AOP的奇妙之处
Posted 花式编程
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了AOP的奇妙之处相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考:http://sishuok.com/forum/blogPost/list/2467.html
blog.csdn.net/qq525099302/article/details/53996344
早之前和朋友聊天,朋友说他写了几天的代码,写了好多,然后给组长看,组长说都删掉吧,然后用AOP,用几行代码就搞定,非常帅,有木有!
后来就一直想学,由于工作原因,和项目没有用到就一直没认真学习,只是略知皮毛,这几天认真学习,从最基层学习,把自己学习心得贴在这里供大家一起学习!
首先贴一张图来展现一下AOP的作用:
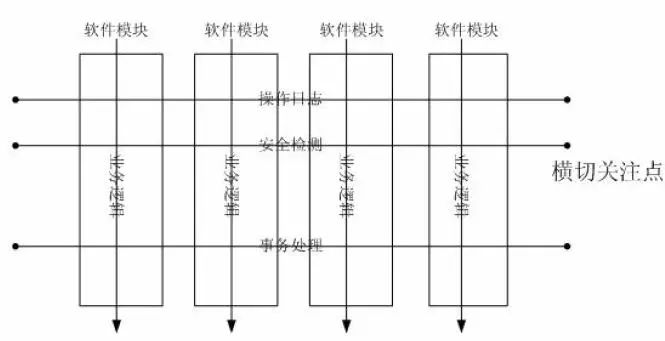
我们传统的编程方式是垂直化的编程,即A->B->C->D这么下去,一个逻辑完毕后执行另外一段逻辑,但是AOP提供了另外一种思路。它的作用是在业务逻辑不知情的情况下对业务代码的功能进行增强,这种编程思想的使用场景有很多,例如事物提交,方法执行之前的权限检测,日志打印,方法调事件等等。
其次我用一个简单的最基础的例子来展现AOP的作用:
1.首先配置pom.xml
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<spring.version>4.1.3.RELEASE</spring.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId>
<version>4.1.3.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2.定义目标类:
public interface IHelloWorldService {
public void sayHello();
}
3.定义目标接口实现
public class HelloWorldService implements IHelloWorldService {
@Override
public void sayHello() {
System.out.println("-----Hello World------");
}
}
4.定义切面接口类:
public class HelloWorldAspect {
//前置通知
public void beforeAdvice(){
System.out.println("------before advice");
}
//后置最终通知
public void afterFinallyAdvice(){
System.out.println("------after finally advice");
}
}
5.在xml中进行配置:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.0.xsd">
<!--配置目标类-->
<bean id="helloWorldService" class="spring.service.HelloWorldService"></bean>
<!--配置切面-->
<bean id="aspect" class="spring.service.HelloWorldAspect"></bean>
//第一种方法:expression="within(spring.service.*)定义在service包下的任意类的执行
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="pointcut" expression="within(spring.service.*)"></aop:pointcut>
<aop:aspect ref="aspect">
<aop:before pointcut-ref="pointcut" method="beforeAdvice"></aop:before>
<aop:after pointcut="within(spring.service.*)" method="afterFinallyAdvice"></aop:after>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
//第二种方法:expression="execution(* spring.service.*.*(..))定义在service包里的任意方法的执行
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="pointcut" expression="execution(* spring.service.*.*(..))"/>
<aop:aspect ref="aspect">
<aop:before pointcut-ref="pointcut" method="beforeAdvice"></aop:before>
<aop:after pointcut="execution(* spring.service.*.*(..))" method="afterFinallyAdvice"></aop:after>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
<beans>
6.测试代码:
public class AopTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("helloworld.xml");
IHelloWorldService helloWorldService = context.getBean("helloWorldService", IHelloWorldService.class);
helloWorldService.sayHello();
}
}
输出结果
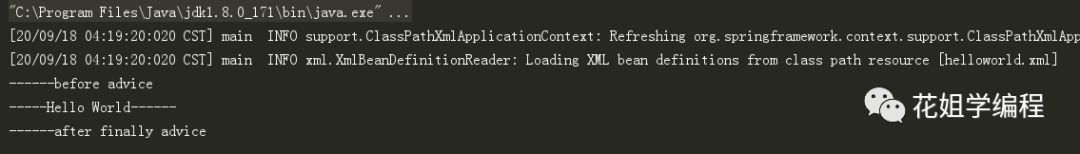
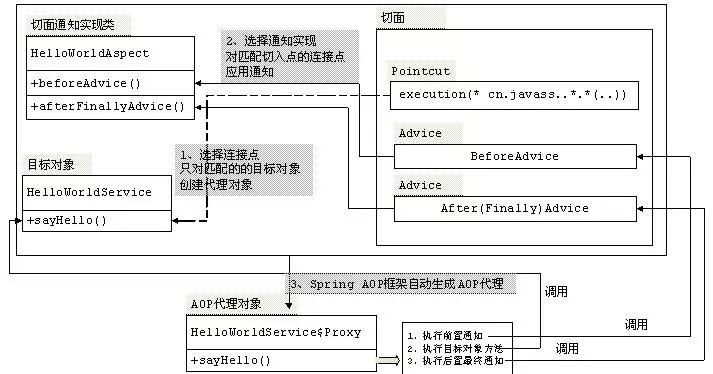
从输出我们可以看出:前置通知在切入点选择的连接点(方法)之前允许,而后置通知将在连接点(方法)之后执行,具体生成AOP代理及执行过程如下图:
最后附上 Spring AOP中pointcut exception表达式解析及配置
任意公共方法的执行:
execution(public * *(..))
任何一个以“set”开始的方法的执行:
execution(* set*(..))
AccountService 接口的任意方法的执行:
execution(* com.xyz.service.AccountService.*(..))
定义在service包里的任意方法的执行:
execution(* com.xyz.service.*.*(..))
定义在service包和所有子包里的任意类的任意方法的执行:
execution(* com.xyz.service..*.*(..))
定义在pointcutexp包和所有子包里的JoinPointObjP2类的任意方法的执行:
execution(* com.test.spring.aop.pointcutexp..JoinPointObjP2.*(..))")
***> 最靠近(..)的为方法名,靠近.*(..))的为类名或者接口名,如上例的JoinPointObjP2.*(..))
pointcutexp包里的任意类.
within(com.test.spring.aop.pointcutexp.*)
pointcutexp包和所有子包里的任意类.
within(com.test.spring.aop.pointcutexp..*)
实现了MyInterface接口的所有类,如果MyInterface不是接口,限定MyInterface单个类.
this(com.test.spring.aop.pointcutexp.MyInterface)
***> 当一个实现了接口的类被AOP的时候,用getBean方法必须cast为接口类型,不能为该类的类型.
带有@MyTypeAnnotation标注的所有类的任意方法.
@within(com.elong.annotation.MyTypeAnnotation)
@target(com.elong.annotation.MyTypeAnnotation)
带有@MyTypeAnnotation标注的任意方法.
@annotation(com.elong.annotation.MyTypeAnnotation)
***> @within和@target针对类的注解,@annotation是针对方法的注解
参数带有@MyMethodAnnotation标注的方法.
@args(com.elong.annotation.MyMethodAnnotation)
参数为String类型(运行是决定)的方法.
args(String)
还有好多好多需要我们学习的,这里就不赘述了,有什么不懂得可以加群一起学习:
点击图片查看更多推荐内容
↓↓↓
Java-GC工作原理
有趣的一题
怎么样才算一个靠谱的程序员!
以上是关于AOP的奇妙之处的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章