数据库之MySQL入门(数据查询2)
Posted 晨沉宸辰
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数据库之MySQL入门(数据查询2)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
连接查询&子查询&视图
一、连接
1.等值连接与非等值连接
- 等值连接:当连接运算符为“=”时,称为等值连接,其他运算符为非等值连接
- 连接谓词中的列名称为连接字段,连接条件中的各连接字段类型必须是可比的,但不必是相同的
例1: 查询每个学生及其选修课程的情况
select *
-> from stu,score
-> where stu.sno=score.sno;
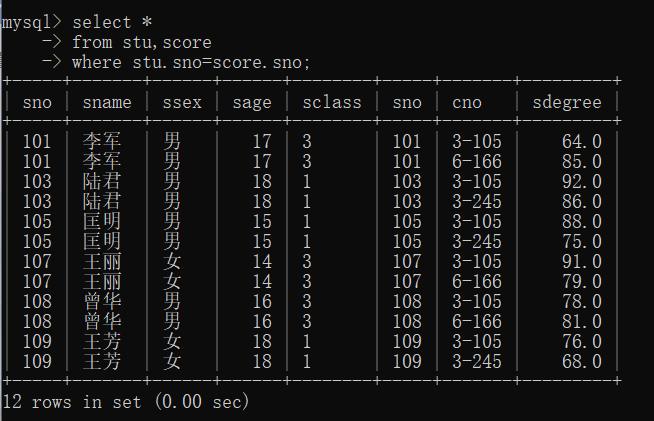
并不会去除重复项
3. 运算中有两种特殊情况,一种称为笛卡尔积连接,另一种称为自然连接。
笛卡尔积
select *
-> from course,score;
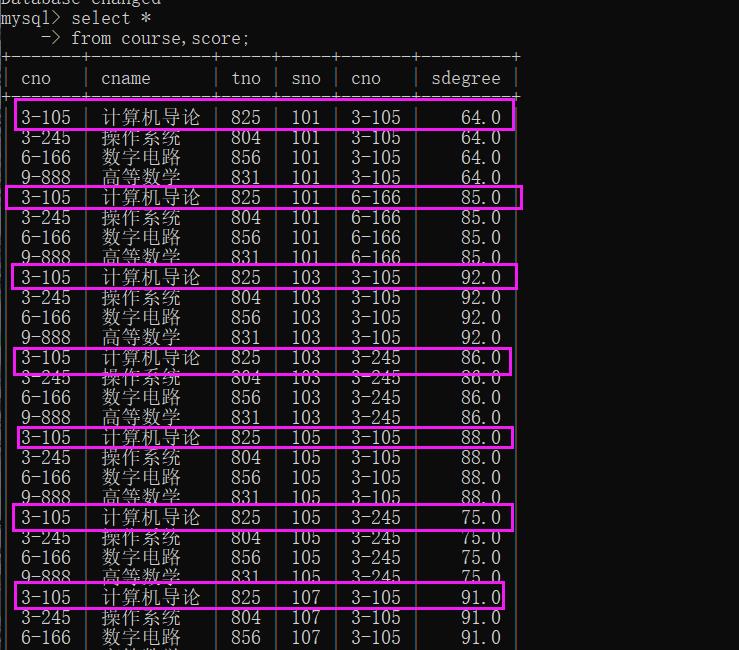
4. 如果按照两个表中的相同属性进行等值连接,且目标列中去掉了重复的属性列,但保留了所有不重复的属性列,则为自然连接
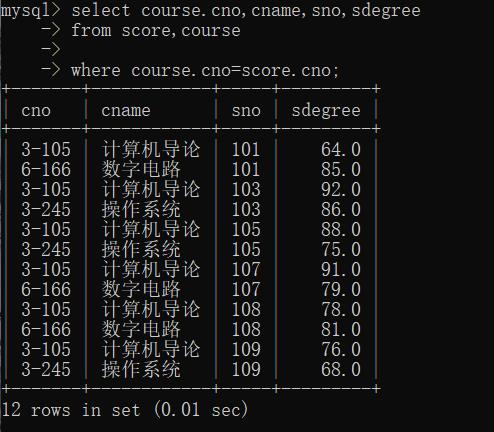
自然连接表
也就是手动选择删除重复的
select course.cno,cname,sno,sdegree
-> from score,course
-> where course.cno=score.cno;
2.自身连接
- 连接操作不仅可以在两个表中进行,也可以是一个表与自身进行连接,也就是自身连接
查询每一门课的间接选修课
首先要进行增加cpno这一列,文章最后将讲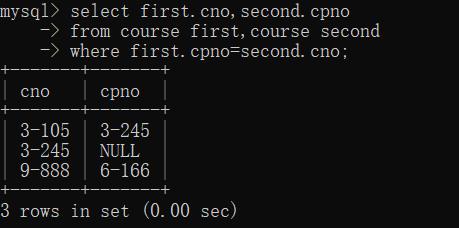
3.外连接
以stu表为主体列出每个学生的基本情况以及其选课情况
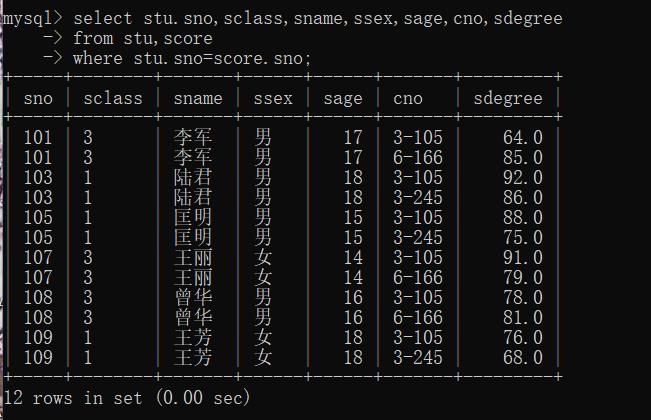
mysql> select stu.sno,sclass,sname,ssex,sage,cno,sdegree
-> from stu,score
-> where stu.sno=score.sno;
+-----+--------+-------+------+------+-------+---------+
| sno | sclass | sname | ssex | sage | cno | sdegree |
+-----+--------+-------+------+------+-------+---------+
| 101 | 3 | 李军 | 男 | 17 | 3-105 | 64.0 |
| 101 | 3 | 李军 | 男 | 17 | 6-166 | 85.0 |
| 103 | 1 | 陆君 | 男 | 18 | 3-105 | 92.0 |
| 103 | 1 | 陆君 | 男 | 18 | 3-245 | 86.0 |
| 105 | 1 | 匡明 | 男 | 15 | 3-105 | 88.0 |
| 105 | 1 | 匡明 | 男 | 15 | 3-245 | 75.0 |
| 107 | 3 | 王丽 | 女 | 14 | 3-105 | 91.0 |
| 107 | 3 | 王丽 | 女 | 14 | 6-166 | 79.0 |
| 108 | 3 | 曾华 | 男 | 16 | 3-105 | 78.0 |
| 108 | 3 | 曾华 | 男 | 16 | 6-166 | 81.0 |
| 109 | 1 | 王芳 | 女 | 18 | 3-105 | 76.0 |
| 109 | 1 | 王芳 | 女 | 18 | 3-245 | 68.0 |
+-----+--------+-------+------+------+-------+---------+
12 rows in set (0.00 sec)
4.复合条件连接
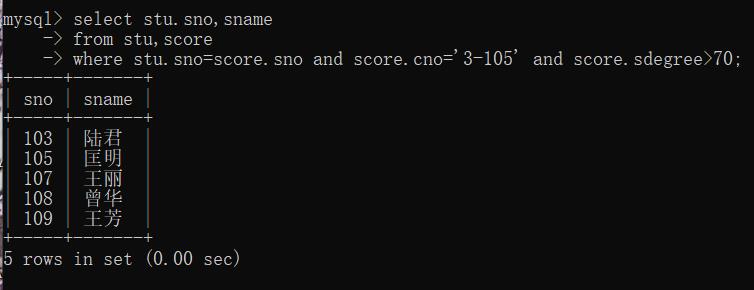
mysql> select stu.sno,sname
-> from stu,score
-> where stu.sno=score.sno and score.cno='3-105' and score.sdegree>70;
5. from子句中的连接查询
1. 内连接
(1)等值连接
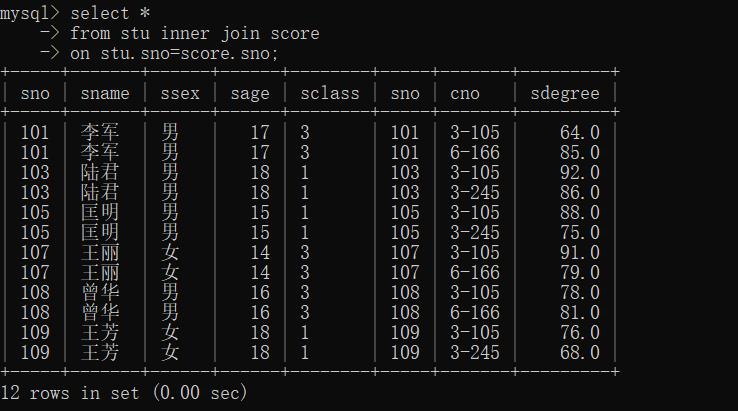
查询等值连接选修了课程的学生的全部信息
mysql> select *
-> from stu inner join score
-> on stu.sno=score.sno;
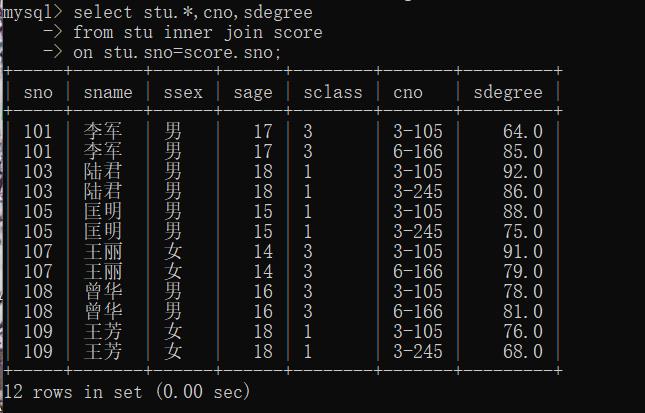
(2)自然连接
没有重复项
mysql> select stu.*,cno,sdegree
-> from stu inner join score
-> on stu.sno=score.sno;
(3)外连接
内连接,返回查询结果集合中仅是符合查询条件的
外连接,返回不止是这些
mysql> select *
-> from stu left join score
-> on stu.sno=score.sno;
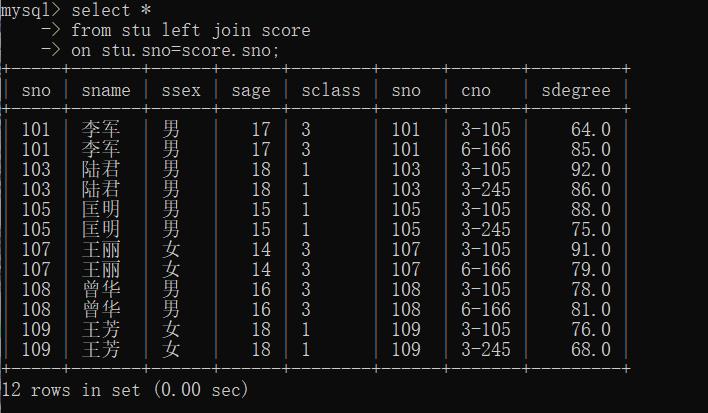
2. 外连接
使用左外连接将stu和score表中的信息连接起来
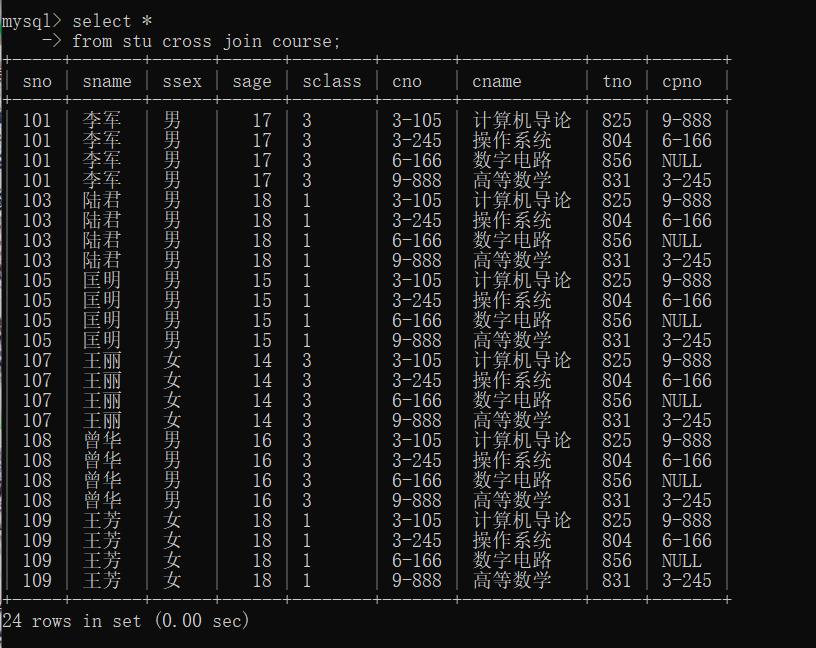
3. 交叉连接
交叉连接不带where子句,它返回被连接的两个表所有数据行的笛卡尔积
mysql> select *
-> from stu cross join course;
二、嵌套查询
- 子查询通常出现where子句中,有时候也出现from子句中,有时候也出现在having短语中
- 子查询的select语句中不能使用order by子句,order by子句永远只能对最终查询结果排序
- 不相关子查询:子查询都在其父查询处理前求解,它的执行不依赖于子查询的任何条件。每个子查询 仅执行一次,子查询的结果集为父查询的where条件占用
- 相关查询:有的查询中,子查询的执行依赖于父查询的某个条件,子查询不止执行一次,这类子查询的查询条件往往依赖于其父查询的属性值
1. 带有比较运算符的子查询
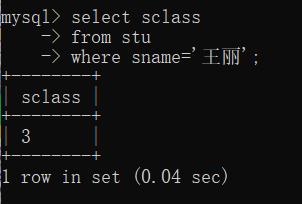
- 确定叫“王丽”所在班级
mysql> select sclass
-> from stu
-> where sname='王丽';
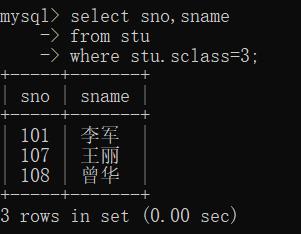
2. 查询班级为3的所有学生的信息
mysql> select sno,sname
-> from stu
-> where stu.sclass=3;
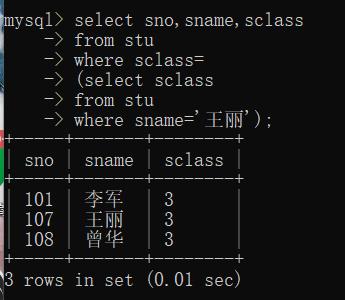
3. 将上述结合,构成不相关子查询
mysql> select sno,sname,sclass
-> from stu
-> where sclass=
-> (select sclass
-> from stu
-> where sname='王丽');
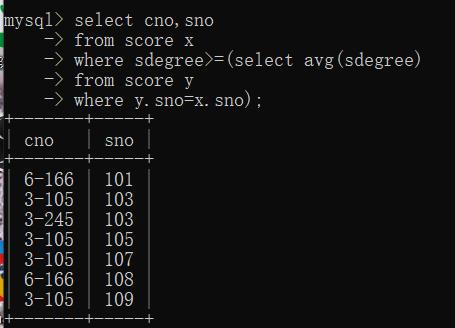
找出每个学生超过他选修课程的平均成绩的课程号
mysql> select cno,sno
-> from score x
-> where sdegree>=(select avg(sdegree)
-> from score y
-> where y.sno=x.sno);
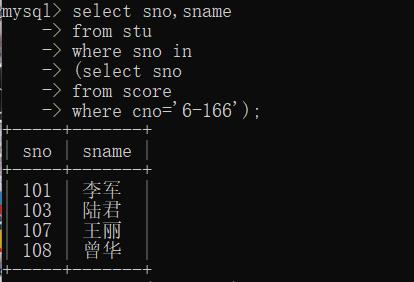
2. 含有IN的子查询
主查询与子查询用谓词IN连接
【例】:
查询所有选修了6-166号课程的学生的学号、姓名
mysql> select sno,sname
-> from stu
-> where sno in
-> (select sno
-> from score
-> where cno='6-166');
3. 含有between and的子查询
4. 含有any all的子查询
5. 带有exists谓词的子查询
以上是关于数据库之MySQL入门(数据查询2)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章