java 多线程—— 创建线程的3种方法
Posted 玛丽莲茼蒿
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了java 多线程—— 创建线程的3种方法相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、复习
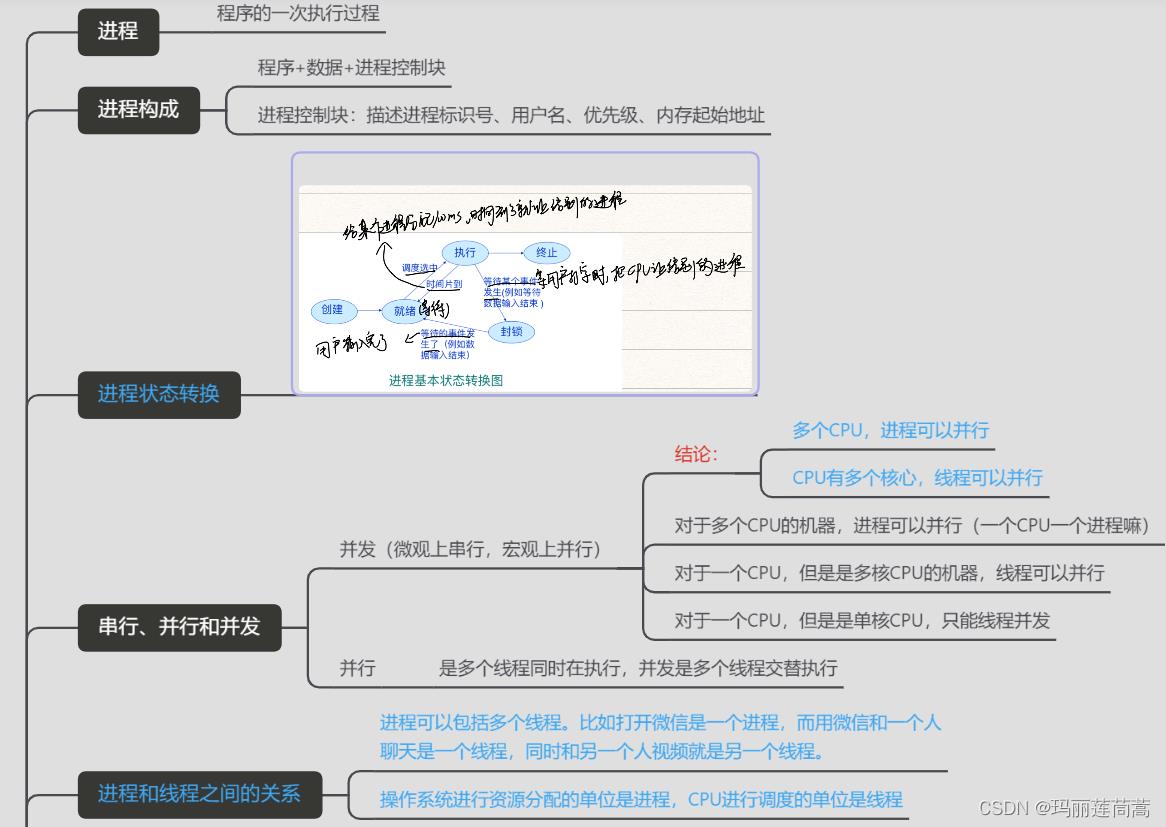
1. 程序、进程、线程
程序:静态的
进程:程序的一次执行过程,动态的
线程:一个QQ.exe是一个进程,聊天发信息是一个线程,聊天接收信息是一个线程,视频通话是一个线程。
进程是操作系统分配资源的单位,线程是CPU调度的单位。
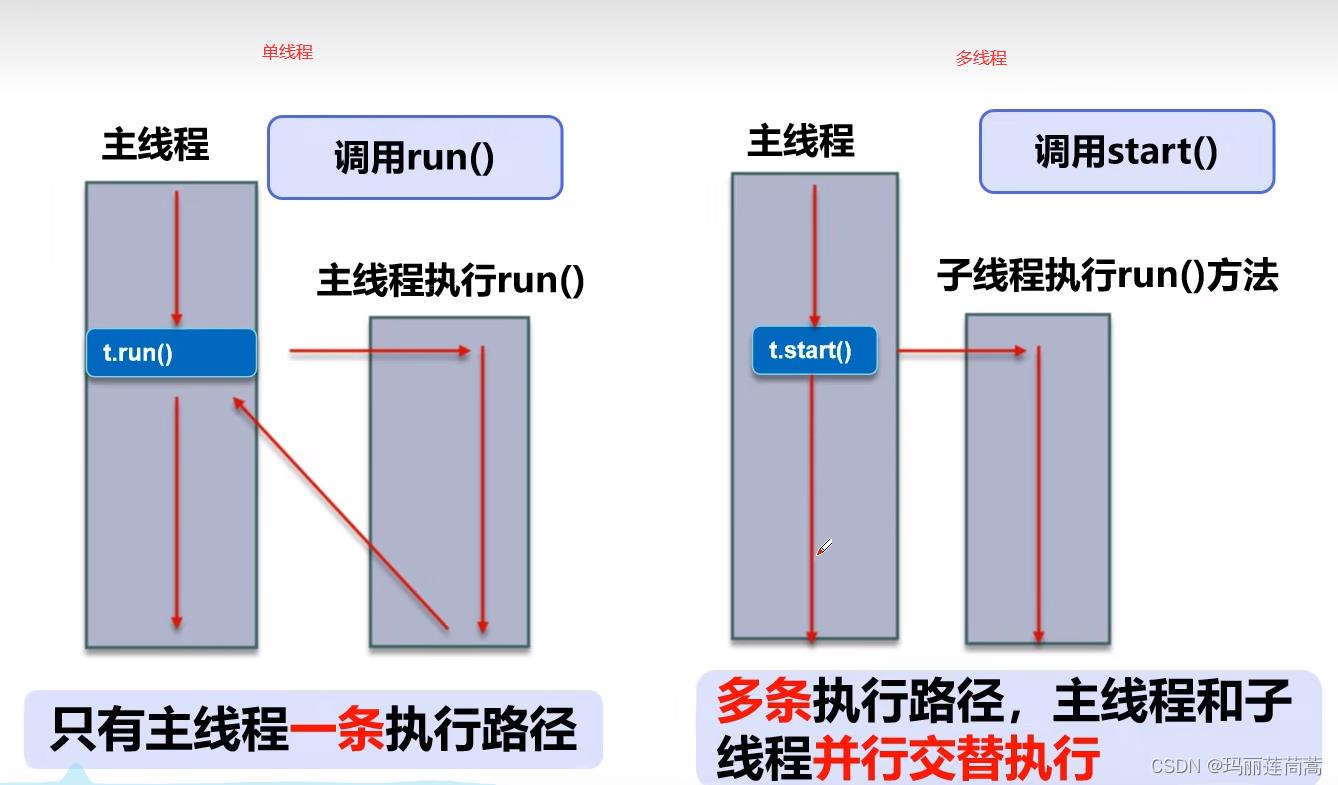
2. 单线程和多线程的区别
3. C++中如何开启子线程
【C++】解决子线程没有被执行的问题_玛丽莲茼蒿的博客-CSDN博客_c++ 线程不执行
4.java中默认的线程
任何一个程序在java中都是多线程的
main线程是肯定有的,还有gc线程。即使这个程序只有System.out.println("hello"),后台也会自动开启gc线程
二、线程的创建的3种方法
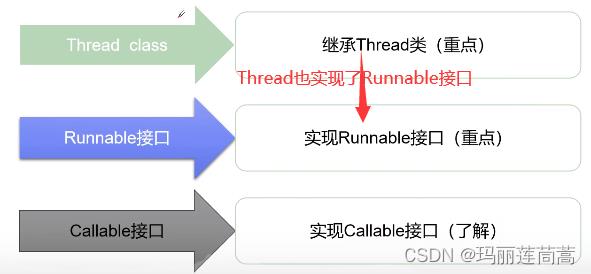
推荐使用Runnable接口
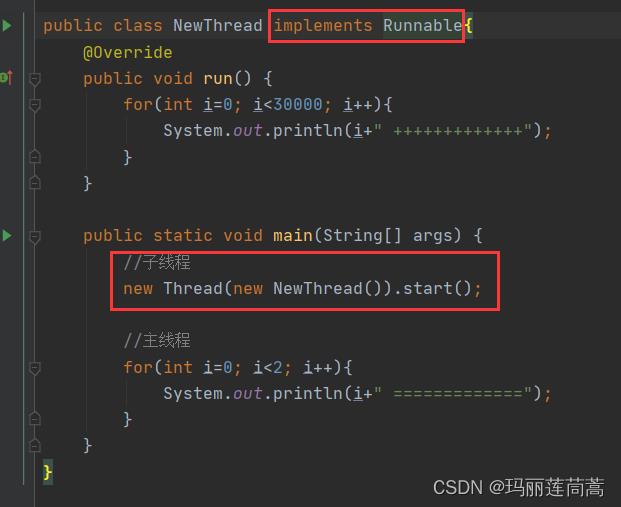
2.1 继承Thread类
2.1.1记忆点
1. 分3步

2. 主线程拥有对CPU的优先使用权。但是和C++不同的是,主线程执行完后,即便不使用sleep,子线程依然能够被执行。这或许是因为Java后台自带的守护进程???

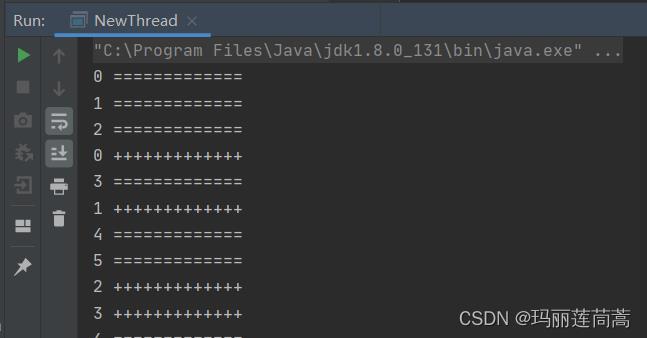
2.1.2 简单演示
public class NewThread extends Thread
@Override
public void run()
for(int i=0; i<200; i++)
System.out.println(i+" +++++++++++++");
public static void main(String[] args)
//子线程
NewThread newThread = new NewThread();
newThread.start();
//主线程
for(int i=0; i<200; i++)
System.out.println(i+" =============");
2.1.3 实战——多线程下载网络图片
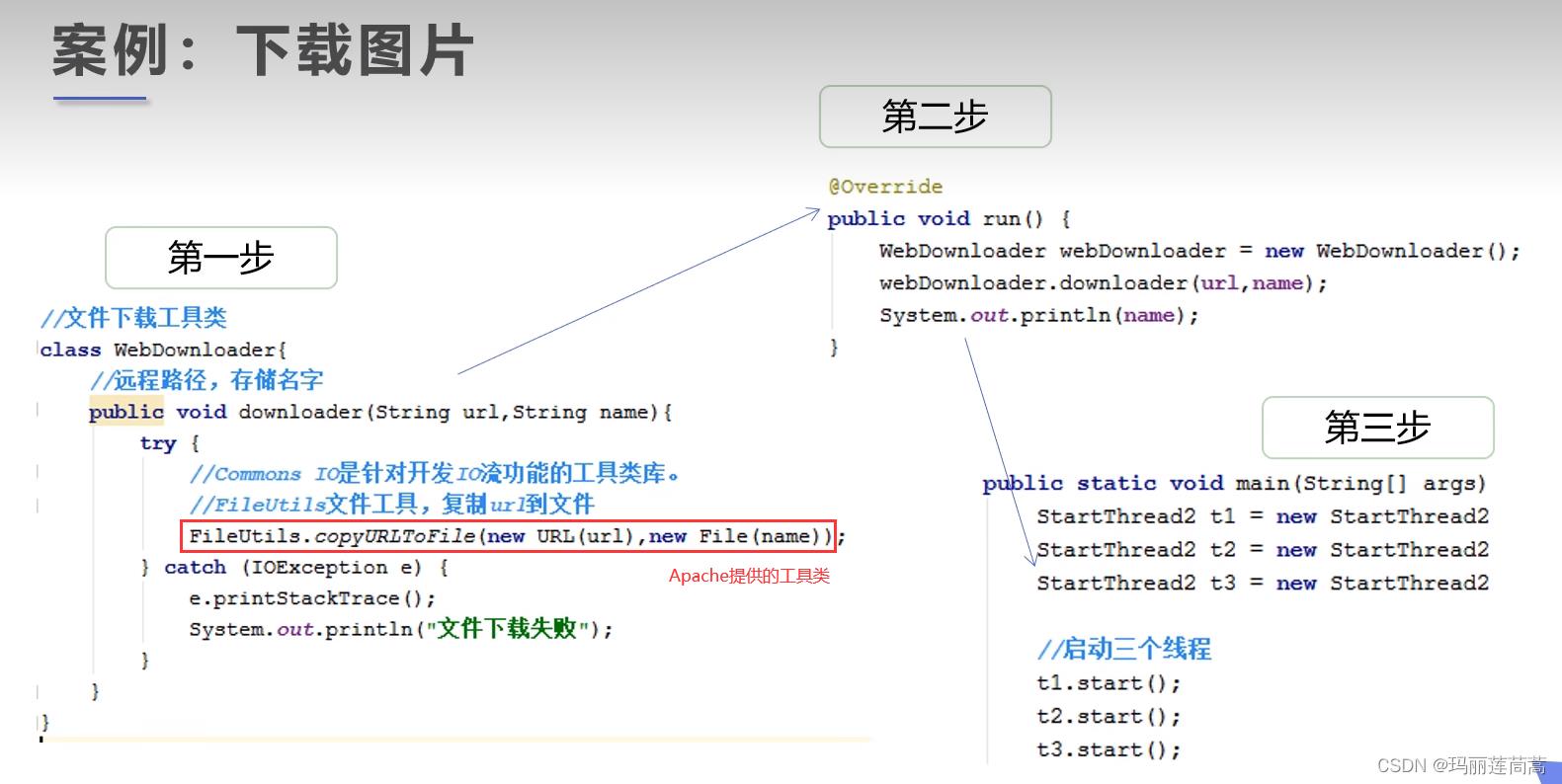
本次实战要用到Apache提供的一个第三方包,官网免费下载:
Commons IO – Download Apache Commons IO
解压后找到下图中的jar包
import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
public class DownLoadURLThread extends Thread
private String url;
private String name;
public DownLoadURLThread(String url, String name)
this.url = url;
this.name = name;
//线程执行体
@Override
public void run()
DownLoader downLoader = new DownLoader();
downLoader.download(this.url,this.name);
System.out.println(this.name+"下载完毕");
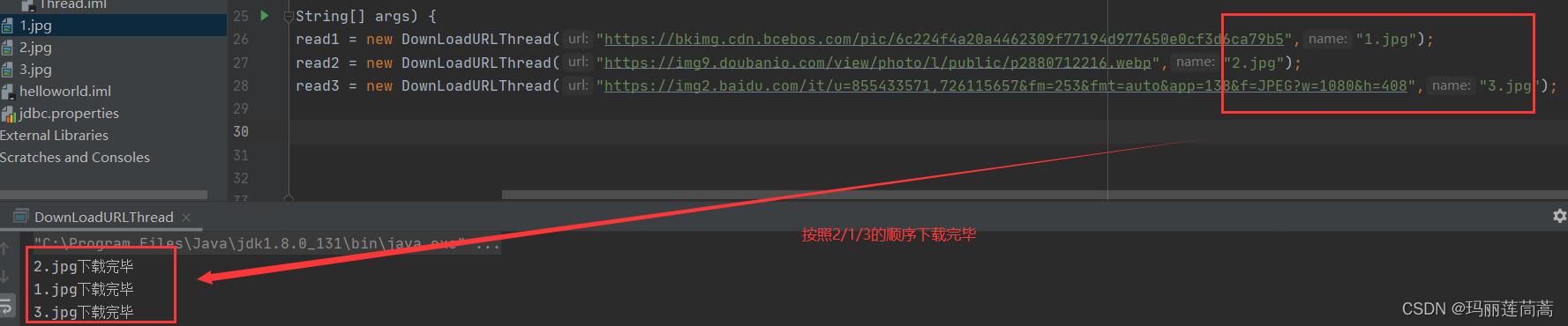
public static void main(String[] args)
DownLoadURLThread thread1 = new DownLoadURLThread("https://bkimg.cdn.bcebos.com/pic/6c224f4a20a4462309f77194d977650e0cf3d6ca79b5","1.jpg");
DownLoadURLThread thread2 = new DownLoadURLThread("https://img9.doubanio.com/view/photo/l/public/p2880712216.webp","2.jpg");
DownLoadURLThread thread3 = new DownLoadURLThread("https://img2.baidu.com/it/u=855433571,726115657&fm=253&fmt=auto&app=138&f=JPEG?w=1080&h=408","3.jpg");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread3.start();
class DownLoader
public void download(String url,String name)
try
FileUtils.copyURLToFile(new URL(url), new File(name));
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
2.2 实现runnable接口


区别在于:
2.1.2 实战——模拟龟兔赛跑
要求:
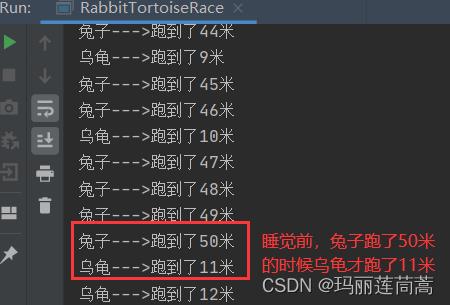
兔子的速度是乌龟的100倍
兔子中途睡了一觉
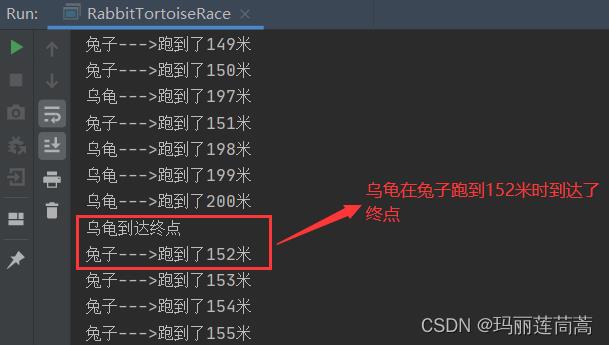
乌龟先达到终点
思路:乌龟和兔子同时在跑,所以这是两个线程在同时跑。由于兔子和乌龟的动作行为不同(速度不同,而且兔子需要睡一觉),所以我们写了一个兔子类和一个乌龟类,这两个类都实现了Runnable接口。
要注意的是,乌龟和兔子赛跑我们写了两个类,但是双十一有1亿个用户并发,我们不可能写1亿个User类各自实现Runnable接口,因为1亿个用户的行为都是一样的,我们写一个类就够了(详见下面的抢票系统)。之所以兔子、乌龟写成两个是兔子乌龟的行为不一样。
/**
* 模拟龟兔赛跑
*/
public class RabbitTortoiseRace
public static void main(String[] args)
new Thread(new Rabbit()).start();
new Thread(new Tortoise()).start();
class Runway
static int length =200; //200米的跑道
class Rabbit implements Runnable
@Override
public void run()
int length = Runway.length;
int rabbitRunLength =0;
while(rabbitRunLength<length)
//for循环模拟兔子跑1米的时间,比乌龟快100倍
for(int i=0; i<=100; i++)
rabbitRunLength++;
System.out.println("兔子--->跑到了"+rabbitRunLength+"米");
//模拟兔子跑到50米时睡了一觉
if(rabbitRunLength == 50)
try
Thread.sleep(2);
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("兔子到达终点");
class Tortoise implements Runnable
@Override
public void run()
int length = Runway.length;
int tortoiseRunLength =0;
while(tortoiseRunLength<length)
//模拟乌龟跑1米的时间
for(int i=0; i<=1000; i++)
tortoiseRunLength++;
System.out.println("乌龟--->跑到了"+tortoiseRunLength+"米");
System.out.println("乌龟到达终点");
2.2.3 实战 —— 模拟抢票系统
这里只是演示如果“多线程的行为相同”,只写一个实现Runnable的类就够了
public class RailwayTicketSystem implements Runnable
private int ticketNums = 10; //系统里有10张票
//抢票行为
@Override
public void run()
while(ticketNums>0)
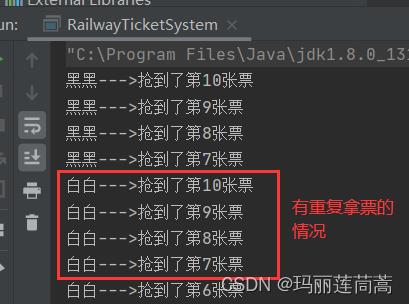
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"--->抢到了第"+ticketNums+"张票");
ticketNums--;
public static void main(String[] args)
new Thread(new RailwayTicketSystem(),"黑黑").start();
new Thread(new RailwayTicketSystem(),"白白").start();
new Thread(new RailwayTicketSystem(),"黄牛党").start();
因为火车票是临界资源,需要进行同步处理,但是这里没有处理,所以出现了重复拿票的情况。
以上是关于java 多线程—— 创建线程的3种方法的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_44886213/article/details/127397913?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_44886213/article/details/127397913?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501