java 图形界面设计制作计算器
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了java 图形界面设计制作计算器相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
在NETBEANS 里写的
我的代码如下:JSQ:
package we;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
public class JSQ extends JFrame implements ActionListener
float i=0;
JPanel jp1=new JPanel();
JPanel jp2=new JPanel();
JPanel jp3=new JPanel();
JButton bt1=new JButton("+");
JButton bt2=new JButton("-");
JButton bt3=new JButton("*");
JButton bt4=new JButton("/");
JButton bt5=new JButton("1");
JButton bt6=new JButton("2");
JButton bt7=new JButton("3");
JButton bt8=new JButton("4");
JButton bt9=new JButton("5");
JButton bt10=new JButton("6");
JButton bt11=new JButton("7");
JButton bt12=new JButton("8");
JButton bt13=new JButton("9");
JButton bt14=new JButton("0");
JButton bt15=new JButton("=");
JLabel je=new JLabel("0");
public JSQ()
super("计算器");
jp1.setBounds(50,150,300,200);
jp1.setBackground(new Color(100,100,150));
this.add(jp1);
jp2.setBounds(50,40,300,30);
jp2.setBackground(new Color(50,100,150));
this.add(jp2);
jp2.add(je);
jp3.setBounds(370,200,70,70);
jp3.setBackground(new Color(100,100,150));
this.add(jp3);
jp1.add(bt1);
jp1.add(bt2);
jp1.add(bt3);
jp1.add(bt4);
jp1.add(bt5);
jp1.add(bt6);
jp1.add(bt7);
jp1.add(bt8);
jp1.add(bt9);
jp1.add(bt10);
jp1.add(bt11);
jp1.add(bt12);
jp1.add(bt13);
jp1.add(bt14);
jp1.add(bt15);
bt1.addActionListener(this);
bt2.addActionListener(this);
bt3.addActionListener(this);
bt4.addActionListener(this);
bt5.addActionListener(this);
bt6.addActionListener(this);
bt7.addActionListener(this);
bt8.addActionListener(this);
bt9.addActionListener(this);
bt10.addActionListener(this);
bt11.addActionListener(this);
bt12.addActionListener(this);
bt13.addActionListener(this);
bt14.addActionListener(this);
bt15.addActionListener(this);
this.setLayout(null);
this.setSize(500,400);
this.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.DISPOSE_ON_CLOSE);
this.setVisible(true);/**
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
Test和JSQ是分开的
Test:
package we;
public class Test
public static void main(String[] args)
JSQ jf=new JSQ();
我写到public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
以后就不会写了,不知道怎么实现按键的连续输入,之前写过一些,失败了,所以空着不会。
我想实现的是:先按“1”再按“2”键,标签显示12,不知道怎么实现。然后我按运算符加减乘除,标签上的数字不变,我再按一个数,然后标签上的12被删除,并且打印上我后面按的那个数,然后我再按等号,就会输出运算结果在标签3上,就像一般的计算器一样,要用到变量,不知道要不要用到append,大家帮帮我吧,期末成绩,我的分不多,谢谢了!!!
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.text.NumberFormat;
public class JSQ extends JFrame implements ActionListener
float i = 0;
JPanel jp1 = new JPanel();
JPanel jp2 = new JPanel();
JPanel jp3 = new JPanel();
JButton bt1 = new JButton("+");
JButton bt2 = new JButton("-");
JButton bt3 = new JButton("*");
JButton bt4 = new JButton("/");
JButton bt5 = new JButton("1");
JButton bt6 = new JButton("2");
JButton bt7 = new JButton("3");
JButton bt8 = new JButton("4");
JButton bt9 = new JButton("5");
JButton bt10 = new JButton("6");
JButton bt11 = new JButton("7");
JButton bt12 = new JButton("8");
JButton bt13 = new JButton("9");
JButton bt14 = new JButton("0");
JButton bt15 = new JButton("=");
JButton bt16 = new JButton("C");
JLabel je = new JLabel("0");
public JSQ()
super("计算器");
jp1.setBounds(50, 150, 300, 200);
jp1.setBackground(new Color(100, 100, 150));
this.add(jp1);
jp2.setBounds(50, 40, 300, 30);
jp2.setBackground(new Color(50, 100, 150));
this.add(jp2);
jp2.add(je);
jp3.setBounds(370, 200, 70, 70);
jp3.setBackground(new Color(100, 100, 150));
this.add(jp3);
jp1.add(bt1);
jp1.add(bt2);
jp1.add(bt3);
jp1.add(bt4);
jp1.add(bt5);
jp1.add(bt6);
jp1.add(bt7);
jp1.add(bt8);
jp1.add(bt9);
jp1.add(bt10);
jp1.add(bt11);
jp1.add(bt12);
jp1.add(bt13);
jp1.add(bt14);
jp1.add(bt15);
bt1.addActionListener(this);
bt2.addActionListener(this);
bt3.addActionListener(this);
bt4.addActionListener(this);
bt5.addActionListener(this);
bt6.addActionListener(this);
bt7.addActionListener(this);
bt8.addActionListener(this);
bt9.addActionListener(this);
bt10.addActionListener(this);
bt11.addActionListener(this);
bt12.addActionListener(this);
bt13.addActionListener(this);
bt14.addActionListener(this);
bt15.addActionListener(this);
bt16.addActionListener(this);
this.setLayout(null);
this.setSize(500, 400);
this.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.DISPOSE_ON_CLOSE);
this.setVisible(true);
StringBuffer val = new StringBuffer();
double data = 0;
char op = '\0';
boolean isComp = false;
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
JButton b = (JButton) e.getSource();
char c = b.getText().charAt(0);
if (Character.isDigit(c))
if (je.getText().equals("0"))
if (c != '0')
val.append(c);
setResult(val.toString());
else
if (isComp)
val.delete(0, val.length());
val.append(c);
setResult(val.toString());
isComp = false;
else
if (!val.toString().equals("0"))
val.append(c);
setResult(val.toString());
else if (c == '+' || c == '-' || c == '*' || c == '/')
if (op != '\0')
isComp = compute();
op = '\0';
op = c;
if (val.length() == 0)
data = 0;
else
data = Double.parseDouble(val.toString());
val.delete(0, val.length());
isComp = false;
else if (c == '=')
isComp = compute();
op = '\0';
private boolean compute()
double data1 = 0;
if (val.length() == 0)
data1 = 0;
else
data1 = Double.parseDouble(val.toString());
val.delete(0, val.length());
switch (op)
case '+' :
val.append(data + data1);
break;
case '-' :
val.append(data - data1);
break;
case '*' :
val.append(data * data1);
break;
case '/' :
if (data1 == 0)
val.append(0);
else
val.append(data / data1);
break;
setResult(val.toString());
return true;
private void setResult(String data)
NumberFormat nf = NumberFormat.getInstance();
nf.setMaximumFractionDigits(16);
je.setText(nf.format(Double.parseDouble(data)));
追问
多出来的我看不懂,能给我解释一下吗?
追答就是点的是数字,就连接起来并显示在标签上
点的是运算符,则将之前拼的数字转成数值型的存起来,并进行一次运算,可能是1+2 接着又+3这种
点的是等于,则根据运算符,进行运算,显示
isComp 是个标志,如果运算完了,又重新输入数字,则清除之前的运算结果
都是些小细节东西
谢谢了
追答1、charAt(0),是去字符串中的第一个字符。b.getText()取出来的虽然是一个字符,但是字符串类型的,转成字符麻烦,就直接用了个取串中第一个字符,省事
2、Character.idDigit(c),是判断c这个字符是否是数字,是返回true,不是返回false
3、val是记录你输入的数据,和最后计算的结果的。你每输一个字符都记录在val里,然后再setResult就显示的Label上了。
4、private你喜欢用啥就用啥吧,没啥关系,你就改成public吧
5、Double.parseDouble(val.toString())是将字符串转换成double类型的数据。toString()是把val转换成字符串类型的数据
书上没有,查是应该能查到的,java api里面都有,很全的,有中文版的
不会写,能写一下吗?后面的功能我也想不出来,谢谢了。
参考技术B 那你java简单计算器开发GUI图形化界面设计与实现(项目源码+课程设计报告)
- 课程目的
1.1. 课程性质
JAVA 程序设计是计算机专业本科生的必修专业主干课程,授课对象为计算
机科学与技术专业、数字媒体技术、信息安全专业等相关专业的本科生。
课程全面、系统地介绍 JAVA 语言的基本知识及程序设计技术,使学生掌握
Java 语言的语法、数据类型、流程控制等基本知识和面向对象程序设计思想的
Java 实现;了解 Java 常用的系统类;学习异常处理、线程、图形用户界面设计、
网络通信等内容。使学生的专业知识进一步完善和丰富,为将来的开发和研究工
作打下一定的基础。
1.2. 课程任务
(1) 巩固和加深学生对 Java 语言课程的基本知识的理解和掌握;
(2) 掌握 Java 语言编程和程序调试的基本技能;
(3) 利用 Java 语言进行基本的程序设计;
(4) 掌握书写程序设计说明文档的能力;
(5) 提高运用 Java 语言解决实际问题的能力。 - 课程设计要求
编写一个计算器,可实现加减乘除等一系列运算。
编程要求:选择某一种运算后,根据输入的数据给出运算结果。
编程提示:在设计出的计算器界面上,通过按钮来实现基本的功能。 - 课程设计内容
3.1. 选题描述
使用图形用户界面,设计计算器,用户通过鼠标依次输入需要计算的数值,
点击相应计算功能按钮,可以完成以下功能:

3.2. 画出流程图
(1) 核心功能流程图

3.3. 题目设计 (代码)
public class Calculator extends MouseAdapter
JFrame list;
// Container con;
JTextField show;
JButton[] jbNum = new JButton[10];
JPanel jpMain; // 主面板
JPanel jpRight; // 右子面板主要用于存放运算符和等号
JPanel jpLight; // 左子面板用于存放数字,符号, “.”
JButton dight; // 小数点
JButton sign; // 正负号
JButton add; // 加号
JButton sub; // 减号
JButton multiply; // 乘号
JButton divide; // 除号
JButton power; // 求幂
JButton cos; // cos
JButton sin; // sin
JButton ln; // ln
JButton ce; // 清除
JButton equal; // 等于
JButton mod; // 取余
JButton sqrt; // sqrt
double sum = 0; // 临时结果
boolean b = false; // 监控运算符是否被点击,错误是否出现,用于实现下一次点击按钮时清空
operator i = operator.un; // 记录等号符点击前某一运算符点击次数,用于实现连加或者连减等
int op; // 记录操作符
// 操作符一包括+-*/%^
enum operator
add, sub, mul, div, mod, pow, sin, cos, sqrt, ln, un
void display()
// 创建主窗口,添加一个Text框,
list = new JFrame("计算器");
list.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
list.setSize(360, 230);
list.setLocation(400, 300);
list.setBackground(Color.LIGHT_GRAY); // 设置窗口背景颜色
list.setResizable(false);
list.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.CENTER));
show = new JTextField(31);
show.setHorizontalAlignment(JTextField.RIGHT); // 文本框内文字右对齐
show.setEditable(false); // 文本框不可编辑
list.add(show);
// 创建面板并设置布局
jpMain = new JPanel();
jpRight = new JPanel();
jpLight = new JPanel();
jpMain.setLayout(new GridLayout(1, 2));
jpRight.setLayout(new GridLayout(4, 3, 3, 3));
jpLight.setLayout(new GridLayout(4, 3, 3, 3));
list.add(jpMain);
jpMain.add(jpLight);
jpMain.add(jpRight);
// 创建0~9按钮对象
for (int i = 9; i >= 0; i--)
jbNum[i] = new JButton(String.valueOf(i));
jbNum[i].setForeground(Color.BLUE);
jpLight.add(jbNum[i]);
jbNum[i].addMouseListener(this);
add = new JButton("+");
sub = new JButton("-");
multiply = new JButton("*");
divide = new JButton("/");
power = new JButton("x^y");
sin = new JButton("sin");
cos = new JButton("cos");
ln = new JButton("ln");
ce = new JButton("CE");
equal = new JButton("=");
mod = new JButton("%");
sqrt = new JButton("sqrt");
jpRight.add(divide);
jpRight.add(sqrt);
jpRight.add(ln);
jpRight.add(multiply);
jpRight.add(sin);
jpRight.add(mod);
jpRight.add(sub);
jpRight.add(cos);
jpRight.add(ce);
jpRight.add(add);
jpRight.add(power);
jpRight.add(equal);
// 给所有按钮注册监听器
dight = new JButton(".");
sign = new JButton("±");
jpLight.add(sign);
jpLight.add(dight);
add.addMouseListener(this);
sub.addMouseListener(this);
multiply.addMouseListener(this);
divide.addMouseListener(this);
power.addMouseListener(this);
sin.addMouseListener(this);
cos.addMouseListener(this);
ln.addMouseListener(this);
ce.addMouseListener(this);
equal.addMouseListener(this);
mod.addMouseListener(this);
sqrt.addMouseListener(this);
dight.addMouseListener(this);
sign.addMouseListener(this);
list.setVisible(true);
public void mouseClicked(MouseEvent e)
// 0~9的输入
if (e.getSource() == jbNum[0])
input(0, e);
if (e.getSource() == jbNum[1])
input(1, e);
if (e.getSource() == jbNum[2])
input(2, e);
if (e.getSource() == jbNum[3])
input(3, e);
if (e.getSource() == jbNum[4])
input(4, e);
if (e.getSource() == jbNum[5])
input(5, e);
if (e.getSource() == jbNum[6])
input(6, e);
if (e.getSource() == jbNum[7])
input(7, e);
if (e.getSource() == jbNum[8])
input(8, e);
if (e.getSource() == jbNum[9])
input(9, e);
// 小数点,正负号,CE,等号
if (e.getSource() == dight)
if (show.getText().indexOf('.') == -1)
show.setText(show.getText() + ".");
if (e.getSource() == sign)
if (show.getText().indexOf("-") == -1)
show.setText("-" + show.getText());
else
show.setText(show.getText().replace('-', '\\0'));
if (e.getSource() == ce)
show.setText("0");
sum = 0;
i = operator.un;
b = false;
outer: if (e.getSource() == equal)
try
if (i == operator.un)
b = true;
else
if (i == operator.add)
sum += Double.parseDouble(show.getText());
if (i == operator.sub)
sum -= Double.parseDouble(show.getText());
if (i == operator.mul)
sum *= Double.parseDouble(show.getText());
if (i == operator.div)
if (Double.parseDouble(show.getText()) != 0)
sum /= Double.parseDouble(show.getText());
else
show.setText("ERROR");
b = true;
sum = 0;
break outer; // 不执行trimIn()方法 屏幕显示错误
if (i == operator.mod)
sum %= Double.parseDouble(show.getText());
if (i == operator.pow)
sum = Math.pow(sum, Double.parseDouble(show.getText()));
trimIn(sum);
catch (Exception ex)
show.setText("ERROR");
b = true;
sum = 0;
sum = 0;
i = operator.un;
b = true;
// 加减乘除//幂指函数//取余
if (e.getSource() == add)
cal(i);
i = operator.add;
b = true;
if (e.getSource() == sub)
cal(i);
i = operator.sub;
b = true;
if (e.getSource() == multiply)
cal(i);
i = operator.mul;
b = true;
if (e.getSource() == divide)
cal(i);
i = operator.div;
b = true;
if (e.getSource() == mod)
cal(i);
i = operator.mod;
b = true;
if (e.getSource() == power)
cal(i);
i = operator.pow;
b = true;
// sqrt,sin,cos,ln
try
if (show.getText() != "ERROR")
if (e.getSource() == sqrt)
sum = Math.sqrt(Double.parseDouble(show.getText()));
trimIn(sum);
b = true;
if (e.getSource() == sin)
sum = Math.sin(Double.parseDouble(show.getText()));
trimIn(sum);
b = true;
if (e.getSource() == cos)
sum = Math.cos(Double.parseDouble(show.getText()));
trimIn(sum);
b = true;
if (e.getSource() == ln)
sum = Math.log(Double.parseDouble(show.getText()));
trimIn(sum);
b = true;
catch (Exception ex)
show.setText("ERROR");
b = true;
3.4. 运行程序(结果截图)
(1) 运行界面
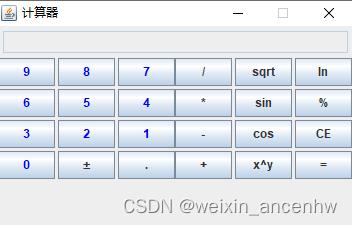
(2)加减乘除(±*/)

(3)清除运算(CE)

(4)开平方根(sqrt)

(5)三角函数(sin\\cos)

-
总结
该文章分析了一个系统设计与实现,实际上就是让我们建立一个技术体现出来,最主要是要明白自己开发的这个程序它到底有哪些功能以上是关于java 图形界面设计制作计算器的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章