Tensorflow入门-实现神经网络
Posted yqtaowhu
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Tensorflow入门-实现神经网络相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
学习tensorflow一段时间了,感觉非常的好用,在使用时,有时候最重要的是想好神经网络的结构,这样就可以随意的在神经网络中加如隐含层了,特别主要的是矩阵的维度相乘的问题,下面将使用tensorflow实现神经网络,做一下自己的理解.
实现无隐含层的神经网络
下面以手写数字识别的例子作为说明.
读入数据
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data/',one_hot=True)查看数据情况:
分为训练数据,验证数据和测试数据三类.
print mnist.train.images.shape
print mnist.train.labels.shape
print mnist.test.images.shape
print mnist.test.labels.shape
print mnist.validation.images.shape
print mnist.validation.labels.shape
######################
##这里有55000*784,784为每一个图片的维度,被拉成一个长的向量
(55000, 784)
(55000, 10)
(10000, 784)
(10000, 10)
(5000, 784)
(5000, 10)这里注意一下,输入训练的x为 n*784 ,w 为 784*10 输出的y为: n*10,即每一个行向量有10个列,表示了其代表0,1…9的概率值.
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,784])其表示,在进行run的时候才读入数据.
y = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(x,W)+b) softmax为转出每个标签的概率,表示预测的结果.其公式为:
可以看到,只不过对输出做了一个概率上的统计而已.
预测作为了,我们还需要一个损失函数,传递误差,所用的损失函数为交叉熵损失:
其中y为真实的值,y’为预测的值
注意reduce_sum的使用:
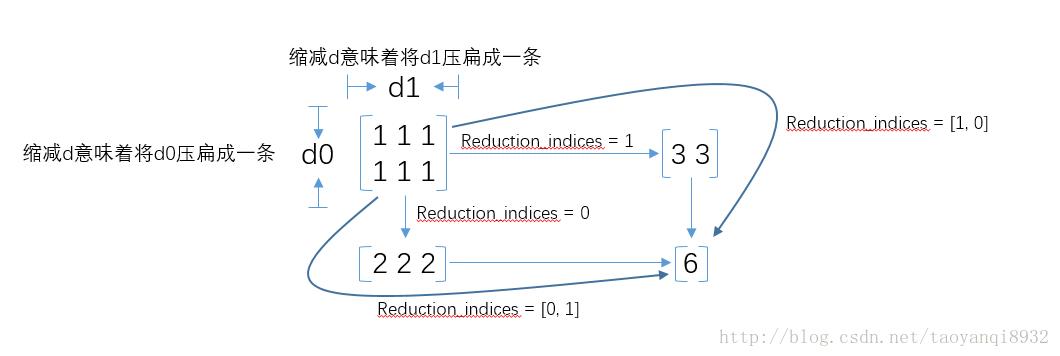
图片来源:知乎
reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(y_*tf.log(y),reduction_indices=[1]))
所以此语句的意思是将每一个样本的损失加起来,然后在用reduce_mean()求平均.因为y,y’都为1*10的向量,这是要注意的.
接下来就是要定义训练的方式,采用梯度下降,来最小话交叉熵.
tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.5).minimize(cross_entropy)
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
#real data
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,784])
y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,10])
W = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784,10]))
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]))
#predict
y = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(x,W)+b)
#loss
cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(y_*tf.log(y),reduction_indices=[1]))
#train ways
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.5).minimize(cross_entropy)进行训练
##重点,全局参数初始化
tf.global_variables_initializer().run()
##迭代1000次,每次取出100个样本进行训练SGD
for i in range(1000):
batch_x,batch_y = mnist.train.next_batch(100)
train_step.run(x:batch_x,y_:batch_y)train_step.run(x:batch_x,y_:batch_y)这种方式为在运行的时候,feed_dict给x,y_的值,其中x为训练样本,y_为对应的真值.
评估
#test
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y,1),tf.argmax(y_,1)) #高维度的
acuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction,tf.float32)) #要用reduce_mean
print acuracy.eval(x:mnist.test.images,y_:mnist.test.labels)最终的结果为:0.9174
实现多层神经网络
为了方便的添加层,写一个添加层的函数,其中in_size,out_size都为神经元的尺度,input为上一层的输出,output为这一层的输出.
完整代码如下:
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/",one_hot=True)
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
#定义添加隐含层的函数
def add_layer(inputs, in_size, out_size,keep_prob=1.0,activation_function=None):
Weights = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([in_size,out_size],stddev=0.1))
biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([out_size]))
Wx_plus_b = tf.matmul(inputs, Weights) + biases
if activation_function is None:
outputs = Wx_plus_b
else:
outputs = activation_function(Wx_plus_b)
outputs = tf.nn.dropout(outputs,keep_prob) #随机失活
return outputs
# holder变量
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,784])
y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,10])
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32) # 概率
h1 = add_layer(x,784,300,keep_prob,tf.nn.relu)
##输出层
w = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([300,10])) #300*10
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]))
y = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(h1,w)+b)
#定义loss,optimizer
cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(y_ * tf.log(y),reduction_indices=[1]))
train_step =tf.train.AdagradOptimizer(0.35).minimize(cross_entropy)
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y,1),tf.argmax(y_,1)) #高维度的
acuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction,tf.float32)) #要用reduce_mean
tf.global_variables_initializer().run()
for i in range(3000):
batch_x,batch_y = mnist.train.next_batch(100)
train_step.run(x:batch_x,y_:batch_y,keep_prob:0.75)
if i%1000==0:
train_accuracy = acuracy.eval(x:batch_x,y_:batch_y,keep_prob:1.0)
print("step %d,train_accuracy %g"%(i,train_accuracy))
###########test
print acuracy.eval(x:mnist.test.images,y_:mnist.test.labels,keep_prob:1.0)运行上述程序,得到正确为:0.9784,而这仅仅是加了一个隐含层而已.
上面的隐含层的节点加的是300个神经元,如果要再加上一层400个神经元的非常的简单.
h1 = add_layer(x,784,300,keep_prob,tf.nn.relu)
h2 = add_layer(h1,300,400,keep_prob,tf.nn.relu)
##输出层
w = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([400,10])) #300*10
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]))
y = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(h2,w)+b)可以看到,你可以随意的添加隐含的节点,和节点的个数,需要注意的是,维度不要搞错就行了.
参考资料:
- https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow
- tensorflow实战
以上是关于Tensorflow入门-实现神经网络的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章