论文精选 | 推荐系统——供应链管理中的重要技术方法
Posted JIM期刊
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了论文精选 | 推荐系统——供应链管理中的重要技术方法相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章发表在JIM期刊, Published: 10 July 2020,
链接: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-020-01619-5
摘要

近年来,推荐系统已经成为克服惊人信息增长所带来挑战的重要手段。推荐系统作为客户兴趣的预测工具,被广泛应用于各种场景中,旨在帮助客户决定、对比、发现和探索产品。因此,对该领域的研究主要集中在提高数据处理的效率方面,以便进行及时准确的推荐。然而,当前的产品推荐方法并没有考虑到供应链的交付约束。这可能导致产品的推荐成本较高或发货时间太长,从而导致可避免的供应链压力增加。本文解决了在产品推荐中考虑交付约束的问题,目标是在电子商务环境中,将需求转化为在给定的时间窗口、周长和最小可接受利润的情况下,推荐可以在当前网络状态交付的产品,而不需要额外的资源。为了实现这一目标,本文提出了一种调整产品推荐的方法,将考虑客户的喜好转移到考虑特定产品上,并考虑是否能继续按预定时间交付。为此,考虑供应链的实时信息以提高推荐列表中可发货产品的数量,从而尽可能提高卡车装载利用率,降低运营成本并缩短交货时间。本文的方法分为两个阶段:第一个阶段是传统推荐系统的推荐计算,第二阶段是四个阶段的推荐调整,主要包括:考虑运输卡车的评估,对运输的物理约束进行评估,对与为每个推荐项目在预定行程中增加提货/交付相关的利润的评估以及对推荐分数的调整。针对所提方法中考虑的每个参数:时间窗、周长半径和最小可接受利润,进行了推荐调整对推荐列表影响的敏感性分析。各种实验结果证明,该方法可以在给定的周长半径、时间窗口和最小利润范围内,利用可用资源增加推荐产品的数量。
文章导读
在不断变化的全球市场激烈竞争环境下,客户要求公司对他们快速变化的需求的响应能力越来越高。因此,公司正在大力投资于开发灵活的解决方案,以提高成本效益。通过使用大数据对市场趋势、客户购买行为、需求水平、生产能力等做出分析,以帮助做出更具针对性的业务决策,从而降低成本。
推荐系统(RS)是用于响应电子商务中客户需求的主要技术之一。RS是使用来自不同学科的算法工具,针对每个用户进行个性化设置,并基于历史购买,用户的个人资料和受众特征,点击流等数据,预测用户对商品(产品,服务等)列表的喜好程度,并推荐具有最高销售潜力的商品子集。
RS以客户为导向,专注于帮助客户发现产品,对比并决定哪个选项是最好的,以及发现新产品。在产品推荐方面,被推荐产品的可见性的增加直接影响到对特定产品的需求。因此,推荐系统对生产计划、库存短缺或过剩、计划、执行和交付成本有直接的影响。然而,目前的RS在推荐时没有考虑供应链的约束,这可能导致从公司的角度给出无益的推荐。为了让推荐系统以一种服务于公司利益的方式,他们需要考虑供应链的管理,如:交货期、卡车装载利用率、每件物品的运输距离都可以被考虑来改善推荐系统对工业需求的响应。
优质卓越的供应链体系被认为是当今企业最重要的竞争力来源。在推荐时考虑供应链约束是一种双赢的局面,在这种情况下,客户可以在短时间内从潜在利益的产品中获益,而企业可以从降低成本和提高物流性能中获益。
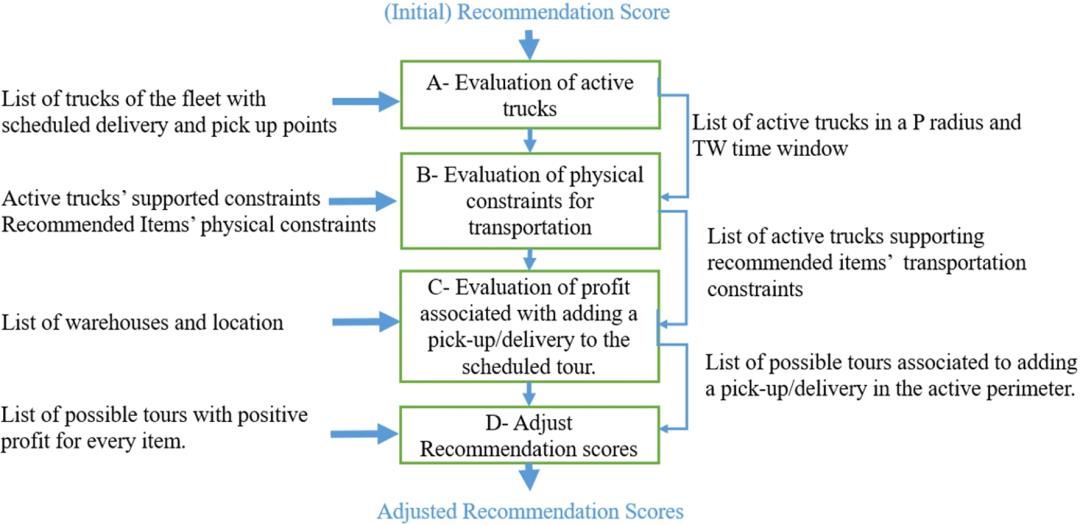
图1 考虑供应链约束的推荐调整算法
本文讨论了在产品推荐中考虑交付约束的问题。其目标是在电子商务环境中,将需求转化为在给定的时间窗口、周长和最小可接受利润的情况下,推荐可以在当前网络状态交付的产品,而不需要额外的资源。为了实现这一目标,本文提出了一种调整产品推荐的方法,将考虑客户的喜好转移到考虑特定产品上,并考虑到是否能继续按预定时间交付。
本文的目的不是追求物流服务KPI,而是选择一些与客户相关的产品,并根据供应链约束来提高其推荐排名,可以当天交货的产品将被选定,从而无需支付过多的额外费用。为此,考虑了使用CPS技术获取的有关供应链网络的准实时信息,以提高推荐列表中的可发货产品数量。如果新的推荐与客户需求符合,那么客户可以订购将在特定时间内交付的产品,并且这一订单满足实际可用的剩余运输能力。因此,本文所提出的方法改善了卡车的利用率和交货时间。进一步的改善包括:更低的运营成本、收入的增加、使用的卡车数量减少、客户的满意度提高、客户保留率提高以及社区交通拥挤和污染的减少。
原文信息

Abstract
In recent years, recommender systems have become necessary in overcoming the challenges related to the incredible growth of information. They are used in a wide range of contexts and applications, mainly as prediction tools for customer interest, designed to help customers decide, compare, discover and explore products (Meyer in Recommender systems in industrial contexts, Sciences et Technologies de l’Information, Grenoble, 2012). Therefore, research in the field has focused on improving the efficiency of data processing for instant and accurate recommendations. Recommendation of products, accordingly, does not take into consideration supply chain constraints for deliveries. This can lead to recommendations for products that can be costly or too long to ship to the customer, resulting in an avoidable increase in the stress on the supply chain. This paper addresses the problem of considering delivery constraints in product recommendations. The objective is to shift demand toward products that can be delivered using the current network state without additional resources in a given time window, perimeter and with a minimum acceptable profit, in the context of e-commerce. To achieve this goal, we propose a methodology to adjust product recommendations in order to shift customers’ interests towards particular products with consideration for remaining unit loads of scheduled deliveries. For this, quasireal-time information about the supply chain is taken into consideration to improve the number of shippable products in the recommendation list, resulting in a possible improvement in truck-load utilization, lower operation costs and reduced lead-times for delivery. This method works in two stages: the first stage is the computation of the recommendation with traditional recommendation systems, and the second stage is recommendation adjustments in four phases that consider the evaluation of active trucks, evaluation of physical constraints for transportation, evaluation of the profits associated with adding a pickup/delivery to a scheduled tour for each recommended item and adjustment of recommendation scores. A sensitivity analysis of the impact of the recommendation adjustment on the recommendation list has been conducted for each of the parameters considered in the proposed method: time window, perimeter radius and minimum acceptable profit. Various experimental results prove that the method permits increasing the number of recommended products that can be shipped using the available resources within a given perimeter radius, time window and minimum profit.
Keywords
E-commerce
Big data
Recommender systems
Supply chain
Agility
Cite this article as:
Dadouchi, C., Agard, B. Recommender systems as an agility enabler in supply chain management. J Intell Manuf (2020).
/本期编辑/
陈妤
上海交通大学 硕士在读
研究方向:复杂网络、调度优化
/本期审核/
许鸿伟
上海交通大学 博士在读
研究方向:工业大数据分析与机器智能。复杂系统建模、分析与优化


聚焦智能制造;传播学术观点;促进合作交流
左边点击“阅读原文”,跳转至原文链接
右边给我一朵小花花
以上是关于论文精选 | 推荐系统——供应链管理中的重要技术方法的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章