加载模型及对测试数据进行预测p41
Posted bohu83
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了加载模型及对测试数据进行预测p41相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
基于resnet训练flower图像分类模型(p31-p37)上一篇,我改成别的笔记本跑完了。按照老师的步骤,进行加载模型及测试数据预测。
我们之前是冻住了,只训练一层,也可以全部训练,我的显卡太低跑时间太长了,这部分没跑。
1加载训练好的模型
model_ft, input_size = initialize_model(model_name, 102, feature_extract, use_pretrained=True)
# GPU模式
model_ft = model_ft.to(device)
# 保存文件的名字
filename='checkpoint.pth'
# 加载模型
checkpoint = torch.load(filename)
best_acc = checkpoint['best_acc']
model_ft.load_state_dict(checkpoint['state_dict'])
2测试数据预处理
测试数据处理方法需要跟训练时一致才可以。输入的大小是一致,标准化用跟训练数据相同的mean和std,PyTorch中颜色通道是第一个维度,跟很多工具包都不一样,需要转换。
def process_image(image_path):
# 读取测试数据
img = Image.open(image_path)
# Resize,thumbnail方法只能进行缩小,所以进行了判断
if img.size[0] > img.size[1]:
img.thumbnail((10000, 256))
else:
img.thumbnail((256, 10000))
# Crop操作
left_margin = (img.width - 224) / 2
bottom_margin = (img.height - 224) / 2
right_margin = left_margin + 224
top_margin = bottom_margin + 224
img = img.crop((left_margin, bottom_margin, right_margin,
top_margin))
# 相同的预处理方法
img = np.array(img) / 255
mean = np.array([0.485, 0.456, 0.406]) # provided mean
std = np.array([0.229, 0.224, 0.225]) # provided std
img = (img - mean) / std
# 注意颜色通道应该放在第一个位置
img = img.transpose((2, 0, 1))
return img
def imshow(image, ax=None, title=None):
"""展示数据"""
if ax is None:
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
# 颜色通道还原
image = np.array(image).transpose((1, 2, 0))
# 预处理还原
mean = np.array([0.485, 0.456, 0.406])
std = np.array([0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
image = std * image + mean
image = np.clip(image, 0, 1)
ax.imshow(image)
ax.set_title(title)
return ax
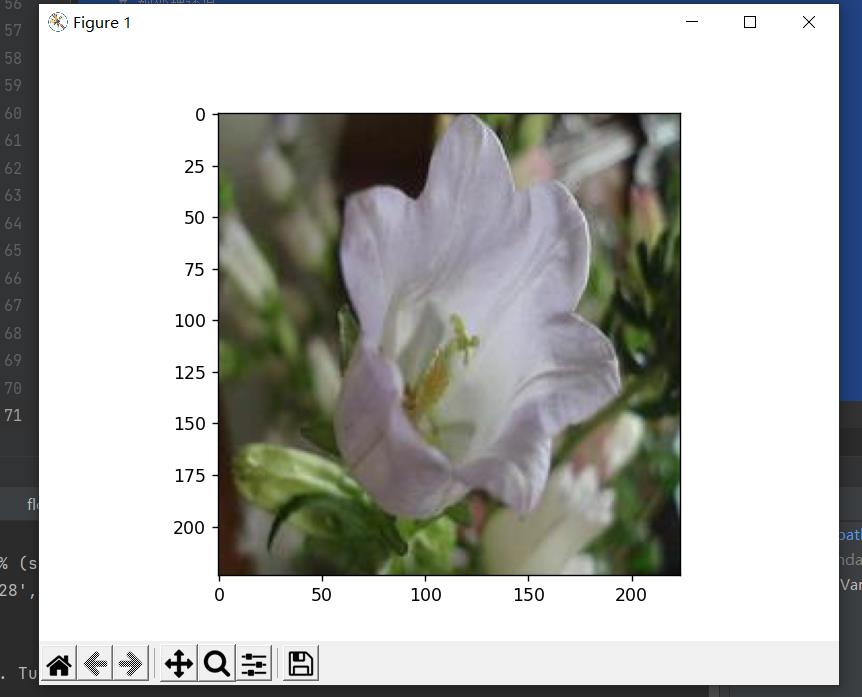
image_path = './data/flower_data/train/3/image_06620.jpg'
img = process_image(image_path)
imshow(img)
在验证集随便选一张花的图片进行测试
3对一个batch的数据进行测试
# 得到一个batch的测试数据
dataiter = iter(dataloaders['valid'])
images, labels = dataiter.next()
model_ft.eval()
if train_on_gpu:
output = model_ft(images.cuda()) #utput表示对一个batch中每一个数据得到其属于各个类别的可能性
else:
output = model_ft(images)
output,有8张图片,每个图片有102种分类结果
得到概率最大的那个
_, preds_tensor = torch.max(output, 1) #得到概率最大的那个
preds = np.squeeze(preds_tensor.numpy()) if not train_on_gpu else np.squeeze(preds_tensor.cpu().numpy())
展示预测结果:
fig=plt.figure(figsize=(20, 12))
columns =4
rows = 2
for idx in range (columns*rows):
ax = fig.add_subplot(rows, columns, idx+1, xticks=[], yticks=[])
plt.imshow(im_convert(images[idx]))
ax.set_title(" ()".format(cat_to_name[str(preds[idx])], cat_to_name[str(labels[idx].item())]),
color=("green" if cat_to_name[str(preds[idx])]==cat_to_name[str(labels[idx].item())] else "red"))
plt.show() #绿色名字为预测正确,红色名字为预测错误

看这个图,效果还不错,跟之前模型的85%的准确率比较符合。
以上是关于加载模型及对测试数据进行预测p41的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章