猿创征文|AnimeGANv2 照片动漫化:如何基于 PyTorch 和神经网络给 GirlFriend 制作漫画风头像?
Posted 白鹿第一帅
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了猿创征文|AnimeGANv2 照片动漫化:如何基于 PyTorch 和神经网络给 GirlFriend 制作漫画风头像?相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、基于 GAN 实现漫画风格实现原理
- 二、AnimeGANv2 照片动漫化
- 三、本次案例部署及实验平台介绍
- 四、获取代码和数据
- 五、安装依赖库
- 六、AnimeGANv2 源码解析
- 七、素材应用照片动漫化
- 八、在线体验
- 总结
前言
将现实世界场景的照片转换为动漫风格图像的方法,这是计算机视觉和艺术风格转换中一项有意义且具有挑战性的任务,而本文中我们介绍的 AnimeGAN 就是 GitHub 上一款爆火的二次元漫画风格迁移工具,可以实现快速的动画风格迁移。该工具是基于神经风格迁移和生成对抗网络 (GAN) 技术打造的,相比于传统的神经网络模型,GAN 是一种全新的非监督式的架构。最近 AnimeGAN 发布了其二代版本,据称更新后 AnimeGANv2 支持了风景照片和风景视频的三种动漫化风格(分别是宫崎骏、新海诚和金敏),视觉效果更佳,模型体量也更小且容易训练了。
一、基于 GAN 实现漫画风格实现原理
1.1、传统漫画风格迁移工具的不足
- 生成的图像没有明显的动画风格纹理。
- 生成的图像丢失了原始图像的内容。
- 网络的参数需要大的存储容量。
1.2、基于生成对抗网络 (GAN) 的漫画风格迁移工具
通过三种新颖的损失函数,使生成的图像具有更好的动画视觉效果,这些损失函数是灰度样式损失、灰度对抗损失和颜色重建损失。AnimeGAN 可以很容易地使用未配对的训练数据进行端到端训练。
- AnimeGAN 的参数需要较低的内存容量。实验结果表明,该方法可以快速将真实世界的照片转换为高质量的动漫图像,并且优于最先进的方法。
- AnimeGAN 的参数需要较低的内存容量。实验结果表明,该方法可以快速将真实世界的照片转换为高质量的动漫图像,并且优于最先进的方法。
- AnimeGAN 的参数需要较低的内存容量。实验结果表明,该方法可以快速将真实世界的照片转换为高质量的动漫图像,并且优于最先进的方法。
实现原理可以参考原论文:https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-981-15-5577-0_18,具体如下图所示:

二、AnimeGANv2 照片动漫化
2.1、与 AnimeGAN 的对比
AnimeGANv2 是照片漫画工具 AnimeGAN 的升级版本,AnimeGANv2 在训练 AI 时 GAN 包括了两套独立的网络 A 和 B,A 网络是需要训练的分类器,用来分辨成图是否符合标准;B 网络是生成器,生成类似于真实样本的随机样本,并将其作为假样本以欺骗网络 A。在 A 和 B 的对抗中,AI 的水平逐渐提升,最后实现质的飞跃,相较于之前版本,AnimeGANv2 主要在以下四个方面进行优化:
- 解决生成图片的高频伪影问题。
- 易于训练,达到实物纸张效果。
- 减少生成器网络参数。
- 尽可能用高质量的图片样式数据。
2.2、AnimeGANv2 效果及项目介绍
AnimeGANv2 可以将现实场景的图片处理为动漫画风,目前支持宫崎骏、新海诚和今敏的三种风格,三者实现效果具体如下图所示:

Github 地址:https://github.com/TachibanaYoshino/AnimeGANv2,详情具体如下图所示:

三、本次案例部署及实验平台介绍
3.1、对象存储服务 OBS
我们将本次案例中的相关代码和数据存放于华为云提供的对象存储服务 OBS 中,推荐大家使用:https://www.huaweicloud.com/product/obs.html,产品详细信息具体如下图所示:
对象存储服务(Object Storage Service,OBS)提供海量、安全、高可靠、低成本的数据存储能力,可供用户存储任意类型和大小的数据。适合企业备份/归档、视频点播、视频监控等多种数据存储场景,在我本人的使用以及测试中对象存储服务 OBS 效果颇好,故推荐给大家使用,具体如下图所示:
3.2、AI 开发平台 ModelArts
本次案例运行的实验平台为华为云的 AI 开发平台 ModelArts,详细信息请点击:https://support.huaweicloud.com/modelarts/index.html,产品详细信息具体如下图所示:

ModelArts 是面向开发者的一站式 AI 开发平台,为机器学习与深度学习提供海量数据预处理及半自动化标注、大规模分布式 Training、自动化模型生成,及端-边-云模型按需部署能力,帮助用户快速创建和部署模型,管理全周期 AI 工作流,在我本人的使用以及测试中 ModelArts 效果颇好且提供了可以满足不同开发需求的运行环境(部分免费),故推荐给大家使用,具体如下图所示:

可以在华为云 AI 开发平台 ModelArts 提供的 JupyterLab 中选择不同的实验环境内核,具体如下图所示:

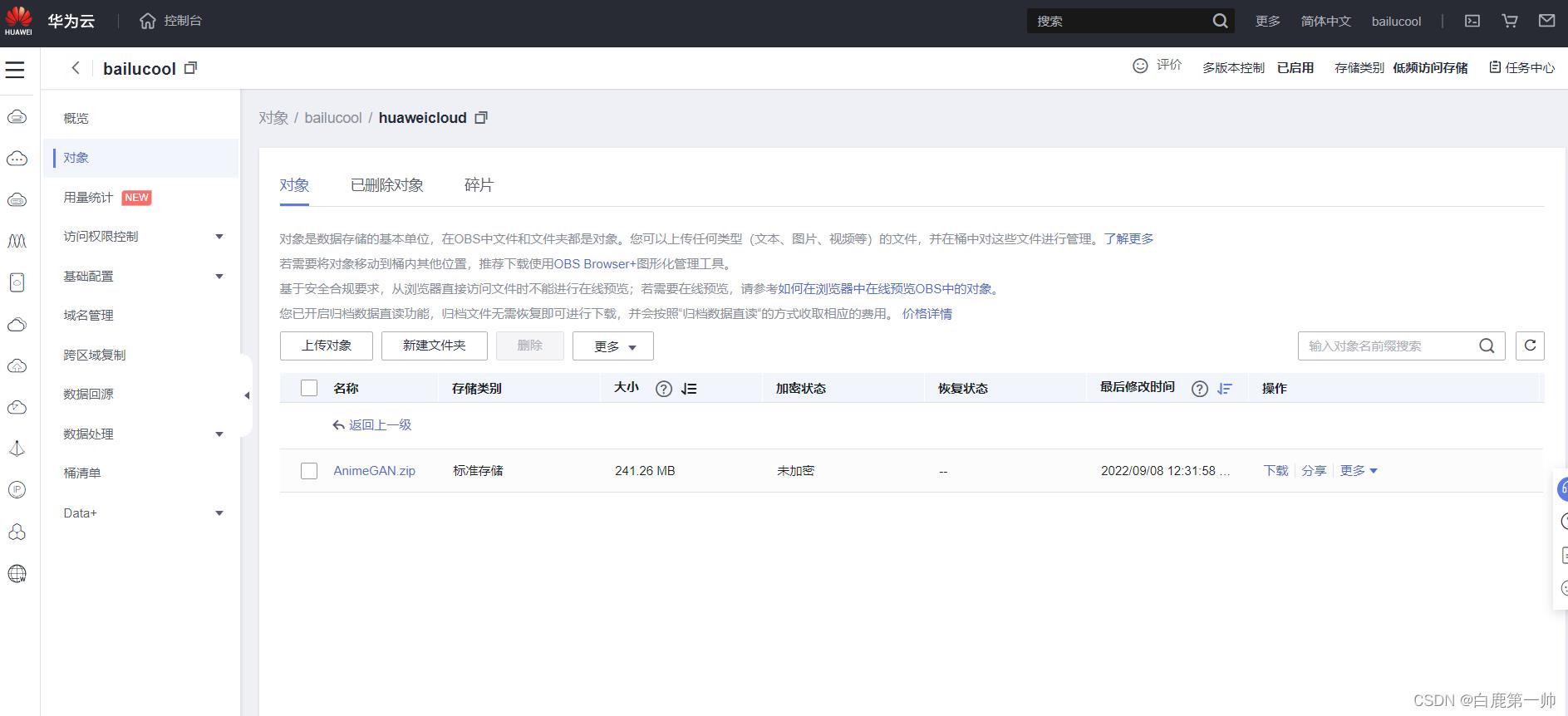
四、获取代码和数据
获取代码和数据,相关实现命令如下所示:
import os
!wget https://obs-aigallery-zc.obs.cn-north-4.myhuaweicloud.com/clf/code/AnimeGAN/AnimeGAN.zip
os.system('unzip AnimeGAN.zip')
我们可以在华为云 AI 开发平台 ModelArts 提供的 JupyterLab 查看具体运行过程和结果,具体如下图所示:

五、安装依赖库
安装依赖库,相关实现命令如下所示:
!pip install dlib
!pip uninstall -y torch
!pip uninstall -y torchvision
!pip install torch
!pip install torchvision
%cd AnimeGANv2
我们可以在华为云 AI 开发平台 ModelArts 提供的 JupyterLab 查看具体运行过程和结果,具体如下图所示:

说明:由于运行结果过于冗长,仅截取首端与末端运行结果。

六、AnimeGANv2 源码解析
## AnimeGANv2源码解析
import os
import dlib
import collections
from typing import Union, List
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def get_dlib_face_detector(predictor_path: str = "shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat"):
if not os.path.isfile(predictor_path):
model_file = "shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat.bz2"
os.system(f"wget http://dlib.net/files/model_file")
os.system(f"bzip2 -dk model_file")
detector = dlib.get_frontal_face_detector()
shape_predictor = dlib.shape_predictor(predictor_path)
def detect_face_landmarks(img: Union[Image.Image, np.ndarray]):
if isinstance(img, Image.Image):
img = np.array(img)
faces = []
dets = detector(img)
for d in dets:
shape = shape_predictor(img, d)
faces.append(np.array([[v.x, v.y] for v in shape.parts()]))
return faces
return detect_face_landmarks
def display_facial_landmarks(
img: Image,
landmarks: List[np.ndarray],
fig_size=[15, 15]
):
plot_style = dict(
marker='o',
markersize=4,
linestyle='-',
lw=2
)
pred_type = collections.namedtuple('prediction_type', ['slice', 'color'])
pred_types =
'face': pred_type(slice(0, 17), (0.682, 0.780, 0.909, 0.5)),
'eyebrow1': pred_type(slice(17, 22), (1.0, 0.498, 0.055, 0.4)),
'eyebrow2': pred_type(slice(22, 27), (1.0, 0.498, 0.055, 0.4)),
'nose': pred_type(slice(27, 31), (0.345, 0.239, 0.443, 0.4)),
'nostril': pred_type(slice(31, 36), (0.345, 0.239, 0.443, 0.4)),
'eye1': pred_type(slice(36, 42), (0.596, 0.875, 0.541, 0.3)),
'eye2': pred_type(slice(42, 48), (0.596, 0.875, 0.541, 0.3)),
'lips': pred_type(slice(48, 60), (0.596, 0.875, 0.541, 0.3)),
'teeth': pred_type(slice(60, 68), (0.596, 0.875, 0.541, 0.4))
fig = plt.figure(figsize=fig_size)
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1)
ax.imshow(img)
ax.axis('off')
for face in landmarks:
for pred_type in pred_types.values():
ax.plot(
face[pred_type.slice, 0],
face[pred_type.slice, 1],
color=pred_type.color, **plot_style
)
plt.show()
# https://github.com/NVlabs/ffhq-dataset/blob/master/download_ffhq.py
import PIL.Image
import PIL.ImageFile
import numpy as np
import scipy.ndimage
def align_and_crop_face(
img: Image.Image,
landmarks: np.ndarray,
expand: float = 1.0,
output_size: int = 1024,
transform_size: int = 4096,
enable_padding: bool = True,
):
# 将五官数据转为数组
# pylint: disable=unused-variable
lm = landmarks
lm_chin = lm[0 : 17] # left-right
lm_eyebrow_left = lm[17 : 22] # left-right
lm_eyebrow_right = lm[22 : 27] # left-right
lm_nose = lm[27 : 31] # top-down
lm_nostrils = lm[31 : 36] # top-down
lm_eye_left = lm[36 : 42] # left-clockwise
lm_eye_right = lm[42 : 48] # left-clockwise
lm_mouth_outer = lm[48 : 60] # left-clockwise
lm_mouth_inner = lm[60 : 68] # left-clockwise
# 计算辅助向量
eye_left = np.mean(lm_eye_left, axis=0)
eye_right = np.mean(lm_eye_right, axis=0)
eye_avg = (eye_left + eye_right) * 0.5
eye_to_eye = eye_right - eye_left
mouth_left = lm_mouth_outer[0]
mouth_right = lm_mouth_outer[6]
mouth_avg = (mouth_left + mouth_right) * 0.5
eye_to_mouth = mouth_avg - eye_avg
# 提取矩形框
x = eye_to_eye - np.flipud(eye_to_mouth) * [-1, 1] # flipud函数实现矩阵的上下翻转;数组乘法,每行对应位置相乘
x /= np.hypot(*x)
x *= max(np.hypot(*eye_to_eye) * 2.0, np.hypot(*eye_to_mouth) * 1.8)
x *= expand
y = np.flipud(x) * [-1, 1]
c = eye_avg + eye_to_mouth * 0.1
quad = np.stack([c - x - y, c - x + y, c + x + y, c + x - y])
qsize = np.hypot(*x) * 2
# 缩放
shrink = int(np.floor(qsize / output_size * 0.5))
if shrink > 1:
rsize = (int(np.rint(float(img.size[0]) / shrink)), int(np.rint(float(img.size[1]) / shrink)))
img = img.resize(rsize, PIL.Image.ANTIALIAS)
quad /= shrink
qsize /= shrink
# 裁剪
border = max(int(np.rint(qsize * 0.1)), 3)
crop = (int(np.floor(min(quad[:,0]))), int(np.floor(min(quad[:,1]))), int(np.ceil(max(quad[:,0]))), int(np.ceil(max(quad[:,1]))))
crop = (max(crop[0] - border, 0), max(crop[1] - border, 0), min(crop[2] + border, img.size[0]), min(crop[3] + border, img.size[1]))
if crop[2] - crop[0] < img.size[0] or crop[3] - crop[1] < img.size[1]:
img = img.crop(crop)
quad -= crop[0:2]
# 填充数据
pad = (int(np.floor(min(quad[:,0]))), int(np.floor(min(quad[:,1]))), int(np.ceil(max(quad[:,0]))), int(np.ceil(max(quad[:,1]))))
pad = (max(-pad[0] + border, 0), max(-pad[1] + border, 0), max(pad[2] - img.size[0] + border, 0), max(pad[3] - img.size[1] + border, 0))
if enable_padding and max(pad) > border - 4:
pad = np.maximum(pad, int(np.rint(qsize * 0.3)))
img = np.pad(np.float32(img), ((pad[1], pad[3]), (pad[0], pad[2]), (0, 0)), 'reflect')
h, w, _ = img.shape
y, x, _ = np.ogrid[:h, :w, :1]
mask = np.maximum(1.0 - np.minimum(np.float32(x) / pad[0], np.float32(w-1-x) / pad[2]), 1.0 - np.minimum(np.float32(y) / pad[1], np.float32(h-1-y) / pad[3]))
blur = qsize * 0.02
img += (scipy.ndimage.gaussian_filter(img, [blur, blur, 0]) - img) * np.clip(mask * 3.0 + 1.0, 0.0, 1.0)
img += (np.median(img, axis=(0,1)) - img) * np.clip(mask, 0.0, 1.0)
img = PIL.Image.fromarray(np.uint8(np.clip(np.rint(img), 0, 255)), 'RGB')
quad += pad[:2]
# 转化图片
img = img.transform((transform_size, transform_size), PIL.Image.QUAD, (quad + 0.5).flatten(), PIL.Image.BILINEAR)
if output_size < transform_size:
img = img.resize((output_size, output_size), PIL.Image.ANTIALIAS)
return img
#@title AnimeGAN model from https://github.com/bryandlee/animegan2-pytorch
# ! git clone https://github.com/bryandlee/animegan2-pytorch
model_fname = "face_paint_512_v2_0.pt"
# model_urls =
# "face_paint_512_v0.pt": "https://drive.google.com/uc?id=1WK5Mdt6mwlcsqCZMHkCUSDJxN1UyFi0-",
# "face_paint_512_v2_0.pt": "https://drive.google.com/uc?id=18H3iK09_d54qEDoWIc82SyWB2xun4gjU",
#
# ! gdown model_urls[model_fname]
import sys
sys.path.append("animegan2-pytorch")
import torch
torch.set_grad_enabled(False)
print(torch.__version__, torch.cuda.is_available())
from model import Generator
device = "cpu"
model = Generator().eval().to(device)
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_fname))
from PIL