手写一个SpringBoot-Starter
Posted 李某乐
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了手写一个SpringBoot-Starter相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
自定义SpringBoot Starter
什么是Starter
SpringBoot中的starter是一种非常重要的机制,能够抛弃以前繁杂的配置,将其统一集成进starter,应用者只需要在maven中引入starter依赖,SpringBoot就能自动扫描到要加载的信息并启动相应的默认配置。starter让我们摆脱了各种依赖库的处理,需要配置各种信息的困扰。SpringBoot会自动通过classpath路径下的类发现需要的Bean,并注册进IOC容器。SpringBoot提供了针对日常企业应用研发各种场景的spring-boot-starter依赖模块。所有这些依赖模块都遵循着约定成俗的默认配置,并允许我们调整这些配置,即遵循“约定大于配置”的理念。
为什么要自定义Starter
在我们的日常开发中,经常会有一些独立于业务之外的配置代码模块例如:数据源、日志、鉴权…等等,通常我们的做法就是将这些保存在一个特定的位置,有项目需要时将代码硬拷贝过去,重新集成一遍,麻烦至极。如果我们将这些可独立于业务代码之外的功配置模块封装成一个个starter,并在starter中给定一个默认值以减少重复配置,复用的时候只需要将其在pom中引用依赖即可,若需要修改参数则提供重写覆盖的方式将参数覆盖(例如数据库IP),这样每次其他项目需要也就是引一下依赖的事。
自定义Starter的场景
- 动态数据源
- 参数校验
- 接口加解密
- 日志记录
自定义Starter的命名规则
SpringBoot官方提供的Starter以spring-boot-starter-xxx的方式命名的。官方建议自定义的Starter使用xxx-spring-boot-starter命名规则,以区分SpringBoot生态提供的Starter。
自定义Starter的实现方法
…
引入相关依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.lijl.encrypy</groupId>
<artifactId>encrypt-spring-boot-startter</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1</version>
<name>encrypt-spring-boot-startter</name>
<description>加解密Starter</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<version>2.4.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<version>2.3.4.RELEASE</version>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<source>8</source>
<target>8</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
创建加解密工具类
依赖添加完成后,我们先来定义一个加密工具类备用,加密这块有多种方案可以选择,对称加密、非对称加密,其中对称加密又可以使用 AES、DES、3DES 等不同算法,这里我们使用 Java 自带的 Cipher 来实现对称加密,使用 AES、DES 算法:
public class AESUtils
private static final String AES_ALGORITHM = "AES/ECB/PKCS5Padding";
/**
* @Author lijiale
* @MethodName getCipher
* @Description 获取 Cipher
* @Date 9:20 2021/3/10
* @Version 1.0
* @param key
* @param model
* @return: javax.crypto.Cipher
**/
private static Cipher getCipher(byte[] key, int model) throws NoSuchPaddingException, NoSuchAlgorithmException, InvalidKeyException
SecretKeySpec secretKeySpec = new SecretKeySpec(key,"AES");
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(AES_ALGORITHM);
cipher.init(model,secretKeySpec);
return cipher;
/**
* @Author lijiale
* @MethodName encrypy
* @Description AES加密
* @Date 9:22 2021/3/10
* @Version 1.0
* @param data
* @param key
* @return: java.lang.String
**/
public static String encrypy(byte[] data, byte[] key) throws NoSuchPaddingException, NoSuchAlgorithmException, InvalidKeyException, BadPaddingException, IllegalBlockSizeException
Cipher cipher = getCipher(key, Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE);
return Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(cipher.doFinal(data));
/**
* @Author lijiale
* @MethodName decrypt
* @Description AES解密
* @Date 9:24 2021/3/10
* @Version 1.0
* @param data
* @param key
* @return: byte[]
**/
public static byte[] decrypt(byte[] data,byte[] key) throws NoSuchPaddingException, NoSuchAlgorithmException, InvalidKeyException, BadPaddingException, IllegalBlockSizeException
Cipher cipher = getCipher(key, Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE);
return cipher.doFinal(Base64.getDecoder().decode(data));
public class DesEncryptUtil
private static SecureRandom sr;
private static SecretKey securekey;
public static Cipher getCipher(String key) throws NoSuchAlgorithmException, NoSuchPaddingException, InvalidKeyException, InvalidKeySpecException
sr = new SecureRandom();
// 从原始密匙数据创建一个DESKeySpec对象
DESKeySpec dks = new DESKeySpec(key.getBytes());
// 创建一个密匙工厂,然后用它把DESKeySpec对象转换成
// 一个SecretKey对象
SecretKeyFactory keyFactory = SecretKeyFactory.getInstance("DES");
securekey = keyFactory.generateSecret(dks);
// Cipher对象实际完成解密操作
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("DES");
return cipher;
/**
* @Author Lijl
* @MethodName 解密
* @Description TODO
* @Date 14:07 2020/10/29
* @Version 1.0
* @param src
* @return: byte[]
**/
public static byte[] decrypt(String key, String src) throws Exception
Cipher cipher = getCipher(key);
// 用密匙初始化Cipher对象
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, securekey, sr);
// 现在,获取数据并解密
// 正式执行解密操作
byte[] bytes = decryptBASE64(src);
return cipher.doFinal(bytes);
/**
* @Author Lijl
* @MethodName encrypt
* @Description 数据加密
* @Date 14:06 2020/10/29
* @Version 1.0
* @param src
* @return: byte[]
**/
public static String encrypt(byte[] src,String key) throws Exception
Cipher cipher = getCipher(key);
// 用密匙初始化Cipher对象
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, securekey, sr);
// 现在,获取数据并加密
// 正式执行加密操作
byte[] bytes = cipher.doFinal(src);
//解决乱码
return encryptBASE64(bytes);
private static String encryptBASE64(byte[] key) throws Exception
return (new BASE64Encoder()).encode(key);
private static byte[] decryptBASE64(String key) throws Exception
return (new BASE64Decoder()).decodeBuffer(key);
这个工具类比较简单,不需要多解释。需要说明的是,加密后的数据可能不具备可读性,因此我们一般需要对加密后的数据再使用 Base64 算法进行编码,获取可读字符串。换言之,上面的 AES 加密方法的返回值是一个 Base64 编码之后的字符串,AES 解密方法的参数也是一个 Base64 编码之后的字符串,先对该字符串进行解码,然后再解密。
接下来我们在创建一个响应工具类
public class RespBean
private Integer status;
private String msg;
private Object obj;
public static RespBean build()
return new RespBean();
public static RespBean ok(String msg)
return new RespBean(200,msg,null);
public static RespBean ok(String msg, Object obj)
return new RespBean(200,msg,obj);
public static RespBean error(String msg)
return new RespBean(500,msg,null);
public static RespBean error(String msg, Object obj)
return new RespBean(500,msg,obj);
public RespBean()
public RespBean(Integer status, String msg, Object obj)
this.status = status;
this.msg = msg;
this.obj = obj;
public Integer getStatus()
return status;
public RespBean setStatus(Integer status)
this.status = status;
return this;
public String getMsg()
return msg;
public RespBean setMsg(String msg)
this.msg = msg;
return this;
public Object getObj()
return obj;
public RespBean setObj(Object obj)
this.obj = obj;
return this;
创建加解密注解
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface Encrpty
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.PARAMETER)
public @interface Decrpty
这两个注解就是两个标记,在以后使用的过程中,哪个接口方法添加了 @Encrypt 注解就对哪个接口的数据加密返回,哪个接口或参数添加了 @Decrypt 注解就对哪个接口或参数进行解密。
创建加密配置类
因为提供了两种加解密方式,并且用户也有可能自定义密钥,所以再来定义一个EncryptProperties 类来读取用户配置的密钥:
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.encrypt")
public class EncryptProperties
private final static String DEFAULT_KEY = "www.lijiaxxx.com";
private final static String DEFAULT_TYPE = "AES";
private String key = DEFAULT_KEY;
private String type = DEFAULT_TYPE;
public String getKey()
return key;
public void setKey(String key)
this.key = key;
public String getType()
return type;
public void setType(String type)
this.type = type;
这里我设置了默认的加解密算法与密钥,如果想使用DES算法进行加解密,或者想自定义密钥的话。只需要在.properties/.yml中配置覆盖默认值即可。
spring.encrypt.key=www.lijiaxxx.com
spring.encrypt.type=DES
spring:
encrypt:
key: www.lijiaxxx.com
type: DES
加密/解密
此篇的重点是Starter,所以就RequestBodyAdvice和ResponseBodyAdvice来做加解密做的过滤操作。写的比较简单,当然想要严谨灵活还是自己定义过滤器更合适,这次的重点不是这个就先用这两个工具类凑合下。
@EnableConfigurationProperties(EncryptProperties.class)
@ControllerAdvice
public class DecryptRequest extends RequestBodyAdviceAdapter
EncryptProperties encryptProperties;
@Autowired
public void setEncryptProperties(EncryptProperties encryptProperties)
this.encryptProperties = encryptProperties;
@Override
public boolean supports(MethodParameter methodParameter, Type type, Class<? extends HttpMessageConverter<?>> aClass)
return methodParameter.hasMethodAnnotation(Decrpty.class) || methodParameter.hasParameterAnnotation(Decrpty.class);
@Override
public HttpInputMessage beforeBodyRead(final HttpInputMessage inputMessage, MethodParameter parameter, Type targetType, Class<? extends HttpMessageConverter<?>> converterType) throws IOException
String type = encryptProperties.getType();
byte[] body = new byte[inputMessage.getBody().available()];
inputMessage.getBody().read(body);
try
byte[] decrypt = new byte[0];
if ("AES".equals(type))
decrypt = AESUtils.decrypt(body,encryptProperties.getKey().getBytes());
else if ("DES".equals(type))
String bodyStr = new String(body);
decrypt = DesEncryptUtil.decrypt(encryptProperties.getKey(),bodyStr);
if (decrypt!=null && decrypt.length>0)
final ByteArrayInputStream bais = new ByteArrayInputStream(decrypt);
return new HttpInputMessage()
@Override
public InputStream getBody()
return bais;
@Override
public HttpHeaders getHeaders()
return inputMessage.getHeaders();
;
catch (Exception e)
e.printStackTrace();
return super.beforeBodyRead(inputMessage, parameter, targetType, converterType);
@EnableConfigurationProperties(EncryptProperties.class)
@ControllerAdvice
public class EncryptResponse implements ResponseBodyAdvice<RespBean>
private final ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
EncryptProperties encryptProperties;
@Autowired
public void setEncryptProperties(EncryptProperties encryptProperties)
this.encryptProperties = encryptProperties;
@Override
public boolean supports(MethodParameter methodParameter, Class<? extends HttpMessageConverter<?>> aClass)
return methodParameter.hasMethodAnnotation(Encrpty.class);
@Override
public RespBean beforeBodyWrite(RespBean respBean, MethodParameter methodParameter, MediaType mediaType, Class<? extends HttpMessageConverter<?>> aClass, ServerHttpRequest serverHttpRequest, ServerHttpResponse serverHttpResponse)
byte[] keyBytes = encryptProperties.getKey().getBytes();
String type = encryptProperties.getType();
try
if (respBean.getObj()!=null)
if ("AES".equals(type))
respBean.setObj(AESUtils.encrypy(om.writeValueAsBytes(respBean.getObj()),keyBytes));
else if ("DES".equals(type))
respBean.setObj(DesEncryptUtil.encrypt(om.writeValueAsBytes(respBean.getObj()),encryptProperties.getKey()));
return respBean;
catch (Exception e)
e.printStackTrace();
respBean.setStatus(500);
respBean.setMsg("加密异常");
respBean.setObj(null);
return respBean;
创建自动化配置类
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.lijl.encrypy")
public class EncryptAutoConfiguration
这个没啥好说的,就是声明这个类是配置类,并声明要扫描的包路径
配置Spring Factories
这个简单说一下,在Spring Boot中有一种非常解耦的扩展机制:Spring Factories,没错我们就用Spring Factories来让程序启动后使封装在starter中的拦截器生效。这种扩展机制实际上是仿照Java中的SPI扩展机制来实现的,至于Java SPI是什么不了百度吧这里就不赘述了。在Spring中也有一种类似与Java SPI的加载机制。它在META-INF/spring.factories文件中配置接口的实现类名称,然后在程序中读取这些配置文件并实例化。这种自定义的SPI机制是Spring Boot Starter实现的基础。具体的实现原理可进入spring-core包下SpringFactoriesLoader类中查看。
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=com.lijl.encrypy.config.EncryptAutoConfiguration
应用
终于终于完事了,剩下的就是结合程序使用了
引入依赖
将Starter通过maven打包,并新建项目,将新打好的包引入到新创建中项目中
<dependency>
<groupId>com.lijl.encrypy</groupId>
<artifactId>encrypt-spring-boot-startter</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1</version>
</dependency>
创建实体
public class User
private String name;
private int age;
public String getName()
return name;
public void setName(String name)
this.name = name;
...
创建测试接口
这里创建两个测试接口,一个用于加密一个用于测试解密
@RestController
public class TestController
@GetMapping(value = "/getUser")
@Encrpty
public RespBean getUser()
User user = new User();
user.setName("李某某");
user.setAge(18);
return RespBean.ok("查询成功",user);
@PutMapping(value = "/putUser")
public RespBean putUser(@RequestBody @Decrpty User user)
String name = user.getName();
int age = user.getAge();
System.out.println("名称:"+name+"\\n年龄:"+age);
return RespBean.ok("成功");
测试
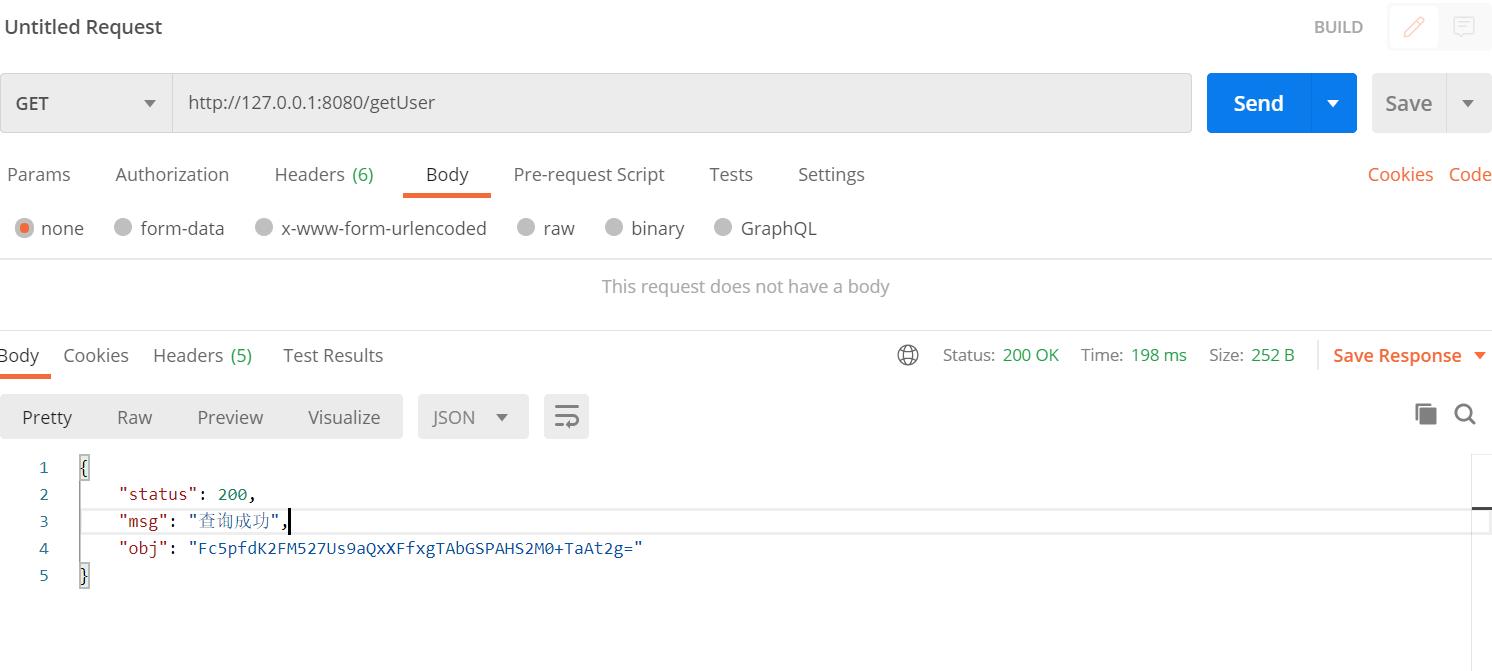
首先测试加密
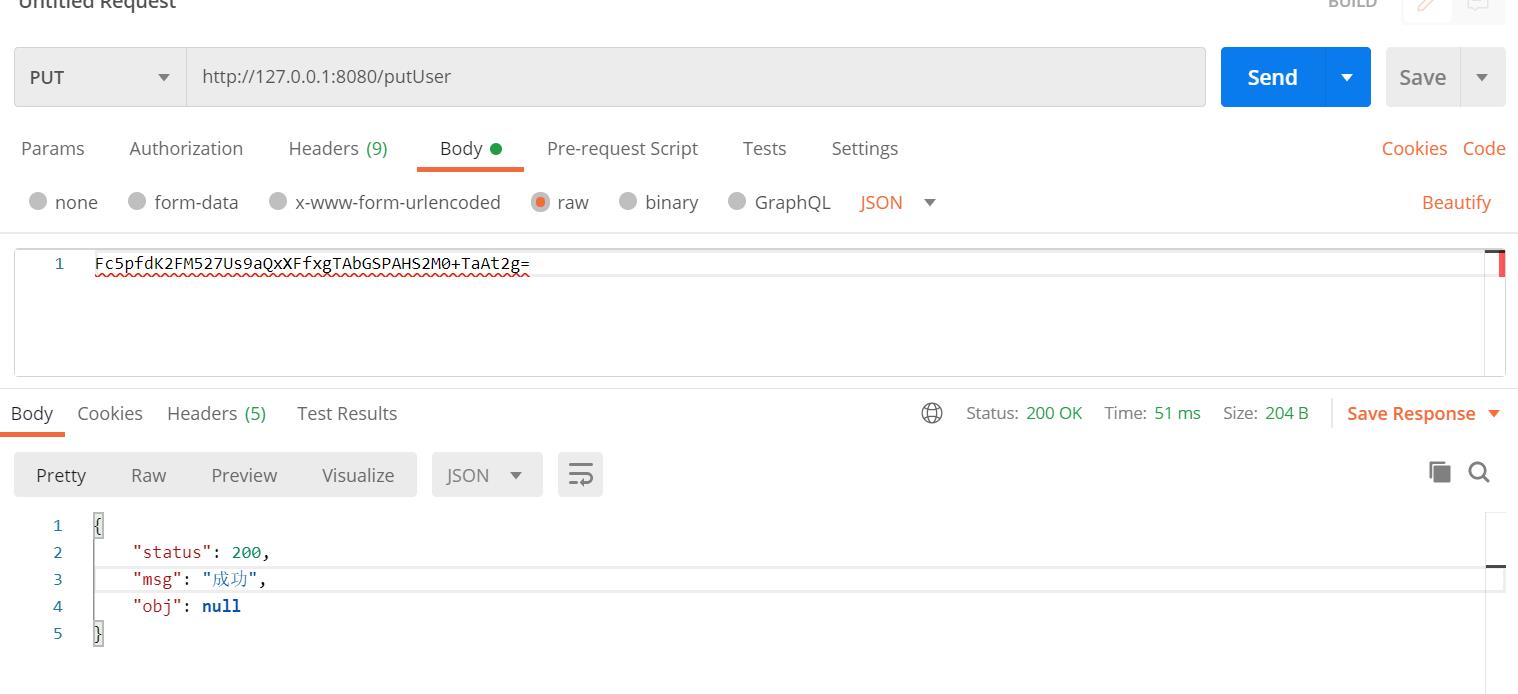
再则就是传入加密的参数解密
以上是关于手写一个SpringBoot-Starter的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章