java集合中的ArrayList源码分析
Posted 李子捌
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了java集合中的ArrayList源码分析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1、集合
1.1 JAVA集合关系图
1.2 ArrayList源码分析
1、简介
ArrayList 是 java 集合框架中比较常用的数据结构了。继承自 AbstractList,实现了 List 接口。底层基于数组实现容量大小动态变化。允许 null 的存在。同时还实现了 RandomAccess、Cloneable、Serializable 接口,所以ArrayList 是支持快速访问、复制、序列化的。
2、重要属性
默认初始容量 10
/*** Default initial capacity.*/private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA与DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA这两个变量使用在构造函数中
这两个空的数组有什么区别?We distinguish this from EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA to know how much to inflate when first element is added.区分第一次添加元素的时候知道elementData从空的构造函数还是有参构造函数初始化的。以便于确认如何扩容。
/*** Shared empty array instance used for empty instances.*/private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};/*** Shared empty array instance used for default sized empty instances*/private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
存储数组列表元素的数组缓冲区
/*** The array buffer into which the elements of the ArrayList are stored.* The capacity of the ArrayList is the length of this array buffer. Any* empty ArrayList with elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA* will be expanded to DEFAULT_CAPACITY when the first element is added.*/transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
数组中元素的大小,size是指elementData中实际有多少个元素,elementData.length为集合容量,表示集合当前最多可以容纳多少个元素
/*** The size of the ArrayList (the number of elements it contains).*/private int size;
modCount定义在父类AbstractList中。记录List的操作次数。主要使用在Iterator中,防止在迭代的过程中集合被修改
/*** The number of times this list has been <i>structurally modified</i>\*/protected transient int modCount = 0;
3、构造函数
3.1 无参构造函数
需要注意的是无参构造函数,给elementData赋值的是一个空的数组,在第一次添加元素的时候才把容量扩大为10,不要被注释给误导了。此处可见无参构造器是将DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA赋值给elementData
/*** Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten.*/public ArrayList() {this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;}
3.2 构造一个初始容量为initialCapacity的ArrayList
当initialCapacity>0,初始化一个大小为initialCapacity的Object数组,赋值给elementData;当initialCapacity==0,将EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA赋值给elementData;否则,抛出异常。
/*** Constructs an empty list with the specified initial capacity.*/public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {if (initialCapacity > 0) {this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;} else {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+ initialCapacity);}}
3.3 通过指定的Collection来初始化一个ArrayList
将Collection转为数组并且赋值给elementData,elementData.length赋值给size;如果size != 0,则判断elementData类型是否为Object[]类型,不是则做一次转换(注意此处其实是一个官方bug解决方案);如果size == 0则将EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA赋值给elementData,相当于new ArrayList(0)
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {elementData = c.toArray();if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) {// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);} else {// replace with empty array.this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;}}
4、核心方法
4.1 add 操作
ensureCapacityInternal();
每次添加元素到集合中都会先确认集合容量的大小;
public boolean add(E e) {ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!elementData[size++] = e;return true;}
判断elementData==DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA则取DEFAULT_CAPACITY和minCapacity的最大值,也就是10;此处验证了在第一次插入的时候才会给数组初始容量10;
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity));}private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) {if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);}return minCapacity;}
modCount++;
记录操作次数;
minCapacity - elementData.length > 0;
数组长度不够时对数组进行扩容,执行grow()函数的逻辑
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {modCount++;// overflow-conscious codeif (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)grow(minCapacity);}
oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1)
默认将数组的大小扩容到原来的1.5倍
newCapacity - minCapacity < 0
如果扩容后的容量不足,则将所需容量minCapacity赋值给newCapacity,扩容后数组大小就是申请的容量
newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0
如果扩容后的数组容量太大,超过了Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8的大小,则数组的大小为hugeCapacity(),(minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
private void grow(int minCapacity) {// overflow-conscious codeint oldCapacity = elementData.length;int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)newCapacity = minCapacity;if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);}private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {if (minCapacity < 0) // overflowthrow new OutOfMemoryError();return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?Integer.MAX_VALUE :MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;}
其余add()方法大同小异
public void add(int index, E element) {rangeCheckForAdd(index);ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, size - index);elementData[index] = element;size++;}public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {Object[] a = c.toArray();int numNew = a.length;ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCountSystem.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, size, numNew);size += numNew;return numNew != 0;}public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {rangeCheckForAdd(index);Object[] a = c.toArray();int numNew = a.length;ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCountint numMoved = size - index;if (numMoved > 0)System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew, numMoved);System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew);size += numNew;return numNew != 0;}
4.2 remove 操作
rangeCheck(index);
检查index是否合法,当index >= size时,抛出IndexOutOfBoundsException异常;
modCount++;
记录集合的操作次数;
E oldValue = elementData(index);
取出移除元素,用于放回给方法调用者;
if (numMoved > 0)
判断当前删除的集合元素是否时数组的最后一个元素,如果不是最后一个元素,则调用System.arraycopy()方法做一次数组拷贝;如果移除的元素是最后一个元素或者在数组复制结束之后,将数组的最后一个元素置为null,等待GC垃圾回收;--size数组的大小减一;
public E remove(int index) {rangeCheck(index);modCount++;E oldValue = elementData(index);int numMoved = size - index - 1;if (numMoved > 0)System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved);elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its workreturn oldValue;}
4.3 get 操作
rangeCheck(index);
检查index是否合法,当index >= size时,抛出IndexOutOfBoundsException异常;
elementData(index);
由于ArrayList的底层是由数组实现的,所有获取元素直接调用数组的随机访问即可;
public E get(int index) {rangeCheck(index);return elementData(index);}
5、Iterator
5.1 前言
Java开发初级工程师在使用for遍历集合的时候,由于使用不正确的API方法对集合进行remove()操作,经常会抛出java.util.ConcurrentModificationException,因此我们来从源码的层面仔细的探究一下为什么会产生ConcurrentModificationException以及如何解决这个异常!foreach循环又称增强for循环,是jdk1.5为了简化数组或者和容器遍历而产生,foreach循环的适用范围:对于任何实现了Iterable接口的容器都可以使用foreach循环。foreach语法的冒号后面可以有两种类型,一种是数组类型;一种是实现了Iterable接口的类,因此在使用foreach循环遍历ArrayList的时候,可以看作就是在使用List的迭代器进行遍历
如下代码,foreach遍历list集合时,调用list.remove(s)方法,控制台输出了预期ConcurrentModificationException异常
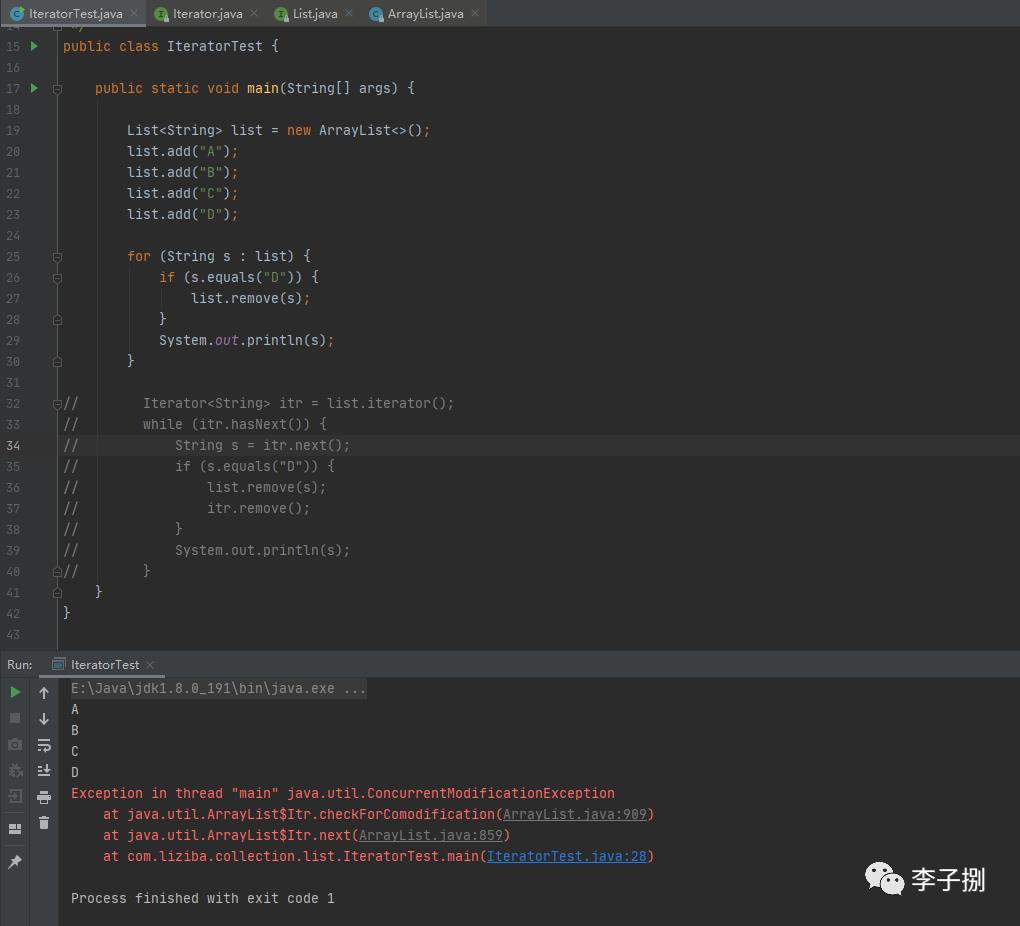
5.2 ArrayList中Iterator
本质上返回的是一个Itr实例化对象
public Iterator<E> iterator() {return new Itr();}
ArrayList定义了一个Itr内部类实现了Iterator接口,Itr内部有三个属性。
cursor:代表的是下一个访问的元素下标;
lastRet:代表的是上一个访问元素的下标,默认值为-1;
expectedModCount:代表的是对ArrayList修改的次数,初始值等于modCount
/*** An optimized version of AbstractList.Itr*/private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {int cursor; // index of next element to returnint lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; -1 if no suchint expectedModCount = modCount;Itr() {}}
hasNext();
判断是否存在下一个元素,返回值只要cursor下一个元素的下标不等于集合的元素个数size就返回true,其他情况返回false
public boolean hasNext() {return cursor != size;}
next() ;
获取集合中的下一个元素
checkForComodification();
判断modCount与expectedModCount是否相等,不相等抛出ConcurrentModificationException异常
i = cursor;i >= size;i >= elementData.length
判断cursor的大小,如果cursor的值大于集合中元素的个数,抛出NoSuchElementException异常;如果cursor大于了数组的长度抛出ConcurrentModificationException异常。
cursor = i + 1;lastRet = i
如果上述情况均满足,则正常获取下一个元素,cursor和lastRet都自增1
public E next() {checkForComodification();int i = cursor;if (i >= size)throw new NoSuchElementException();Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;if (i >= elementData.length)throw new ConcurrentModificationException();cursor = i + 1;return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];}final void checkForComodification() {if (modCount != expectedModCount)throw new ConcurrentModificationException();}
lastRet < 0;
如果lastRet 小于0,则抛出IllegalStateException异常,由此可以看出,调用remove()之前,必须先调用next()方法重置lastRet的值,否则在lastRet默认值为-1的情况下,对集合中的元素进行移除会直接抛出异常;
checkForComodification();
判断modCount与expectedModCount是否相等,不相等抛出ConcurrentModificationException异常
ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet);
调用ArrayList的remove方法,移除元素
cursor = lastRet;lastRet = -1;expectedModCount = modCount;
将lastRet的值赋值给cursor,相当于-1;将lastRet 重置为-1;将modCount赋值给expectedModCount
public void remove() {if (lastRet < 0)throw new IllegalStateException();checkForComodification();try {ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet);cursor = lastRet;lastRet = -1;// 注意这一步非常关键,重新赋值modCount给expectedModCount,是不会出现ConcurrentModificationException异常的关键expectedModCount = modCount;} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {throw new ConcurrentModificationException();}}final void checkForComodification() {if (modCount != expectedModCount)throw new ConcurrentModificationException();}
5.3 图解
初始化时Itr中的cursor=0;lastRet=-1;modCount = 4;expectedModCount=4;注意modCount 的值是在调用ArrayList方法的add()方法时进行modCount++;而expectedModCount的值Itr初始化时,默认等于modCount。
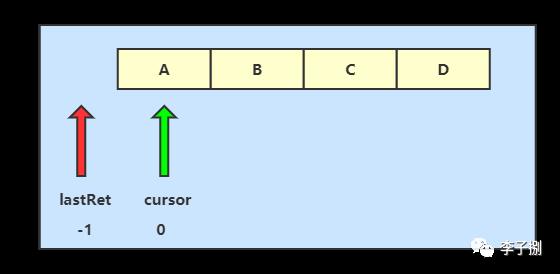
当foreach循环到D元素的时候,cursor=2;lastRet=1;modCount = 4;expectedModCount=4;
当调用list.remove(s)移除了元素“D”之后,cursor=2;lastRet=1;modCount = 5;expectedModCount=4;注意此处调用的时ArrayList的remove()方法
由于ArrayList的foreach遍历实质上相当于ArrayList中的Itr迭代,所以在Itr内部类中的next()方法被调用时,checkForComodification()方法中比较modCount 和 expectedModCount的值,发现二者不相等,则抛出ConcurrentModificationException异常!
public E next() {// 检查modCount 与 expectedModCount的值是否相等checkForComodification();int i = cursor;if (i >= size)throw new NoSuchElementException();Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;if (i >= elementData.length)throw new ConcurrentModificationException();cursor = i + 1;return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];}// 检查modCount 与 expectedModCount的值是否相等final void checkForComodification() {// 不相等则抛出ConcurrentModificationException异常if (modCount != expectedModCount)throw new ConcurrentModificationException();}
5.4 异常解决
调用Iterator的remove()方法即可
public void remove() {// 需要注意的是lastRet<0会直接抛出异常,lastRet在初始化时和移除元素之后会被赋值为-1if (lastRet < 0)throw new IllegalStateException();checkForComodification();try {ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet);cursor = lastRet;// 将lastRet重置为-1lastRet = -1;// 此处会对expectedModCount重新赋值,因而不会出现expectedModCount!=modCountexpectedModCount = modCount;} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {throw new ConcurrentModificationException();}}
以上是关于java集合中的ArrayList源码分析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
JAVA——底层源码阅读——集合ArrayList的实现底层源码分析