Lex/Yacc 初识Lex
Posted zj510
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Lex/Yacc 初识Lex相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
因工作需要接触了一下Lex和Yacc,个人感觉挺有趣的,所以就写下来了。
Lex是Lexical的缩写,大概就可以理解为词汇提取。
Yacc是Yet another compiler compiler, 可以翻译为“还有另一个编译器的编译器”,挺拗口的,不过没关系,先不管它。
安装Lex和Yacc
Lex和Yacc是一种标准,当然会有很多的实现了,其中有2个是免费的(好像还有商业版本),那就是flex和bison。如果在ubuntu上安装(也有windows版本),会很简单:
sudo apt-get install flex bison
这样就ok了。
第一个Lex文件
首先我们直接来看一段代码:
%
int wordCount = 0;
int spaceCount = 0;
int numberCount = 0;
%
chars [A-Za-z\\_\\'\\.\\"]
numbers ([0-9])+
delim [" "\\n\\t]
whitespace delim+
words chars+
%%
words wordCount++;
whitespace spaceCount++;
numbers numberCount++;
%%
void main()
yylex();
printf(" Number of words: %d\\n", wordCount);
printf(" Number of spaces: %d\\n", spaceCount);
printf(" Number of nubmers: %d\\n", numberCount);
int yywrap()
return 1;
简单说明一下:
1. 第一个%%之前是Lex语法的一些定义,% ** %里面是c语言的一些变量定义。后面的chars,numbers等等是一些正则表达式吧。具体的意思可以查阅Lex说明。
第二段(也就是第一个%%和第二个%%之间),用来计算单词个个数,空格个数和数字个数。
第三段,main函数,这其实是个c函数。
我们创建一个lex文件,叫做test.lex。如:

编译lex
我们已经创建了一个简单的lex文件,那么现在就应该编译它了,直接用一条命令,如:
flex test.lex
发生什么了呢,看截图:
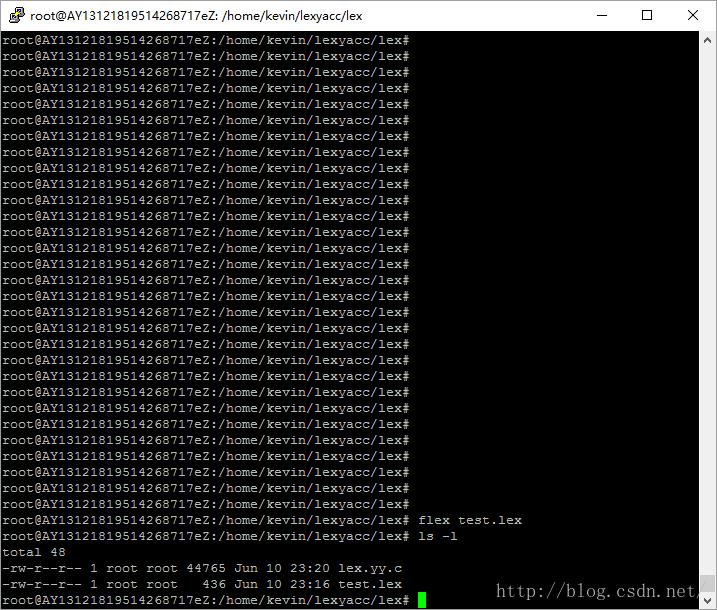
发现多了个lex.yy.c文件,这个文件是由flex test.lex生成的,它是个标准的c语言文件。内容可以看最后的附件,我们先管具体的内容。
编译C文件
我们已经有了lex.yy.c文件,现在编译它。直接用gcc好了。看截图:

编译完,发现多了个a.out,这个是个可执行文件。
使用lex
lex说穿了,基本套路就是:
1. 创建lex文件
2. 使用flex xxx.lex来生成.c文件
3. 使用c编译器(如gcc),来生成一个可执行文件。
那么如何使用呢?刚才的lex的例子就是用来计算一段数据里面有几个英文单词,几个数字,几个空格的。
我们可以这么来测试:
1. 创建一个test.txt测试文件
2. 里面放入:hello world 2016 6 10
3. 使用命令:./a.out < test.txt
如下:

ok,成功了,计算出了单词数2个,数字3个,空格5个。
总结:
简单说来,lex就是用来提取一段给定数据里面的符合lex文件定义的词汇。
附:
test.lex生成的对应c文件:
#line 3 "lex.yy.c"
#define YY_INT_ALIGNED short int
/* A lexical scanner generated by flex */
#define FLEX_SCANNER
#define YY_FLEX_MAJOR_VERSION 2
#define YY_FLEX_MINOR_VERSION 5
#define YY_FLEX_SUBMINOR_VERSION 35
#if YY_FLEX_SUBMINOR_VERSION > 0
#define FLEX_BETA
#endif
/* First, we deal with platform-specific or compiler-specific issues. */
/* begin standard C headers. */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
/* end standard C headers. */
/* flex integer type definitions */
#ifndef FLEXINT_H
#define FLEXINT_H
/* C99 systems have <inttypes.h>. Non-C99 systems may or may not. */
#if defined (__STDC_VERSION__) && __STDC_VERSION__ >= 199901L
/* C99 says to define __STDC_LIMIT_MACROS before including stdint.h,
* if you want the limit (max/min) macros for int types.
*/
#ifndef __STDC_LIMIT_MACROS
#define __STDC_LIMIT_MACROS 1
#endif
#include <inttypes.h>
typedef int8_t flex_int8_t;
typedef uint8_t flex_uint8_t;
typedef int16_t flex_int16_t;
typedef uint16_t flex_uint16_t;
typedef int32_t flex_int32_t;
typedef uint32_t flex_uint32_t;
#else
typedef signed char flex_int8_t;
typedef short int flex_int16_t;
typedef int flex_int32_t;
typedef unsigned char flex_uint8_t;
typedef unsigned short int flex_uint16_t;
typedef unsigned int flex_uint32_t;
/* Limits of integral types. */
#ifndef INT8_MIN
#define INT8_MIN (-128)
#endif
#ifndef INT16_MIN
#define INT16_MIN (-32767-1)
#endif
#ifndef INT32_MIN
#define INT32_MIN (-2147483647-1)
#endif
#ifndef INT8_MAX
#define INT8_MAX (127)
#endif
#ifndef INT16_MAX
#define INT16_MAX (32767)
#endif
#ifndef INT32_MAX
#define INT32_MAX (2147483647)
#endif
#ifndef UINT8_MAX
#define UINT8_MAX (255U)
#endif
#ifndef UINT16_MAX
#define UINT16_MAX (65535U)
#endif
#ifndef UINT32_MAX
#define UINT32_MAX (4294967295U)
#endif
#endif /* ! C99 */
#endif /* ! FLEXINT_H */
#ifdef __cplusplus
/* The "const" storage-class-modifier is valid. */
#define YY_USE_CONST
#else /* ! __cplusplus */
/* C99 requires __STDC__ to be defined as 1. */
#if defined (__STDC__)
#define YY_USE_CONST
#endif /* defined (__STDC__) */
#endif /* ! __cplusplus */
#ifdef YY_USE_CONST
#define yyconst const
#else
#define yyconst
#endif
/* Returned upon end-of-file. */
#define YY_NULL 0
/* Promotes a possibly negative, possibly signed char to an unsigned
* integer for use as an array index. If the signed char is negative,
* we want to instead treat it as an 8-bit unsigned char, hence the
* double cast.
*/
#define YY_SC_TO_UI(c) ((unsigned int) (unsigned char) c)
/* Enter a start condition. This macro really ought to take a parameter,
* but we do it the disgusting crufty way forced on us by the ()-less
* definition of BEGIN.
*/
#define BEGIN (yy_start) = 1 + 2 *
/* Translate the current start state into a value that can be later handed
* to BEGIN to return to the state. The YYSTATE alias is for lex
* compatibility.
*/
#define YY_START (((yy_start) - 1) / 2)
#define YYSTATE YY_START
/* Action number for EOF rule of a given start state. */
#define YY_STATE_EOF(state) (YY_END_OF_BUFFER + state + 1)
/* Special action meaning "start processing a new file". */
#define YY_NEW_FILE yyrestart(yyin )
#define YY_END_OF_BUFFER_CHAR 0
/* Size of default input buffer. */
#ifndef YY_BUF_SIZE
#ifdef __ia64__
/* On IA-64, the buffer size is 16k, not 8k.
* Moreover, YY_BUF_SIZE is 2*YY_READ_BUF_SIZE in the general case.
* Ditto for the __ia64__ case accordingly.
*/
#define YY_BUF_SIZE 32768
#else
#define YY_BUF_SIZE 16384
#endif /* __ia64__ */
#endif
/* The state buf must be large enough to hold one state per character in the main buffer.
*/
#define YY_STATE_BUF_SIZE ((YY_BUF_SIZE + 2) * sizeof(yy_state_type))
#ifndef YY_TYPEDEF_YY_BUFFER_STATE
#define YY_TYPEDEF_YY_BUFFER_STATE
typedef struct yy_buffer_state *YY_BUFFER_STATE;
#endif
extern int yyleng;
extern FILE *yyin, *yyout;
#define EOB_ACT_CONTINUE_SCAN 0
#define EOB_ACT_END_OF_FILE 1
#define EOB_ACT_LAST_MATCH 2
#define YY_LESS_LINENO(n)
/* Return all but the first "n" matched characters back to the input stream. */
#define yyless(n) \\
do \\
\\
/* Undo effects of setting up yytext. */ \\
int yyless_macro_arg = (n); \\
YY_LESS_LINENO(yyless_macro_arg);\\
*yy_cp = (yy_hold_char); \\
YY_RESTORE_YY_MORE_OFFSET \\
(yy_c_buf_p) = yy_cp = yy_bp + yyless_macro_arg - YY_MORE_ADJ; \\
YY_DO_BEFORE_ACTION; /* set up yytext again */ \\
\\
while ( 0 )
#define unput(c) yyunput( c, (yytext_ptr) )
#ifndef YY_TYPEDEF_YY_SIZE_T
#define YY_TYPEDEF_YY_SIZE_T
typedef size_t yy_size_t;
#endif
#ifndef YY_STRUCT_YY_BUFFER_STATE
#define YY_STRUCT_YY_BUFFER_STATE
struct yy_buffer_state
FILE *yy_input_file;
char *yy_ch_buf; /* input buffer */
char *yy_buf_pos; /* current position in input buffer */
/* Size of input buffer in bytes, not including room for EOB
* characters.
*/
yy_size_t yy_buf_size;
/* Number of characters read into yy_ch_buf, not including EOB
* characters.
*/
int yy_n_chars;
/* Whether we "own" the buffer - i.e., we know we created it,
* and can realloc() it to grow it, and should free() it to
* delete it.
*/
int yy_is_our_buffer;
/* Whether this is an "interactive" input source; if so, and
* if we're using stdio for input, then we want to use getc()
* instead of fread(), to make sure we stop fetching input after
* each newline.
*/
int yy_is_interactive;
/* Whether we're considered to be at the beginning of a line.
* If so, '^' rules will be active on the next match, otherwise
* not.
*/
int yy_at_bol;
int yy_bs_lineno; /**< The line count. */
int yy_bs_column; /**< The column count. */
/* Whether to try to fill the input buffer when we reach the
* end of it.
*/
int yy_fill_buffer;
int yy_buffer_status;
#define YY_BUFFER_NEW 0
#define YY_BUFFER_NORMAL 1
/* When an EOF's been seen but there's still some text to process
* then we mark the buffer as YY_EOF_PENDING, to indicate that we
* shouldn't try reading from the input source any more. We might
* still have a bunch of tokens to match, though, because of
* possible backing-up.
*
* When we actually see the EOF, we change the status to "new"
* (via yyrestart()), so that the user can continue scanning by
* just pointing yyin at a new input file.
*/
#define YY_BUFFER_EOF_PENDING 2
;
#endif /* !YY_STRUCT_YY_BUFFER_STATE */
/* Stack of input buffers. */
static size_t yy_buffer_stack_top = 0; /**< index of top of stack. */
static size_t yy_buffer_stack_max = 0; /**< capacity of stack. */
static YY_BUFFER_STATE * yy_buffer_stack = 0; /**< Stack as an array. */
/* We provide macros for accessing buffer states in case in the
* future we want to put the buffer states in a more general
* "scanner state".
*
* Returns the top of the stack, or NULL.
*/
#define YY_CURRENT_BUFFER ( (yy_buffer_stack) \\
? (yy_buffer_stack)[(yy_buffer_stack_top)] \\
: NULL)
/* Same as previous macro, but useful when we know that the buffer stack is not
* NULL or when we need an lvalue. For internal use only.
*/
#define YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE (yy_buffer_stack)[(yy_buffer_stack_top)]
/* yy_hold_char holds the character lost when yytext is formed. */
static char yy_hold_char;
static int yy_n_chars; /* number of characters read into yy_ch_buf */
int yyleng;
/* Points to current character in buffer. */
static char *yy_c_buf_p = (char *) 0;
static int yy_init = 0; /* whether we need to initialize */
static int yy_start = 0; /* start state number */
/* Flag which is used to allow yywrap()'s to do buffer switches
* instead of setting up a fresh yyin. A bit of a hack ...
*/
static int yy_did_buffer_switch_on_eof;
void yyrestart (FILE *input_file );
void yy_switch_to_buffer (YY_BUFFER_STATE new_buffer );
YY_BUFFER_STATE yy_create_buffer (FILE *file,int size );
void yy_delete_buffer (YY_BUFFER_STATE b );
void yy_flush_buffer (YY_BUFFER_STATE b );
void yypush_buffer_state (YY_BUFFER_STATE new_buffer );
void yypop_buffer_state (void );
static void yyensure_buffer_stack (void );
static void yy_load_buffer_state (void );
static void yy_init_buffer (YY_BUFFER_STATE b,FILE *file );
#define YY_FLUSH_BUFFER yy_flush_buffer(YY_CURRENT_BUFFER )
YY_BUFFER_STATE yy_scan_buffer (char *base,yy_size_t size );
YY_BUFFER_STATE yy_scan_string (yyconst char *yy_str );
YY_BUFFER_STATE yy_scan_bytes (yyconst char *bytes,int len );
void *yyalloc (yy_size_t );
void *yyrealloc (void *,yy_size_t );
void yyfree (void * );
#define yy_new_buffer yy_create_buffer
#define yy_set_interactive(is_interactive) \\
\\
if ( ! YY_CURRENT_BUFFER ) \\
yyensure_buffer_stack (); \\
YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE = \\
yy_create_buffer(yyin,YY_BUF_SIZE ); \\
\\
YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_is_interactive = is_interactive; \\
#define yy_set_bol(at_bol) \\
\\
if ( ! YY_CURRENT_BUFFER )\\
yyensure_buffer_stack (); \\
YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE = \\
yy_create_buffer(yyin,YY_BUF_SIZE ); \\
\\
YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_at_bol = at_bol; \\
#define YY_AT_BOL() (YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_at_bol)
/* Begin user sect3 */
typedef unsigned char YY_CHAR;
FILE *yyin = (FILE *) 0, *yyout = (FILE *) 0;
typedef int yy_state_type;
extern int yylineno;
int yylineno = 1;
extern char *yytext;
#define yytext_ptr yytext
static yy_state_type yy_get_previous_state (void );
static yy_state_type yy_try_NUL_trans (yy_state_type current_state );
static int yy_get_next_buffer (void );
static void yy_fatal_error (yyconst char msg[] );
/* Done after the current pattern has been matched and before the
* corresponding action - sets up yytext.
*/
#define YY_DO_BEFORE_ACTION \\
(yytext_ptr) = yy_bp; \\
yyleng = (size_t) (yy_cp - yy_bp); \\
(yy_hold_char) = *yy_cp; \\
*yy_cp = '\\0'; \\
(yy_c_buf_p) = yy_cp;
#define YY_NUM_RULES 4
#define YY_END_OF_BUFFER 5
/* This struct is not used in this scanner,
but its presence is necessary. */
struct yy_trans_info
flex_int32_t yy_verify;
flex_int32_t yy_nxt;
;
static yyconst flex_int16_t yy_accept[14] =
0,
0, 0, 5, 4, 2, 1, 1, 3, 2, 1,
1, 3, 0
;
static yyconst flex_int32_t yy_ec[256] =
0,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 2, 1, 3, 1, 1, 1, 1, 4, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 4, 1, 5, 5, 5,
5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4,
4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4,
4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4,
1, 1, 1, 1, 4, 1, 4, 4, 4, 4,
4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4,
4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4,
4, 4, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1
;
static yyconst flex_int32_t yy_meta[6] =
0,
1, 2, 3, 4, 5
;
static yyconst flex_int16_t yy_base[17] =
0,
0, 0, 14, 15, 0, 4, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 15, 7, 8, 8
;
static yyconst flex_int16_t yy_def[17] =
0,
13, 1, 13, 13, 14, 13, 15, 16, 14, 6,
15, 16, 0, 13, 13, 13
;
static yyconst flex_int16_t yy_nxt[21] =
0,
4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 9, 9,
11, 11, 12, 13, 3, 13, 13, 13, 13, 13
;
static yyconst flex_int16_t yy_chk[21] =
0,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 6, 6, 6, 14, 14,
15, 15, 16, 3, 13, 13, 13, 13, 13, 13
;
static yy_state_type yy_last_accepting_state;
static char *yy_last_accepting_cpos;
extern int yy_flex_debug;
int yy_flex_debug = 0;
/* The intent behind this definition is that it'll catch
* any uses of REJECT which flex missed.
*/
#define REJECT reject_used_but_not_detected
#define yymore() yymore_used_but_not_detected
#define YY_MORE_ADJ 0
#define YY_RESTORE_YY_MORE_OFFSET
char *yytext;
#line 1 "test.lex"
#line 2 "test.lex"
int wordCount = 0;
int spaceCount = 0;
int numberCount = 0;
#line 467 "lex.yy.c"
#define INITIAL 0
#ifndef YY_NO_UNISTD_H
/* Special case for "unistd.h", since it is non-ANSI. We include it way
* down here because we want the user's section 1 to have been scanned first.
* The user has a chance to override it with an option.
*/
#include <unistd.h>
#endif
#ifndef YY_EXTRA_TYPE
#define YY_EXTRA_TYPE void *
#endif
static int yy_init_globals (void );
/* Accessor methods to globals.
These are made visible to non-reentrant scanners for convenience. */
int yylex_destroy (void );
int yyget_debug (void );
void yyset_debug (int debug_flag );
YY_EXTRA_TYPE yyget_extra (void );
void yyset_extra (YY_EXTRA_TYPE user_defined );
FILE *yyget_in (void );
void yyset_in (FILE * in_str );
FILE *yyget_out (void );
void yyset_out (FILE * out_str );
int yyget_leng (void );
char *yyget_text (void );
int yyget_lineno (void );
void yyset_lineno (int line_number );
/* Macros after this point can all be overridden by user definitions in
* section 1.
*/
#ifndef YY_SKIP_YYWRAP
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" int yywrap (void );
#else
extern int yywrap (void );
#endif
#endif
static void yyunput (int c,char *buf_ptr );
#ifndef yytext_ptr
static void yy_flex_strncpy (char *,yyconst char *,int );
#endif
#ifdef YY_NEED_STRLEN
static int yy_flex_strlen (yyconst char * );
#endif
#ifndef YY_NO_INPUT
#ifdef __cplusplus
static int yyinput (void );
#else
static int input (void );
#endif
#endif
/* Amount of stuff to slurp up with each read. */
#ifndef YY_READ_BUF_SIZE
#ifdef __ia64__
/* On IA-64, the buffer size is 16k, not 8k */
#define YY_READ_BUF_SIZE 16384
#else
#define YY_READ_BUF_SIZE 8192
#endif /* __ia64__ */
#endif
/* Copy whatever the last rule matched to the standard output. */
#ifndef ECHO
/* This used to be an fputs(), but since the string might contain NUL's,
* we now use fwrite().
*/
#define ECHO do if (fwrite( yytext, yyleng, 1, yyout )) while (0)
#endif
/* Gets input and stuffs it into "buf". number of characters read, or YY_NULL,
* is returned in "result".
*/
#ifndef YY_INPUT
#define YY_INPUT(buf,result,max_size) \\
if ( YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_is_interactive ) \\
\\
int c = '*'; \\
size_t n; \\
for ( n = 0; n < max_size && \\
(c = getc( yyin )) != EOF && c != '\\n'; ++n ) \\
buf[n] = (char) c; \\
if ( c == '\\n' ) \\
buf[n++] = (char) c; \\
if ( c == EOF && ferror( yyin ) ) \\
YY_FATAL_ERROR( "input in flex scanner failed" ); \\
result = n; \\
\\
else \\
\\
errno=0; \\
while ( (result = fread(buf, 1, max_size, yyin))==0 && ferror(yyin)) \\
\\
if( errno != EINTR) \\
\\
YY_FATAL_ERROR( "input in flex scanner failed" ); \\
break; \\
\\
errno=0; \\
clearerr(yyin); \\
\\
\\
\\
#endif
/* No semi-colon after return; correct usage is to write "yyterminate();" -
* we don't want an extra ';' after the "return" because that will cause
* some compilers to complain about unreachable statements.
*/
#ifndef yyterminate
#define yyterminate() return YY_NULL
#endif
/* Number of entries by which start-condition stack grows. */
#ifndef YY_START_STACK_INCR
#define YY_START_STACK_INCR 25
#endif
/* Report a fatal error. */
#ifndef YY_FATAL_ERROR
#define YY_FATAL_ERROR(msg) yy_fatal_error( msg )
#endif
/* end tables serialization structures and prototypes */
/* Default declaration of generated scanner - a define so the user can
* easily add parameters.
*/
#ifndef YY_DECL
#define YY_DECL_IS_OURS 1
extern int yylex (void);
#define YY_DECL int yylex (void)
#endif /* !YY_DECL */
/* Code executed at the beginning of each rule, after yytext and yyleng
* have been set up.
*/
#ifndef YY_USER_ACTION
#define YY_USER_ACTION
#endif
/* Code executed at the end of each rule. */
#ifndef YY_BREAK
#define YY_BREAK break;
#endif
#define YY_RULE_SETUP \\
YY_USER_ACTION
/** The main scanner function which does all the work.
*/
YY_DECL
register yy_state_type yy_current_state;
register char *yy_cp, *yy_bp;
register int yy_act;
#line 11 "test.lex"
#line 656 "lex.yy.c"
if ( !(yy_init) )
(yy_init) = 1;
#ifdef YY_USER_INIT
YY_USER_INIT;
#endif
if ( ! (yy_start) )
(yy_start) = 1; /* first start state */
if ( ! yyin )
yyin = stdin;
if ( ! yyout )
yyout = stdout;
if ( ! YY_CURRENT_BUFFER )
yyensure_buffer_stack ();
YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE =
yy_create_buffer(yyin,YY_BUF_SIZE );
yy_load_buffer_state( );
while ( 1 ) /* loops until end-of-file is reached */
yy_cp = (yy_c_buf_p);
/* Support of yytext. */
*yy_cp = (yy_hold_char);
/* yy_bp points to the position in yy_ch_buf of the start of
* the current run.
*/
yy_bp = yy_cp;
yy_current_state = (yy_start);
yy_match:
do
register YY_CHAR yy_c = yy_ec[YY_SC_TO_UI(*yy_cp)];
if ( yy_accept[yy_current_state] )
(yy_last_accepting_state) = yy_current_state;
(yy_last_accepting_cpos) = yy_cp;
while ( yy_chk[yy_base[yy_current_state] + yy_c] != yy_current_state )
yy_current_state = (int) yy_def[yy_current_state];
if ( yy_current_state >= 14 )
yy_c = yy_meta[(unsigned int) yy_c];
yy_current_state = yy_nxt[yy_base[yy_current_state] + (unsigned int) yy_c];
++yy_cp;
while ( yy_base[yy_current_state] != 15 );
yy_find_action:
yy_act = yy_accept[yy_current_state];
if ( yy_act == 0 )
/* have to back up */
yy_cp = (yy_last_accepting_cpos);
yy_current_state = (yy_last_accepting_state);
yy_act = yy_accept[yy_current_state];
YY_DO_BEFORE_ACTION;
do_action: /* This label is used only to access EOF actions. */
switch ( yy_act )
/* beginning of action switch */
case 0: /* must back up */
/* undo the effects of YY_DO_BEFORE_ACTION */
*yy_cp = (yy_hold_char);
yy_cp = (yy_last_accepting_cpos);
yy_current_state = (yy_last_accepting_state);
goto yy_find_action;
case 1:
YY_RULE_SETUP
#line 12 "test.lex"
wordCount++;
YY_BREAK
case 2:
/* rule 2 can match eol */
YY_RULE_SETUP
#line 13 "test.lex"
spaceCount++;
YY_BREAK
case 3:
YY_RULE_SETUP
#line 14 "test.lex"
numberCount++;
YY_BREAK
case 4:
YY_RULE_SETUP
#line 15 "test.lex"
ECHO;
YY_BREAK
#line 760 "lex.yy.c"
case YY_STATE_EOF(INITIAL):
yyterminate();
case YY_END_OF_BUFFER:
/* Amount of text matched not including the EOB char. */
int yy_amount_of_matched_text = (int) (yy_cp - (yytext_ptr)) - 1;
/* Undo the effects of YY_DO_BEFORE_ACTION. */
*yy_cp = (yy_hold_char);
YY_RESTORE_YY_MORE_OFFSET
if ( YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_buffer_status == YY_BUFFER_NEW )
/* We're scanning a new file or input source. It's
* possible that this happened because the user
* just pointed yyin at a new source and called
* yylex(). If so, then we have to assure
* consistency between YY_CURRENT_BUFFER and our
* globals. Here is the right place to do so, because
* this is the first action (other than possibly a
* back-up) that will match for the new input source.
*/
(yy_n_chars) = YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_n_chars;
YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_input_file = yyin;
YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_buffer_status = YY_BUFFER_NORMAL;
/* Note that here we test for yy_c_buf_p "<=" to the position
* of the first EOB in the buffer, since yy_c_buf_p will
* already have been incremented past the NUL character
* (since all states make transitions on EOB to the
* end-of-buffer state). Contrast this with the test
* in input().
*/
if ( (yy_c_buf_p) <= &YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_ch_buf[(yy_n_chars)] )
/* This was really a NUL. */
yy_state_type yy_next_state;
(yy_c_buf_p) = (yytext_ptr) + yy_amount_of_matched_text;
yy_current_state = yy_get_previous_state( );
/* Okay, we're now positioned to make the NUL
* transition. We couldn't have
* yy_get_previous_state() go ahead and do it
* for us because it doesn't know how to deal
* with the possibility of jamming (and we don't
* want to build jamming into it because then it
* will run more slowly).
*/
yy_next_state = yy_try_NUL_trans( yy_current_state );
yy_bp = (yytext_ptr) + YY_MORE_ADJ;
if ( yy_next_state )
/* Consume the NUL. */
yy_cp = ++(yy_c_buf_p);
yy_current_state = yy_next_state;
goto yy_match;
else
yy_cp = (yy_c_buf_p);
goto yy_find_action;
else switch ( yy_get_next_buffer( ) )
case EOB_ACT_END_OF_FILE:
(yy_did_buffer_switch_on_eof) = 0;
if ( yywrap( ) )
/* Note: because we've taken care in
* yy_get_next_buffer() to have set up
* yytext, we can now set up
* yy_c_buf_p so that if some total
* hoser (like flex itself) wants to
* call the scanner after we return the
* YY_NULL, it'll still work - another
* YY_NULL will get returned.
*/
(yy_c_buf_p) = (yytext_ptr) + YY_MORE_ADJ;
yy_act = YY_STATE_EOF(YY_START);
goto do_action;
else
if ( ! (yy_did_buffer_switch_on_eof) )
YY_NEW_FILE;
break;
case EOB_ACT_CONTINUE_SCAN:
(yy_c_buf_p) =
(yytext_ptr) + yy_amount_of_matched_text;
yy_current_state = yy_get_previous_state( );
yy_cp = (yy_c_buf_p);
yy_bp = (yytext_ptr) + YY_MORE_ADJ;
goto yy_match;
case EOB_ACT_LAST_MATCH:
(yy_c_buf_p) =
&YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_ch_buf[(yy_n_chars)];
yy_current_state = yy_get_previous_state( );
yy_cp = (yy_c_buf_p);
yy_bp = (yytext_ptr) + YY_MORE_ADJ;
goto yy_find_action;
break;
default:
YY_FATAL_ERROR(
"fatal flex scanner internal error--no action found" );
/* end of action switch */
/* end of scanning one token */
/* end of yylex */
/* yy_get_next_buffer - try to read in a new buffer
*
* Returns a code representing an action:
* EOB_ACT_LAST_MATCH -
* EOB_ACT_CONTINUE_SCAN - continue scanning from current position
* EOB_ACT_END_OF_FILE - end of file
*/
static int yy_get_next_buffer (void)
register char *dest = YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_ch_buf;
register char *source = (yytext_ptr);
register int number_to_move, i;
int ret_val;
if ( (yy_c_buf_p) > &YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_ch_buf[(yy_n_chars) + 1] )
YY_FATAL_ERROR(
"fatal flex scanner internal error--end of buffer missed" );
if ( YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_fill_buffer == 0 )
/* Don't try to fill the buffer, so this is an EOF. */
if ( (yy_c_buf_p) - (yytext_ptr) - YY_MORE_ADJ == 1 )
/* We matched a single character, the EOB, so
* treat this as a final EOF.
*/
return EOB_ACT_END_OF_FILE;
else
/* We matched some text prior to the EOB, first
* process it.
*/
return EOB_ACT_LAST_MATCH;
/* Try to read more data. */
/* First move last chars to start of buffer. */
number_to_move = (int) ((yy_c_buf_p) - (yytext_ptr)) - 1;
for ( i = 0; i < number_to_move; ++i )
*(dest++) = *(source++);
if ( YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_buffer_status == YY_BUFFER_EOF_PENDING )
/* don't do the read, it's not guaranteed to return an EOF,
* just force an EOF
*/
YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_n_chars = (yy_n_chars) = 0;
else
int num_to_read =
YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_buf_size - number_to_move - 1;
while ( num_to_read <= 0 )
/* Not enough room in the buffer - grow it. */
/* just a shorter name for the current buffer */
YY_BUFFER_STATE b = YY_CURRENT_BUFFER;
int yy_c_buf_p_offset =
(int) ((yy_c_buf_p) - b->yy_ch_buf);
if ( b->yy_is_our_buffer )
int new_size = b->yy_buf_size * 2;
if ( new_size <= 0 )
b->yy_buf_size += b->yy_buf_size / 8;
else
b->yy_buf_size *= 2;
b->yy_ch_buf = (char *)
/* Include room in for 2 EOB chars. */
yyrealloc((void *) b->yy_ch_buf,b->yy_buf_size + 2 );
else
/* Can't grow it, we don't own it. */
b->yy_ch_buf = 0;
if ( ! b->yy_ch_buf )
YY_FATAL_ERROR(
"fatal error - scanner input buffer overflow" );
(yy_c_buf_p) = &b->yy_ch_buf[yy_c_buf_p_offset];
num_to_read = YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_buf_size -
number_to_move - 1;
if ( num_to_read > YY_READ_BUF_SIZE )
num_to_read = YY_READ_BUF_SIZE;
/* Read in more data. */
YY_INPUT( (&YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_ch_buf[number_to_move]),
(yy_n_chars), (size_t) num_to_read );
YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_n_chars = (yy_n_chars);
if ( (yy_n_chars) == 0 )
if ( number_to_move == YY_MORE_ADJ )
ret_val = EOB_ACT_END_OF_FILE;
yyrestart(yyin );
else
ret_val = EOB_ACT_LAST_MATCH;
YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_buffer_status =
YY_BUFFER_EOF_PENDING;
else
ret_val = EOB_ACT_CONTINUE_SCAN;
if ((yy_size_t) ((yy_n_chars) + number_to_move) > YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_buf_size)
/* Extend the array by 50%, plus the number we really need. */
yy_size_t new_size = (yy_n_chars) + number_to_move + ((yy_n_chars) >> 1);
YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_ch_buf = (char *) yyrealloc((void *) YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_ch_buf,new_size );
if ( ! YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_ch_buf )
YY_FATAL_ERROR( "out of dynamic memory in yy_get_next_buffer()" );
(yy_n_chars) += number_to_move;
YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_ch_buf[(yy_n_chars)] = YY_END_OF_BUFFER_CHAR;
YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_ch_buf[(yy_n_chars) + 1] = YY_END_OF_BUFFER_CHAR;
(yytext_ptr) = &YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_ch_buf[0];
return ret_val;
/* yy_get_previous_state - get the state just before the EOB char was reached */
static yy_state_type yy_get_previous_state (void)
register yy_state_type yy_current_state;
register char *yy_cp;
yy_current_state = (yy_start);
for ( yy_cp = (yytext_ptr) + YY_MORE_ADJ; yy_cp < (yy_c_buf_p); ++yy_cp )
register YY_CHAR yy_c = (*yy_cp ? yy_ec[YY_SC_TO_UI(*yy_cp)] : 1);
if ( yy_accept[yy_current_state] )
(yy_last_accepting_state) = yy_current_state;
(yy_last_accepting_cpos) = yy_cp;
while ( yy_chk[yy_base[yy_current_state] + yy_c] != yy_current_state )
yy_current_state = (int) yy_def[yy_current_state];
if ( yy_current_state >= 14 )
yy_c = yy_meta[(unsigned int) yy_c];
yy_current_state = yy_nxt[yy_base[yy_current_state] + (unsigned int) yy_c];
return yy_current_state;
/* yy_try_NUL_trans - try to make a transition on the NUL character
*
* synopsis
* next_state = yy_try_NUL_trans( current_state );
*/
static yy_state_type yy_try_NUL_trans (yy_state_type yy_current_state )
register int yy_is_jam;
register char *yy_cp = (yy_c_buf_p);
register YY_CHAR yy_c = 1;
if ( yy_accept[yy_current_state] )
(yy_last_accepting_state) = yy_current_state;
(yy_last_accepting_cpos) = yy_cp;
while ( yy_chk[yy_base[yy_current_state] + yy_c] != yy_current_state )
yy_current_state = (int) yy_def[yy_current_state];
if ( yy_current_state >= 14 )
yy_c = yy_meta[(unsigned int) yy_c];
yy_current_state = yy_nxt[yy_base[yy_current_state] + (unsigned int) yy_c];
yy_is_jam = (yy_current_state == 13);
return yy_is_jam ? 0 : yy_current_state;
static void yyunput (int c, register char * yy_bp )
register char *yy_cp;
yy_cp = (yy_c_buf_p);
/* undo effects of setting up yytext */
*yy_cp = (yy_hold_char);
if ( yy_cp < YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_ch_buf + 2 )
/* need to shift things up to make room */
/* +2 for EOB chars. */
register int number_to_move = (yy_n_chars) + 2;
register char *dest = &YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_ch_buf[
YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_buf_size + 2];
register char *source =
&YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_ch_buf[number_to_move];
while ( source > YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_ch_buf )
*--dest = *--source;
yy_cp += (int) (dest - source);
yy_bp += (int) (dest - source);
YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_n_chars =
(yy_n_chars) = YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_buf_size;
if ( yy_cp < YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_ch_buf + 2 )
YY_FATAL_ERROR( "flex scanner push-back overflow" );
*--yy_cp = (char) c;
(yytext_ptr) = yy_bp;
(yy_hold_char) = *yy_cp;
(yy_c_buf_p) = yy_cp;
#ifndef YY_NO_INPUT
#ifdef __cplusplus
static int yyinput (void)
#else
static int input (void)
#endif
int c;
*(yy_c_buf_p) = (yy_hold_char);
if ( *(yy_c_buf_p) == YY_END_OF_BUFFER_CHAR )
/* yy_c_buf_p now points to the character we want to return.
* If this occurs *before* the EOB characters, then it's a
* valid NUL; if not, then we've hit the end of the buffer.
*/
if ( (yy_c_buf_p) < &YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_ch_buf[(yy_n_chars)] )
/* This was really a NUL. */
*(yy_c_buf_p) = '\\0';
else
/* need more input */
int offset = (yy_c_buf_p) - (yytext_ptr);
++(yy_c_buf_p);
switch ( yy_get_next_buffer( ) )
case EOB_ACT_LAST_MATCH:
/* This happens because yy_g_n_b()
* sees that we've accumulated a
* token and flags that we need to
* try matching the token before
* proceeding. But for input(),
* there's no matching to consider.
* So convert the EOB_ACT_LAST_MATCH
* to EOB_ACT_END_OF_FILE.
*/
/* Reset buffer status. */
yyrestart(yyin );
/*FALLTHROUGH*/
case EOB_ACT_END_OF_FILE:
if ( yywrap( ) )
return EOF;
if ( ! (yy_did_buffer_switch_on_eof) )
YY_NEW_FILE;
#ifdef __cplusplus
return yyinput();
#else
return input();
#endif
case EOB_ACT_CONTINUE_SCAN:
(yy_c_buf_p) = (yytext_ptr) + offset;
break;
c = *(unsigned char *) (yy_c_buf_p); /* cast for 8-bit char's */
*(yy_c_buf_p) = '\\0'; /* preserve yytext */
(yy_hold_char) = *++(yy_c_buf_p);
return c;
#endif /* ifndef YY_NO_INPUT */
/** Immediately switch to a different input stream.
* @param input_file A readable stream.
*
* @note This function does not reset the start condition to @c INITIAL .
*/
void yyrestart (FILE * input_file )
if ( ! YY_CURRENT_BUFFER )
yyensure_buffer_stack ();
YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE =
yy_create_buffer(yyin,YY_BUF_SIZE );
yy_init_buffer(YY_CURRENT_BUFFER,input_file );
yy_load_buffer_state( );
/** Switch to a different input buffer.
* @param new_buffer The new input buffer.
*
*/
void yy_switch_to_buffer (YY_BUFFER_STATE new_buffer )
/* TODO. We should be able to replace this entire function body
* with
* yypop_buffer_state();
* yypush_buffer_state(new_buffer);
*/
yyensure_buffer_stack ();
if ( YY_CURRENT_BUFFER == new_buffer )
return;
if ( YY_CURRENT_BUFFER )
/* Flush out information for old buffer. */
*(yy_c_buf_p) = (yy_hold_char);
YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_buf_pos = (yy_c_buf_p);
YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_n_chars = (yy_n_chars);
YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE = new_buffer;
yy_load_buffer_state( );
/* We don't actually know whether we did this switch during
* EOF (yywrap()) processing, but the only time this flag
* is looked at is after yywrap() is called, so it's safe
* to go ahead and always set it.
*/
(yy_did_buffer_switch_on_eof) = 1;
static void yy_load_buffer_state (void)
(yy_n_chars) = YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_n_chars;
(yytext_ptr) = (yy_c_buf_p) = YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_buf_pos;
yyin = YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_input_file;
(yy_hold_char) = *(yy_c_buf_p);
/** Allocate and initialize an input buffer state.
* @param file A readable stream.
* @param size The character buffer size in bytes. When in doubt, use @c YY_BUF_SIZE.
*
* @return the allocated buffer state.
*/
YY_BUFFER_STATE yy_create_buffer (FILE * file, int size )
YY_BUFFER_STATE b;
b = (YY_BUFFER_STATE) yyalloc(sizeof( struct yy_buffer_state ) );
if ( ! b )
YY_FATAL_ERROR( "out of dynamic memory in yy_create_buffer()" );
b->yy_buf_size = size;
/* yy_ch_buf has to be 2 characters longer than the size given because
* we need to put in 2 end-of-buffer characters.
*/
b->yy_ch_buf = (char *) yyalloc(b->yy_buf_size + 2 );
if ( ! b->yy_ch_buf )
YY_FATAL_ERROR( "out of dynamic memory in yy_create_buffer()" );
b->yy_is_our_buffer = 1;
yy_init_buffer(b,file );
return b;
/** Destroy the buffer.
* @param b a buffer created with yy_create_buffer()
*
*/
void yy_delete_buffer (YY_BUFFER_STATE b )
if ( ! b )
return;
if ( b == YY_CURRENT_BUFFER ) /* Not sure if we should pop here. */
YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE = (YY_BUFFER_STATE) 0;
if ( b->yy_is_our_buffer )
yyfree((void *) b->yy_ch_buf );
yyfree((void *) b );
#ifndef __cplusplus
extern int isatty (int );
#endif /* __cplusplus */
/* Initializes or reinitializes a buffer.
* This function is sometimes called more than once on the same buffer,
* such as during a yyrestart() or at EOF.
*/
static void yy_init_buffer (YY_BUFFER_STATE b, FILE * file )
int oerrno = errno;
yy_flush_buffer(b );
b->yy_input_file = file;
b->yy_fill_buffer = 1;
/* If b is the current buffer, then yy_init_buffer was _probably_
* called from yyrestart() or through yy_get_next_buffer.
* In that case, we don't want to reset the lineno or column.
*/
if (b != YY_CURRENT_BUFFER)
b->yy_bs_lineno = 1;
b->yy_bs_column = 0;
b->yy_is_interactive = file ? (isatty( fileno(file) ) > 0) : 0;
errno = oerrno;
/** Discard all buffered characters. On the next scan, YY_INPUT will be called.
* @param b the buffer state to be flushed, usually @c YY_CURRENT_BUFFER.
*
*/
void yy_flush_buffer (YY_BUFFER_STATE b )
if ( ! b )
return;
b->yy_n_chars = 0;
/* We always need two end-of-buffer characters. The first causes
* a transition to the end-of-buffer state. The second causes
* a jam in that state.
*/
b->yy_ch_buf[0] = YY_END_OF_BUFFER_CHAR;
b->yy_ch_buf[1] = YY_END_OF_BUFFER_CHAR;
b->yy_buf_pos = &b->yy_ch_buf[0];
b->yy_at_bol = 1;
b->yy_buffer_status = YY_BUFFER_NEW;
if ( b == YY_CURRENT_BUFFER )
yy_load_buffer_state( );
/** Pushes the new state onto the stack. The new state becomes
* the current state. This function will allocate the stack
* if necessary.
* @param new_buffer The new state.
*
*/
void yypush_buffer_state (YY_BUFFER_STATE new_buffer )
if (new_buffer == NULL)
return;
yyensure_buffer_stack();
/* This block is copied from yy_switch_to_buffer. */
if ( YY_CURRENT_BUFFER )
/* Flush out information for old buffer. */
*(yy_c_buf_p) = (yy_hold_char);
YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_buf_pos = (yy_c_buf_p);
YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE->yy_n_chars = (yy_n_chars);
/* Only push if top exists. Otherwise, replace top. */
if (YY_CURRENT_BUFFER)
(yy_buffer_stack_top)++;
YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE = new_buffer;
/* copied from yy_switch_to_buffer. */
yy_load_buffer_state( );
(yy_did_buffer_switch_on_eof) = 1;
/** Removes and deletes the top of the stack, if present.
* The next element becomes the new top.
*
*/
void yypop_buffer_state (void)
if (!YY_CURRENT_BUFFER)
return;
yy_delete_buffer(YY_CURRENT_BUFFER );
YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE = NULL;
if ((yy_buffer_stack_top) > 0)
--(yy_buffer_stack_top);
if (YY_CURRENT_BUFFER)
yy_load_buffer_state( );
(yy_did_buffer_switch_on_eof) = 1;
/* Allocates the stack if it does not exist.
* Guarantees space for at least one push.
*/
static void yyensure_buffer_stack (void)
int num_to_alloc;
if (!(yy_buffer_stack))
/* First allocation is just for 2 elements, since we don't know if this
* scanner will even need a stack. We use 2 instead of 1 to avoid an
* immediate realloc on the next call.
*/
num_to_alloc = 1;
(yy_buffer_stack) = (struct yy_buffer_state**)yyalloc
(num_to_alloc * sizeof(struct yy_buffer_state*)
);
if ( ! (yy_buffer_stack) )
YY_FATAL_ERROR( "out of dynamic memory in yyensure_buffer_stack()" );
memset((yy_buffer_stack), 0, num_to_alloc * sizeof(struct yy_buffer_state*));
(yy_buffer_stack_max) = num_to_alloc;
(yy_buffer_stack_top) = 0;
return;
if ((yy_buffer_stack_top) >= ((yy_buffer_stack_max)) - 1)
/* Increase the buffer to prepare for a possible push. */
int grow_size = 8 /* arbitrary grow size */;
num_to_alloc = (yy_buffer_stack_max) + grow_size;
(yy_buffer_stack) = (struct yy_buffer_state**)yyrealloc
((yy_buffer_stack),
num_to_alloc * sizeof(struct yy_buffer_state*)
);
if ( ! (yy_buffer_stack) )
YY_FATAL_ERROR( "out of dynamic memory in yyensure_buffer_stack()" );
/* zero only the new slots.*/
memset((yy_buffer_stack) + (yy_buffer_stack_max), 0, grow_size * sizeof(struct yy_buffer_state*));
(yy_buffer_stack_max) = num_to_alloc;
/** Setup the input buffer state to scan directly from a user-specified character buffer.
* @param base the character buffer
* @param size the size in bytes of the character buffer
*
* @return the newly allocated buffer state object.
*/
YY_BUFFER_STATE yy_scan_buffer (char * base, yy_size_t size )
YY_BUFFER_STATE b;
if ( size < 2 ||
base[size-2] != YY_END_OF_BUFFER_CHAR ||
base[size-1] != YY_END_OF_BUFFER_CHAR )
/* They forgot to leave room for the EOB's. */
return 0;
b = (YY_BUFFER_STATE) yyalloc(sizeof( struct yy_buffer_state ) );
if ( ! b )
YY_FATAL_ERROR( "out of dynamic memory in yy_scan_buffer()" );
b->yy_buf_size = size - 2; /* "- 2" to take care of EOB's */
b->yy_buf_pos = b->yy_ch_buf = base;
b->yy_is_our_buffer = 0;
b->yy_input_file = 0;
b->yy_n_chars = b->yy_buf_size;
b->yy_is_interactive = 0;
b->yy_at_bol = 1;
b->yy_fill_buffer = 0;
b->yy_buffer_status = YY_BUFFER_NEW;
yy_switch_to_buffer(b );
return b;
/** Setup the input buffer state to scan a string. The next call to yylex() will
* scan from a @e copy of @a str.
* @param yystr a NUL-terminated string to scan
*
* @return the newly allocated buffer state object.
* @note If you want to scan bytes that may contain NUL values, then use
* yy_scan_bytes() instead.
*/
YY_BUFFER_STATE yy_scan_string (yyconst char * yystr )
return yy_scan_bytes(yystr,strlen(yystr) );
/** Setup the input buffer state to scan the given bytes. The next call to yylex() will
* scan from a @e copy of @a bytes.
* @param yybytes the byte buffer to scan
* @param _yybytes_len the number of bytes in the buffer pointed to by @a bytes.
*
* @return the newly allocated buffer state object.
*/
YY_BUFFER_STATE yy_scan_bytes (yyconst char * yybytes, int _yybytes_len )
YY_BUFFER_STATE b;
char *buf;
yy_size_t n;
int i;
/* Get memory for full buffer, including space for trailing EOB's. */
n = _yybytes_len + 2;
buf = (char *) yyalloc(n );
if ( ! buf )
YY_FATAL_ERROR( "out of dynamic memory in yy_scan_bytes()" );
for ( i = 0; i < _yybytes_len; ++i )
buf[i] = yybytes[i];
buf[_yybytes_len] = buf[_yybytes_len+1] = YY_END_OF_BUFFER_CHAR;
b = yy_scan_buffer(buf,n );
if ( ! b )
YY_FATAL_ERROR( "bad buffer in yy_scan_bytes()" );
/* It's okay to grow etc. this buffer, and we should throw it
* away when we're done.
*/
b->yy_is_our_buffer = 1;
return b;
#ifndef YY_EXIT_FAILURE
#define YY_EXIT_FAILURE 2
#endif
static void yy_fatal_error (yyconst char* msg )
(void) fprintf( stderr, "%s\\n", msg );
exit( YY_EXIT_FAILURE );
/* Redefine yyless() so it works in section 3 code. */
#undef yyless
#define yyless(n) \\
do \\
\\
/* Undo effects of setting up yytext. */ \\
int yyless_macro_arg = (n); \\
YY_LESS_LINENO(yyless_macro_arg);\\
yytext[yyleng] = (yy_hold_char); \\
(yy_c_buf_p) = yytext + yyless_macro_arg; \\
(yy_hold_char) = *(yy_c_buf_p); \\
*(yy_c_buf_p) = '\\0'; \\
yyleng = yyless_macro_arg; \\
\\
while ( 0 )
/* Accessor methods (get/set functions) to struct members. */
/** Get the current line number.
*
*/
int yyget_lineno (void)
return yylineno;
/** Get the input stream.
*
*/
FILE *yyget_in (void)
return yyin;
/** Get the output stream.
*
*/
FILE *yyget_out (void)
return yyout;
/** Get the length of the current token.
*
*/
int yyget_leng (void)
return yyleng;
/** Get the current token.
*
*/
char *yyget_text (void)
return yytext;
/** Set the current line number.
* @param line_number
*
*/
void yyset_lineno (int line_number )
yylineno = line_number;
/** Set the input stream. This does not discard the current
* input buffer.
* @param in_str A readable stream.
*
* @see yy_switch_to_buffer
*/
void yyset_in (FILE * in_str )
yyin = in_str ;
void yyset_out (FILE * out_str )
yyout = out_str ;
int yyget_debug (void)
return yy_flex_debug;
void yyset_debug (int bdebug )
yy_flex_debug = bdebug ;
static int yy_init_globals (void)
/* Initialization is the same as for the non-reentrant scanner.
* This function is called from yylex_destroy(), so don't allocate here.
*/
(yy_buffer_stack) = 0;
(yy_buffer_stack_top) = 0;
(yy_buffer_stack_max) = 0;
(yy_c_buf_p) = (char *) 0;
(yy_init) = 0;
(yy_start) = 0;
/* Defined in main.c */
#ifdef YY_STDINIT
yyin = stdin;
yyout = stdout;
#else
yyin = (FILE *) 0;
yyout = (FILE *) 0;
#endif
/* For future reference: Set errno on error, since we are called by
* yylex_init()
*/
return 0;
/* yylex_destroy is for both reentrant and non-reentrant scanners. */
int yylex_destroy (void)
/* Pop the buffer stack, destroying each element. */
while(YY_CURRENT_BUFFER)
yy_delete_buffer(YY_CURRENT_BUFFER );
YY_CURRENT_BUFFER_LVALUE = NULL;
yypop_buffer_state();
/* Destroy the stack itself. */
yyfree((yy_buffer_stack) );
(yy_buffer_stack) = NULL;
/* Reset the globals. This is important in a non-reentrant scanner so the next time
* yylex() is called, initialization will occur. */
yy_init_globals( );
return 0;
/*
* Internal utility routines.
*/
#ifndef yytext_ptr
static void yy_flex_strncpy (char* s1, yyconst char * s2, int n )
register int i;
for ( i = 0; i < n; ++i )
s1[i] = s2[i];
#endif
#ifdef YY_NEED_STRLEN
static int yy_flex_strlen (yyconst char * s )
register int n;
for ( n = 0; s[n]; ++n )
;
return n;
#endif
void *yyalloc (yy_size_t size )
return (void *) malloc( size );
void *yyrealloc (void * ptr, yy_size_t size )
/* The cast to (char *) in the following accommodates both
* implementations that use char* generic pointers, and those
* that use void* generic pointers. It works with the latter
* because both ANSI C and C++ allow castless assignment from
* any pointer type to void*, and deal with argument conversions
* as though doing an assignment.
*/
return (void *) realloc( (char *) ptr, size );
void yyfree (void * ptr )
free( (char *) ptr ); /* see yyrealloc() for (char *) cast */
#define YYTABLES_NAME "yytables"
#line 15 "test.lex"
void main()
yylex();
printf(" Number of words: %d\\n", wordCount);
printf(" Number of spaces: %d\\n", spaceCount);
printf(" Number of nubmers: %d\\n", numberCount);
int yywrap()
return 1;
以上是关于Lex/Yacc 初识Lex的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章