以太坊RPC机制
Posted 七芒星实验室
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了以太坊RPC机制相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
RPC简介
RPC(remote process call),即远程过程调用,意思就是两台物理位置不同的服务器,其中一台服务器的应用想调用另一台服务器上某个应用的函数或者方法,由于不在同一个内存空间不能直接调用,因此需要通过网络来表达语义以及传入的参数,RPC是跨操作系统,跨编程语言的网络通信方式。
RPC启动
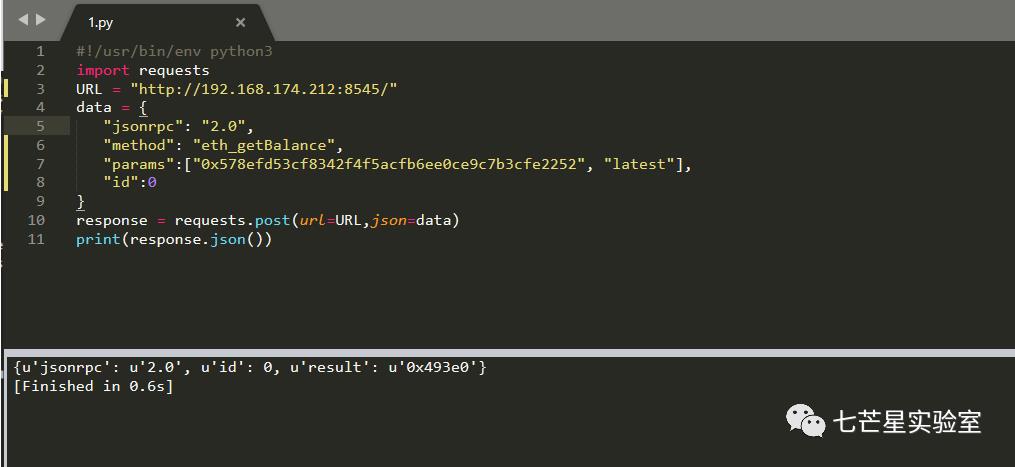
我们可以通过执行以下命令来启动RPC:
geth --networkid 666 --datadir /home/ubuntu/Private_eth/eth1 --identity "node1" --rpc --rpcport "8545" --rpcaddr "192.168.174.212" --nodiscover --rpcapi "eth,net,web3,txpool,debug,miner" 之后我们可以通过以下脚本进行RPC测试:
#!/usr/bin/env python3import requestsURL = "http://192.168.174.212:8545/"data = {"jsonrpc": "2.0","method": "eth_getBalance","params":["0x578efd53cf8342f4f5acfb6ee0ce9c7b3cfe2252", "latest"],"id":0}response = requests.post(url=URL,json=data)print(response.json())
源码分析
以太坊有四种RPC:HTTP RPC、Inproc RPC、IPC RPC、WS RPC,它们主要的实现逻辑都在rpc/server.go和rpc/client.go,各自根据自己的实现方式派生自己的client实例,建立各自的net.conn通道,由于HTTP RPC是基于短链接请求,实现方式和其他的不太一样,这里仅对RPC服务的启动以及HTTP RPC请求、HTTP RPC和非HTTP请求类的请求和响应做一个简单的介绍分析~
服务启动
RPC服务的启动与否是我们在通过geth来启动链节点时有参数--rpc来决定的,在geth函数中会调用startNode来启动一个node:
// filedir:go-ethereum-1.10.2\cmd\geth\main.go L308// geth is the main entry point into the system if no special subcommand is ran.// It creates a default node based on the command line arguments and runs it in// blocking mode, waiting for it to be shut down.func geth(ctx *cli.Context) error {if args := ctx.Args(); len(args) > 0 {return fmt.Errorf("invalid command: %q", args[0])}prepare(ctx)stack, backend := makeFullNode(ctx)defer stack.Close()startNode(ctx, stack, backend)stack.Wait()return nil}
startNode进而转去调用utils的StartNode函数,此处的utils为github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/cmd/utils
// filedir:go-ethereum-1.10.2\cmd\geth\main.go L325// startNode boots up the system node and all registered protocols, after which// it unlocks any requested accounts, and starts the RPC/IPC interfaces and the// miner.func startNode(ctx *cli.Context, stack *node.Node, backend ethapi.Backend) {debug.Memsize.Add("node", stack)// Start up the node itselfutils.StartNode(ctx, stack)......
之后再go-ethereum-1.10.2\cmd\utils\cmd.go的startNode函数中转而调用Node的start函数来启动服务,之后开启监听:
func StartNode(ctx *cli.Context, stack *node.Node) {if err := stack.Start(); err != nil {Fatalf("Error starting protocol stack: %v", err)}go func() {sigc := make(chan os.Signal, 1)signal.Notify(sigc, syscall.SIGINT, syscall.SIGTERM)defer signal.Stop(sigc)minFreeDiskSpace := ethconfig.Defaults.TrieDirtyCacheif ctx.GlobalIsSet(MinFreeDiskSpaceFlag.Name) {minFreeDiskSpace = ctx.GlobalInt(MinFreeDiskSpaceFlag.Name)} else if ctx.GlobalIsSet(CacheFlag.Name) || ctx.GlobalIsSet(CacheGCFlag.Name) {minFreeDiskSpace = ctx.GlobalInt(CacheFlag.Name) * ctx.GlobalInt(CacheGCFlag.Name) / 100}if minFreeDiskSpace > 0 {go monitorFreeDiskSpace(sigc, stack.InstanceDir(), uint64(minFreeDiskSpace)*1024*1024)}<-sigclog.Info("Got interrupt, shutting down...")go stack.Close()for i := 10; i > 0; i-- {<-sigcif i > 1 {log.Warn("Already shutting down, interrupt more to panic.", "times", i-1)}}debug.Exit() // ensure trace and CPU profile data is flushed.debug.LoudPanic("boom")}()}
Node.start函数进而去调用openEndpoints去开启RPC端点:
// filedir: go-ethereum-1.10.2\node\node.go// Start starts all registered lifecycles, RPC services and p2p networking.// Node can only be started once.func (n *Node) Start() error {n.startStopLock.Lock()defer n.startStopLock.Unlock()n.lock.Lock()switch n.state {case runningState:n.lock.Unlock()return ErrNodeRunningcase closedState:n.lock.Unlock()return ErrNodeStopped}n.state = runningState// open networking and RPC endpointserr := n.openEndpoints()lifecycles := make([]Lifecycle, len(n.lifecycles))copy(lifecycles, n.lifecycles)n.lock.Unlock()// Check if endpoint startup failed.if err != nil {n.doClose(nil)return err}// Start all registered lifecycles.var started []Lifecyclefor _, lifecycle := range lifecycles {if err = lifecycle.Start(); err != nil {break}started = append(started, lifecycle)}// Check if any lifecycle failed to start.if err != nil {n.stopServices(started)n.doClose(nil)}return err}
之后的openEndpoints调用startRPC来启动RPC服务:
// filedir:go-ethereum-1.10.2\node\node.go L260// openEndpoints starts all network and RPC endpoints.func (n *Node) openEndpoints() error {// start networking endpointsn.log.Info("Starting peer-to-peer node", "instance", n.server.Name)if err := n.server.Start(); err != nil {return convertFileLockError(err)}// start RPC endpointserr := n.startRPC()if err != nil {n.stopRPC()n.server.Stop()}return err}
startRPC具体实现如下:
// filedir: go-ethereum-1.10.2\node\node.go// configureRPC is a helper method to configure all the various RPC endpoints during node// startup. It's not meant to be called at any time afterwards as it makes certain// assumptions about the state of the node.func (n *Node) startRPC() error {if err := n.startInProc(); err != nil {return err}// Configure IPC.if n.ipc.endpoint != "" {if err := n.ipc.start(n.rpcAPIs); err != nil {return err}}// Configure HTTP.if n.config.HTTPHost != "" {config := httpConfig{CorsAllowedOrigins: n.config.HTTPCors,Vhosts: n.config.HTTPVirtualHosts,Modules: n.config.HTTPModules,prefix: n.config.HTTPPathPrefix,}if err := n.http.setListenAddr(n.config.HTTPHost, n.config.HTTPPort); err != nil {return err}if err := n.http.enableRPC(n.rpcAPIs, config); err != nil {return err}}// Configure WebSocket.if n.config.WSHost != "" {server := n.wsServerForPort(n.config.WSPort)config := wsConfig{Modules: n.config.WSModules,Origins: n.config.WSOrigins,prefix: n.config.WSPathPrefix,}if err := server.setListenAddr(n.config.WSHost, n.config.WSPort); err != nil {return err}if err := server.enableWS(n.rpcAPIs, config); err != nil {return err}}if err := n.http.start(); err != nil {return err}return n.ws.start()}
在这里会调用startInProc来注册所有的RPC API接口信息:
// startInProc registers all RPC APIs on the inproc server.func (n *Node) startInProc() error {for _, api := range n.rpcAPIs {if err := n.inprocHandler.RegisterName(api.Namespace, api.Service); err != nil {return err}}return nil}
调用n.ipc.start(n.rpcAPIs)启动IPC
// filedir: go-ethereum-1.10.2\node\rpcstack.go// Start starts the httpServer's http.Serverfunc (is *ipcServer) start(apis []rpc.API) error {is.mu.Lock()defer is.mu.Unlock()if is.listener != nil {return nil // already running}listener, srv, err := rpc.StartIPCEndpoint(is.endpoint, apis)if err != nil {is.log.Warn("IPC opening failed", "url", is.endpoint, "error", err)return err}is.log.Info("IPC endpoint opened", "url", is.endpoint)is.listener, is.srv = listener, srvreturn nil}
调用n.http.enableRPC启动RPC服务并注册Handler:
// filedir:go-ethereum-1.10.2\node\rpcstack.go L272// enableRPC turns on JSON-RPC over HTTP on the server.func (h *httpServer) enableRPC(apis []rpc.API, config httpConfig) error {h.mu.Lock()defer h.mu.Unlock()if h.rpcAllowed() {return fmt.Errorf("JSON-RPC over HTTP is already enabled")}// Create RPC server and handler.srv := rpc.NewServer()if err := RegisterApisFromWhitelist(apis, config.Modules, srv, false); err != nil {return err}h.httpConfig = configh.httpHandler.Store(&rpcHandler{Handler: NewHTTPHandlerStack(srv, config.CorsAllowedOrigins, config.Vhosts),server: srv,})return nil}
Handler注册跟踪如下(下面的ServeHTTP其实已经到了处理请求的逻辑了,这里不再深入,后面再做探究):
// filedir: go-ethereum-1.10.2\node\rpcstack.go// NewHTTPHandlerStack returns wrapped http-related handlersfunc NewHTTPHandlerStack(srv http.Handler, cors []string, vhosts []string) http.Handler {// Wrap the CORS-handler within a host-handlerhandler := newCorsHandler(srv, cors)handler = newVHostHandler(vhosts, handler)return newGzipHandler(handler)}// filedir:go-ethereum-1.10.2\node\rpcstack.gofunc newGzipHandler(next http.Handler) http.Handler {return http.HandlerFunc(func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {if !strings.Contains(r.Header.Get("Accept-Encoding"), "gzip") {next.ServeHTTP(w, r)return}w.Header().Set("Content-Encoding", "gzip")gz := gzPool.Get().(*gzip.Writer)defer gzPool.Put(gz)gz.Reset(w)defer gz.Close()next.ServeHTTP(&gzipResponseWriter{ResponseWriter: w, Writer: gz}, r)})}// filedir: go-ethereum-1.10.2\rpc\http.go// ServeHTTP serves JSON-RPC requests over HTTP.func (s *Server) ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {// Permit dumb empty requests for remote health-checks (AWS)if r.Method == http.MethodGet && r.ContentLength == 0 && r.URL.RawQuery == "" {w.WriteHeader(http.StatusOK)return}if code, err := validateRequest(r); err != nil {http.Error(w, err.Error(), code)return}// All checks passed, create a codec that reads directly from the request body// until EOF, writes the response to w, and orders the server to process a// single request.ctx := r.Context()ctx = context.WithValue(ctx, "remote", r.RemoteAddr)ctx = context.WithValue(ctx, "scheme", r.Proto)ctx = context.WithValue(ctx, "local", r.Host)if ua := r.Header.Get("User-Agent"); ua != "" {ctx = context.WithValue(ctx, "User-Agent", ua)}if origin := r.Header.Get("Origin"); origin != "" {ctx = context.WithValue(ctx, "Origin", origin)}w.Header().Set("content-type", contentType)codec := newHTTPServerConn(r, w)defer codec.close()s.serveSingleRequest(ctx, codec)}
调用server.enableWS启动Websocket:
// filedir:go-ethereum-1.10.2\node\rpcstack.go// enableWS turns on JSON-RPC over WebSocket on the server.func (h *httpServer) enableWS(apis []rpc.API, config wsConfig) error {h.mu.Lock()defer h.mu.Unlock()if h.wsAllowed() {return fmt.Errorf("JSON-RPC over WebSocket is already enabled")}// Create RPC server and handler.srv := rpc.NewServer()if err := RegisterApisFromWhitelist(apis, config.Modules, srv, false); err != nil {return err}h.wsConfig = configh.wsHandler.Store(&rpcHandler{Handler: srv.WebsocketHandler(config.Origins),server: srv,})return nil}
Handler注册:
// filedir: go-ethereum-1.10.2\rpc\websocket.go L45// WebsocketHandler returns a handler that serves JSON-RPC to WebSocket connections.//// allowedOrigins should be a comma-separated list of allowed origin URLs.// To allow connections with any origin, pass "*".func (s *Server) WebsocketHandler(allowedOrigins []string) http.Handler {var upgrader = websocket.Upgrader{ReadBufferSize: wsReadBuffer,WriteBufferSize: wsWriteBuffer,WriteBufferPool: wsBufferPool,CheckOrigin: wsHandshakeValidator(allowedOrigins),}return http.HandlerFunc(func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {conn, err := upgrader.Upgrade(w, r, nil)if err != nil {log.Debug("WebSocket upgrade failed", "err", err)return}codec := newWebsocketCodec(conn)s.ServeCodec(codec, 0)})}// filedir: go-ethereum-1.10.2\rpc\websocket.go L241func newWebsocketCodec(conn *websocket.Conn) ServerCodec {conn.SetReadLimit(wsMessageSizeLimit)wc := &websocketCodec{jsonCodec: NewFuncCodec(conn, conn.WriteJSON, conn.ReadJSON).(*jsonCodec),conn: conn,pingReset: make(chan struct{}, 1),}wc.wg.Add(1)go wc.pingLoop()return wc}// filedir: go-ethereum-1.10.2\rpc\server.go// ServeCodec reads incoming requests from codec, calls the appropriate callback and writes// the response back using the given codec. It will block until the codec is closed or the// server is stopped. In either case the codec is closed.//// Note that codec options are no longer supported.func (s *Server) ServeCodec(codec ServerCodec, options CodecOption) {defer codec.close()// Don't serve if server is stopped.if atomic.LoadInt32(&s.run) == 0 {return}// Add the codec to the set so it can be closed by Stop.s.codecs.Add(codec)defer s.codecs.Remove(codec)c := initClient(codec, s.idgen, &s.services)<-codec.closed()c.Close()}
最后调用start启动HTTP Server
// start starts the HTTP server if it is enabled and not already running.func (h *httpServer) start() error {h.mu.Lock()defer h.mu.Unlock()if h.endpoint == "" || h.listener != nil {return nil // already running or not configured}// Initialize the server.h.server = &http.Server{Handler: h}if h.timeouts != (rpc.HTTPTimeouts{}) {CheckTimeouts(&h.timeouts)h.server.ReadTimeout = h.timeouts.ReadTimeouth.server.WriteTimeout = h.timeouts.WriteTimeouth.server.IdleTimeout = h.timeouts.IdleTimeout}// Start the server.listener, err := net.Listen("tcp", h.endpoint)if err != nil {// If the server fails to start, we need to clear out the RPC and WS// configuration so they can be configured another time.h.disableRPC()h.disableWS()return err}h.listener = listenergo h.server.Serve(listener)if h.wsAllowed() {url := fmt.Sprintf("ws://%v", listener.Addr())if h.wsConfig.prefix != "" {url += h.wsConfig.prefix}h.log.Info("WebSocket enabled", "url", url)}// if server is websocket only, return after loggingif !h.rpcAllowed() {return nil}// Log http endpoint.h.log.Info("HTTP server started","endpoint", listener.Addr(),"prefix", h.httpConfig.prefix,"cors", strings.Join(h.httpConfig.CorsAllowedOrigins, ","),"vhosts", strings.Join(h.httpConfig.Vhosts, ","),)// Log all handlers mounted on server.var paths []stringfor path := range h.handlerNames {paths = append(paths, path)}sort.Strings(paths)logged := make(map[string]bool, len(paths))for _, path := range paths {name := h.handlerNames[path]if !logged[name] {log.Info(name+" enabled", "url", "http://"+listener.Addr().String()+path)logged[name] = true}}return nil}
至此,启动完成~
以上是关于以太坊RPC机制的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章