右子树保持不变
const tmp = node.right;
// 将节点Y的右子节点置为节点X的左子节点Z
node.right = tmp.left;
// 将节点X的左子节点置为节点Y
tmp.left = node;
return tmp;
}
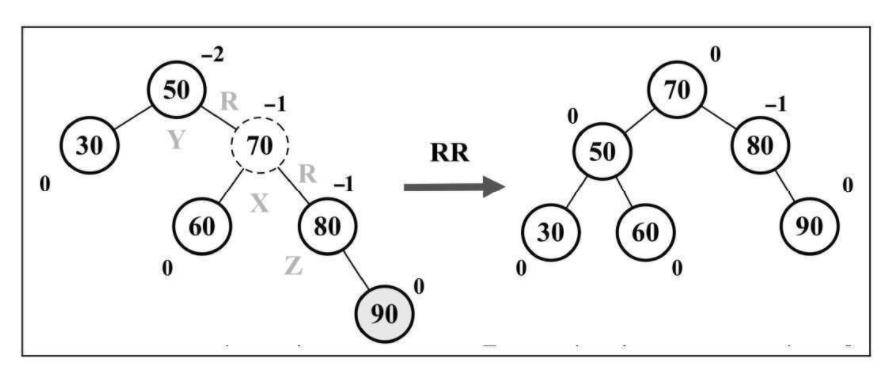
- 左 - 右(LR): 向右的双旋转(先LL旋转,再RR旋转)
这种情况出现于左侧子节点的高度大于右侧子节点的高度,并且左侧子节点右侧较重。
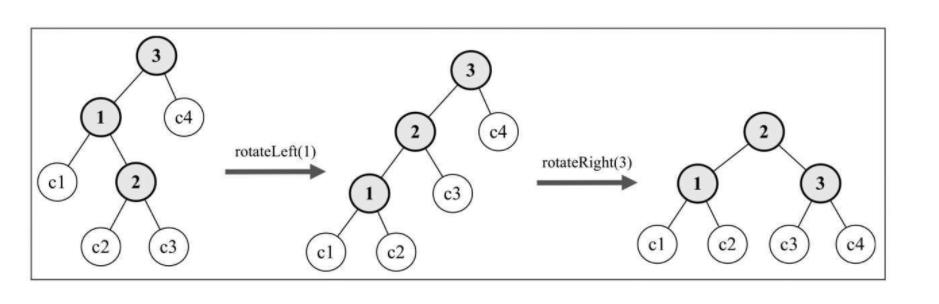
rotationLR(node) {
node.left = this.rotationRR(node.left);
return this.rotationLL(node);
}
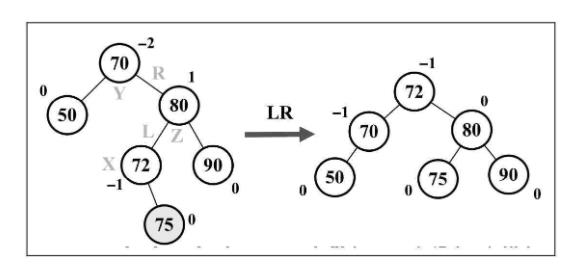
- 右 - 左(RL): 向左的双旋转(先RR旋转,再LL旋转)
右-左的情况和左-右的情况相反。这种情况出现于右侧子节点的高度大于左侧子节点的高度,并且右侧子节点左侧较重。
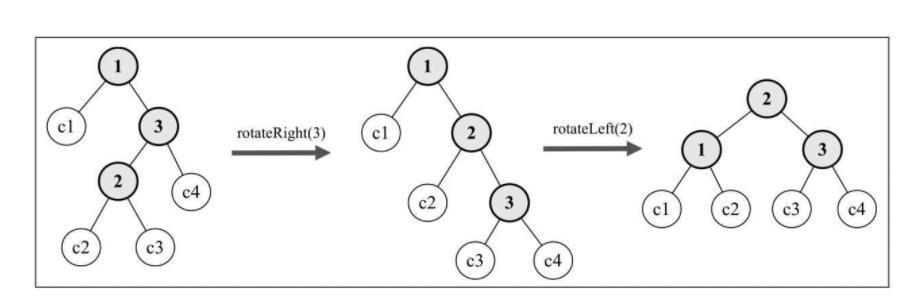
rotationRL(node) {
node.right = this.rotationLL(node.right);
return this.rotationRR(node);
}
 二叉树和二叉查找树--数据结构与算法JavaScript描述(10)
二叉树和二叉查找树--数据结构与算法JavaScript描述(10)