TensorRT python接口搭建常用技巧
Posted 帅的发光发亮
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了TensorRT python接口搭建常用技巧相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
PyTorch的Batch Normalization
PyTorch提供的BN层的定义,位于torch.nn.BatchNorm2d,公式已经在注释中说明,或者直接看文档也行:
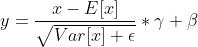
简单地, 是batch的均值,
是batch的均值,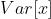 是batch的方差,
是batch的方差, 为了防止除0,
为了防止除0,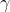 对应batch学习得到的权重,
对应batch学习得到的权重, 就是偏置。在PyTorch中相对应的,对于任意一个in层,它会有如下的结构:
就是偏置。在PyTorch中相对应的,对于任意一个in层,它会有如下的结构:
weights = torch.load(your_model_dict_state_path)
in_gamma = weights['in.weight'].numpy() # in gamma
in_beta = weights['in.bias'].numpy() # in beta
in_mean = weights['in.running_mean'].numpy() # in mean
in_var = weights['in.running_var'].numpy() # in var sqrt
上面的weights可以由torch.load()得到,而in就是你自己定义的BN层。
TRT API实现
既然已经知道了BN的公式,那就按照公式实现就可以了。这里因为输入x是卷积后的结果,一般是个4维矩阵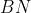 层中的乘法是对4维矩阵按通道数进行矩阵乘法,因此需要使用TRT API提供的IScaleLayer。官方文档中提到,使用
层中的乘法是对4维矩阵按通道数进行矩阵乘法,因此需要使用TRT API提供的IScaleLayer。官方文档中提到,使用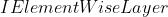 构建,这样做太复杂,不推荐。
构建,这样做太复杂,不推荐。

IScaleLayer的文档见链接,它提供操作,并且有三种模式,我们需要的就是trt.ScaleMode.CHANNEL。代码如下:
import tensorrt as trt
weights = torch.load(your_model_dict_state_path)
in_gamma = weights['in.weight'].numpy() # in gamma
in_beta = weights['in.bias'].numpy() # in beta
in_mean = weights['in.running_mean'].numpy() # in mean
in_var = weights['in.running_var'].numpy() # in var sqrt
eps = 1e-05
in_var = np.sqrt(in_var + eps)
in_scale = in_gamma / in_var
in_shift = - in_mean / in_var * in_gamma + in_beta
in = network.add_scale(input=last_layer.get_output(0), mode=trt.ScaleMode.CHANNEL, shift=in_shift, scale=in_scale)
此处,power未规定则默认为1。
fused Batch Normalization
进一步,实际上卷积层和BN层在推理过程中是可以融合在一起的,简单来讲,卷积层的过程为:
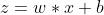
这里的 替换掉BN公式的
替换掉BN公式的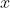 就可以得到:
就可以得到:

当然这里也是矩阵操作。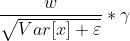 就是新的
就是新的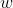 ,
,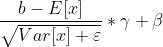 就是新的
就是新的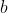 了。
了。
代码如下:
import tensorrt as trt
weights = torch.load(your_model_dict_state_path)
conv_w = weights['conv.weight'].numpy() # conv weight
conv_b = weights['conv.bias'].numpy() # conv bias
in_gamma = weights['in.weight'].numpy() # in gamma
in_beta = weights['in.bias'].numpy() # in beta
in_mean = weights['in.running_mean'].numpy() # in mean
in_var = weights['in.running_var'].numpy() # in var sqrt
eps = 1e-05
in_var = np.sqrt(in_var + eps)
fused_conv_w = conv_w * (in_gamma / in_var).reshape([conv_w.shape[0], 1, 1, 1])
fused_conv_b = (conv_b - in_mean) / in_var * in_gamma + in_beta
fused_conv = network.add_convolution(input=last_layer.get_output(0), num_output_maps=your_conv_out, kernel_shape=(your_conv_kernel, your_conv_kernel), kernel=fused_conv_w, bias=fused_conv_b)
fused_conv.padding = (your_conv_pad, your_conv_pad)
fused_conv.stride = (your_conv_stride, your_conv_stride)
其中,conv是需要融合的卷积层,fused_conv是与in融合后的卷积层,你需要规定fused_conv与conv拥有相同的参数(padding, stride, kernel_shape, num_output_maps)。
hswish的TRT实现
参考PyTorch的hswish的实现:
class hswish(nn.Module):
def forward(self, x):
out = x * F.relu6(x + 3, inplace=True) / 6
return out
那么relu6又是怎么实现的呢,参考relu6的公式:
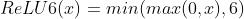
因此我们可以得到如下TRT的实现代码:
import tensorrt as trt
# x + 3
shape = (1, ) * len(your_input_shape)
tensor = 3.0 * torch.ones(shape, dtype=trt.float32).cpu().numpy()
trt_3 = network.add_constant(shape, tensor)
tmp = network.add_elementwise(last_layer.get_output(0), trt_3.get_output(0), trt.ElementWiseOperation.SUM)
# relu6(x + 3)
relu = network.add_activation(input=tmp.get_output(0), type=trt.ActivationType.RELU)
shape = (1, ) * len(your_input_shape)
tensor = 6.0 * torch.ones(shape, dtype=trt.float32).cpu().numpy()
trt_6 = network.add_constant(shape, tensor)
relu_6 = network.add_elementwise(relu.get_output(0), trt_6.get_output(0), trt.ElementWiseOperation.MIN)
# x * relu6(x + 3)
tmp = network.add_elementwise(last_layer.get_output(0), tmp.get_output(0), trt.ElementWiseOperation.PROD)
# x * relu6(x + 3) / 6
out = network.add_elementwise(tmp.get_output(0), trt_6.get_output(0), trt.ElementWiseOperation.DIV)
以上是关于TensorRT python接口搭建常用技巧的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章