微CLI工具箱-WeToolkit
Posted 何小有
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了微CLI工具箱-WeToolkit相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
当需要将一个Python脚本快速提供给用户使用时,直接提供纯命令行指令给用户,不友好。如果开发可视化的GUI界面,又太废时间,而且无法在Linux服务器上使用,于是就整了这个微CLI工具箱-WeToolkit,解决这个问题。
微CLI工具箱-WeToolkit,是一个可以快速集成Python脚本到GUI界面上的小轮子,因为GUI部分是直接使用命令行绘制实现,所以可以实现跨平台执行(只要支持命令行就行),具体实现的效果如下图。
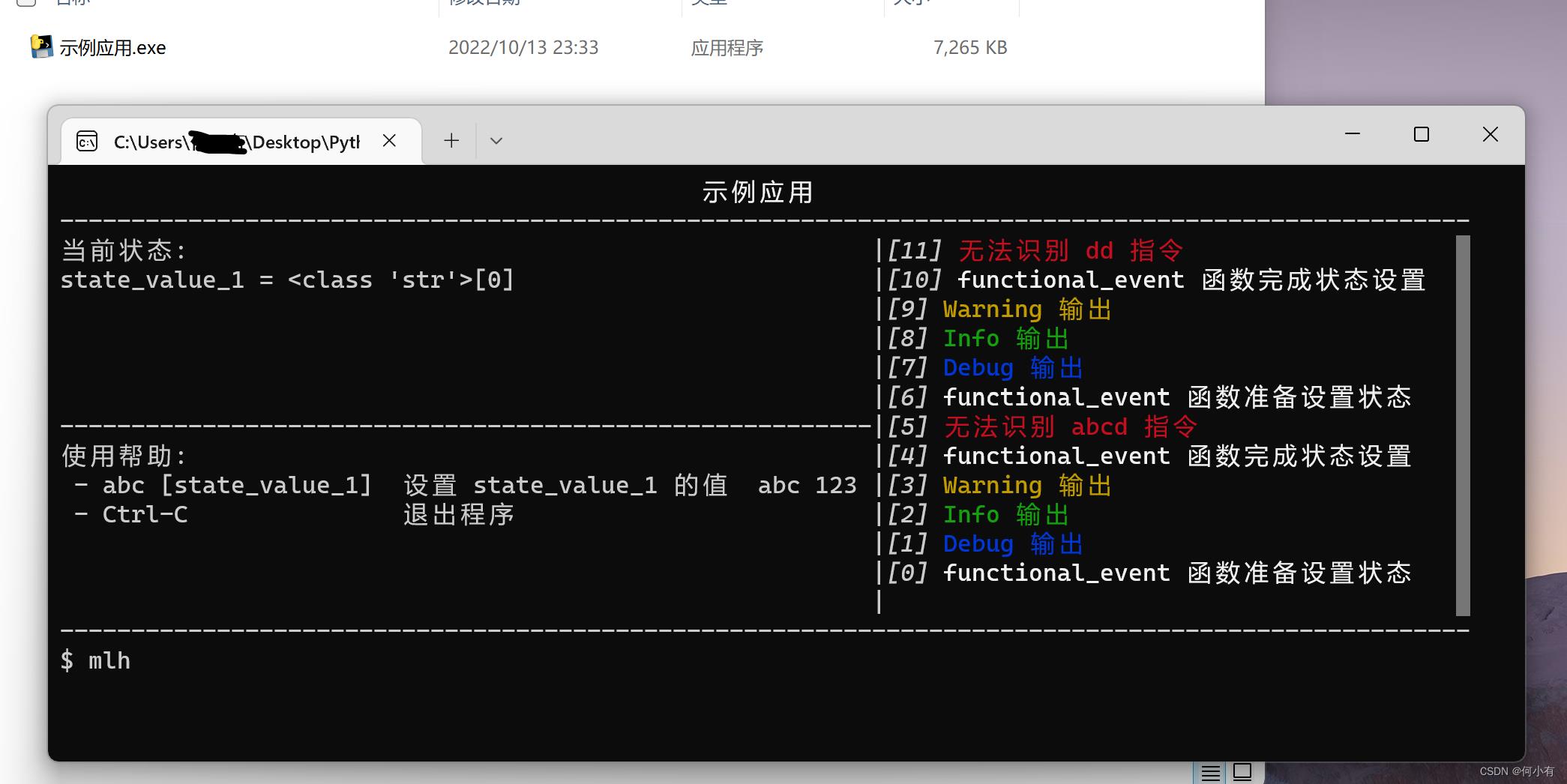
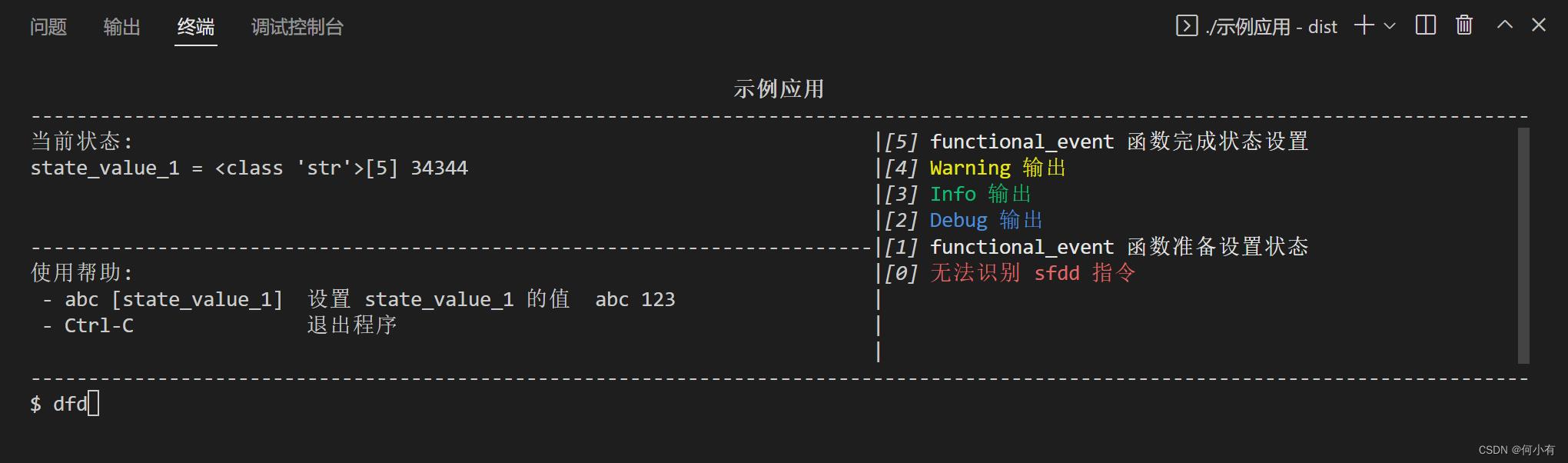
微CLI工具箱-WeToolkit的核心代码只有一个 we_toolkit.py 文件,依赖的第三方库有两个。
- pip install prompt_toolkit
- pip install pyinstaller
import logging
from prompt_toolkit.buffer import Buffer
from prompt_toolkit import Application, html
from prompt_toolkit.layout.layout import Layout
from prompt_toolkit.key_binding import KeyBindings
from prompt_toolkit.layout.processors import BeforeInput
from prompt_toolkit.layout.margins import ScrollbarMargin
from prompt_toolkit.layout.controls import BufferControl, FormattedTextControl
from prompt_toolkit.layout.containers import VSplit, Window, HSplit, WindowAlign
for log_name, log_obj in logging.Logger.manager.loggerDict.items():
# 让其他 Logging 保持沉默, 也可以通过 log_name 判断是否禁用
log_obj.disabled = True
class WeToolkit:
def __init__(
self,
app_title='示例应用',
control_prompt=' - abc [state_value_1] 设置 state_value_1 的值 abc 123\\n - Ctrl-C 退出程序'
):
self.app_title = app_title
self.control_prompt = FormattedTextControl(
text=f'使用帮助:\\ncontrol_prompt')
self.state_control = FormattedTextControl(text='当前状态:')
self.show_control = FormattedTextControl()
self.show_control_cache = []
self.show_control_rows = 0
self.show_control_offset = 0
self.state_dict =
self.input_buffer = Buffer()
self.kb = KeyBindings()
self.layout = self.__root_container()
self.__binding_event()
def __root_container(self):
return Layout(container=HSplit(children=[
Window(
height=1,
align=WindowAlign.CENTER,
content=FormattedTextControl(text=HTML(
value=f'<b>self.app_title</b>', ), ),
),
Window(height=1, char='-', style='class:line'),
VSplit([
HSplit([
Window(content=self.state_control, wrap_lines=True),
Window(height=1, char='-', style='class:line'),
Window(content=self.control_prompt, wrap_lines=True),
]),
Window(width=1, char='|', style='class:line'),
Window(
content=self.show_control,
wrap_lines=True,
right_margins=[
ScrollbarMargin(),
],
),
]),
Window(height=1, char='-', style='class:line'),
Window(
wrap_lines=True,
content=BufferControl(
buffer=self.input_buffer,
input_processors=[
BeforeInput('$ '),
],
),
),
], ), )
def __refresh(self):
self.show_control.text = HTML(value='\\n'.join(
self.show_control_cache[self.show_control_offset:]), )
state_list = []
for state_k, state_v in self.state_dict.items():
if type(state_v) is list:
state_list.append(
f'state_k = type(state_v)[len(state_v)]')
elif type(state_v) is str:
vs = state_v
if len(vs) > 13:
vs = f'vs[:13]...'
state_list.append(
f'state_k = type(state_v)[len(state_v)] vs')
else:
state_list.append(f'state_k = state_v')
self.state_control.text = '当前状态:\\n' + '\\n'.join(state_list)
def _log(self, message: str, level: str = ''):
if level == 'warning':
mag = f'<ansiyellow>message</ansiyellow>'
elif level == 'error':
mag = f'<ansired>message</ansired>'
elif level == 'info':
mag = f'<ansigreen>message</ansigreen>'
elif level == 'debug':
mag = f'<ansiblue>message</ansiblue>'
else:
mag = f'<ansiwhite>message</ansiwhite>'
self.show_control_cache.insert(
0, f'<i>[self.show_control_rows]</i> mag')
self.show_control_rows += 1
self.__refresh()
def functional_event(self, event: str):
if 'abc ' in event:
self._log(message='functional_event 函数准备设置状态')
self._log(message='Debug 输出', level='debug')
self._log(message='Info 输出', level='info')
self._log(message='Warning 输出', level='warning')
self.state_dict['state_value_1'] = event.split(' ')[1]
self._log(message='functional_event 函数完成状态设置')
else:
self._log(message=f'无法识别 event 指令', level='error')
def __binding_event(self):
@self.kb.add('c-m')
def _(event):
""" 按 Enter 触发 """
if not self.input_buffer.text:
return
self.functional_event(self.input_buffer.text)
self.__refresh()
self.input_buffer.text = ''
@self.kb.add('up')
def _(event):
""" 按 方向上键 触发 """
if self.show_control_offset < self.show_control_rows:
self.show_control_offset += 1
self.__refresh()
@self.kb.add('down')
def _(event):
""" 按 方向下键 触发 """
if self.show_control_offset >= 1:
self.show_control_offset -= 1
self.__refresh()
@self.kb.add('c-c')
def _(event):
""" 按 Ctrl-C 触发 """
event.app.exit()
def run(self):
app = Application(
layout=self.layout,
key_bindings=self.kb,
full_screen=True,
)
app.run()
if __name__ == '__main__':
# pyinstaller -F we_toolkit.py -n 示例应用
app = WeToolkit()
app.run()
具体开发时,可以使用下面的命令快速生成虚拟环境:
python -m venv venv
# Linux下进入虚拟环境
# source venv/bin/activate
# Windows下进入虚拟环境
venv/Scripts/activate
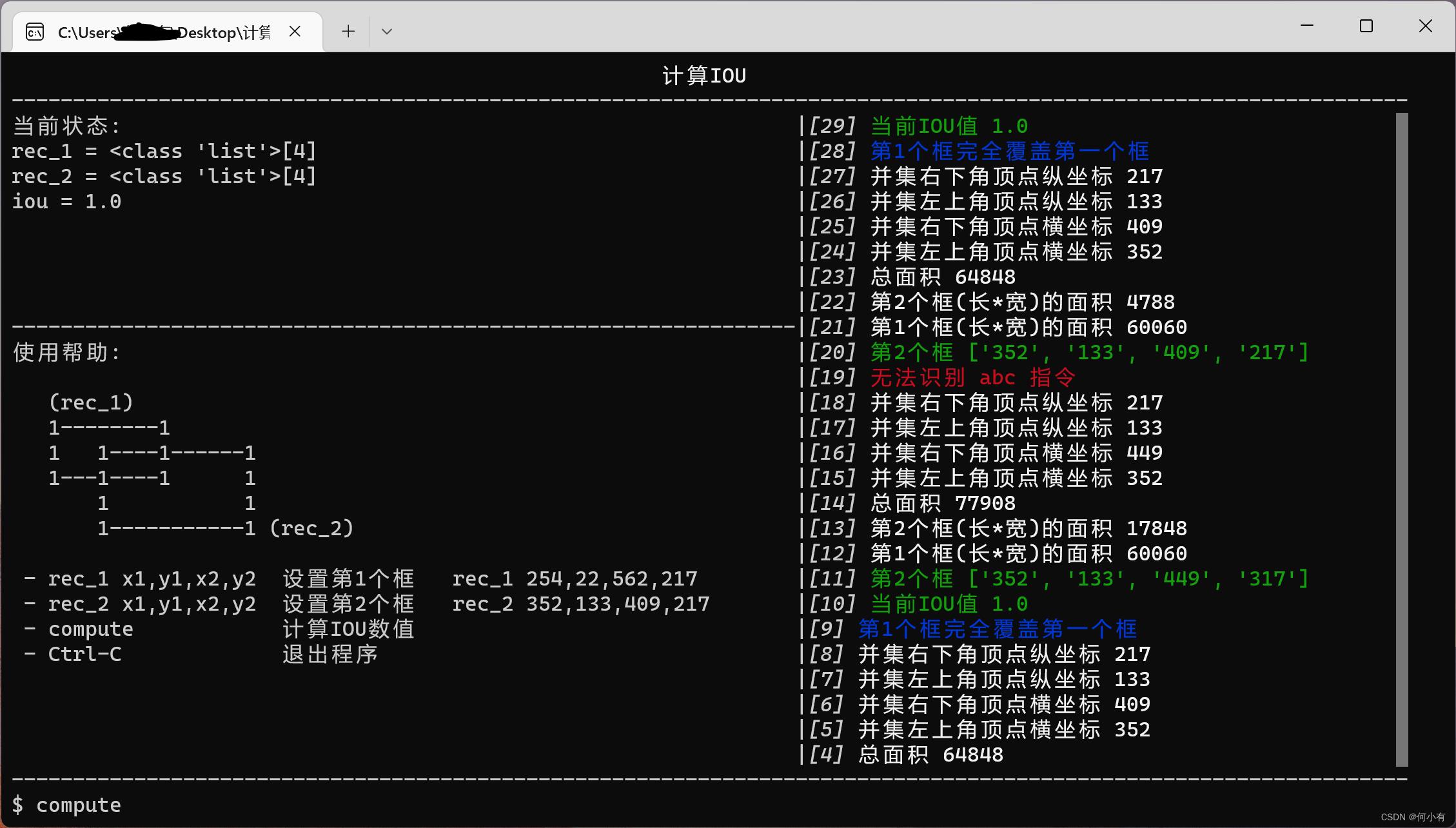
快速使用一:IOU计算工具
使用微CLI工具箱-WeToolkit很简单,只需要在开头导入 WeToolkit (from we_toolkit import WeToolkit) 就可以快速编写脚本功能,比如下面创建的一个 compute_iou.py 文件。
from we_toolkit import WeToolkit
class ComputeIOU(WeToolkit):
def __init__(self):
super(ComputeIOU, self).__init__(
'计算IOU',
'\\n'.join([
'''
(rec_1)
1--------1
1 1----1------1
1---1----1 1
1 1
1-----------1 (rec_2)
''',
' - rec_1 x1,y1,x2,y2 设置第1个框 rec_1 254,22,562,217',
' - rec_2 x1,y1,x2,y2 设置第2个框 rec_2 352,133,409,217',
' - compute 计算IOU数值',
' - Ctrl-C 退出程序',
]),
)
def functional_event(self, event: str):
if 'rec_1 ' in event:
self.state_dict['rec_1'] = event.split(' ')[1].split(',')
self._log(
message=f'第1个框 self.state_dict["rec_1"]',
level='info',
)
elif 'rec_2 ' in event:
self.state_dict['rec_2'] = event.split(' ')[1].split(',')
self._log(
message=f'第2个框 self.state_dict["rec_2"]',
level='info',
)
elif 'compute' in event:
rec_1 = (int(self.state_dict['rec_1'][0]),
int(self.state_dict['rec_1'][1]),
int(self.state_dict['rec_1'][2]),
int(self.state_dict['rec_1'][3]))
rec_2 = (int(self.state_dict['rec_2'][0]),
int(self.state_dict['rec_2'][1]),
int(self.state_dict['rec_2'][2]),
int(self.state_dict['rec_2'][3]))
s_rec1 = (rec_1[2] - rec_1[0]) * (rec_1[3] - rec_1[1])
self._log(message=f'第1个框(长*宽)的面积 s_rec1')
s_rec2 = (rec_2[2] - rec_2[0]) * (rec_2[3] - rec_2[1])
self._log(message=f'第2个框(长*宽)的面积 s_rec2')
sum_s = s_rec1 + s_rec2
self._log(message=f'总面积 sum_s')
left = max(rec_1[0], rec_2[0])
self._log(message=f'并集左上角顶点横坐标 left')
right = min(rec_1[2], rec_2[2])
self._log(message=f'并集右下角顶点横坐标 right')
bottom = max(rec_1[1], rec_2[1])
self._log(message=f'并集左上角顶点纵坐标 bottom')
top = min(rec_1[3], rec_2[3])
self._log(message=f'并集右下角顶点纵坐标 top')
if left >= right or top <= bottom: # 不存在并集的情况
iou = 0
elif s_rec1 > s_rec2:
if rec_2[0] >= rec_1[0] and rec_2[2] <= rec_1[2] and rec_2[
1] >= rec_1[1] and rec_2[3] <= rec_1[3]:
self._log(message='第1个框完全覆盖第一个框', level='debug')
iou = 1.0
else:
inter = (right - left) * (top - bottom) # 求并集面积
iou = (inter / (sum_s - inter)) * 1.0 # 计算IOU
self.state_dict['iou'] = iou
self._log(
message=f'当前IOU值 self.state_dict["iou"]',
level='info' if self.state_dict['iou'] else 'warning',
)
else:
self._log(message=f'无法识别 event 指令', level='error')
if __name__ == '__main__':
# pyinstaller -F compute_iou.py -n 计算IOU
app = ComputeIOU()
app.run()
然后在 Linux 或 Windows 环境下执行 pyinstaller -F compute_iou.py -n 计算IOU 就可以生成一个可执行文件。
快速使用二:词频提取工具
要实现文本词频和关键词提取,需要依赖下面两个第三方库。
- pip install zhon
- pip install jieba
同样在开头导入 WeToolkit (from we_toolkit import WeToolkit),再创建一个 word_frequency.py 文件。
import string
import jieba
# https://blog.csdn.net/lucyTheSlayer/article/details/92795220
import jieba.analyse
import operator
from zhon.hanzi import punctuation
from we_toolkit import WeToolkit
class WordFrequency(WeToolkit):
def __init__(self):
super(WordFrequency, self).__init__(
'词频与关键词提取',
'\\n'.join([
' - load [txt_file] 加载文件 load demo.txt',
' - frequency 文本词频分析',
' - extraction 文本关键词提取',
' - export [txt_file] 导出结果文件 export export.txt',
' - Ctrl-C 退出程序',
]),
)
def functional_event(self, event: str):
if 'load ' in event:
self.state_dict['file_path'] = event.split(' ')[1]
file_str = open(self.state_dict['file_path'],
'r',
encoding='UTF-8').read()
self.state_dict['raw_rows'] = file_str.split('\\n')
# 删除文本中的空格/回车/换行/中英文符号
for rs in [' ', '\\n', '\\r']:
file_str = file_str.replace(rs, '')
for i in punctuation:
file_str = file_str.replace(i, '')
for j in string.punctuation:
file_str = file_str.replace(j